| IN THE MATTER OF:
TIERED APPROACH TO CORRECTIVE ACTION OBJECTIVES (TACO): 35 ILL. ADM. CODE PART 742 |
)
) ) ) ) |
R97-12 (A) (Rulemaking - Land) |
| “Residential Property” MEANS ANY REAL PROPERTY THAT IS USED FOR HABITATION BY INDIVIDUALS, or where children have the opportunity for exposure to contaminants through soil ingestion or inhalation at educational facilities, health care facilities, child care facilities, or outdoor recreational areas. |
| 742.100 | Intent and Purpose |
| 742.105 | Applicability |
| 742.110 | Overview of Tiered Approach |
| 742.115 | Key Elements |
| 742.120 | Site Characterization |
| 742.200 | Definitions |
| 742.205 | Severability |
| 742.210 | Incorporations by Reference |
| 742.215 | Determination of Soil Attenuation Capacity |
| 742.220 | Determination of Soil Saturation Limit |
| 742.225 | Demonstration of Compliance with Remediation Objectives |
| 742.230 | Agency Review and Approval |
| 742.300 | Exclusion of Exposure Route |
| 742.305 | Contaminant Source and Free Product Determination |
| 742.310 | Inhalation Exposure Route |
| 742.315 | Soil Ingestion Exposure Route |
| 742.320 | Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
| 742.400 | Area Background |
| 742.405 | Determination of Area Background for Soil |
| 742.410 | Determination of Area Background for Groundwater |
| 742.415 | Use of Area Background Concentrations |
| 742.500 | Tier 1 Evaluation Overview |
| 742.505 | Tier 1 Soil and Groundwater Remediation Objectives |
| 742.510 | Tier 1 Remediation Objectives |
| 742.600 | Tier 2 Evaluation Overview |
| 742.605 | Land Use |
| 742.610 | Chemical and Site Properties |
| 742.700 | Tier 2 Soil Evaluation Overview |
| 742.705 | Parameters for Soil Remediation Objective Equations |
| 742.710 | SSL Soil Equations |
| 742.715 | RBCA Soil Equations |
| 742.720 | Chemicals with Cumulative Noncarcinogenic Effects |
| 742.800 | Tier 2 Groundwater Evaluation Overview |
| 742.805 | Tier 2 Groundwater Remediation Objectives |
| 742.810 | Calculations to Predict Impacts from Remaining Groundwater Contamination |
| 742.900 | Tier 3 Evaluation Overview |
| 742.905 | Modifications of Parameters |
| 742.910 | Alternative Models |
| 742.915 | Formal Risk Assessments |
| 742.920 | Impractical Remediation |
| 742.925 | Exposure Routes |
| 742.930 | Derivation of Toxicological Data |
| 742.1000 | Institutional Controls |
| 742.1005 | No Further Remediation Letters |
| 742.1010 | Restrictive Covenants, Deed Restrictions and Negative Easements |
| 742.1015 | Ordinances |
| 742.1020 | Highway Authority Agreements |
| 742.1100 | Engineered Barriers |
| 742.1105 | Engineered Barrier Requirements |
| APPENDIX A | General |
| ILLUSTRATION A | |
| Developing Soil Remediation Objectives Under the Tiered Approach | |
| ILLUSTRATION B | |
| Developing Groundwater Remediation Objectives Under the Tiered Approach | |
| Table A | Soil Saturation Limits (Csat) for Chemicals Whose Melting Point is Less Than 300C |
| Table B | Tolerance Factor (K) |
| Table C | Coefficients {AN-I+1} for W Test of Normality, for N=2(1)50 |
| Table D | Percentage Points of the W Test for N=3(1)50 |
| Table E | Chemicals with Noncarcinogenic Toxic Effects on Specific Target Organs/Organ Systems or Similar Modes of Action |
| Table F | Chemicals with Carcinogenic Toxic Effects on Specific Target Organs/Organ Systems or Similar Modes of Action |
| Table G | Concentrations of Inorganic Chemicals in Background Soils |
| APPENDIX B | Tier 1 Tables and Illustrations |
| ILLUSTRATION A | |
| Tier 1 Evaluation | |
| Table A | Tier 1 Soil Remediation Objectives for Residential Properties |
| Table B | Tier 1 Soil Remediation Objectives for Industrial/Commercial Properties |
| Table C | pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class I Groundwater) |
| Table D | pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class II Groundwater) |
| Table E | Tier 1 Groundwater Remediation Objectives for the Groundwater Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route |
| Table F | Values Used to Calculate the Tier 1 Soil Remediation Objectives for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route |
| APPENDIX C | Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| ILLUSTRATION A | |
| Tier 2 Evaluation for Soil | |
| ILLUSTRATION B | |
| Tier 2 Evaluation for Groundwater | |
| ILLUSTRATION C | |
| US Department of Agriculture Soil Texture Classification | |
| Table A | SSL Equations |
| Table B | SSL Parameters |
| Table C | RBCA Equations |
| Table D | RBCA Parameters |
| Table E | Default Physical and Chemical Parameters |
| Table F | Methods for Determining Physical Soil Parameters |
| Table G | Error Function (erf) |
| Table H | Q/C Values by Source Area |
| Table I | Koc Values for Ionizing Organics as a Function of pH (cm3/g or L/kg) |
| Table J | Values to be Substituted for ks When Evaluating Inorganics as a Function of pH (cm3water/gsoil) |
| Table K | Parameter Estimates for Calculating Water-Filled Soil Porosity (q w) |
| Section 742.100 | |
| Intent and Purpose |
| a) | This Part sets forth procedures for evaluating the risk to human health posed by environmental conditions and developing remediation objectives that achieve acceptable risk levels. |
| b) | The purpose of these procedures is to provide for the adequate protection of human health and the environment based on the risks to human health posed by environmental conditions while incorporating site related information. |
| a) | Any person, including a person required to perform an investigation pursuant to the Illinois Environmental Protection Act (415 ILCS 5/1 et seq.) (Act), may elect to proceed under this Part to the extent allowed by State or federal law and regulations and the provisions of this Part. A person proceeding under this Part may do so to the extent such actions are consistent with the requirements of the program under which site remediation is being addressed. |
| b) | This Part is to be used in conjunction with the procedures and requirements applicable to the following programs: |
| 1) | Leaking Underground Storage Tanks (35 Ill. Adm. Code 731 and 732); |
| 2) | Site Remediation Program (35 Ill. Adm. Code 740); and |
| 3) | RCRA Part B Permits and Closure Plans (35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 and 725). |
| c) | The procedures in this Part may not be used if their use would delay response action to address imminent and substantial threats to human health and the environment. This Part may only be used after actions to address such threats have been completed. |
| d) | This Part may be used to develop remediation objectives to protect surface waters, sediments or ecological concerns, when consistent with the regulations of other programs, and as approved by the Agency. |
| e) | A no further remediation determination issued by the Agency prior to July 1, 1997 pursuant to Section 4(y) of the Act or one of the programs listed in subsection (b) of this Section that approves completion of remedial action relative to a release shall remain in effect in accordance with the terms of that determination. |
| f) | Site specific groundwater remediation objectives determined under this Part for contaminants of concern may exceed the groundwater quality standards established pursuant to the rules promulgated under the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act (415 ILCS 55) as long as done in accordance with Sections 742.805(a) and 742.900(c)(9). [See 415 ILCS 5/58.5(d)(4).] |
| g) | Where contaminants of concern include polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), a person may need to evaluate the applicability of regulations adopted under the Toxic Substances Control Act. (15 U.S.C. 2601) |
| Section 742.110 | |
| Overview of Tiered Approach | |
| a) | This Part presents an approach for developing remediation objectives (see Appendix A, Illustrations A and B) that include an option for exclusion of pathways from further consideration, use of area background concentrations as remediation objectives and three tiers for selecting applicable remediation objectives. An understanding of human exposure routes is necessary to properly conduct an evaluation under this approach. In some cases, applicable human exposure route(s) can be excluded from further consideration prior to any tier evaluation. Selecting which tier or combination of tiers to be used to develop remediation objectives is dependent on the site-specific conditions and remediation goals. Tier 1 evaluations and Tier 2 evaluations are not prerequisites to conducting Tier 3 evaluations. |
| b) | A Tier 1 evaluation compares the concentration of contaminants detected at a site to the corresponding remediation objectives for residential and industrial/commercial properties contained in Appendix B, Tables A, B, C, D and E. To complete a Tier 1 evaluation, the extent and concentrations of the contaminants of concern, the groundwater class, the land use classification, human exposure routes at the site, and, if appropriate, soil pH, must be known. If remediation objectives are developed based on industrial/commercial property use, then institutional controls under Subpart J are required. |
| c) | A Tier 2 evaluation uses the risk based equations from the Soil Screening Level (SSL) and Risk Based Corrective Action (RBCA) listed in Appendix C, Tables A and C, respectively. In addition to the information that is required for a Tier 1 evaluation, site-specific information is used to calculate Tier 2 remediation objectives. As in Tier 1, Tier 2 evaluates residential and industrial/commercial properties only. If remediation objectives are developed based on industrial/commercial property use, then institutional controls under Subpart J are required. |
| d) | A Tier 3 evaluation allows alternative parameters and factors, not available under a Tier 1 or Tier 2 evaluation, to be considered when developing remediation objectives. Remediation objectives developed for conservation and agricultural properties can only be developed under Tier 3. |
| e) | Remediation objectives may be developed using area background concentrations or any of the three tiers if the evaluation is conducted in accordance with applicable requirements in Subparts D through I. When contaminant concentrations do not exceed remediation objectives developed under one of the tiers or area background procedures under Subpart D, further evaluation under any of the other tiers is not required. |
| a) | Exposure Routes |
| 1) | This Part identifies the following as potential exposure routes to be addressed: |
| A) | Inhalation; |
| B) | Soil ingestion; |
| C) | Groundwater ingestion; and |
| D) | Dermal contact with soil. |
| 2) | The evaluation of exposure routes under subsections (a)(1)(A),(a)(1)(B) and (a)(1)(C) of this Section is required for all sites when developing remediation objectives or excluding exposure pathways. Evaluation of the dermal contact exposure route is required for use of RBCA equations in Appendix C, Table C or use of formal risk assessment under Section 742.915. |
| 3) | The groundwater ingestion exposure route is comprised of two components: |
| A) | Migration from soil to groundwater (soil component); and |
| B) | Direct ingestion of groundwater (groundwater component). |
| b) | Contaminants of Concern |
| 1) | The materials and wastes managed at the site; |
| 2) | The extent of the no further remediation determination being requested from the Agency pursuant to a specific program; and |
| 3) | The requirements applicable to the specific program, as listed at Section 742.105(b) under which the remediation is being performed. |
| c) | Land Use |
| 1) | Residential property; |
| 2) | Conservation property; |
| 3) | Agricultural property; or |
| 4) | Industrial/commercial property. |
| Section 742.120 | |
| Site Characterization |
| Section 742.200 | |
| Definitions | |
| Section 742.205 | |
| Severability | |
| a) | The Board incorporates the following material by reference: |
| b) | CFR (Code of Federal Regulations). Available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402 (202) 783-3238: |
| c) | This Section incorporates no later editions or amendments. |
| Section 742.215 | |
| Determination of Soil Attenuation Capacity |
| a) | The concentrations of organic contaminants of concern remaining in the soil shall not exceed the attenuation capacity of the soil, as determined under subsection (b) of this Section. |
| b) | The soil attenuation capacity is not exceeded if: |
| 1) | The sum of the organic contaminant residual concentrations analyzed for the purposes of the remediation program for which the analysis is performed, at each discrete sampling point, is less than the natural organic carbon fraction of the soil. If the information relative to the concentration of other organic contaminants is available, such information shall be included in the sum. The natural organic carbon fraction (foc) shall be either: |
| A) | A default value of 6000 mg/kg for soils within the top meter and 2000 mg/kg for soils below one meter of the surface; or |
| B) | A site-specific value as measured by ASTM D2974-87, Nelson and Sommers, or by SW-846 Method 9060: Total Organic Carbon, as incorporated by reference in Section 742.210; |
| 2) | The total petroleum hydrocarbon concentration is less than the natural organic carbon fraction of the soil as demonstrated using a method approved by the Agency. The method selected shall be appropriate for the contaminants of concern to be addressed; or |
| 3) | Another method, approved by the Agency, shows that the soil attenuation capacity is not exceeded. |
| a) | For any organic contaminant that has a melting point below 300C, the remediation objective for the inhalation exposure route developed under Tier 2 or Tier 3 shall not exceed the soil saturation limit, as determined under subsection (c) of this Section. |
| b) | For any organic contaminant, the remediation objective under Tier 2 or Tier 3 for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route shall not exceed the soil saturation limit, as determined under subsection (c) of this Section. |
| c) | The soil saturation limit shall be: |
| 1) | The value listed in Appendix A, Table A for that specific contaminant; |
| 2) | A value derived from Equation S29 in Appendix C, Table A; or |
| 3) | A value derived from another method approved by the Agency. |
| Section 742.225 | Demonstration of Compliance with Remediation Objectives |
| a) | Compliance with groundwater remediation objectives developed under Subparts D through F and H through I shall be demonstrated by comparing the contaminant concentrations of discrete samples at each sample point to the applicable groundwater remediation objective. Sample points shall be determined by the program under which remediation is performed. |
| b) | Unless the person elects to composite samples or average sampling results as provided in subsections (c) and (d) of this Section, compliance with soil remediation objectives developed under Subparts D through G and I shall be demonstrated by comparing the contaminant concentrations of discrete samples to the applicable soil remediation objective. |
| 1) | Except as provided in subsections (c) and (d) of this Section, compositing of samples is not allowed. |
| 2) | Except as provided in subsections (c) and (d) of this Section, averaging of sample results is not allowed. |
| 3) | Notwithstanding subsections (c) and (d) of this Section, compositing of samples and averaging of sample results is not allowed for the construction worker population. |
| 4) | The number of sampling points required to demonstrate compliance is determined by the requirements applicable to the program under which remediation is performed. |
| c) | If a person chooses to composite soil samples or average soil sample results to demonstrate compliance relative to the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route, the following requirements apply: |
| 1) | A minimum of two sampling locations for every 0.5 acre of contaminated area is required, with discrete samples at each sample location obtained at every two feet of depth, beginning at six inches below the ground surface and continuing through the zone of contamination. Alternatively, a sampling method may be approved by the Agency based on an appropriately designed site-specific evaluation. Samples obtained at or below the water table shall not be used in compositing or averaging. |
| 2) | For contaminants of concern other than volatile organic contaminants: |
| A) | Discrete samples from the same boring may be composited. |
| B) | Discrete sample results from the same boring may be averaged. |
| 3) | For volatile organic contaminants: |
| A) | Compositing of samples is not allowed. |
| B) | Discrete sample results from the same boring may be averaged. |
| d) | If a person chooses to composite soil samples or average soil sample results to demonstrate compliance relative to the inhalation exposure route or ingestion exposure route, the following requirements apply: |
| 1) | A person shall submit a sampling plan for Agency approval, based upon a site-specific evaluation; |
| 2) | For volatile organic compounds, compositing of samples is not allowed; and |
| e) | When averaging under this Section, if no more than 50% of sample results are reported as "non-detect", "no contamination", "below detection limits", or similar terms, such results shall be included in the averaging calculation as one-half of the reported analytical detection limit for the contaminant. If more than 50% of sample results are "non-detect", another statistically valid procedure approved by the Agency may be used to determine an average. |
| a) | Documents and requests filed with the Agency under this Part shall be submitted in accordance with the procedures applicable to the specific program under which remediation is performed. |
| b) | Agency review and approval of documents and requests under this Part shall be performed in accordance with the procedures applicable to the specific program under which the remediation is performed. |
| Section 742.300 | |
| Exclusion of Exposure Route |
| a) | This Subpart sets forth requirements to demonstrate that an actual or potential impact to a receptor or potential receptor from a contaminant of concern can be excluded from consideration from one or more exposure routes. If an evaluation under this Part demonstrates the applicable requirements for excluding an exposure route are met, then the exposure route is excluded from consideration and no remediation objective(s) need be developed for that exposure route. |
| b) | No exposure route may be excluded from consideration until characterization of the extent and concentrations of contaminants of concern at a site has been performed. The actual steps and methods taken to characterize a site shall be determined by the specific program requirements under which the site remediation is being addressed. |
| c) | As an alternative to the use of the requirements in this Part, a person may use the procedures for evaluation of exposure routes under Tier 3 as set forth in Section 742.925. |
| Section 742.305 | |
| Contaminant Source and Free Product Determination |
| a) | The sum of the concentrations of all organic contaminants of concern shall not exceed the attenuation capacity of the soil as determined under Section 742.215; |
| b) | The concentrations of any organic contaminants of concern remaining in the soil shall not exceed the soil saturation limit as determined under Section 742.220; |
| c) | Any soil which contains contaminants of concern shall not exhibit any of the characteristics of reactivity for hazardous waste as determined under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.123; |
| d) | Any soil which contains contaminants of concern shall not exhibit a pH less than or equal to 2.0 or greater than or equal to 12.5, as determined by SW-846 Method 9040B:pH Electrometric for soils with 20 % or greater aqueous (moisture) content or by SW-846 Method 9045C:Soil pH for soils with less than 20% aqueous (moisture) content as incorporated by reference in Section 742.210; and |
| e) | Any soil which contains contaminants of concern in the following list of inorganic chemicals or their salts shall not exhibit any of the characteristics of toxicity for hazardous waste as determined by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.124, or an alternative method approved by the Agency: arsenic, barium, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury, selenium or silver. |
| a) | The requirements of Sections 742.300 and 742.305 are met; and |
| b) | An institutional control, in accordance with Subpart J, is in place that meets the following requirements: |
| 1) | Either: |
| A) | The concentration of any contaminant of concern the land surface or any man-made pathway shall not exceed the Tier 1 remediation objective under Subpart E for the inhalation exposure route; or |
| B) | An engineered barrier, as set forth in Subpart K and approved by the Agency, is in place; and |
| 2) | Requires safety precautions for the construction worker if the Tier 1 construction worker remediation objectives are exceeded. |
| a) | The requirements of Sections 742.300 and 742.305 are met; and |
| b) | An institutional control, in accordance with Subpart J, is in place that meets the following requirements: |
| 1) | Either: |
| A) | The concentration of any contaminant of concern within three feet of the land surface shall not exceed the Tier 1 remediation objective under Subpart E for the ingestion of soil exposure route; or |
| B) | An engineered barrier, as set forth in Subpart K and approved by the Agency, is in place; and |
| 2) | Requires safety precautions for the construction worker if the Tier 1 construction worker remediation objectives are exceeded. |
| Section 742.320 | |
| Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
| a) | The requirements of Sections 742.300 and 742.305 are met; |
| b) | The corrective action measures have been completed to remove any free product to the maximum extent practicable; |
| c) | The source of the release is not located within the minimum or designated maximum setback zone or within a regulated recharge area of a potable water supply well; |
| d) | As demonstrated in accordance with Section 742.1015, for any area within 2500 feet from the source of the release, an ordinance adopted by a unit of local government is in place that effectively prohibits the installation of potable water supply wells (and the use of such wells); |
| e) | As demonstrated using Equation R26, in Appendix C, Table C, in accordance with Section 742.810, the concentration of any contaminant of concern in groundwater within the minimum or designated maximum setback zone of an existing potable water supply well will meet the applicable Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective; and |
| f) | As demonstrated using Equation R26, in Appendix C, Table C, in accordance with Section 742.810, the concentration of any contaminant of concern in groundwater discharging into a surface water will meet the applicable surface water quality standard under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302. |
| Section 742.400 | |
| Area Background |
| Section 742.405 | |
| Determination of Area Background for Soil |
| a) | Soil sampling results shall be obtained for purposes of determining area background levels in accordance with the following procedures: |
| 1) | For volatile organic contaminants, sample results shall be based on discrete samples; |
| 2) | Unless an alternative method is approved by the Agency, for contaminants other than volatile organic contaminants, sample results shall be based on discrete samples or composite samples. If a person elects to use composite samples, each 0.5 acre of the area to be sampled shall be divided into quadrants and 5 aliquots of equal volume per quadrant shall be composited into 1 sample; |
| 3) | Samples shall be collected from similar depths and soil types, which shall be consistent with the depths and soil types in which maximum levels of contaminants are found in the areas of known or suspected releases; and |
| 4) | Samples shall be collected from areas of the site or adjacent to the site that are unaffected by known or suspected releases at or from the site. If the sample results show an impact from releases at or from the site, then the sample results shall not be included in determining area background levels under this Part. |
| b) | Area background shall be determined according to one of the following approaches: |
| 1) | Statewide Area Background Approach: |
| A) | The concentrations of inorganic chemicals in background soils listed in Appendix A, Table G may be used as the upper limit of the area background concentration for the site. The first column to the right of the chemical name presents inorganic chemicals in background soils for counties within Metropolitan Statistical Areas. Counties within Metropolitan Statistical Areas are identified in Appendix A, Table G, Footnote a. Sites located in counties outside Metropolitan Statistical Areas shall use the concentrations of inorganic chemicals in background soils shown in the second column to the right of the chemical name. |
| B) | Soil area background concentrations determined according to this statewide area background approach shall be used as provided in Section 742.415(b) of this Part. For each parameter whose sampling results demonstrate concentrations above those in Appendix A, Table G, the person shall develop appropriate soil remediation objectives in accordance with this Part, or may determine area background in accordance with subsection (b)(2) of this Section. |
| 2) | A statistically valid approach for determining area background concentrations appropriate for the characteristics of the data set, and approved by the Agency. |
| Section 742.410 | |
| Determination of Area Background for Groundwater |
| a) | Groundwater sampling results shall be obtained for purposes of determining area background in accordance with the following procedures: |
| 1) | Samples shall be collected from areas of the site or adjacent to the site that are unaffected by releases at the site; |
| 2) | The background monitoring wells shall be sufficient in number to account for the spatial and temporal variability, size, and number of known or suspected off-site releases of contaminants of concern, and the hydrogeological setting of the site; |
| 3) | The samples shall be collected in consecutive quarters for a minimum of one year for each well unless another sample schedule is approved by the Agency; |
| 4) | The samples shall be collected from the same stratigraphic unit(s) as the groundwater contamination at the site; and |
| 5) | The background monitoring wells shall be located hydraulically upgradient from the release(s) of contaminants of concern, unless a person demonstrates to the Agency that the upgradient location is undefinable or infeasible. |
| b) | Area background shall be determined according to one of the following approaches: |
| 1) | Prescriptive Approach: |
| A) | If more than 15% of the groundwater sampling results for a chemical obtained in accordance with subsection (a) of this Section are less than the appropriate detection limit for that chemical, the Prescriptive Approach may not be used for that chemical. If 15% or less of the sampling results are less than the appropriate detection limit, a concentration equal to one-half the detection limit shall be used for that chemical in the calculations contained in this Prescriptive Approach. |
| B) | The groundwater sampling results obtained in accordance with subsection (a) of this Section shall be used to determine if the sample set is normally distributed. The Shapiro-Wilk Test of Normality shall be used to determine whether the sample set is normally distributed, if the sample set for the background well(s) contains 50 or fewer samples. Values necessary for the Shapiro-Wilk Test of Normality shall be determined using Appendix A, Tables C and D. If the computed value of W is greater than the 5% Critical Value in Appendix A, Table D, the sample set shall be assumed to be normally distributed, and the Prescriptive Approach is allowed. If the computed value of W is less than 5% Critical Value in Appendix A, Table D, the sample set shall be assumed to not be normally distributed, and the Prescriptive Approach shall not be used. |
| C) | If the sample set contains at least ten sample results, the Upper Tolerance Limit (UTL) of a normally distributed sample set may be calculated using the mean (x) and standard deviation(s), from: |
| D) | If the sample set contains at least ten sample results, the UTL shall be the upper limit of the area background concentration for the site. If the sample set contains fewer than ten sample results, the maximum value of the sample set shall be the upper limit of the area background concentration for the site. |
| E) | This Prescriptive Approach shall not be used for determining area background for the parameter pH. |
| 2) | Another statistically valid approach for determining area background concentrations appropriate for the characteristics of the data set, and approved by the Agency. |
| Section 742.415 | |
| Use of Area Background Concentration |
| a) | A person may request that area background concentration |
| 1) | The natural or man-made pathways of any suspected off-site contamination reaching the site; |
| 2) | Physical and chemical properties of suspected off-site contaminants of concern reaching the site; and |
| 3) | The location and justification of all background sampling points. |
| b) | Except as specified in subsections (c) and (d) of this Section, an area background concentration may be used as follows: |
| 1) | To support a request to exclude a chemical as a contaminant of concern from further consideration for remediation at a site due to its presence as a result of background conditions; or |
| 2) | As a remediation objective for a contaminant of concern at a site in lieu of an objective developed pursuant to the other procedures of this Part. |
| c) | An area background concentration shall not be used IN THE EVENT THAT THE AGENCY HAS DETERMINED IN WRITING THAT THE BACKGROUND LEVEL FOR A REGULATED SUBSTANCE POSES AN ACUTE THREAT TO HUMAN HEALTH OR THE ENVIRONMENT AT THE SITE WHEN CONSIDERING THE POST-REMEDIAL ACTION LAND USE. (Section 58.5(b)(3) of the Act) |
| d) | IN THE EVENT THAT THE CONCENTRATION OF A REGULATED SUBSTANCE OF CONCERN ON THE SITE EXCEEDS A REMEDIATION OBJECTIVE ADOPTED BY THE BOARD FOR RESIDENTIAL LAND USE, THE PROPERTY MAY NOT BE CONVERTED TO RESIDENTIAL USE UNLESS SUCH REMEDIATION OBJECTIVE OR AN ALTERNATIVE RISK-BASED REMEDIATION OBJECTIVE FOR THAT REGULATED SUBSTANCE OF CONCERN IS FIRST ACHIEVED. If the land use is restricted, there shall be an institutional control in place in accordance with Subpart J. (Section 58.5(b)(2) of the Act) |
| Section 742.500 | |
| Tier 1 Evaluation Overview |
| a) | A Tier 1 evaluation compares the concentration of each contaminant of concern detected at a site to the baseline remediation objectives provided in Appendix B, Tables A, B, C, D and E. Use of Tier 1 remediation objectives requires only limited site-specific information: concentrations of contaminants of concern, groundwater classification, land use classification, and, if appropriate, soil pH. (See Appendix B, Illustration A.) |
| b) | Although Tier 1 allows for differentiation between residential and industrial/commercial property use of a site, an institutional control under Subpart J is required where remediation objectives are based on an industrial/commercial property use. |
| c) | Any given exposure route is not a concern if the concentration of each contaminant of concern detected at the site is below the Tier 1 value of that given route. In such a case, no further evaluation of that route is necessary. |
| Section 742.505 | |
| Tier 1 Soil and Groundwater Remediation Objectives |
| a) | Soil |
| 1) | Inhalation Exposure Route |
| A) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon residential property use are listed in Appendix B, Table A. |
| B) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon industrial/commercial property use are listed in Appendix B, Table B. Soil remediation objective determinations relying on this table require use of institutional controls in accordance with Subpart J. |
| 2) | Ingestion Exposure Route |
| A) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon residential property use are listed in Appendix B, Table A. |
| B) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon industrial/commercial property use are listed in Appendix B, Table B. Soil remediation objective determinations relying on this table require use of institutional controls in accordance with Subpart J. |
| 3) | Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route |
| A) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon residential property use are listed in Appendix B, Table A. |
| B) | The Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route based upon industrial/commercial property use are listed in Appendix B, Table B. |
| C) | The pH-dependent Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for identified ionizable organics or inorganics for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route (based on the total amount of contaminants present in the soil sample results and groundwater classification) are provided in Appendix B, Tables C and D. |
| D) | Values used to calculate the Tier 1 soil remediation objectives for this exposure route are listed in Appendix B, Table F. |
| 4) | Evaluation of the dermal contact with soil exposure route is not required under Tier 1. |
| b) | Groundwater |
| 1) | The Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives for the groundwater component of the groundwater ingestion route are listed in Appendix B, Table E. |
| 2) | The Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives for this exposure route are given for Class I and Class II groundwaters, respectively. |
| 3) | The Class I groundwater remediation objectives set forth in Appendix B, Table E shall be corrected for cumulative effect of mixtures of similar-acting noncarcinogenic chemicals in accordance with the methodologies set forth in either subsection (b)(3)(A) or (B), if more than one chemical listed in Appendix A, Table E is detected at a site and if such chemicals affect the same target organ (i.e., has the same critical effect as defined by the RfD): |
| A) | Calculate the weighted average using the following equations: |
| Wave = |
| Wave= Weighted Average |
| x1 through xa = | Concentration of each individual contaminant at the location of concern. Note that, depending on the target organ/mode of action, the actual number of contaminants will range from 2 to 14. |
| CUO x a = | A Tier 1 remediation objective each xa from Appendix B, Table E. |
| ii) | If the value of the weighted average calculated in accordance with the equations above is less than or equal to 1.0, then the remediation objectives are met for those chemicals. |
| ii) | If the value of the weighted average calculated in accordance with the equations above is greater than 1.0, then additional remediation must be carried out until the level of contaminants remaining in the remediated area have a weighted average calculated in accordance with the equation above less than or equal to one; |
| B) | Divide each individual chemical's remediation objective by the number of chemicals in that specific target organ group that were detected at the site. Each of the contaminant concentrations at the site is then compared to the remediation objectives that have been adjusted to account for this potential additivity. |
| Section 742.510 | |
| Tier 1 Remediation Objectives Tables |
| a) | Soil remediation objectives are listed in Appendix B, Tables A, B, C and D. |
| 1) | Appendix B, Table A is based upon residential property use. |
| A) | The first column to the right of the chemical name lists soil remediation objectives for the soil ingestion exposure route. |
| B) | The second column lists the soil remediation objectives for the inhalation exposure route. |
| C) | The third and fourth columns list soil remediation objectives for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route for the respective classes of groundwater: |
| i) | Class I groundwater; and |
| ii) | Class II groundwater. |
| D) | The final column lists the Acceptable Detection Limit (ADL), only where applicable. |
| 2) | Appendix B, Table B is based upon industrial/commercial property use. |
| A) | The first and third columns to the right of the chemical name list the soil remediation objectives for the soil ingestion exposure route based on two receptor populations: |
| i) | Industrial/commercial; and |
| ii) | Construction worker. |
| B) | The second and fourth columns to the right of the chemical name list the soil remediation objectives for the inhalation exposure route based on two receptor populations: |
| i) | Industrial/commercial; and |
| ii) | Construction worker. |
| C) | The fifth and sixth columns to the right of the chemical name list the soil remediation objectives for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route for two classes of groundwater: |
| i) | Class I groundwater; and |
| ii) | Class II groundwater. |
| 3) | Appendix B, Tables C and D set forth pH specific soil remediation objectives for inorganic and ionizing organic chemicals for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion route. |
| A) | Table C sets forth remediation objectives based on Class I groundwater and Table D sets forth remediation objectives based on Class II groundwater. |
| B) | The first column in Tables C and D lists the chemical names. |
| C) | The second through ninth columns to the right of the chemical names list the pH based soil remediation objectives. |
| 4) | For the inorganic chemicals listed in Appendix B, Tables A and B, the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route shall be evaluated using TCLP (SW-846 Method 1311) or SPLP (SW-846 Method 1312), incorporated by reference at Section 742.210 unless a person chooses to evaluate the soil component on the basis of the total amount of contaminant in a soil sample result in accordance with subsection (a)(5) of this Section. |
| 5) | For those inorganic and ionizing organic chemicals listed in Appendix B, Tables C and D, if a person elects to evaluate the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route based on the total amount of contaminant in a soil sample result (rather than TCLP or SPLP analysis), the person shall determine the soil pH at the site and then select the appropriate soil remediation objectives based on Class I and Class II groundwaters from Tables C and D, respectively. If the soil pH is less than 4.5 or greater than 8.0, then Tables C and D cannot be used. |
| 6) | Unless one or more exposure routes are excluded from consideration under Subpart C, the most stringent soil remediation objective of the exposure routes (i.e., soil ingestion exposure route, inhalation exposure route, and soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route) shall be compared to the concentrations of soil contaminants of concern measured at the site. When using Appendix B, Table B to select soil remediation objectives for the ingestion exposure route and inhalation exposure route, the remediation objective shall be the more stringent soil remediation objective of the industrial/commercial populations and construction worker populations. |
| 7) | Confirmation sample results may be averaged or soil samples may be composited in accordance with Section 742.225. |
| 8) | If a soil remediation objective for a chemical is less than the ADL, the ADL shall serve as the soil remediation objective. |
| b) | Groundwater remediation objectives for the groundwater component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route are listed in Appendix B, Table E. However, Appendix B, Table E must be corrected for cumulative effect of mixtures of similar-acting noncarcinogenic chemicals as set forth in Section 742.505(b)(3). |
| 1) | The first column to the right of the chemical name lists groundwater remediation objectives for Class I groundwater, and the second column lists the groundwater remediation objectives for Class II groundwater. |
| 2) | To use Appendix B, Table E of this Part, the 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620 classification for groundwater at the site shall be determined. The concentrations of groundwater contaminants of concern at the site are compared to the applicable Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives for the groundwater component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route in Appendix B, Table E. |
| c) | For contaminants of concern not listed in Appendix B, Tables A, B and E, a person may request site-specific remediation objectives from the Agency or propose site-specific remediation objectives in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620, Subpart I of this Part, or both. |
| Section 742.600 | |
| Tier 2 Evaluation Overview |
| a) | Tier 2 remediation objectives are developed through the use of equations which allow site-specific data to be used. (See Appendix C, Illustrations A and B.) The equations, identified in Appendix C, Tables A and C may be used to develop Tier 2 remediation objectives. |
| b) | Tier 2 evaluation is only required for contaminants of concern and corresponding exposure routes (except where excluded from further consideration under Subpart C) exceeding the Tier 1 remediation objectives. When conducting Tier 2 evaluations, the values used in the calculations must have the appropriate units of measure as identified in Appendix C, Tables B and D. |
| c) | Any development of remediation objectives using site-specific information or equations outside the Tier 2 framework shall be evaluated under Tier 3. |
| d) | Any development of a remediation objective under Tier 2 shall not use a target hazard quotient greater than one at the point of human exposure or a target cancer risk greater than 1 in 1,000,000 at the point of human exposure. |
| e) | In conducting a Tier 2 evaluation, the following conditions shall be met: |
| 1) | For each discrete sample, the total soil contaminant concentration of either a single contaminant or multiple contaminants of concern shall not exceed the attenuation capacity of the soil as provided in Section 742.215. |
| 2) | Remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic compounds which affect the same target organ, organ system or similar mode of action shall meet the requirements of Section 742.720. |
| 3) | The soil remediation objectives based on the inhalation and the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure routes shall not exceed the soil saturation limit as provided in Section 742.220. |
| f) | If the calculated Tier 2 soil remediation objective for an applicable exposure route is more stringent than the corresponding Tier 1 remediation objective, then the Tier 1 remediation objective applies. |
| g) | If the calculated Tier 2 soil remediation objective for an exposure route is more stringent than the Tier 1 soil remediation objective(s) for the other exposure routes, then the Tier 2 calculated soil remediation objective applies and Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the other exposure routes are not required. |
| h) | If the calculated Tier 2 soil remediation objective is less stringent than one or more of the soil remediation objectives for the remaining exposure routes, then the Tier 2 values are calculated for the remaining exposure route(s) and the most stringent Tier 2 calculated value applies. |
| a) | Present and post-remediation land use is evaluated in a Tier 2 evaluation. Acceptable exposure factors for the Tier 2 evaluation for residential, industrial/commercial, and construction worker populations are provided in the far right column of both Appendix C, Tables B and D. Use of exposure factors different from those in Appendix C, Tables B and D must be approved by the Agency as part of a Tier 3 evaluation. |
| b) | If a Tier 2 evaluation is based on an industrial/commercial property use, then: |
| 1) | Construction worker populations shall also be evaluated; and |
| 2) | Institutional controls are required in accordance with Subpart J. |
| Section 742.610 | |
| Chemical and Site Properties |
| a) | Physical and Chemical Properties of Contaminants |
| b) | Soil and Groundwater Parameters |
| 1) | A Tier 2 evaluation requires examination of soil and groundwater parameters. The parameters that may be varied, and the conditions under which these parameters are determined as part of Tier 2, are summarized in Appendix C, Tables B and D. If a person proposes to vary site-specific parameters outside of the framework of these tables, the evaluation shall be considered under Tier 3. |
| 2) | To determine site-specific physical soil parameters, a minimum of one boring per 0.5 acre of contamination shall be collected. This boring must be deep enough to allow the collection of the required field measurements. The site-specific physical soil parameters must be determined from the portion of the boring representing the stratigraphic unit(s) being evaluated. For example, if evaluating the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route, two samples from the boring will be required: |
| A) | A sample of the predominant soil type for the vadose zone; and |
| B) | A sample of the predominant soil type for the saturated zone. |
| 3) | A site-specific SSL dilution factor (used in developing soil remediation objectives based upon the protection of groundwater) may be determined by substituting site information in Equation S22 in Appendix C, Table A. To make this demonstration, a minimum of three monitoring wells shall be used to determine the hydraulic gradient. As an alternative, the default dilution factor value listed in Appendix C, Table B may be used. If monitoring wells are used to determine the hydraulic gradient, the soil taken from the borings shall be visually inspected to ensure there are no significant differences in the stratigraphy. If there are similar soil types in the field, one boring shall be used to determine the site-specific physical soil parameters. If there are significant differences, all of the borings shall be evaluated before determining the site-specific physical soil parameters for the site. |
| 4) | Not all of the parameters identified in Appendix C, Tables B and D need to be determined on a site-specific basis. A person may choose to collect partial site-specific information and use default values as listed in Appendix C, Tables B and D for the rest of the parameters. |
| Section 742.700 | |
| Tier 2 Soil Evaluation Overview |
| a) | Tier 2 remediation objectives are developed through the use of models which allow site-specific data to be considered. Appendix C, Tables A and C list equations that shall be used under a Tier 2 evaluation to calculate soil remediation objectives prescribed by SSL and RBCA models, respectively. (See also Appendix C, Illustration A.) |
| b) | Appendix C, Table A lists equations that are used under the SSL model. (See also Appendix C, Illustration A.) The SSL model has equations to evaluate the following human exposure routes: |
| 1) | Soil ingestion exposure route; |
| 2) | Inhalation exposure route for: |
| A) | Volatiles; |
| B) | Fugitive dust; and |
| 3) | Soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route. |
| c) | Evaluation of the dermal exposure route is not required under the SSL model. |
| d) | Appendix C, Table C lists equations that are used under the RBCA model. (See also Appendix C, Illustration A.) The RBCA model has equations to evaluate human exposure based on the following: |
| 1) | The combined exposure routes of inhalation of vapors and particulates, soil ingestion and dermal contact with soil; |
| 2) | The ambient vapor inhalation (outdoor) route from subsurface soils; |
| 3) | Soil component of the groundwater ingestion route; and |
| 4) | Groundwater ingestion exposure route. |
| e) | The equations in either Appendix C, Table A or C may be used to calculate remediation objectives for each contaminant of concern under Tier 2, if the following requirements are met: |
| 1) | The Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the ingestion and inhalation exposure routes shall use the applicable equations from the same approach (i.e., SSL equations in Appendix C, Table C). |
| 2) | The equations used to calculate soil remediation objectives for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route are not dependent on the approach utilized to calculate soil remediation objectives for the other exposure routes. For example, it is acceptable to use the SSL equations for calculating Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the ingestion and inhalation exposure routes, and the RBCA equations for calculating Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route. |
| 3) | Combining equations from Appendix C, Tables A and C to form a new model is not allowed. In addition, Appendix C, Tables A and C must use their own applicable parameters identified in Appendix C, Tables B and D, respectively. |
| f) | In calculating soil remediation objectives for industrial/commercial property use, applicable calculations shall be performed twice: once using industrial/commercial population default values and once using construction worker population default values. The more stringent soil remediation objectives derived from these calculations must be used for further Tier 2 evaluations. |
| g) | Tier 2 data sheets provided by the Agency shall be used to present calculated Tier 2 remediation objectives, if required by the particular program for which remediation is being performed. |
| h) | The RBCA equations which rely on the parameter Soil Water Sorption Coefficient (ks) can only be used for ionizing organics and inorganics by substituting values for ks from Appendix C, Tables I and J, respectively. This will also require the determination of a site-specific value for soil pH. |
| Section 742.705 | |
| Parameters for Soil Remediation Objective Equations |
| a) | Appendix C, Tables B and D list the input parameters for the SSL and RBCA equations, respectively. The first column lists each symbol as it is presented in the equation. The next column defines the parameters. The third column shows the units for the parameters. The fourth column identifies where information on the parameters can be obtained (i.e., field measurement, applicable equation(s), reference source, or default value). The last column identifies how the parameters can be generated. |
| b) | Default Values |
| c) | Site-specific Information |
| 1) | Physical soil parameters identified in Appendix C, Table F. The second column identifies the location where the sample is to be collected. Acceptable methods for measuring or calculating these soil parameters are identified in the last column of Appendix C, Table F; |
| 2) | Institutional controls or engineered barriers, pursuant to Subparts J and K, describe applicable institutional controls and engineered barriers under a Tier 2 evaluation; and |
| 3) | Land use classification |
| d) | Toxicological-specific Information |
| 1) | Toxicological-specific information is used to calculate Tier 2 remediation objectives for the following parameters, if applicable: |
| A) | Oral Chronic Reference Dose (RfDo, expressed in mg/kg-d); |
| B) | Oral Subchronic Reference Dose (RfDs, expressed in mg/kg-d, shall be used for construction worker remediation objective calculations); |
| C) | Oral Slope Factor (SFo, expressed in (mg/kg-d)-1); |
| D) | Inhalation Unit Risk Factor (URF expressed in (m g/m3)-1); |
| E) | Inhalation Chronic Reference Concentration (RfC, expressed in mg/m3); |
| F) | Inhalation Subchronic Reference Concentration (RfCs, expressed in mg/m3, shall be used for construction worker remediation objective calculations); |
| G) | Inhalation Chronic Reference Dose (RfDi, expressed in mg/kg-d); |
| H) | Inhalation Subchronic Reference Dose (RfDis, expressed in mg/kg-d, shall be used for construction worker remediation objective calculations); and |
| I) | Inhalation Slope Factor (SFi, expressed in (mg/kg-d)-1); |
| 2) | Toxicological information can be obtained from IRIS, as incorporated by reference in Section 742.210, or the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| e) | Chemical-specific Information |
| f) | Calculations |
| Section 742.710 | |
| SSL Soil Equations |
| a) | This Section sets forth the equations and parameters used to develop Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the three exposure routes using the SSL approach. |
| b) | Soil Ingestion Exposure Route |
| 1) | Equations S1 through S3 form the basis for calculating Tier 2 remediation objectives for the soil ingestion exposure route using the SSL approach. Equation S1 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic contaminants. Equations S2 and S3 are used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic contaminants for residential populations and industrial/commercial and construction worker populations, respectively. |
| 2) | For Equations S1 through S3, the SSL default values cannot be modified with site-specific information. |
| c) | Inhalation Exposure Route |
| 1) | Equations S4 through S16, S26 and S27 are used to calculate Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the inhalation exposure route using the SSL approach. To address this exposure route, volatiles must be evaluated separately from fugitive dust using their own equations set forth in subsections (c)(2) and (c)(3) of this Section, respectively. |
| 2) | Volatiles |
| A) | Equations S4 through S10 are used to calculate Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for volatile contaminants based on the inhalation exposure route. Equation S4 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic volatile contaminants in soil for residential and industrial/commercial populations. Equation S5 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic volatile contaminants in soil for construction worker populations. Equation S6 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic volatile contaminants in soil for residential and industrial/commercial populations. Equation S7 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic volatile contaminants in soil for construction worker populations. Equations S8 through S10, S27 and S28 are used for calculating numerical values for some of the parameters in Equations S4 through S7. |
| B) | For Equation S4, a numerical value for the Volatilization Factor (VF) can be calculated in accordance with subsection (c)(2)(F) of this Section. The remaining parameters in Equation S4 have either SSL default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., RfC), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| C) | For Equation S5, a numerical value for the Volatilization Factor adjusted for Agitation (VF') can be calculated in accordance with subsection (c)(2)(G) of this Section. The remaining parameters in Equation S5 have either SSL default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., RfC), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| D) | For Equation S6, a numerical value for VF can be calculated in accordance with subsection (c)(2)(F) of this Section. The remaining parameters in Equation S6 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., URF), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| E) | For Equation S7, a numerical value for VF' can be calculated in accordance with subsection (c)(2)(G) of this Section. The remaining parameters in Equation S7 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., URF), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| F) | The VF can be calculated for residential and industrial/commercial populations using one of the following equations based on the information known about the contaminant source and receptor population: |
| i) | Equation S8, in conjunction with Equation S10, is used to calculate VF assuming an infinite source of contamination; or |
| ii) | If the area and depth of the contaminant source are known or can be estimated reliably, mass limit considerations may be used to calculate VF using Equation S26. |
| G) | The VF' can be calculated for the construction worker populations using one of the following equations based on the information known about the contaminant source: |
| i) | Equation S9 is used to calculate VF' assuming an infinite source of contamination; or |
| ii) | If the area and depth of the contaminant source are known or can be estimated reliably, mass limit considerations may be used to calculate VF' using Equation S27. |
| 3) | Fugitive Dust |
| A) | Equations S11 through S16 are used to calculate Tier 2 soil remediation objectives using the SSL fugitive dust model for the inhalation exposure route. Equation S11 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic contaminants in fugitive dust for residential and industrial/commercial populations. Equation S12 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic contaminants in fugitive dust for construction worker populations. Equation S13 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic contaminants in fugitive dust for residential and industrial/commercial populations. Equation S14 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic contaminants in fugitive dust for construction worker populations. Equations S15 and S16 are used for calculating numerical quantities for some of the parameters in Equations S11 through S14. |
| B) | For Equation S11, a numerical value can be calculated for the Particulate Emission Factor (PEF) using Equation S15. This equation relies on various input parameters from a variety of sources. The remaining parameters in Equation S11 have either SSL default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., RfC), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| C) | For Equation S12, a numerical value for the Particulate Emission Factor for Construction Worker (PEF') can be calculated using Equation S16. The remaining parameters in Equation S12 have either SSL default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., RfC), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| D) | For Equation S13, a numerical value for PEF can be calculated using Equation S15. The remaining parameters in Equation S13 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., URF), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| E) | For Equation S14, a numerical value for PEF' can be calculated using Equation S16. The remaining parameters in Equation S14 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table B or toxicological-specific information (i.e., URF), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| d) | Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
| 1) | Equation S17 is used to calculate the remediation objective assuming an infinite source of contamination. |
| A) | The numerical quantities for four parameters in Equation S17, the Target Soil Leachate Concentration (Cw), Soil-Water Partition Coefficient (Kd) for non-ionizing organics, Water-Filled Soil Porosity (q w) and Air-Filled Soil Porosity ( q a), are calculated using Equations S18, S19, S20 and S21, respectively. Equations S22, S23, S24 and S25 are also needed to calculate numerical values for Equations S18 and S21. The pH-dependent Kd values for ionizing organics can be calculated using Equation S19 and the pH-dependent Koc values in Appendix C, Table I. |
| B) | The remaining parameters in Equation S17 are Henry's Law Constant (H'), a chemical specific value listed in Appendix C, Table E and Dry Soil Bulk Density (r b), a site-specific based value listed in Appendix C, Table B. |
| C) | The default value for GWobj is the Tier 1 groundwater objective. For chemicals for which there is no Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective, the value for GWobj shall be the Health Advisory concentration determined according to the procedures specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620, Subpart F. As an alternative to using Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives or Health Advisory concentrations, GWobj may be developed using Equations R25 and R26, if approved institutional controls are in place as required in Subpart J |
| 2) | If the area and depth of the contaminant source are known or can be estimated reliably, mass limit considerations may be used to calculate the remediation objective for this exposure route using Equation S28. The parameters in Equation S28 have default values listed in Appendix C, Table B. |
| Section 742.715 | |
| RBCA Soil Equations |
| a) | This Section presents the RBCA model and describes the equations and parameters used to develop Tier 2 soil remediation objectives. |
| b) | Ingestion, Inhalation, and Dermal Contact |
| 1) | The two sets of equations in subsections (b)(2) and (b)(3) of this Section shall be used to generate Tier 2 soil remediation objectives for the combined ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact with soil exposure routes. |
| 2) | Combined Exposure Routes of Soil Ingestion, Inhalation of Vapors and Particulates, and Dermal Contact with Soil |
| A) | Equations R1 and R2 form the basis for deriving Tier 2 remediation objectives for the set of equations that evaluates the combined exposure routes of soil ingestion, inhalation of vapors and particulates, and dermal contact with soil using the RBCA approach. Equation R1 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic contaminants. Equation R2 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic contaminants. Soil remediation objectives for the ambient vapor inhalation (outdoor) route from subsurface soils must also be calculated in accordance with the procedures outlined in subsection (b)(3) of this Section and compared to the values generated from Equations R1 or R2. The smaller value (i.e., R1 and R2 compared to R7 and R8, respectively) from these calculations is the Tier 2 soil remediation objective for the combined exposure routes of soil ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact with soil. |
| B) | In Equation R1, numerical values are calculated for two parameters: |
| i) | The volatilization factor for surficial soils (VFss) using Equations R3 and R4; and |
| ii) | The volatilization factor for subsurface soils regarding particulates (VFp) using Equation R5. |
| C) | VFss uses Equations R3 and R4 to derive a numerical value. Equation R3 requires the use of Equation R6. Both equations must be used to calculate the VFss. The lowest calculated value from these equations must be substituted into Equation R1. |
| D) | The remaining parameters in Equation R1 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table D or toxicological-specific information (i.e., SFo, SFi), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| E) | For Equation R2, the parameters VFss and VFp are calculated. The remaining parameters in Equation R2 have either default values listed in Appendix C, Table D or toxicological-specific information (i.e., RfDo, RfDi), which can be obtained from IRIS or requested from the program under which the remediation is being performed. |
| F) | For chemicals other than inorganics which do not have default values for the dermal absorption factor (RAFd) in Appendix C, Table D, a dermal absorption factor of 0.5 shall be used for Equations R1 and R2. For inorganics, dermal absorption may be disregarded (i.e., RAFd=0). |
| 3) | Ambient Vapor Inhalation (outdoor) route from Subsurface Soils (soil below one meter) |
| A) | Equations R7 and R8 form the basis for deriving Tier 2 remediation objectives for the ambient vapor inhalation (outdoor) route from subsurface soils using the RBCA approach. Equation R7 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for carcinogenic contaminants. Equation R8 is used to calculate soil remediation objectives for noncarcinogenic contaminants. |
| B) | For Equation R7, the carcinogenic risk-based screening level for air (RBSLair) and the volatilization factor for soils below one meter to ambient air (VFsamb) have numerical values that are calculated using Equations R9 and R11, respectively. Both equations rely on input parameters from a variety of sources. |
| C) | The noncarcinogenic risk-based screening level for air (RBSLair) and the volatilization factor for soils below one meter to ambient air (VFsamb) in Equation R8 have numerical values that can be calculated using Equations R10 and R11, respectively. |
| c) | Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
| 1) | Equation R12 forms the basis for deriving Tier 2 remediation objectives for the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route using the RBCA approach. The parameters, groundwater at the source (GWsource), and Leaching Factor (LFsw), have numerical values that are calculated using Equations R13 and R14, respectively. |
| 2) | Equation R13 requires numerical values that are calculated using Equation R15. |
| 3) | Equation R14 requires numerical values that are calculated using Equations R21, R22, and R24. For non-ionizing organics, the Soil Water Sorption Coefficient (ks) shall be calculated using Equation R20. For ionizing organics and inorganics, the values for ks are listed in Appendix C, Tables I and J, respectively. The pH-dependent ks values for ionizing organics can be calculated using Equation R20 and the pH-dependent Koc values in Appendix C, Table I. The remaining parameters in Equation R14 are field measurements or default values listed in Appendix C, Table D. |
| d) | The default value for GWcomp is the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective. For chemicals for which there is no Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective, the value for GWcomp shall be the Health Advisory concentration determined according to the procedures specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620, Subpart F. As an alternative to using the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives or Health Advisory concentrations, GWcomp may be developed using Equations R25 and R26, if approved institutional controls are in place as may be required in Subpart J. |
| Section 742.720 | |
| Chemicals with Cumulative Noncarcinogenic Effects |
| a) | Calculate the weighted average using the following equations: |
| x1 through xa = | Concentration of each individual contaminant at the location of concern. Note that, depending on the target organ/mode of action, the actual number of contaminants will range from 2 to 14. |
| CUO x a = | A Tier 2 remediation objective must be developed for each xa. |
| b) | Divide each individual chemical's remediation objective by the number of chemicals in that specific target organ group that were detected at the site. Each of the contaminant concentrations at the site is then compared to the remediation objectives that have been adjusted to account for this potential additivity. For the noncarcinogenic contaminants listed in Appendix A, Table E, a respective soil remediation objective need be no lower than the respective value listed in Appendix B, Table A or B. |
| Section 742.800 | |
| Tier 2 Groundwater Evaluation Overview |
| a) | Demonstrate that the groundwater ingestion exposure route is excluded from consideration pursuant to Subpart C; |
| b) | Demonstrate that the groundwater contamination is at or below area background concentrations in accordance with Subpart D and, if necessary, an institutional control restricting usage of the groundwater is in place in accordance with Subpart J; |
| c) | Remediate to Tier 1 remediation objectives; |
| d) | Propose and obtain approval of Tier 2 groundwater remediation objectives in accordance with Section 742.805 and remediate to that level, if necessary; |
| e) | Conduct a Tier 3 evaluation in accordance with Subpart I; or |
| f) | Obtain approval from the Board to: |
| 1) | Reclassify the groundwater pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.260; or |
| 2) | Use an adjusted standard pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act. [415 ILCS 5/28.1]. |
| Section 742.805 | |
| Tier 2 Groundwater Remediation Objectives |
| a) | To develop a groundwater remediation objective under this Section that exceeds the applicable Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective, a person may request approval from the Agency if the person has performed the following: |
| 1) | Identified the horizontal and vertical extent of groundwater for which the Tier 2 groundwater remediation objective is sought; |
| 2) | Taken corrective action, to the maximum extent practicable to remove any free product; |
| 3) | Using Equation R26 in accordance with Section 742.810, demonstrated that the concentration of any contaminant of concern in groundwater will meet: |
| A) | The applicable Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective at the point of human exposure; or |
| B) | For any contaminant of concern for which there is no Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective, the Health Advisory concentration determined according to the procedures specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620, Subpart F at the point of human exposure. A person may request the Agency to provide these concentrations or may propose these concentrations under Subpart I;. |
| 4) | Using Equation R26 in accordance with Section 742.810, demonstrated that the concentration of any contaminant of concern in groundwater within the minimum or designated maximum setback zone of an existing potable water supply well will meet the applicable Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective or if there is no Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective, the Health Advisory concentration; |
| 5) | Using Equation R26 in accordance with Section 742.810, demonstrated that the concentration of any contaminant of concern in groundwater discharging into a surface water will meet the applicable water quality standard under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302; |
| 6) | Demonstrated that the source of the release is not located within the minimum or designated maximum setback zone or within a regulated recharge area of an existing potable water supply well; and |
| 7) | If the selected corrective action includes an engineered barrier as set forth in Subpart K to minimize migration of contaminant of concern from the soil to the groundwater, demonstrated that the engineered barrier will remain in place for post-remediation land use through an institutional control as set forth in Subpart J. |
| b) | A groundwater remediation objective that exceeds the water solubility of that chemical (refer to Appendix C, Table E for solubility values) is not allowed. |
| c) | Groundwater remediation objectives for chemicals which affect the same target organ, organ system or similar mode of action shall meet the requirements of Section 742.505(b)(3). Contaminants of concern for which a Tier 1 remediation objective has been developed shall be included in any mixture of similar-acting substances under consideration in Tier 2. |
| Section 742.810 | |
| Calculations to Predict Impacts from Remaining Groundwater Contamination |
| a) | Equation R26 predicts the contaminant concentration along the centerline of a plume emanating from a vertical planar source in the aquifer (dimensions Sw wide and Sd deep). This model accounts for both three-dimensional dispersion (x is the direction of groundwater flow, y is the other horizontal direction, and z is the vertical direction) and biodegradation. |
| 1) | The parameters in this equation are: |
| X = | distance from the planar source to the location of concern, along the centerline of the plume (i.e., y=0, z=0) |
| Cx = | the concentration of the contaminant at a distance X from the source, along the centerline of the plume |
| Csource= | the greatest potential concentration of the contaminant of concern in the groundwater at the source of the contamination, based on the concentrations of contaminants in groundwater due to the release and the projected concentration of the contaminant migrating from the soil to the groundwater. As indicated above, the model assumes a planar source discharging groundwater at a concentration equal to Csource | |
| a x = | dispersivity in the x direction (i.e., Equation R16) |
| a y = | dispersivity in the y direction (i.e., Equation R17) |
| a z = | dispersivity in the z direction (i.e., Equation R18) | |
| U = | specific discharge (i.e., actual groundwater flow velocity through a porous medium; takes into account the fact that the groundwater actually flows only through the pores of the subsurface materials) where the aquifer hydraulic conductivity (K), the hydraulic gradient (I) and the total soil porosity (q T) must be known (i.e., Equation R19) |
| l = | first order degradation constant obtained from Appendix C, Table E or from measured groundwater data | |
| Sw = | width of planar source in the y direction |
| Sd = | depth of planar source in the z direction |
| 2) | The following parameters are determined through field measurements: U, K, I, q T, Sw, Sd. |
| A) | The determination of values for U, K, I and q T can be obtained through the appropriate laboratory and field techniques; |
| B) | From the immediate down-gradient edge of the source of the groundwater contamination values for Sw and Sd shall be determined. Sw is defined as the width of groundwater at the source which exceeds the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective. Sd is defined as the depth of groundwater at the source which exceeds the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective; and |
| C) | Total soil porosity can also be calculated using Equation R23. |
| b) | Once values are obtained for all the input parameters identified in subsection (a) of this Section, the contaminant concentration along the centerline of the plume at a distance X from the source shall be calculated such that that distance from the down-gradient edge of the source of the contamination at the site to the point where the contaminant concentration is equal to the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective or Health Advisory concentration. |
| 1) | If there are any potable water supply wells located within the calculated distance X, then the Tier 1 groundwater remediation objective or Health Advisory concentration shall be met at the edge of the minimum or designated maximum setback zone of the nearest potable water supply well down-gradient of the source. If no potable water supply wells exist within the calculated distance X, then it can be determined that no existing potable water supply wells are adversely impacted. |
| 2) | To demonstrate that no surface water is adversely impacted, X shall be the distance from the down-gradient edge of the source of the contamination at the site to the nearest surface water body. This calculation must show that the contaminant in the groundwater at this location (Cx) does not exceed the applicable water quality standard. |
| Section 742.900 | |
| Tier 3 Evaluation Overview |
| a) | Tier 3 sets forth a flexible framework to develop remediation objectives outside of the requirements of Tiers 1 and 2. Although Tier 1 and Tier 2 evaluations are not prerequisites to conduct Tier 3 evaluations, data from Tier 1 and Tier 2 can assist in developing remediation objectives under a Tier 3 evaluation. |
| b) | The level of detail required to adequately characterize a site depends on the particular use of Tier 3. Tier 3 can require additional investigative efforts beyond those described in Tier 2 to characterize the physical setting of the site. However, in situations where remedial efforts have simply reached a physical obstruction additional investigation may not be necessary for a Tier 3 submittal. |
| c) | Situations that can be considered for a Tier 3 evaluation include, but are not limited to: |
| 1) | Modification of parameters not allowed under Tier 2; |
| 2) | Use of models different from those used in Tier 2; |
| 3) | Use of additional site data to improve or confirm predictions of exposed receptors to contaminants of concern; |
| 4) | Analysis of site-specific risks using formal risk assessment, probabilistic data analysis, and sophisticated fate and transport models (e.g., requesting a target hazard quotient greater than 1 or a target cancer risk greater than 1 in 1,000,000); |
| 5) | Requests for site-specific remediation objectives because an assessment indicates further remediation is not practical; |
| 6) | Incomplete human exposure pathway(s) not excluded under Subpart C; |
| 7) | Use of toxicological-specific information not available from the sources listed in Tier 2; |
| 8) | Land uses which are substantially different from the assumed residential or industrial/commercial property uses of a site (e.g., a s site will be used for recreation in the future and cannot be evaluated in Tiers 1 or 2); and |
| 9) | Requests for site-specific remediation objectives which exceed Tier 1 groundwater remediation objectives so long as the following is demonstrated: |
| |
|
| |
| d) | For requests of a target cancer risk ranging between 1 in 1,000,000 and 1 in 10,000 at the point of human exposure or a target hazard quotient greater than 1 at the point of human exposure, the requirements of Section 742.915 shall be followed. Requests for a target cancer risk exceeding 1 in 10,000 at the point of human exposure are not allowed. |
| e) | Requests for approval of a Tier 3 evaluation must be submitted to the Agency for review under the specific program under which remediation is performed. When reviewing a submittal under Tier 3, the Agency shall consider WHETHER THE INTERPRETATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS REACHED ARE SUPPORTED BY THE INFORMATION GATHERED. (Section 58.7(e)(1) of the Act) The Agency shall approve a Tier 3 evaluation if the person submits the information required under this Part and establishes through such information that public health is protected and that specified risks to human health and the environment have been minimized. |
| a) | The justification for the modification; and |
| b) | The technical and mathematical basis for the modification. |
| Section 742.910 | |
| Alternative Models |
| a) | Physical and chemical properties of contaminants of concern; |
| b) | Contaminant movement properties; |
| c) | Contaminant availability to receptors; |
| d) | Receptor exposure to the contaminants of concern; |
| e) | Mathematical and technical justification for the model proposed; |
| f) | A licensed copy of the model, if the Agency does not have a licensed copy of the model currently available for use; and |
| g) | Demonstration that the models were correctly applied. |
| a) | Whether the risk assessment procedure used is nationally recognized and accepted including, but not limited to, those procedures incorporated by reference in Section 742.210; |
| b) | Whether the site-specific data reflects actual site conditions; |
| c) | The adequacy of the investigation of present and post-remediation exposure routes and risks to receptors identified at the site; |
| d) | The appropriateness of the sampling and analysis; |
| e) | The adequacy and appropriateness of toxicity information; |
| f) | The extent of contamination; |
| g) | Whether the calculations were accurately performed; and |
| h) | Proposals seeking to modify the target risk consistent with Section 742.900(d) shall address the following factors: |
| 1) | the presence of sensitive populations; |
| 2) | the number of receptors potentially impacted; |
| 3) | the duration of risk at the differing target levels; and |
| 4) | the characteristics of the chemical of concern. |
| a) | The reason(s) why the remediation is impractical; |
| b) | The extent of contamination; |
| c) | Geology, including soil types; |
| d) | The potential impact to groundwater; |
| e) | Results and locations of sampling events; |
| f) | Map of the area, including all utilities and structures; and |
| g) | Present and post-remediation uses of the area of contamination, including human receptors at risk. |
| a) | A description of the route evaluated; |
| b) | Technical support including a discussion of the natural or man-made barriers to exposure through that route, calculations, and modeling results; |
| c) | Physical and chemical properties of contaminants of concern; |
| d) | Contaminant migration properties; |
| e) | Description of the site and physical site characteristics; and |
| f) | Discussion of the result and possibility of the route becoming active in the future. |
| Section 742.930 | |
| Derivation of Toxicological Data |
| a) | Institutional controls in accordance with this Subpart must be placed on the property when remediation objectives are based on any of the following assumptions: |
| 1) | Industrial/Commercial property use; |
| 2) | Target cancer risk greater than 1 in 1,000,000; |
| 3) | Target hazard quotient greater than 1; |
| 4) | Engineered barrier(s); |
| 5) | The point of human exposure is located at a place other than at the source; |
| 6) | Exclusion of exposure routes under Subpart C; or |
| 7) | Any combination of the above. |
| b) | The Agency shall not approve any remediation objective under this Part that is based on the use of institutional controls unless the person has proposed institutional controls meeting the requirements of this Subpart and the requirements of the specific program under which the institutional control is proposed. A proposal for approval of institutional controls shall provide identification of the selected institutional controls from among the types recognized in this Subpart. |
| c) | The following instruments may be institutional controls, subject to the requirements of this Subpart J and the requirements of the specific program under which the institutional control is proposed: |
| 1) | No Further Remediation Letters; |
| 2) | Restrictive covenants and deed restrictions; |
| 3) | Negative easements; |
| 4) | Ordinances adopted and administered by a unit of local government; and |
| 5) | Agreements between a property owner and a highway authority with respect to any contamination remaining under highways. |
| d) | An institutional control is transferred with the property. |
| Section 742.1005 | |
| No Further Remediation Letters |
| a) | A No Further Remediation Letter issued by the Agency under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 732 or 742 may be used as an institutional control under this Part if the requirements of subsection (b) of this Section are met. |
| b) | A request for approval of a No Further Remediation Letter as an institutional control shall meet the requirements applicable to the specific program under which the remediation is performed. |
| Section 742.1010 | |
| Restrictive Covenants, Deed Restrictions and Negative Easements | |
| a) | A restrictive covenant, deed restriction or negative easement may be used as an institutional control under this Part if the requirements of this Section are met and the Agency has determined that no further remediation is required as to the property(ies) to which the institutional control is to apply. |
| b) | A request for approval of a restrictive covenant, deed restriction or negative easement as an acceptable institutional control shall provide the following: |
| 1) | A copy of the restrictive covenant, deed restriction, or negative easement in the form it will be recorded with the Office of the Recorder or Registrar of Titles in the county where the site is located; |
| 2) | A scaled map showing the horizontal extent of contamination above the applicable remediation objectives; |
| 3) | Information showing the concentration of contaminants of concern in which the applicable remediation objectives are exceeded; |
| 4) | A scaled map showing the legal boundaries of all properties under which contamination is located that exceeds the applicable remediation objectives and which are subject to the restrictive covenant, deed restriction, or negative; |
| 5) | Information identifying the current owner(s) of each property identified in subsection (b)(4) of this Section; and |
| 6) | Authorization by the current owner(s), or person authorized by law to act on behalf of the owner, of each property identified in subsection (b)(5) of this Section to record the restrictive covenant or deed restriction. |
| c) | Any restrictive covenant, deed restriction, or negative easement approved by the Agency pursuant to this Section shall be recorded in the Office of the Recorder or Registrar of Titles of the county in which the site is located together with the instrument memorializing the Agency’s no further remediation determination pursuant to the specific program within 45 days after receipt of the Agency’s no further remediation determination. |
| d) | An institutional control approved under this Section shall not become effective until officially recorded in accordance with subsection (c) of this Section. The person receiving the approval shall obtain and submit to the Agency within 30 days after recording a copy of the institutional control demonstrating that it has been recorded. |
| e) | At no time shall any site for which land use has been restricted under an institutional control approved under this Section be used in a manner inconsistent with such land use limitation unless further investigation or remedial action has been conducted that documents the attainment of remediation objectives appropriate for such land use and a new institutional control, if necessary, is approved and recorded in accordance with subsection (c) of this Section. |
| f) | Violation of the terms of an institutional control approved under this Section shall be grounds for voidance of the institutional control and the instrument memorializing the Agency's no further remediation determination. |
| a) | An ordinance adopted by a unit of local government that effectively prohibits the installation of potable water supply wells (and the use of such wells) may be used as an institutional control to meet the requirements of Section 742.320(d) or 742.805(a)(3) if the requirements of this Section are met. Ordinances prohibiting the installation of potable water supply wells (and the use of such wells) that do not expressly prohibit the installation of potable water supply wells (and the use of such wells) by units of local government may be acceptable as institutional controls if the requirements of this Section are met and a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is entered into under subsection (i) of this Section. |
| b) | A request for approval of a local ordinance as an institutional control shall provide the following: |
| 1) | A copy of the ordinance restricting groundwater use certified by an official of the unit of local government in which the site is located that it is the latest, most current copy of the ordinance, unless the Agency and the unit of local government have entered an agreement under subsection (i) of this Section, in which case the request may alternatively reference the MOU. The ordinance must demonstrate that potable use of groundwater from potable water supply wells is prohibited; |
| 2) | A scaled map(s) delineating the areal extent of groundwater contamination (measured or modeled) above the applicable remediation objectives; |
| 3) | Information showing the concentration of contaminants of concern in which the applicable remediation objectives are exceeded; |
| 4) | A scaled map delineating the boundaries of all properties under which groundwater is located which exceeds the applicable groundwater remediation objectives; |
| 5) | Information identifying the current owner(s) of each property identified in subsection (b)(4) of this Section; and |
| 6) | A copy of the proposed submission of the information to the current owners identified in subsection (b)(5) of this Section of the information required in subsections (b)(1) through (b)(5) of this Section and proof that the notification required in subsection (c) of this Section has been submitted. |
| c) | Each of the property owners identified in subsection (b)(5) of this Section and the unit of local government must receive written notification from the party desiring to use the institutional control that groundwater remediation objectives have been approved by the Agency. Written proof of this notification shall be submitted to the Agency within 45 days from the date of the instrument memorializing the Agency’s no further remediation determination. The notification shall include: |
| 1) | The name and address of the unit of local government; |
| 2) | The citation to the ordinance; |
| 3) | A description of the property being sent notice by adequate legal description or by reference to a plat showing the boundaries; |
| 4) | A statement that the ordinance restricting groundwater use has been used by the Agency in reviewing a request for a groundwater remediation objective; |
| 5) | A statement as to the nature of the release and response action with the site name, address, and Agency site number or Illinois inventory identification number; and |
| 6) | A statement as to where more information may be obtained regarding the ordinance. |
| d) | Unless the Agency and the unit of local government have entered into a MOU under subsection (i) of this Section, the current owner or successors in interest of a site who have received approval of use of an ordinance as an institutional control under this Section shall: |
| 1) | Monitor activities of the unit of local government relative to variance requests or changes in the ordinance relative to the use of potable groundwater at properties identified in subsection (b)(4) of this Section; and |
| 2) | Notify the Agency of any approved variance requests or ordinance changes within 30 days after the date such action has been approved. |
| e) | The information required in subsections (b)(1) through (b)(6) of this Section and the Agency letter approving the groundwater remediation objective shall be submitted to the unit of local government. Proof that the information has been filed with the unit of local government shall be provided to the Agency. |
| f) | Any ordinance or MOU used as an institutional control pursuant to this Section shall be recorded in the Office of the Recorder or Registrar of Titles of the county in which the site is located together with the instrument memorializing the Agency’s no further remediation determination pursuant to the specific program within 45 days after receipt of the Agency’s no further remediation. |
| g) | An institutional control approved under this Section shall not become effective until officially recorded in accordance with subsection (f) of this Section. The person receiving the approval shall obtain and submit to the Agency within 30 days after recording a copy of the institutional control demonstrating that it has been recorded. |
| h) | The following shall be grounds for voidance of the ordinance as an institutional control and the instrument memorializing the Agency's no further remediation determination: |
| 1) | Modification of the ordinance by the unit of local government to allow potable use of groundwater; |
| 2) | Approval of a site-specific request, such as a variance, to allow potable use of groundwater at a site identified in subsection (b)(4) of this Section; or |
| 3) | Violation of the terms of an institutional control recorded under Section 742.1005 or Section 742.1010. |
| i) | The Agency and a unit of local government may enter into a MOU under this Section if the unit of local government has adopted an ordinance satisfying subsection (a) of this Section and if the requirements of this subsection are met. The MOU shall include the following: |
| 1) | Identification of the authority of the unit of local government to enter the MOU; |
| 2) | Identification of the legal boundaries, or equivalent, under which the ordinance is applicable; |
| 3) | A certified copy of the ordinance; |
| 4) | A commitment by the unit of local government to notify the Agency of any variance requests or proposed ordinance changes at least 30 days prior to the date the local government is scheduled to take action on the request or proposed change; |
| 5) | A commitment by the unit of local government to maintain a registry of all sites within the unit of local government that have received no further remediation determinations pursuant to specific programs and |
| 6) | If the ordinance does not expressly prohibit the installation of potable water supply wells (and the use of such wells) by units of local government, a commitment by the unit of local government: |
| A) | To review the registry of sites established under subsection (i)(5) of this Section prior to siting potable water supply wells within the area covered by the ordinance; |
| B) | To determine whether the potential source of potable water may be or has been affected by contamination left in place at those sites; and |
| C) | To take whatever steps are necessary to ensure that the potential source of potable water is protected from the contamination or treated before it is used as a potable water supply. |
| Section 742.1020 | |
| Highway Authority Agreements |
| a) | An agreement with a highway authority may be used as an institutional control where the requirements of this Section are met and the Agency has determined that no further remediation is required as to the property(ies) to which the agreement is to apply. |
| b) | As part of the agreement the highway authority shall agree to: |
| 1) | Prohibit the use of groundwater under the highway right of way that is contaminated above residential Tier 1 remediation objectives from the release as a potable supply of water. |
| 2) | Limit access to soil contamination under the highway right of way that is contaminated above residential Tier 1 remediation objectives from the release. Access to soil contamination may be allowed if, during and after any access, public health and the environment are protected. |
| c) | A request for approval of an agreement as an institutional control shall provide the following: |
| 1) | A copy of the agreement executed by the highway authority and the owner of the property from which the release occurred; |
| 2) | A scaled map delineating the areal extent of soil and groundwater contamination above the applicable Tier 1 remediation objectives; |
| 3) | Information showing the concentration of contaminants of concern within the zone in which the applicable Tier 1 remediation objectives are exceeded; |
| 4) | A stipulation of the information required by subsection (b) of this Section in the agreement if it is not practical to obtain the information by sampling the highway right-of-way; and |
| 5) | Information identifying the current fee owner of the highway right-of-way and highway authority having jurisdiction. |
| d) | Violation of the terms of an Agreement approved by the Agency as an institutional control under this Section shall be grounds for voidance of the Agreement as an institutional control and the instrument memorializing the Agency's no further remediation determination. |
| Section 742.1100 | |
| Engineered Barriers |
| a) | Any person who develops remediation objectives under this Part based on engineered barriers shall meet the requirements of this Subpart and the requirements of Subpart J relative to institutional controls. |
| b) | The Agency shall not approve any remediation objective under this Part that is based on the use of engineered barriers unless the person has proposed engineered barriers meeting the requirements of this Subpart. |
| c) | The use of engineered barriers can be recognized in calculating remediation objectives only if the engineered barriers are intended for use as part of the final corrective action. |
| d) | Any no further remediation determination based upon the use of engineered barriers shall require effective maintenance of the engineered barrier. The maintenance requirements shall be included in an institutional control under Subpart J. This institutional control shall address provisions for temporary breaches of the barrier by requiring the following if intrusive construction work is to be performed in which the engineered barrier is to be temporarily breached: |
| 1) | The construction workers shall be notified by the site owner/operator in advance of intrusive activities. Such notification shall enumerate the contaminant of concern known to be present; and |
| 2) | The site owner/operator shall require construction workers to implement protective measures consistent with good industrial hygiene practice. |
| e) | Failure to maintain an engineered barrier in accordance with the no further remediation determination shall be grounds for voidance of that determination and the instrument memorializing the Agency’s no further remediation determination. |
| Section 742.1105 | |
| Engineered Barrier Requirements |
| a) | Natural attenuation, access controls, and point of use treatment shall not be considered engineered barriers. Engineered barriers may not be used to prevent direct human exposure to groundwater without the use of institutional controls. |
| b) | For purposes of determining remediation objectives under Tier 1, engineered barriers are not recognized. |
| c) | The following engineered barriers are recognized for purposes of calculating remediation objectives that exceed residential remediation objectives: |
| 1) | For the soil component of the groundwater ingestion exposure route, the following engineered barriers are recognized: |
| A) | Caps, covering the contaminated media, constructed of compacted clay, asphalt, concrete or other material approved by the Agency; and |
| B) | Permanent structures such as buildings and highways. |
| 2) | For the soil ingestion exposure route, the following engineered barriers are recognized: |
| A) | Caps, covering the contaminated media, constructed of compacted clay, asphalt, concrete, or other material approved by the Agency; |
| B) | Permanent structures such as buildings and highways; and |
| C) | Clean soil, covering the contaminated media, that is a minimum of 3 feet in depth. |
| 3) | For the inhalation exposure route, the following engineered barriers are recognized: |
| A) | Caps, covering the contaminated media, constructed of compacted clay, asphalt, concrete, or other material approved by the Agency; |
| B) | Permanent structures such as buildings and highways; and |
| C) | Clean soil covering the contaminated media, that is a minimum of 10 feet in depth and not within 10 feet of any manmade pathway. |
| 4) | For the ingestion of groundwater exposure route, the following engineered barriers are recognized: |
| A) | Slurry walls; and |
| B) | Hydraulic control of groundwater. |
| d) | Unless otherwise prohibited under Section 742.1100, any other type of engineered barrier may be proposed if it will be as effective as the options listed in subsection (c) of this Section. |
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
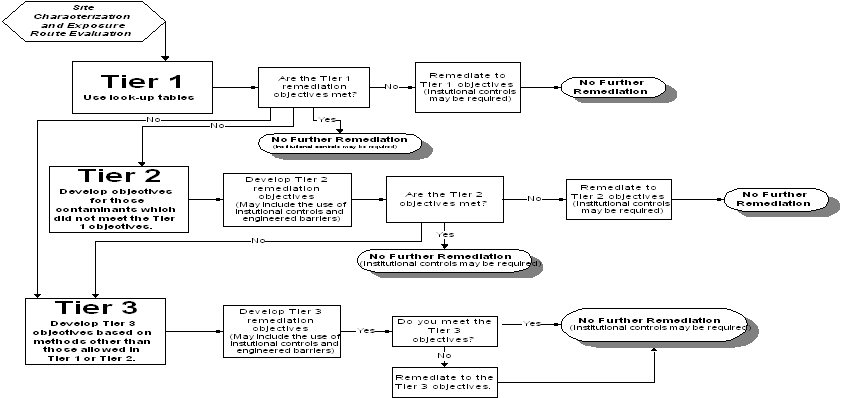
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
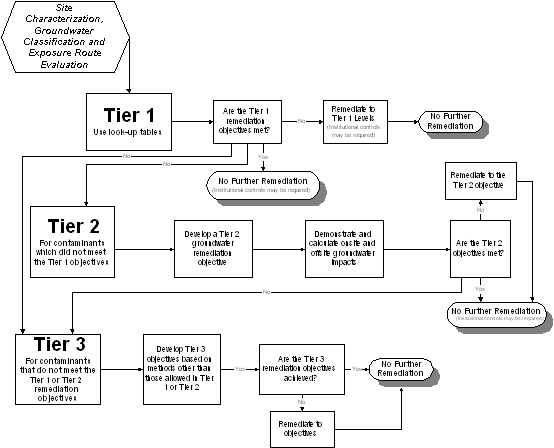
| Section 742.TABLE A: | Soil Saturation Limits (Csat)for Chemicals Whose Melting Point is Less than 30° C |
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Csat (mg/kg)
|
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 100,000
|
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 870
|
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 3,300
|
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 31,000
|
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane (Dichlorobromomethane) | 3,000
|
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 1,900
|
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 10,000
|
| 85-68-7 | Butyl benzyl phthalate | 930
|
| 75-15-0 | Carbon disulfide | 720
|
| 56-23-5 | Carbon tetrachloride | 1,100
|
| 108-90-7 | Chlorobenzene (Monochlorobenzene) | 680
|
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane (Dibromochloromethane) | 1,300
|
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 2,900
|
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 1,400
|
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane (Ethylene dibromide) | 2,800
|
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl phthalate | 2,300
|
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene (o-Dichlorobenzene) | 560
|
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 1,700
|
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane (Ethylene dichloride) | 1,800
|
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | 1,500
|
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 1,200
|
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 3,100
|
| 78-87-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 1,100
|
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropene (1,3-Dichloropropylene, cis + trans) | 1,400
|
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Csat (mg/kg)
|
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl phthalate | 2,000
|
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 10,000
|
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 400
|
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 2,200
|
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 4,600
|
| 74-83-9 | Methyl bromide (Bromomethane) | 3,200
|
| 75-09-2 | Methylene chloride (Dichloromethane) | 2,400
|
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene | 1,000
|
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 1,500
|
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene (Perchloroethylene) | 240
|
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 650
|
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 3,200
|
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | 1,200
|
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 1,800
|
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 1,300
|
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl acetate | 2,700
|
| 75-01-4 | Vinyl chloride | 1,200
|
| 108-38-3 | m-Xylene | 420
|
| 95-47-6 | o-Xylene | 410
|
| 106-42-3 | p-Xylene | 460
|
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 410
|
| Ionizable Organics | ||
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 53,000
|
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
| n | K | n | K |
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
| Section 742.TABLE C: | |
| Coefficients {AN-I+1} for W Test of Normality, for N=2(1)50 |
| i/n | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| 1 | 0.7071 | 0.7071 | 0.6872 | 0.6646 | 0.6431 | 0.6233 | 0.6052 | 0.5888 | 0.5739 | |
| 2 | --- | .0000 | .1677 | .2413 | .2806 | .3031 | .3164 | .3244 | .3291 | |
| 3 | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0875 | .1401 | .1743 | .1976 | .2141 | |
| 4 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0561 | .0947 | .1224 | |
| 5 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0399 |
| i/n | 11
|
12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
16
|
17
|
18
|
19
|
20
|
| 1 | 0.5601 | 0.5475 | 0.5359 | 0.5251 | 0.5150 | 0.5056 | 0.4968 | 0.4886 | 0.4808 | 0.4734 |
| 2 | .3315 | .3325 | .3325 | .3318 | .3306 | .3290 | .3273 | .3253 | .3232 | .3211 |
| 3 | .2260 | .2347 | .2412 | .2460 | .2495 | .2521 | .2540 | .2553 | .2561 | .2565 |
| 4 | .1429 | .1586 | .1707 | .1802 | .1878 | .1939 | .1988 | .2027 | .2059 | .2085 |
| 5 | .0695 | .0922 | .1099 | .1240 | .1353 | .1447 | .1524 | .1587 | .1641 | .1686 |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0303 | 0.0539 | 0.0727 | 0.0880 | 0.1005 | 0.1109 | 0.1197 | 0.1271 | 0.1334 |
| 7 | --- | --- | .0000 | .0240 | .0433 | .0593 | .0725 | .0837 | .0932 | .1013 |
| 8 | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0196 | .0359 | .0496 | .0612 | .0711 |
| 9 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0163 | .0303 | .0422 |
| 10 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0140 |
| i/n | 21
|
22
|
23
|
24
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
29
|
30
|
| 1 | 0.4643 | 0.4590 | 0.4542 | 0.4493 | 0.4450 | 0.4407 | 0.4366 | 0.4328 | 0.4291 | 0.4254 |
| 2 | .3185 | .3156 | .3126 | .3098 | .3069 | .3043 | .3018 | .2992 | .2968 | .2944 |
| 3 | .2578 | .2571 | .2563 | .2554 | .2543 | .2533 | .2522 | .2510 | .2499 | .2487 |
| 4 | .2119 | .2131 | .2139 | .2145 | .2148 | .2151 | .2152 | .2151 | .2150 | .2148 |
| 5 | .1736 | .1764 | .1787 | .1807 | .1822 | .1836 | .1848 | .1857 | .1864 | .1870 |
| 6 | 0.1399 | 0.1443 | 0.1480 | 0.1512 | 0.1539 | 0.1563 | 0.1584 | 0.1601 | 0.1616 | 0.1630 |
| 7 | .1092 | .1150 | .1201 | .1245 | .1283 | .1316 | .1346 | .1372 | .1395 | .1415 |
| 8 | .0804 | .0878 | .0941 | .0997 | .1046 | .1089 | .1128 | .1162 | .1192 | .1219 |
| 9 | .0530 | .0618 | .0696 | .0764 | .0823 | .0876 | .0923 | .0965 | .1002 | .1036 |
| 10 | .0263 | .0368 | .0459 | .0539 | .0610 | .0672 | .0728 | .0778 | .0822 | .0862 |
| 11 | 0.0000 | 0.0122 | 0.0228 | 0.0321 | 0.0403 | 0.0476 | 0.0540 | 0.0598 | 0.0650 | 0.0697 |
| 12 | --- | --- | .0000 | .0107 | .0200 | .0284 | .0358 | .0424 | .0483 | .0537 |
| 13 | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0094 | .0178 | .0253 | .0320 | .0381 |
| 14 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0084 | .0159 | .0227 |
| 15 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0076 |
| i/n | 31
|
32
|
33
|
34
|
35
|
36
|
37
|
38
|
39
|
40
|
| 1 | 0.4220 | 0.4188 | 0.4156 | 0.4127 | 0.4096 | 0.4068 | 0.4040 | 0.4015 | 0.3989 | 0.3964 |
| 2 | .2921 | .2898 | .2876 | .2854 | .2834 | .2813 | .2794 | .2774 | .2755 | .2737 |
| 3 | .2475 | .2463 | .2451 | .2439 | .2427 | .2415 | .2403 | .2391 | .2380 | .2368 |
| 4 | .2145 | .2141 | .2137 | .2132 | .2127 | .2121 | .2116 | .2110 | .2104 | .2098 |
| 5 | .1874 | .1878 | .1880 | .1882 | .1883 | .1883 | .1883 | .1881 | .1880 | .1878 |
| i/n | 31
|
32
|
33
|
34
|
35
|
36
|
37
|
38
|
39
|
40
|
| 6 | 0.1641 | 0.1651 | 0.1660 | 0.1667 | 0.1673 | 0.1678 | 0.1683 | 0.1686 | 0.1689 | 0.1691 |
| 7 | .1433 | .1449 | .1463 | .1475 | .1487 | .1496 | .1503 | .1513 | .1520 | .1526 |
| 8 | .1243 | .1265 | .1284 | .1301 | .1317 | .1331 | .1344 | .1356 | .1366 | .1376 |
| 9 | .1066 | .1093 | .1118 | .1140 | .1160 | .1179 | .1196 | .1211 | .1225 | .1237 |
| 10 | .0899 | .0931 | .0961 | .0988 | .1013 | .1036 | .1056 | .1075 | .1092 | .1108 |
| 11 | 0.0739 | 0.0777 | 0.0812 | 0.0844 | 0.0873 | 0.0900 | 0.0924 | 0.0947 | 0.0967 | 0.0986 |
| 12 | .0585 | .0629 | .0669 | .0706 | .0739 | .0770 | .0798 | .0824 | .0848 | .0870 |
| 13 | .0435 | .0485 | .0530 | .0572 | .0610 | .0645 | .0677 | .0706 | .0733 | .0759 |
| 14 | .0289 | .0344 | .0395 | .0441 | .0484 | .0523 | .0559 | .0592 | .0622 | .0651 |
| 15 | .0144 | .0206 | .0262 | .0314 | .0361 | .0404 | .0444 | .0481 | .0515 | .0546 |
| 16 | 0.0000 | 0.0068 | 0.0131 | 0.0187 | 0.0239 | 0.0287 | 0.0331 | 0.0372 | 0.0409 | 0.0444 |
| 17 | --- | --- | .0000 | .0062 | .0119 | .0172 | .0220 | .0264 | .0305 | .0343 |
| 18 | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0057 | .0110 | .0158 | .0203 | .0244 |
| 19 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0053 | .0101 | .0146 |
| 20 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0049 |
| i/n | 41
|
42
|
43
|
44
|
45
|
46
|
47
|
48
|
49
|
50
|
| 1 | 0.3940 | 0.3917 | 0.3894 | 0.3872 | 0.3850 | 0.3830 | 0.3808 | 0.3789 | 0.3770 | 0.3751 |
| 2 | .2719 | .2701 | .2684 | .2667 | .2651 | .2635 | .2620 | .2604 | .2589 | .2574 |
| 3 | .2357 | .2345 | .2334 | .2323 | .2313 | .2302 | .2291 | .2281 | .2271 | .2260 |
| 4 | .2091 | .2085 | .2078 | .2072 | .2065 | .2058 | .2052 | .2045 | .2038 | .2032 |
| 5 | .1876 | .1874 | .1871 | .1868 | .1865 | .1862 | .1859 | .1855 | .1851 | .1847 |
| i/n | 41
|
42
|
43
|
44
|
45
|
46
|
47
|
48
|
49
|
50
|
| 6 | 0.1693 | 0.1694 | 0.1695 | 0.1695 | 0.1695 | 0.1695 | 0.1695 | 0.1693 | 0.1692 | 0.1691 |
| 7 | .1531 | .1535 | .1539 | .1542 | .1545 | .1548 | .1550 | .1551 | .1553 | .1554 |
| 8 | .1384 | .1392 | .1398 | .1405 | .1410 | .1415 | .1420 | .1423` | .1427 | .1430 |
| 9 | .1249 | .1259 | .1269 | .1278 | .1286 | .1293 | .1300 | .1306 | .1312 | .1317 |
| 10 | .1123 | .1136 | .1149 | .1160 | .1170 | .1180 | .1189 | .1197 | .1205 | .1212 |
| 11 | 0.1004 | 0.1020 | 0.1035 | 0.1049 | 0.1062 | 0.1073 | 0.1085 | 0.1095 | 0.1105 | 0.1113 |
| 12 | .0891 | .0909 | .0927 | .0943 | .0959 | .0972 | .0986 | .0998 | .1010 | .1020 |
| 13 | .0782 | .0804 | .0824 | .0842 | .0860 | .0876 | .0892 | .0906 | .0919 | .0932 |
| 14 | .0677 | .0701 | .0724 | .0745 | .0775 | .0785 | .0801 | .0817 | .0832 | .0846 |
| 15 | .0575 | .0602 | .0628 | .0651 | .0673 | .0694 | .0713 | .0731 | .0748 | .0764 |
| 16 | 0.0476 | 0.0506 | 0.0534 | 0.0560 | 0.0584 | 0.0607 | 0.0628 | 0.0648 | 0.0667 | 0.0685 |
| 17 | .0379 | .0411 | .0442 | .0471 | .0497 | .0522 | .0546 | .0568 | .0588 | .0608 |
| 18 | .0283 | .0318 | .0352 | .0383 | .0412 | .0439 | .0465 | .0489 | .0511 | .0532 |
| 19 | .0188 | .0227 | .0263 | .0296 | .0328 | .0357 | .0385 | .0411 | .0436 | .0459 |
| 20 | .0094 | .0136 | .0175 | .0211 | .0245 | .0277 | .0307 | .0335 | .0361 | .0386 |
| 21 | 0.0000 | 0.0045 | 0.0087 | 0.0126 | 0.0163 | 0.0197 | 0.0229 | 0.0259 | 0.0288 | 0.0314 |
| 22 | --- | --- | .0000 | .0042 | .0081 | .0118 | .0153 | .0185 | .0215 | .0244 |
| 23 | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0039 | .0076 | .0111 | .0143 | .0174 |
| 24 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0037 | .0071 | .0104 |
| 25 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | .0000 | .0035 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
| Section 742.TABLE D: | |
| Percentage Points of the W Test for N=3(1)50 |
n
|
0.01
|
0.05
|
| 3 | 0.753 | 0.767 |
| 4 | 0.687 | 0.748 |
| 5 | 0.686 | 0.762 |
| 6 | 0.713 | 0.788 |
| 7 | 0.730 | 0.803 |
| 8 | 0.749 | 0.818 |
| 9 | 0.764 | 0.829 |
| 10 | 0.781 | 0.842 |
| 11 | 0.792 | 0.850 |
| 12 | 0.805 | 0.859 |
| 13 | 0.814 | 0.866 |
| 14 | 0.825 | 0.874 |
| 15 | 0.835 | 0.881 |
| 16 | 0.844 | 0.887 |
| 17 | 0.851 | 0.892 |
| 18 | 0.858 | 0.897 |
| 19 | 0.863 | 0.901 |
| 20 | 0.868 | 0.905 |
| 21 | 0.873 | 0.908 |
| 22 | 0.878 | 0.911 |
| 23 | 0.881 | 0.914 |
| 24 | 0.884 | 0.916 |
| 25 | 0.888 | 0.918 |
| 26 | 0.891 | 0.920 |
| 27 | 0.894 | 0.923 |
| 28 | 0.896 | 0.924 |
| 29 | 0.898 | 0.926 |
| 30 | 0.900 | 0.927 |
| 31 | 0.902 | 0.929 |
| 32 | 0.904 | 0.930 |
| 33 | 0.906 | 0.931 |
| 34 | 0.908 | 0.933 |
| 35 | 0.910 | 0.934 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
| Section 742.TABLE E: | Chemicals with Noncarcinogenic Toxic Effects on Specific Target Organs/Organ Systems or Similar Modes of Action |
| 1,2 Dibromo-3-Chloropropane (Inhalation only) |
| p-Chloroaniline | |
| Section 742.TABLE F: | Chemicals With Carcinogenic Toxic Effects on Specific Target Organs/Organ Systems or Similar Modes of Action |
| Section 742.APPENDIX A: | |
| General | |
| Chemical Name | Counties Within
Metropolitan Statistical Areasa (mg/kg) |
Counties Outside
Metropolitan Statistical Areas (mg/kg) |
| Aluminum | 9,500
|
9,200
|
| Antimony | 4.0
|
3.3
|
| Arsenic | 7.2
|
5.2
|
| Barium | 110`
|
122
|
| Beryllium | 0.59
|
0.56
|
| Cadmium | 0.6
|
0.50
|
| Calcium | 9,300
|
5,525
|
| Chromium | 16.2
|
13.0
|
| Cobalt | 8.9
|
8.9
|
| Copper | 19.6
|
12.0
|
| Cyanide | 0.51
|
0.50
|
| Iron | 15,900
|
15,000
|
| Lead | 36.0
|
20.9
|
| Magnesium | 4,820
|
2,700
|
| Manganese | 636
|
630
|
| Mercury | 0.06
|
0.05
|
|
aCounties within Metropolitan Statistical Areas: Boone, Champaign, Clinton, Cook, DuPage, Grundy, Henry, Jersey, Kane, Kankakee, Kendall, Lake, Macon, Madison, McHenry, McLean, Menard, Monroe, Peoria, Rock Island, Sangamon, St. Clair, Tazewell, Will, Winnebago and Woodford. |
| Chemical Name | Counties Within
Metropolitan Statistical Areasa (mg/kg) |
Counties Outside
Metropolitan Statistical Areas (mg/kg) |
| Nickel | 18.0
|
13.0
|
| Potassium | 1,268
|
1,100
|
| Selenium | 0.48
|
0.37
|
| Silver | 0.55
|
0.50
|
| Sodium | 130
|
130.0
|
| Sulfate | 85.5
|
110
|
| Sulfide | 3.1
|
2.9
|
| Thallium | 0.32
|
0.42
|
| Vanadium | 25.2
|
25.0
|
| Zinc | 95.0
|
60.2
|
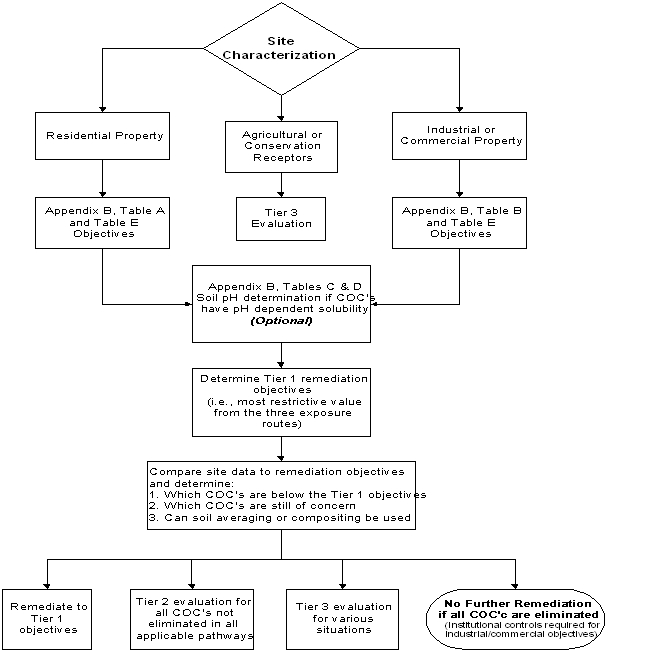
| Section 742.APPENDIX B: | Tier 1 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.TABLE A: | |
| Tier 1 Soil Remediation Objectivesa for Residential Properties |
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 83-32-9 | Acenaphthene | 4,700b
|
---c
|
570b
|
2,900
|
*
|
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 7,800b
|
100,000d
|
16b
|
16
|
*
|
| 15972-60-8 | Alachloro | 8e
|
---c
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
NA
|
| 116-06-3 | Aldicarbo | 78b
|
---c
|
0.013
|
0.07
|
NA
|
| 309-00-2 | Aldrin | 0.04e
|
3e
|
0.5e
|
2.5
|
*
|
| 120-12-7 | Anthracene | 23,000b
|
---c
|
12,000b
|
59,000
|
*
|
| 1912-24-9 | Atrazineo | 2700b
|
---c
|
0.066
|
0.33
|
NA
|
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 22e
|
0.8e
|
0.03
|
0.17
|
*
|
| 56-55-3 | Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.9e
|
---c
|
2
|
8
|
*
|
| 205-99-2 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.9e
|
---c
|
5
|
25
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 207-08-9 | Benzo(k)fluroanthene | 9e
|
---c
|
49
|
250
|
*
|
| 50-32-8 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.09e,f
|
---c
|
8
|
82
|
*
|
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 0.6e
|
0.2e,f
|
0.0004e,f
|
0.0004
|
0.66
|
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 46e
|
31,000d
|
3,600
|
31,000d
|
*
|
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane) |
10e
|
3,000d
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
*
|
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 81e
|
53e
|
0.8
|
0.8
|
*
|
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 7,800b
|
10,000d
|
17b
|
17
|
NA
|
| 85-68-7 | Butyl benzyl phthalate | 16,000b
|
930d
|
930d
|
930d
|
*
|
| 86-74-8 | Carbazole | 32e
|
---c
|
0.6e
|
2.8
|
NA
|
| 1563-66-2 | Carbofurano | 390b
|
---c
|
0.22
|
1.1
|
NA
|
| 75-15-0 | Carbon disulfide | 7,800b
|
720d
|
32b
|
160
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 56-23-5 | Carbon tetrachloride | 5e
|
0.3e
|
0.07
|
0.33
|
*
|
| 57-74-9 | Chlordane | 0.5e
|
20e
|
10
|
48
|
*
|
| 106-47-8 | 4-Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline) |
310b
|
---c
|
0.7b
|
0.7
|
1.3
|
| 108-90-7 | Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene) |
1,600b
|
130b
|
1
|
6.5
|
*
|
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane) |
1,600b
|
1,300d
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
*
|
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 100e
|
0.3e
|
0.6
|
2.9
|
*
|
| 218-01-9 | Chrysene | 88e
|
---c
|
160
|
800
|
*
|
| 94-75-7 | 2,4-D | 780b
|
---c
|
1.5
|
7.7
|
*
|
| 75-99-0 | Dalapon | 2,300b
|
---c
|
0.85
|
8.5
|
1.2
|
| 72-54-8 | DDD | 3e
|
---c
|
16e
|
80
|
*
|
| 72-55-9 | DDE | 2e
|
---c
|
54e
|
270
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 50-29-3 | DDT | 2e
|
---g
|
32e
|
160
|
*
|
| 53-70-3 | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 0.09e,f
|
---c
|
2
|
7.6
|
*
|
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 0.46e
|
11b
|
0.002
|
0.002
|
*
|
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide) |
0.0075e
|
0.17e
|
0.0004
|
0.004
|
0.005
|
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl phthalate | 7,800b
|
2,300d
|
2,300d
|
2,300d
|
*
|
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o - Dichlorobenzene) |
7,000b
|
560d
|
17
|
43
|
*
|
| 106-46-7 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p - Dichlorobenzene) |
---c
|
---g
|
2
|
11
|
*
|
| 91-94-1 | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 1e
|
---c
|
0.007e,f
|
0.033
|
1.3
|
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 7,800b
|
1,300b
|
23b
|
110
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride) |
7e
|
0.4e
|
0.02
|
0.1
|
*
|
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | 700b
|
1,500d
|
0.06
|
0.3
|
*
|
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 780b
|
1,200d
|
0.4
|
1.1
|
*
|
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 1,600b
|
3,100d
|
0.7
|
3.4
|
*
|
| 78-87-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 9e
|
15b
|
0.03
|
0.15
|
*
|
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichloropropylene, cis + trans) |
4e
|
0.1e
|
0.004e
|
0.02
|
0.005
|
| 60-57-1 | Dieldrinn | 0.04e
|
1e
|
0.004e
|
0.02
|
*
|
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl phthalate | 63,000b
|
2,000d
|
470b
|
470
|
*
|
| 105-67-9 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 1,600b
|
---c
|
9b
|
9
|
*
|
| 121-14-2 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 0.9e
|
---c
|
0.0008e,f
|
0.0008
|
0.013
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 606-20-2 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene | 0.9e
|
---c
|
0.0007e,f
|
0.0007
|
0.0067
|
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 1,600b
|
10,000d
|
10,000d
|
10,000d
|
*
|
| 115-29-7 | Endosulfan | 470b
|
---c
|
18b
|
90
|
*
|
| 145-73-3 | Endothallo | 1,600b
|
---c
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
NA
|
| 72-20-8 | Endrin | 23b
|
---c
|
1
|
5
|
*
|
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 7,800b
|
400d
|
13
|
19
|
*
|
| 206-44-0 | Fluoranthene | 3,100b
|
---c
|
4,300b
|
21,000
|
*
|
| 86-73-7 | Fluorene | 3,100b
|
---c
|
560b
|
2,800
|
*
|
| 76-44-8 | Heptachlor | 0.1e
|
0.1e
|
23
|
110
|
*
|
| 1024-57-3 | Heptachlor epoxide | 0.07e
|
5e
|
0.7
|
3.3
|
*
|
| 118-74-1 | Hexachlorobenzene | 0.4e
|
1e
|
2
|
11
|
*
|
| 319-84-6 | alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC) | 0.1e
|
0.8e
|
0.0005e,f
|
0.003
|
0.002
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 58-89-9 | gamma-HCH (Lindane)n | 0.5e
|
---c
|
0.009
|
0.047
|
*
|
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 550b
|
10b
|
400
|
2,200d
|
*
|
| 67-72-1 | Hexachloroethane | 78b
|
---c
|
0.5b
|
2.6
|
*
|
| 193-39-5 | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 0.9e
|
---c
|
14
|
69
|
*
|
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 15,600b
|
4,600d
|
8b
|
8
|
*
|
| 72-43-5 | Methoxychlor | 390b
|
---c
|
160
|
780
|
*
|
| 74-83-9 | Methyl bromide
(Bromomethane) |
110b
|
10b
|
0.2b
|
1.2
|
*
|
| 75-09-2 | Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane) |
85e
|
13e
|
0.02e
|
0.2
|
*
|
| 95-48-7 | 2-Methylphenol
(o - Cresol) |
3,900b
|
---c
|
15b
|
15
|
*
|
| 91-20-3 | Naphthalene | 3,100b
|
---c
|
84b
|
420
|
*
|
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene | 39b
|
92b
|
0.1b,f
|
0.1
|
0.26
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 86-30-6 | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 130e
|
---c
|
1e
|
5.6
|
*
|
| 621-64-7 | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 0.09e,f
|
---c
|
0.00005e,f
|
0.00005
|
0.66
|
| 108-95-2 | Phenol | 47,000b
|
---c
|
100b
|
100
|
*
|
| 1918-02-1 | Picloramo | 5,500b
|
---c
|
2
|
20
|
NA
|
| 1336-36-3 | Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)n | 1; 10h
|
---c,h
|
---h
|
---h
|
*
|
| 129-00-0 | Pyrene | 2,300b
|
---c
|
4,200b
|
21,000
|
*
|
| 122-34-9 | Simazineo | 390b
|
---c
|
0.04
|
0.37
|
NA
|
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 16,000b
|
1,500d
|
4
|
18
|
*
|
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene) |
12e
|
11e
|
0.06
|
0.3
|
*
|
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 16,000b
|
650d
|
12
|
29
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 8001-35-2 | Toxaphenen | 0.6e
|
89e
|
31
|
150
|
*
|
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 780b
|
3,200b
|
5
|
53
|
*
|
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | ---c
|
1,200d
|
2
|
9.6
|
*
|
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 310b
|
1,800d
|
0.02
|
0.3
|
*
|
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 58e
|
5e
|
0.06
|
0.3
|
*
|
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl acetate | 78,000b
|
1,000b
|
170b
|
170
|
*
|
| 75-01-4 | Vinyl chloride | 0.3e
|
0.03e
|
0.01f
|
0.07
|
*
|
| 108-38-3 | m-Xylene | 160,000b
|
420d
|
210
|
210
|
*
|
| 95-47-6 | o-Xylene | 160,000b
|
410d
|
190
|
190
|
*
|
| 106-42-3 | p-Xylene | 160,000b
|
460d
|
200
|
200
|
*
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
Values |
| ||||
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 160,000b
|
410d
|
150
|
150
|
*
|
| Ionizable Organics | ||||||
| 65-85-0 | Benzoic Acid | 310,000b
|
---c
|
400b,i
|
400i
|
*
|
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 390b
|
53,000d
|
4b,i
|
4i
|
*
|
| 120-83-2 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 230b
|
---c
|
1b,i
|
1i
|
*
|
| 51-28-5 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 160b
|
---c
|
0.2b,f
|
0.2
|
3.3
|
| 88-85-7 | Dinosebo | 78b
|
---c
|
0.34b,i
|
3.4i
|
*
|
| 87-86-5 | Pentachlorophenol | 3e,j
|
---c
|
0.03f,i
|
0.14i
|
2.4
|
| 93-72-1 | 2,4,5-TP
(Silvex) |
630b
|
---c
|
11i
|
55i
|
*
|
| 95-95-4 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 7,800b
|
---c
|
270b,i
|
1,400i
|
*
|
| 88-06-2 | 2,4,6 Trichlorophenol | 58e
|
200e
|
0.2e,f,i
|
0.77i
|
0.43
|
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
|
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
Values |
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| Inorganics | ||||||
| 7440-36-0 | Antimony | 31b
|
---c
|
0.006m
|
0.024m
|
*
|
| 7440-38-2 | Arsenicl,n | 0.4e,t
|
750e
|
0.05m
|
0.2m
|
*
|
| 7440-39-3 | Barium | 5,500b
|
690,000b
|
2.0m
|
2.0m
|
*
|
| 7440-41-7 | Beryllium | 0.1e,t
|
1,300e
|
0.004m
|
0.5m
|
*
|
| 7440-42-8 | Boron | 7,000b
|
---g
|
2.0m
|
2.0m
|
*
|
| 7440-43-9 | Cadmiuml,n | 78b, r
|
1,800e
|
0.005m
|
0.05m
|
*
|
| 16887-00-6 | Chloride | ---c
|
---c
|
200m
|
200m
|
*
|
| 7440-47-3 | Chromium, total | 390b
|
270e
|
0.1m
|
1.0m
|
*
|
| 16065-83-1 | Chromium, ion, trivalent | 78,000b
|
---c
|
---g
|
---g
|
*
|
| 18540-29-9 | Chromium, ion, hexavalent | 390b
|
270e
|
---
|
---
|
*
|
| 7440-48-4 | Cobalt | 4,700b
|
---c
|
1.0m
|
1.0m
|
*
|
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
|
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
Values |
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 7440-50-8 | Coppern | 2,900b
|
---c
|
0.65m
|
0.65m
|
*
|
| 57-12-5 | Cyanide (amenable) | 1,600b
|
---c
|
0.2q
|
0.6q
|
*
|
| 7782-41-4 | Fluoride | 4,700b
|
---c
|
4.0m
|
4.0m
|
*
|
| 15438-31-0 | Iron | ---c
|
---c
|
5.0m
|
5.0m
|
*
|
| 7439-92-1 | Lead | 400k
|
---c
|
0.0075m
|
0.1m
|
*
|
| 7439-96-5 | Manganese | 3,700b
|
69,000b
|
0.15m
|
10.0m
|
*
|
| 7439-97-6 | Mercuryl,n | 23b,s
|
10b,i
|
0.002m
|
0.01m
|
*
|
| 7440-02-0 | Nickell | 1,600b
|
13,000e
|
0.1m
|
2.0m
|
*
|
| 14797-55-8 | Nitrate as Np | 130,000b
|
---c
|
10.0q
|
100q
|
*
|
| 7782-49-2 | Seleniuml,n | 390b
|
---c
|
0.05m
|
0.05m
|
*
|
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
|
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
Values |
| CAS No. | Chemical Name | Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 7440-22-4 | Silver | 390b
|
---c
|
0.05m
|
---
|
*
|
| 14808-79-8 | Sulfate | ---c
|
---c
|
400m
|
400m
|
*
|
| 7440-28-0 | Thallium | 6.3b,u
|
---c
|
0.002m
|
0.02m
|
*
|
| 7440-62-2 | Vanadium | 550b
|
---c
|
0.049m
|
---
|
*
|
| 7440-66-6 | Zincl | 23,000b
|
---c
|
5.0m
|
10m
|
*
|
| "*" indicates that the ADL is less than or equal to the specified remediation objective. | ||
| a | Soil remediation objectives based on human health criteria only. |
| b | Calculated values correspond to a target hazard quotient of 1. |
| c | No toxicity criteria available for the route of exposure. |
| d | Soil saturation concentration (Csat) = the concentration at which the absorptive limits of the soil particles, the solubility limits of the available soil moisture, and saturation of soil pore air have been reached. Above the soil saturation concentration, the assumptions regarding vapor transport to air and/or dissolved phase transport to groundwater (for chemicals which are liquid at ambient soil temperatures) have been violated, and alternative modeling approaches are required. |
| e | Calculated values correspond to a cancer risk level of 1 in 1,000,000. |
| f | Level is at or below Contract Laboratory Program required quantitation limit for Regular Analytical Services (RAS). |
| g | Chemical-specific properties are such that this route is not of concern at any soil contaminant concentration. |
| h | A preliminary goal of 1 ppm has been set for PCBs based on Guidance on Remedial Actions for Superfund Sites with PCB Contamination, EPA/540G-90/007, and on USEPA efforts to manage PCB contamination. See 40 CFR 761.120 - USEPA "PCB Spill Cleanup Policy." This regulation goes on to say that the remediation goal for an unrestricted area is 10 ppm and 25 ppm for a restricted area, provided both have at least 10 inches of clean cover. |
| i | Soil remediation objective for pH of 6.8. If soil pH is other than 6.8, refer to Appendix B, Tables C and D of this Part. |
| j | Ingestion soil remediation objective adjusted by a factor of 0.5 to account for dermal route. |
| k | A preliminary remediation goal of 400 mg/kg has been set for lead based on Revised Interim Soil Lead Guidance for CERCLA Sites and RCRA Corrective Action Facilities, OSWER Directive #9355.4-12. |
| l | Potential for soil-plant-human exposure. |
| m | The person conducting the remediation has the option to use: 1) TCLP or SPLP test results to compare with the remediation objectives listed in this Table; or 2) the total amount of contaminant in the soil sample results to compare with pH specific remediation objectives listed in Appendix B, Table C or D of this Part. (See Section 742.510.) If the person conducting the remediation wishes to calculate soil remediation objectives based on background concentrations, this should be done in accordance with Subpart D of this Part. |
| n | The Agency reserves the right to evaluate the potential for remaining contaminant concentrations to pose significant threats to crops, livestock, or wildlife. |
| o | For agrichemical facilities, remediation objectives for surficial soils which are based on field application rates may be more appropriate for currently registered pesticides. Consult the Agency for further information. |
| p | For agrichemical facilities, soil remediation objectives based on site-specific background concentrations of Nitrate as N may be more appropriate. Such determinations shall be conducted in accordance with the procedures set forth in Subparts D and I of this Part. |
| t | |||
| Note that Table value is likely to be less than background concentration for this chemical; screening or remediation concentrations using the procedures of Subpart D of this Part may be more appropriate. |
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
ClassII
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 83-32-9 | Acenaphthene | 120,000b | -----c | 120,000b | -----c | 570b | 2,900 | *
|
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 200,000b | 100,000d | 200,000b | 100,000d | 16b | 16 | *
|
| 15972-60-8 | Alachloro | 72e | -----c | 1,600e | -----c | 0.04 | 0.2 | NA
|
| 116-06-3 | Aldicarbo | 2,000b | -----c | 200b | -----c | 0.013 | 0.07 | NA
|
| 309-00-2 | Aldrin | 0.3e | 6.6e | 6.1b | 9.3e | 0.5e | 2.5 | *
|
| 120-12-7 | Anthracene | 610,000b | -----c | 610,000b | -----c | 12,000b | 59,000 | *
|
| 1912-24-9 | Atrazineo | 72,000b | -----c | 7,100b | -----c | 0.066 | 0.33 | NA
|
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 200e | 1.5e | 4,300e | 2.1e | 0.03 | 0.17 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 56-55-3 | Benzo(a)anthracene | 8e | -----c | 170e | -----c | 2 | 8 | *
|
| 205-99-2 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 8e | -----c | 170e | -----c | 5 | 25 | *
|
| 207-08-9 | Benzo(k)fluroanthene | 78e | -----c | 1,700e | -----c | 49 | 250 | *
|
| 50-32-8 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.8e | -----c | 17e | -----c | 8 | 82 | *
|
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 5e | 0.47e | 75e | 0.66e | 0.0004e,f | 0.0004 | 0.66
|
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 410e | 31,000d | 4,100b | 31,000d | 3,600 | 31,000d | *
|
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane) |
92e | 3,000d | 2,000e | 3,000d | 0.6 | 0.6 | *
|
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 720e | 100e | 16,000e | 140e | 0.8 | 0.8 | *
|
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 200,000b | 10,000d | 200,000b | 10,000d | 17b | 17 | NA
|
| 85-68-7 | Butyl benzyl phthalate | 410,000b | 930d | 410,000b | 930d | 930d | 930d | *
|
| 86-74-8 | Carbazole | 290e | -----c | 6,200e | -----c | 0.6e | 2.8 | NA
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 1563-66-2 | Carbofurano | 10,000b | -----c | 1,000b | -----c | 0.22 | 1.1 | NA
|
| 75-15-0 | Carbon disulfide | 200,000b | 720d | 20,000b | 9.0b | 32b | 160 | *
|
| 56-23-5 | Carbon tetrachloride | 44e | 0.64e | 410b | 0.90e | 0.07 | 0.33 | *
|
| 57-74-9 | Chlordane | 4e | 38e | 12b | 53e | 10 | 48 | *
|
| 106-47-8 | 4 - Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline) |
8,200b | -----c | 820b | -----c | 0.7b | 0.7 | 1.3
|
| 108-90-7 | Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene) |
41,000b | 210b | 4,100b | 1.3b | 1 | 6.5 | *
|
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane) |
41,000b | 1,300d | 41,000b | 1,300d | 0.4 | 0.4 | *
|
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 940e | 0.54e | 2,000b | 0.76e | 0.6 | 2.9 | *
|
| 218-01-9 | Chrysene | 780e | -----c | 17,000e | -----e | 160 | 800 | *
|
| 94-75-7 | 2,4-D | 20,000b | -----c | 2,000b | -----c | 1.5 | 7.7 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 75-99-0 | Dalapon | 61,000b | -----c | 6,100b | -----c | 0.85 | 8.5 | 1.2
|
| 72-54-8 | DDD | 24e | -----c | 520e | -----c | 16e | 80 | *
|
| 72-55-9 | DDE | 17e | -----c | 370e | -----c | 54e | 270 | *
|
| 50-29-3 | DDT | 17e | 1,500e | 100b | 2,100e | 32e | 160 | *
|
| 53-70-3 | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 0.8e | -----c | 17e | -----c | 2 | 7.6 | *
|
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 4e | 17b | 89e | 0.11b | 0.002 | 0.002 | *
|
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide) |
0.07e | 0.32e | 1.5e | 0.45e | 0.0004 | 0.004 | 0.005
|
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl phthalate | 200,000b | 2,300d | 200,000b | 2,300d | 2,300d | 2,300d | *
|
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o - Dichlorobenzene) |
180,000b | 560d | 18,000b | 310b | 17 | 43 | *
|
| 106-46-7 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p - Dichlorobenzene) |
-----c | 17,000b | -----c | 340b | 2 | 11 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 91-94-1 | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 13e | -----c | 280e | -----c | 0.007e,f | 0.033 | 1.3
|
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 200,000b | 1,700d | 200,000b | 130b | 23b | 110 | *
|
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride) |
63e | 0.70e | 1,400e | 0.99e | 0.02 | 0.1 | *
|
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | 18,000b | 1,500d | 1,800b | 1,500d | 0.06 | 0.3 | *
|
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 20,000b | 1,200d | 20,000b | 1,200d | 0.4 | 1.1 | *
|
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 41,000b | 3,100d | 41,000b | 3,100d | 0.7 | 3.4 | *
|
| 78-87-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 84e | 23b | 1,800e | 0.50b | 0.03 | 0.15 | *
|
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichloropropylene, cis + trans) |
33e | 0.23e | 610b | 0.33e | 0.004e | 0.02 | 0.005
|
| 60-57-1 | Dieldrinn | 0.4e | 2.2e | 7.8e | 3.1e | 0.004e | 0.02 | 0.0013
|
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl phthalate | 1,000,000b | 2,000d | 1,000,000b | 2,000d | 470b | 470 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 105-67-9 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 41,000b | -----c | 41,000b | -----c | 9b | 9 | *
|
| 121-14-2 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 8.4e | -----c | 180e | -----c | 0.0008e,f | 0.0008 | 0.013
|
| 606-20-2 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene | 8.4e | -----c | 180e | -----c | 0.0007e,f | 0.0007 | 0.0067
|
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 41,000e | 10,000d | 4,100b | 10,000d | 10,000d | 10,000d | *
|
| 115-29-7 | Endosulfan | 12,000b | -----c | 1,200b | -----c | 18b | 90 | *
|
| 145-73-3 | Endothallo | 41,000c | -----c | 4,100b | -----c | 0.4 | 0.4 | NA
|
| 72-20-8 | Endrin | 610b | -----c | 61b | -----c | 1 | 5 | *
|
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 200,000b | 400d | 20,000b | 58b | 13 | 19 | *
|
| 206-44-0 | Fluoranthene | 82,000b | -----c | 82,000b | -----c | 4,300b | 21,000 | *
|
| 86-73-7 | Fluorene | 82,000b | -----c | 82,000b | -----c | 560b | 2,800 | *
|
| 76-44-8 | Heptachlor | 1e | 11e | 28e | 16e | 23 | 110 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 1024-57-3 | Heptachlor epoxide | 0.6e | 9.2e | 2.7b | 13e | 0.7 | 3.3 | *
|
| 118-74-1 | Hexachlorobenzene | 4e | 1.8e | 78e | 2.6e | 2 | 11 | *
|
| 319-84-6 | alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC) | 0.9e | 1.5e | 20e | 2.1e | 0.0005e,f | 0.003 | 0.002
|
| 58-89-9 | gamma-HCH (Lindane)n | 4e | -----c | 96e | -----c | 0.009 | 0.047 | *
|
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 14,000b | 16b | 14,000b | 1.1b | 400 | 2,200d | *
|
| 67-72-1 | Hexachloroethane | 2,000b | -----c | 2,000b | -----c | 0.5b | 2.6 | *
|
| 193-39-5 | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 8e | -----c | 170e | -----c | 14 | 69 | *
|
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 410,000b | 4,600d | 410,000b | 4,600d | 8b | 8 | *
|
| 72-43-5 | Methoxychlor | 10,000b | -----c | 1,000b | -----c | 160 | 780 | *
|
| 74-83-9 | Methyl bromide
(Bromomethane) |
2,900b | 15b | 1,000b | 3.9b | 0.2b | 1.2 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 75-09-2 | Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane) |
760e | 24e | 12,000b | 34e | 0.02e | 0.2 | *
|
| 95-48-7 | 2-Methylphenol
(o - Cresol) |
100,000b | -----c | 100,000b | -----c | 15b | 15 | *
|
| 86-30-6 | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 1,200e | -----c | 25,000e | -----c | 1e | 5.6 | 0.66
|
| 621-64-7 | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 0.8e | -----c | 18e | -----c | 0.00005e,f | 0.00005 | 0.66
|
| 91-20-3 | Naphthalene | 82,000b | -----c | 8,200b | -----c | 84b | 420 | *
|
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene | 1,000b | 140b | 1,000b | 9.4b | 0.1b,f | 0.1 | 0.26
|
| 108-95-2 | Phenol | 1,000,000b | -----c | 120,000b | -----c | 100b | 100 | *
|
| 1918-02-1 | Picloramo | 140,000b | -----c | 14,000b | -----c | 2 | 20 | NA
|
| 1336-36-3 | Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)n | 1; 10; 25h | -----c,h | 1h | -----c,h | -----h | -----h | *
|
| 129-00-0 | Pyrene | 61,000b | -----c | 61,000b | -----c | 4,200b | 21,000 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 122-34-9 | Simazineo | 10,000b | -----c | 1,000b | -----c | 0.04 | 0.37 | NA
|
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 410,000b | 1,500d | 41,000b | 430b | 4 | 18 | *
|
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene) |
110e | 20e | 2,400e | 28e | 0.06 | 0.3 | *
|
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 410,000b | 650d | 410,000b | 42b | 12 | 29 | *
|
| 8001-35-2 | Toxaphenen | 5.2e | 170e | 110e | 240e | 31 | 150 | *
|
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 20,000b | 3,200d | 2,000b | 920b | 5 | 53 | *
|
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | -----c | 1,200d | -----c | 1,200d | 2 | 9.6 | *
|
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 8,200b | 1,800d | 8,200b | 1,800d | 0.02 | 0.3 | *
|
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 520e | 8.9e | 1,200b | 12e | 0.06 | 0.3 | *
|
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl acetate | 1,000,000b | 1,600b | 200,000b | 10b | 170b | 170 | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 75-01-4 | Vinyl chloride | 3e | 0.06e | 65e | 0.08e | 0.01f | 0.07 | *
|
| 108-38-3 | m-Xylene | 1,000,000 | 420d | 410,000b | 420d | 210 | 210 | *
|
| 95-47-6 | o-Xylene | 1,000,000 | 410d | 410,000b | 410d | 190 | 190 | *
|
| 106-42-3 | p-Xylene | 1,000,000 | 460d | 410,000b | 460d | 200 | 200 | *
|
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 1,000,000b | 410d | 410,000b | 410d | 150 | 150 | *
|
| Ionizable Organics | ||||||||
| 65-85-0 | Benzoic Acid | 1,000,000b | -----c | 820,000b | -----c | 400b,i | 400i | *
|
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 10,000b | 53,000d | 10,000b | 53,000d | 4b,i | 20i | *
|
| 120-83-2 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 6,100b | -----c | 610b | -----c | 1b,i | 1i | *
|
| 51-28-5 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 4,100b | -----c | 410b | -----c | 0.2b,f,i | 0.2i | 3.3
|
| 88-85-7 | Dinosebo | 2,000b | -----c | 200b | -----c | 0.34b,i | 3.4i | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils |
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route |
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
|
Worker Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/kg) |
Class II
(mg/kg) |
ADL
(mg/kg) |
| 87-86-5 | Pentachlorophenol | 24e,j | -----c | 520e,j | -----c | 0.03f,i | 0.14i | 2.4
|
| 93-72-1 | 2,4,5-TP
(Silvex) |
16,000b | -----c | 1,600b | -----c | 11i | 55i | *
|
| 95-95-4 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 200,000b | -----c | 200,000b | -----c | 270b,i | 1,400i | *
|
| 88-06-2 | 2,4,6- Trichlorophenol | 520e | 390e | 11,000e | 540e | 0.2e,f,i | 0.77i | 0.43
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
|
| ||||||
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
| Worker
Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
|
| Inorganics | ||||||||
| 7440-36-0 | Antimony | 820b | -----c | 82b | -----c | 0.006m | 0.024m | *
|
| 7440-38-2 | Arsenicl,n | 3e,t | 1,200e | 61b | 25,000e | 0.05m | 0.2m | |
| 7440-39-3 | Barium | 140,000b | 910,000b | 14,000b | 870,000b | 2.0m | 2.0m | *
|
| 7440-41-7 | Beryllium | 1e,t | 2,100e | 29e | 44,000e | 0.004m | 0.5m | *
|
| 7440-42-8 | Boron | 180,000b | 1,000,000 | 18,000b | 1,000,000 | 2.0m | 2.0m | *
|
| 7440-43-9 | Cadmiuml,n | 2,000b,r | 2,800e | 200b,r | 59,000e | 0.005m | 0.05m | *
|
| 16887-00-6 | Chloride | -------c | -----c | -----c | -----c | 200m | 200m | *
|
| 7440-47-3 | Chromium, total | 10,000b | 420e | 4,100b | 8,800e | 0.1m | 1.0m | *
|
| 16065-83-1 | Chromium, ion, trivalent | 1,000,000b | -----c | 330,000b | -----c | -----g | -----g | *
|
| 18540-29-9 | Chromium, ion, hexavalent | 10,000b | 420e | 4,100b | 8,800e | ----- | ----- | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
|
| ||||||
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
| Worker
Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
|
| 7440-48-4 | Cobalt | 120,000b | -----c | 12,000b | -----c | 1.0m | 1.0m | *
|
| 7440-50-8 | Coppern | 82,000b | -----c | 8,200b | -----c | 0.65m | 0.65m | *
|
| 57-12-5 | Cyanide (amenable) | 41,000b | -----c | 4,100b | -----c | 0.2q | 0.6q | *
|
| 7782-41-4 | Fluoride | 120,000b | -----c | 12,000b | -----c | 4.0m | 4.0m | *
|
| 15438-31-0 | Iron | -----c | -----c | -----c | -----c | 5.0m | 5.0m | *
|
| 7439-92-1 | Lead | 400k | -----c | 400k | -----c | 0.0075m | 0.1m | *
|
| 7439-96-5 | Manganese | 96,000b | 91,000b | 9,600b | 8,700b | 0.15m | 10.0m | *
|
| 7439-97-6 | Mercuryl,n | 610b | 540,000b | 61b,s | 52,000b | 0.002m | 0.01m | *
|
| 7440-02-0 | Nickell | 41,000b | 21,000e | 4,100b | 440,000e | 0.1m | 2.0m | *
|
| 14797-55-8 | Nitrate as Np | 1,000,000b | -----c | 330,000b | -----c | 10.0q | 100q | *
|
| 7782-49-2 | Seleniuml,n | 10,000b | -----c | 1,000b | -----c | 0.05m | 0.05m | *
|
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
|
|
| ||||||
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
| Worker
Values
|
|
| |||||
CAS No.
|
Chemical
Name |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Ingestion
(mg/kg) |
Inhalation
(mg/kg) |
Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
|
| 7440-22-4 | Silver | 10,000b | -----c | 1,000b | -----c | 0.05m | ----- | *
|
| 14808-79-8 | Sulfate | -----c | -----c | -----c | -----c | 400m | 400m | *
|
| 7440-28-0 | Thallium | 160b,u | -----c | 160b,u | -----c | 0.002m | 0.02m | *
|
| 7440-62-2 | Vanadium | 14,000b | -----c | 1,400b | -----c | 0.049m | ----- | *
|
| 7440-66-6 | Zincl | 610,000b | -----c | 61,000b | -----c | 5.0m | 10m | *
|
| d | Soil saturation concentration (Csat)= the concentration at which the absorptive limits of the soil particles, the solubility limits of the available soil moisture, and saturation of soil pore air have been reached. Above the soil saturation concentration, the assumptions regarding vapor transport to air and/or dissolved phase transport to groundwater (for chemicals which are liquid at ambient soil temperatures) have been violated, and alternative modeling approaches are required. |
| e | Calculated values correspond to a cancer risk level of 1 in 1,000,000. |
| f | Level is at or below Contract Laboratory Program required quantitation limit for Regular Analytical Services (RAS). |
| g | Chemical-specific properties are such that this route is not of concern at any soil contaminant concentration. |
| h | A preliminary goal of 1 ppm has been set for PCBs based on Guidance on Remedial Actions for Superfund Sites with PCB Contamination, EPA/540G-90/007, and on USEPA efforts to manage PCB contamination. See 40 CFR 761.120 for USEPA "PCB Spill Cleanup Policy." This regulation goes on to say that the remediation goal for an unrestricted area is 10 ppm and 25 ppm for a restricted area, provided both have at least 10 inches of clean cover. |
| i | Soil remediation objective for pH of 6.8. If soil pH is other than 6.8, refer to Appendix B, Tables C and D in this Part. |
| j | Ingestion soil remediation objective adjusted by a factor of 0.5 to account for dermal route. |
| k | A preliminary remediation goal of 400 mg/kg has been set for lead based on Revised Interim Soil Lead Guidance for CERCLA Sites and RCRA Corrective Action Facilities, OSWER Directive #9355.4-12. |
| l | Potential for soil-plant-human exposure. |
| m | The person conducting the remediation has the option to use: (1) TCLP or SPLP test results to compare with the remediation objectives listed in this Table; or (2) the total amount of contaminant in the soil sample results to compare with pH specific remediation objectives listed in Appendix B, Table C or D of this Part. (See Section 742.510.) If the person conducting the remediation wishes to calculate soil remediation objectives based on background concentrations, this should be done in accordance with Subpart D of this Part. |
| n | The Agency reserves the right to evaluate the potential for remaining contaminant concentrations to pose significant threats to crops, livestock, or wildlife. |
| o | For agrichemical facilities, remediation objectives for surficial soils which are based on field application rates may be more appropriate for currently registered pesticides. Consult the Agency for further information. |
| p | For agrichemical facilities, soil remediation objectives based on site-specific background concentrations of Nitrate as N may be more appropriate. Such determinations shall be conducted in accordance with the located in Subparts D and I of this Part. |
| q | The TCLP extraction must be done using water at a pH of 7.0. |
| r | Value based on dietary Reference Dose. |
| s | Value based on Reference Dose for Mercuric chloride (CAS No. 7487-94-7). |
| t | Note that Table value is likely to be less than background concentration for this chemical; screening or remediation concentrations using the procedures of Subpart D of this Part. |
| u | Value based on Reference Dose for thallium sulfate (CAS No. 7446-18-6). |
| Section 742.Table C: | pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class I Groundwater) |
|
Chemical (totals) (mg/kg) |
pH 4.5 to 4.74 | pH 4.75 to 5.24 | pH 5.25 to 5.74 | pH 5.75 to 6.24 | pH 6.25 to 6.64 | pH 6.65 to 6.89 | pH 6.9
to 7.24 |
pH 7.25
to 7.74 |
pH 7.75
to 8.0 |
| Inorganics | |||||||||
| Antimony | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Arsenic | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
| Barium | 260 | 490 | 850 | 1,200 | 1,500 | 1,600 | 1,700 | 1,800 | 2,100 |
| Beryllium | 1.1 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 6.6 | 22 | 63 | 140 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Cadmium | 1.0 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 11 | 59 | 430 |
| Chromium (+6) | 70 | 62 | 54 | 46 | 40 | 38 | 36 | 32 | 28 |
| Copper | 330 | 580 | 2,100 | 11,000 | 59,000 | 130,000 | 200,000 | 330,000 | 330,000 |
| Cyanide | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Mercury | 0.01 | 0.01` | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 2.1 | 3.3 | 6.4 | 8.0 |
| Nickel | 20 | 36 | 56 | 76 | 100 | 130 | 180 | 700 | 3,800 |
| Selenium | 24 | 17 | 12 | 8.8 | 6.3 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 3.3 | 2.4 |
| Silver | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.62 | 1.5 | 4.4 | 8.5 | 13 | 39 | 110 |
|
Chemical (totals) (mg/kg) |
pH 4.5 to 4.74 | pH 4.75 to 5.24 | pH 5.25 to 5.74 | pH 5.75 to 6.24 | pH 6.25 to 6.64 | pH 6.65 to 6.89 | pH 6.9
to 7.24 |
pH 7.25
to 7.74 |
pH 7.75
to 8.0 |
| Thallium | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 3.8 |
| Vanadium | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 | 980 |
| Zinc | 1,000 | 1,800 | 2,600 | 3,600 | 5,100 | 6,200 | 7,500 | 16,000 | 53,000 |
| Organics |
| Benzoic Acid | 440 | 420 | 410 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| 2-Chlorophenol | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.6 | 3.1 |
| 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.69 |
| Dinoseb | 8.4 | 4.5 | 1.9 | 0.82 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.25 |
| Pentachlorophenol | 0.54 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 2,4,5-TP (Silvex) | 26 | 16 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 400 | 390 | 390 | 370 | 320 | 270 | 230 | 130 | 64 |
| 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
Section 742.APPENDIX B
| Section 742.Table D: | pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class II Groundwater) |
| Chemical (totals)
(mg/kg) |
pH 4.5 to 4.74 | pH 4.75 to 5.24 | pH 5.25 to 5.74 | pH 5.75 to 6.24 | pH 6.25 to 6.64 | pH 6.65 to 6.89 | pH 6.9
to 7.24 |
pH 7.25
to 7.74 |
pH 7.75
to 8.0 |
| Inorganics | |||||||||
| Antimony | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Arsenic | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 110 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Barium | 260 | 490 | 850 | 1,200 | 1,500 | 1,600 | 1,700 | 1,800 | 2,100 |
| Beryllium | 140 | 260 | 420 | 820 | 2,800 | 7,900 | 17,000 | 130,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Cadmium | 10 | 17 | 27 | 37 | 52 | 75 | 110 | 590 | 4,300 |
| Chromium (+6) | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data | No Data |
| Copper | 330 | 580 | 2,100 | 11,000 | 59,000 | 130,000 | 200,000 | 330,000 | 330,000 |
| Cyanide | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Mercury | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.75 | 4.4 | 10 | 16 | 32 | 40 |
| Nickel | 400 | 730 | 1,100 | 1,500 | 2,000 | 2,600 | 3,500 | 14,000 | 76,000 |
| Selenium | 24 | 17 | 12 | 8.8 | 6.3 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 3.3 | 2.4 |
| Thallium | 16 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 34 | 38 |
| Zinc | 2,000 | 3,600 | 5,200 | 7,200 | 10,000 | 12,000 | 15,000 | 32,000 | 110,000 |
| Chemical (totals)
(mg/kg) |
pH 4.5 to 4.74 | pH 4.75 to 5.24 | pH 5.25 to 5.74 | pH 5.75 to 6.24 | pH 6.25 to 6.64 | pH 6.65 to 6.89 | pH 6.9
to 7.24 |
pH 7.25
to 7.74 |
pH 7.75
to 8.0 |
| Organics | |||||||||
| Benzoic Acid | 440 | 420 | 410 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| 2-Chlorophenol | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 3.6 | 3.1 |
| 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.86 | 0.69 |
| Dinoseb | 84 | 45 | 19 | 8.2 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 2.5 |
| Pentachlorophenol | 2.7 | 1.6 | 0.75 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.10 |
| 2,4,5-TP (Silvex) | 130 | 79 | 62 | 57 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 |
| 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 2,000 | 2,000 | 1,900 | 1,800 | 1,600 | 1,400 | 1,200 | 640 | 64 |
| 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX B: | |
| Tier 1 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.TABLE E: | Tier 1 Groundwater Remediation Objectives for the Groundwater Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 83-32-9 | Acenaphthene | 0.42 | 2.1 |
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 15972-60-8 | Alachlor | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 116-06-3 | Aldicarb | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 309-00-2 | Aldrin | 0.00004a | 0.0002 |
| 120-12-7 | Anthracene | 2.1 | 10.5 |
| 1912-24-9 | Atrazine | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 56-55-3 | Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.00013a | 0.00065 |
| 205-99-2 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.00018a | 0.0009 |
| 207-08-9 | Benzo(k)fluroanthene | 0.00017a | 0.00085 |
| 50-32-8 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.0002a,c | 0.002c |
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 0.01a | 0.01 |
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 0.006a,c | 0.06c |
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane) |
0.00002a | 0.00002 |
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 0.0002a | 0.0002 |
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 85-68-7 | Butyl benzyl phthalate | 1.4 | 7.0 |
| 86-74-8 | Carbazole | --- | --- |
| 1563-66-2 | Carbofuran | 0.04c | 0.2c |
| 75-15-0 | Carbon disulfide | 0.7 | 3.5 |
| 56-23-5 | Carbon tetrachloride | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 57-74-9 | Chlordane | 0.002c | 0.01c |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 108-90-7 | Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene) |
0.1c | 0.5c |
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane) |
0.14 | 0.14 |
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 0.00002a | 0.0001 |
| 218-01-9 | Chrysene | 0.0015a | 0.0075 |
| 94-75-7 | 2,4-D | 0.07c | 0.35c |
| 75-99-0 | Dalapon | 0.2c | 2.0c |
| 72-54-8 | DDD | 0.00011a | 0.00055 |
| 72-55-9 | DDE | 0.00004a | 0.0002 |
| 50-29-3 | DDT | 0.00012a | 0.0006 |
| 53-70-3 | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 0.0003a | 0.0015 |
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 0.0002c | 0.0002c |
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide) |
0.00005a,c | 0.0005c |
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl phthalate | 0.7 | 3.5 |
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o - Dichlorobenzene) |
0.6c | 1.5c |
| 106-46-7 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p - Dichlorobenzene) |
0.075c | 0.375c |
| 91-94-1 | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 0.02a | 0.1 |
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 0.7 | 3.5 |
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride) |
0.005c | 0.025c |
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethyleneb | 0.007c | 0.035c |
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 0.07c | 0.2c |
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 0.1c | 0.5c |
| 78-87-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichloropropylene, cis + trans) |
0.001a | 0.005 |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 60-57-1 | Dieldrin | 0.00002a | 0.0001 |
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl phthalate | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| 121-14-2 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluenea | 0.00002 | 0.00002 |
| 606-20-2 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluenea | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 88-85-7 | Dinoseb | 0.007c | 0.07c |
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 0.14 | 0.7 |
| 115-29-7 | Endosulfan | 0.042 | 0.21 |
| 145-73-3 | Endothall | 0.1c | 0.1c |
| 72-20-8 | Endrin | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 0.7c | 1.0c |
| 206-44-0 | Fluoranthene | 0.28 | 1.4 |
| 86-73-7 | Fluorene | 0.28 | 1.4 |
| 76-44-8 | Heptachlor | 0.0004c | 0.002c |
| 1024-57-3 | Heptachlor epoxide | 0.0002c | 0.001c |
| 118-74-1 | Hexachlorobenzene | 0.00006a | 0.0003 |
| 319-84-6 | alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC) | 0.00003a | 0.00015 |
| 58-89-9 | gamma-HCH (Lindane) | 0.0002c | 0.001c |
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 0.05c | 0.5c |
| 67-72-1 | Hexachloroethane | 0.007 | 0.035 |
| 193-39-5 | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 0.00043a | 0.00215 |
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| 72-43-5 | Methoxychlor | 0.04c | 0.2c |
| 74-83-9 | Methyl bromide
(Bromomethane) |
0.0098 | 0.049 |
| 75-09-2 | Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane) |
0.005c | 0.05c |
| 91-20-3 | Naphthalene2 | 0.025 | 0.039 |
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene2 | 0.0035 | 0.0035 |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 1918-02-1 | Picloram | 0.5c | 5.0c |
| 1336-36-3 | Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)n | 0.0005c | 0.0025c |
| 129-00-0 | Pyrene | 0.21 | 1.05 |
| 122-34-9 | Simazine | 0.004c | 0.04c |
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 0.1c | 0.5c |
| 93-72-1 | 2,4,5-TP
(Silvex) |
0.05c | 0.25c |
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene) |
0.005c | 0.025c |
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 1.0c | 2.5c |
| 8001-35-2 | Toxaphene | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 0.07c | 0.7c |
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane2 | 0.2c | 1.0c |
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 0.005c | 0.05c |
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl acetate | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| 75-01-4 | Vinyl chloride | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 10.0c | 10.0c |
| Ionizable Organics | |||
| 65-85-0 | Benzoic Acid | 28 | 28 |
| 106-47-8 | 4-Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline) |
0.028 | 0.028 |
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 0.035 | 0.175 |
| 120-83-2 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 0.021 | 0.021 |
| 105-67-9 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| 51-28-5 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| 95-48-7 | 2-Methylphenol
(o - Cresol) |
0.35 | 0.35 |
| 86-30-6 | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 0.01a | 0.05 |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 621-64-7 | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 0.01a | 0.01 |
| 87-86-5 | Pentachlorophenol | 0.001a,c | 0.005c |
| 108-95-2 | Phenol | 0.1c | 0.1c |
| 95-95-4 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 0.7 | 3.5 |
| 88-06-2 | 2,4,6 Trichlorophenol | 0.0064a | 0.032 |
| Inorganics | |||
| 7440-36-0 | Antimony | 0.006c | 0.024c |
| 7440-38-2 | Arsenic | 0.05c | 0.2c |
| 7440-39-3 | Barium | 2.0c | 2.0c |
| 7440-41-7 | Beryllium | 0.004c | 0.5c |
| 7440-42-8 | Boron | 2.0c | 2.0c |
| 7440-43-9 | Cadmium | 0.005c | 0.05c |
| 16887-00-6 | Chloride | 200c | 200c |
| 7440-47-3 | Chromium, total | 0.1c | 1.0c |
| 18540-29-9 | Chromium, ion, hexavalent | --- | --- |
| 7440-48-4 | Cobalt | 1.0c | 1.0c |
| 7440-50-8 | Copper | 0.65c | 0.65c |
| 57-12-5 | Cyanide | 0.2c | 0.6c |
| 7782-41-4 | Fluoride | 4.0c | 4.0c |
| 15438-31-0 | Iron | 5.0c | 5.0c |
| 7439-92-1 | Lead | 0.0075c | 0.1c |
| 7439-96-5 | Manganese | 0.15c | 10.0c |
| 7439-97-6 | Mercury | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 7440-02-0 | Nickel | 0.1c | 2.0c |
| 14797-55-8 | Nitrate as N | 10.0c | 100c |
| 7782-49-2 | Selenium | 0.05c | 0.05c |
| 7440-22-4 | Silver | 0.05c | --- |
| 14808-79-8 | Sulfate | 400c | 400c |
Groundwater Remediation Objective
|
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 7440-28-0 | Thallium | 0.002c | 0.02c |
| 7440-62-2 | Vanadium2 | 0.049 | --- |
| 7440-66-6 | Zinc | 5.0c | 10c |
| a | The groundwater Health Advisory concentration is equal to ADL for carcinogens. |
| b | Oral Reference Dose and/or Reference Concentration under review by USEPA. Listed values subject to change. |
| c | Value listed is also the Groundwater Quality Standard for this chemical pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.410 for Class I Groundwater or 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.420 for Class II Groundwater. |
| Section 742.APPENDIX B: | |
| Tier 1 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.TABLE F: | Values Used to Calculate the Tier 1 Soil Remediation Objectives for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 83-32-9 | Acenaphthene | 2.0b | 10 |
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 4.0b | 4.0 |
| 15972-60-8 | Alachlor | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 116-06-3 | Aldicarb | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 309-00-2 | Aldrin | 5.0E-6b | 2.5E-5 |
| 120-12-7 | Anthracene | 10b | 50 |
| 1912-24-9 | Atrazine | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 56-55-3 | Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.0001b | 0.0005 |
| 205-99-2 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.0001b | 0.0005 |
| 207-08-9 | Benzo(k)fluroanthene | 0.001b | 0.005 |
| 50-32-8 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.0002a,c | 0.002c |
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 8.0E-5b | 8.0E-5 |
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 0.006a,c | 0.06c |
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane) |
0.1b | 0.1 |
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 0.1b | 0.01 |
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 4.0b | 4.0 |
| 85-68-7 | Butyl benzyl phthalate | 7.0b | 35 |
| 86-74-8 | Carbazole | 0.004b | 0.02 |
| 1563-66-2 | Carbofuran | 0.04c | 0.2c |
| 75-15-0 | Carbon disulfide | 4.0b | 20 |
| 56-23-5 | Carbon tetrachloride | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 57-74-9 | Chlordane | 0.002c | 0.01c |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 108-90-7 | Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene) |
0.1c | 0.5c |
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane) |
0.06b | 0.06 |
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 0.1b | 0.5 |
| 218-01-9 | Chrysene | 0.1b | 0.05 |
| 94-75-7 | 2,4-D | 0.07c | 0.35c |
| 75-99-0 | Dalapon | 0.2c | 2.0c |
| 72-54-8 | DDD | 0.0004b | 0.002 |
| 72-55-9 | DDE | 0.0003b | 0.0015 |
| 50-29-3 | DDT | 0.0003b | 0.0015 |
| 53-70-3 | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 1.0E-5b | 5.0E-5 |
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 0.0002c | 0.0002c |
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide) |
0.00005a,c | 0.0005c |
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl phthalate | 4.0b | 20 |
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o - Dichlorobenzene) |
0.6c | 1.5c |
| 106-46-7 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p - Dichlorobenzene) |
0.075c | 0.375c |
| 91-94-1 | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine | 0.0002b | 0.001 |
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 4.0b | 20 |
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride) |
0.005c | 0.025c |
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | 0.007c | 0.035c |
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 0.07c | 0.2c |
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 0.1c | 0.5c |
| 78-97-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichloropropylene, cis + trans) |
0.0005b | 0.0025 |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 60-57-1 | Dieldrin | 5.0E-6b | 2.5E-5 |
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl phthalate | 30b | 30 |
| 121-14-2 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 0.0001b | 0.0001 |
| 606-20-2 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 88-85-7 | Dinoseb | 0.007c | 0.07c |
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 0.7b | 3.5 |
| 115-29-7 | Endosulfan | 0.2b | 1.0 |
| 145-73-3 | Endothall | 0.1c | 0.1c |
| 72-20-8 | Endrin | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 0.7c | 1.0c |
| 206-44-0 | Fluoranthene | 1.0b | 5.0 |
| 86-73-7 | Fluorene | 1.0b | 5.0 |
| 76-44-8 | Heptachlor | 0.0004c | 0.002c |
| 1024-57-3 | Heptachlor epoxide | 0.0002c | 0.001c |
| 118-74-1 | Hexachlorobenzene | 0.001b | 0.005 |
| 319-84-6 | alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC) | 1.0E-5b | 5.0E-5 |
| 58-89-9 | gamma-HCH (Lindane) | 0.0002c | 0.001c |
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 0.05c | 0.5c |
| 67-72-1 | Hexachloroethane | 0.007 | 0.035 |
| 193-39-5 | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 0.0001b | 0.0005 |
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| 72-43-5 | Methoxychlor | 0.04c | 0.2c |
| 74-83-9 | Methyl bromide
(Bromomethane) |
0.05b | 0.25 |
| 75-09-2 | Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane) |
0.005c | 0.05c |
| 91-20-3 | Naphthalene | 1.0b | 5.0 |
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene | 0.02b | 0.02 |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 1918-02-1 | Picloram | 0.5c | 5.0c |
| 1336-36-3 | Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) | --- | --- |
| 129-00-0 | Pyrene | 1.0b | 5.0 |
| 122-34-9 | Simazine | 0.004c | 0.04c |
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 0.1c | 0.5c |
| 93-72-1 | 2,4,5-TP
(Silvex) |
0.05c | 0.25c |
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene) |
0.005c | 0.025c |
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 1.0c | 2.5c |
| 8001-35-2 | Toxaphene | 0.003c | 0.015c |
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 0.07c | 0.7c |
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane2 | 0.2c | 1.0c |
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 0.005c | 0.05c |
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 0.005c | 0.025c |
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl acetate | 40b | 40 |
| 75-01-4 | Vinyl chloride | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 10.0c | 10.0c |
| Ionizable Organics | |||
| 65-85-0 | Benzoic Acid | 100b | 100 |
| 106-47-8 | 4-Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline) |
0.1b | 0.1 |
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 0.2b | 1.0 |
| 120-83-2 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 0.1b | 0.1 |
| 105-67-9 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 0.7b | 0.7 |
| 51-28-5 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 0.04b | 0.04 |
| 95-48-7 | 2-Methylphenol
(o - Cresol) |
2.0b | 2.0 |
| 86-30-6 | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 0.02b | 0.1 |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 621-64-7 | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 1.0E-5b | 1.0E-5 |
| 87-86-5 | Pentachlorophenol | 0.001a,c | 0.005c |
| 108-95-2 | Phenol | 0.1c | 0.1c |
| 95-95-4 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 4.0b | 20 |
| 88-06-2 | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 0.008b | 0.04 |
| Inorganics | |||
| 7440-36-0 | Antimony | 0.006c | 0.024c |
| 7440-38-2 | Arsenic | 0.05c | 0.2c |
| 7440-39-3 | Barium | 2.0c | 2.0c |
| 7440-41-7 | Beryllium | 0.004c | 0.5c |
| 7440-42-8 | Boron | 2.0c | 2.0c |
| 7440-43-9 | Cadmium | 0.005c | 0.05c |
| 16887-00-6 | Chloride | 200c | 200c |
| 7440-47-3 | Chromium, total | 0.1c | 1.0c |
| 18540-29-9 | Chromium, ion, hexavalent | --- | --- |
| 7440-48-4 | Cobalt | 1.0c | 1.0c |
| 7440-50-8 | Copper | 0.65c | 0.65c |
| 57-12-5 | Cyanide | 0.2c | 0.6c |
| 7782-41-4 | Fluoride | 4.0c | 4.0c |
| 15438-31-0 | Iron | 5.0c | 5.0c |
| 7439-92-1 | Lead | 0.0075c | 0.1c |
| 7439-96-5 | Manganese | 0.15c | 10.0c |
| 7439-97-6 | Mercury | 0.002c | 0.01c |
| 7440-02-0 | Nickel | 0.1c | 2.0c |
| 14797-55-8 | Nitrate as N | 10.0c | 100c |
| 7782-49-2 | Selenium | 0.05c | 0.05c |
| 7440-22-4 | Silver | 0.05c | --- |
| 14808-79-8 | Sulfate | 400c | 400c |
GWobj Concentration used to Calculate
Tier 1 Soil Rememdiation Objectivesa |
CAS No.
|
Chemical Name | Class I
(mg/L) |
Class II
(mg/L) |
| 7440-28-0 | Thallium | 0.002c | 0.02c |
| 7440-62-2 | Vanadium | 0.049 | --- |
| 7440-66-6 | Zinc | 5.0c | 10c |
| a | The Equation S17 is used to calculate the Soil Remediation Objective for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route; this equation requires calculation of the Target Soil Leachate Concentration (Cw) from Equation S18: Cw = DF x GWobj. |
| b | Value listed is the Water Health Based Limit (HBL) for this chemical from Soil Screening Guidance: User’s Guide, incorporated by reference at Section 742.210; for carcinogens, the HBL is equal to a cancer risk of 1.0E-6, and for noncarcinogens is equal to a Hazard Quotient of 1.0. NOTE: These GWobj concentrations are not equal to the Tier 1 Groundwater Remediation Objectives for the Direct Ingestion of Groundwater Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route, listed in Section 742.Appendix B, Table E. |
| c | Value listed is also the Groundwater Quality Standard for this chemical pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.410 for Class I Groundwater or 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.420 for Class II Groundwater. |
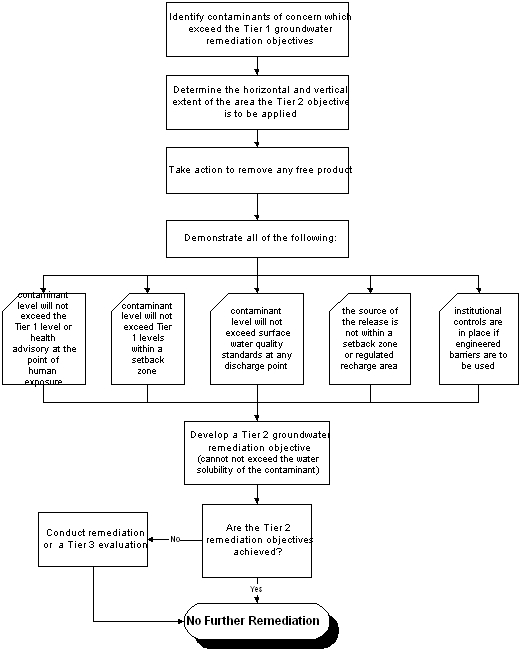
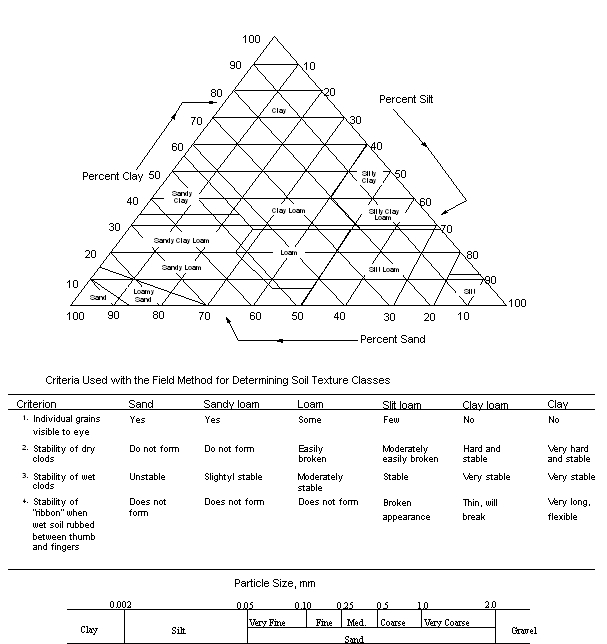
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Equations for Soil Ingestion Exposure Route | Remediation Objectives for Noncarcinogenic Contaminants
(mg/kg) |
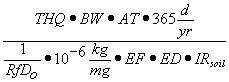
|
S1 |
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants - Residential
(mg/kg) |
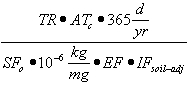
|
S2 |
|
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic
Contaminants - Industrial/ Commercial, Construction Worker (mg/kg) |
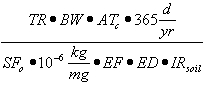
|
S3 |
|
| Equations for Inhalation Exposure Route (Volatiles)
|
Remediation Objectives for Noncarcinogenic Contaminants - Residential, Industrial/Commercial (mg/kg) | 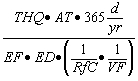
|
S4 |
| Remediation Objectives for Noncarcinogenic Contaminants - Construction Worker (mg/kg) | 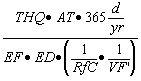
|
S5 |
|
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants - Residential, Industrial/ Commercial (mg/kg) | 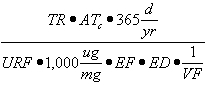
|
S6 |
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants - Construction Worker (mg/kg)
|
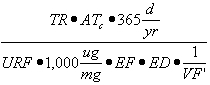
|
S7 |
|
| Equation for Derivation of the Volatilization Factor - Residential, Industrial/ Commercial, VF (m3/kg) | 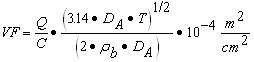
|
S8 |
|
| Equation for Derivation of the Volatilization Factor - Construction Worker, VF ¢ (m3/kg) |
S9 |
||
| Equation for Derivation
of Apparent Diffusivity, DA (cm2/s) |
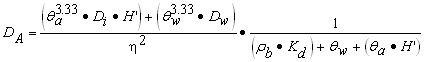
|
S10 |
| Equations for Inhalation Exposure Route (Fugitive Dusts) | Remediation Objectives for Noncarcinogenic Contaminants - Residential, Industrial/Commercial (mg/kg) | 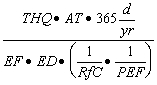
|
S11 |
| Remediation Objectives for Noncarcinogenic Contaminants - Construction Worker (mg/kg) | 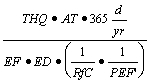
|
S12 |
|
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants - Residential, Industrial/ Commercial (mg/kg) | 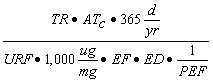
|
S13 |
|
| Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants - Construction Worker (mg/kg) | 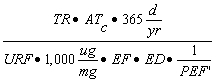
|
S14 |
|
| Equation for Derivation of Particulate Emission Factor, PEF (m3/kg) | 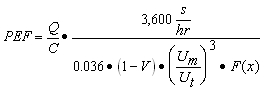
|
S15 |
| Equation for Derivation of Particulate Emission Factor, PEF ¢ - Construction Worker (m3/kg) | NOTE: PEF must be the industrial/commercial value |
S16 |
|
| Equations for the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route | Remediation Objective
(mg/kg) |
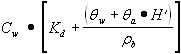
NOTE: This equation can only be used to model contaminant migration not in the water bearing unit. |
S17 |
| Target Soil Leachate Concentration, Cw
(mg/L) |
|
S18 |
|
| Soil-Water Partition Coefficient, Kd
(cm3/g) |
S19 |
||
| Water-Filled Soil Porosity,
q
w
(Lwater/Lsoil) |
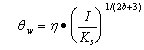
|
S20 |
|
| Air-Filled Soil Porosity,
q
a
(Lair/Lsoil) |
S21 |
||
| Dilution Factor, DF (unitless) |
S22 |
| Groundwater Remediation Objective for Carcinogenic Contaminants, GWobj
(mg/L) |
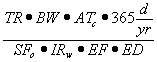
|
S23 |
|
| Total Soil Porosity,
h
(Lpore/Lsoil) |
S24 |
||
| Equation for Estimation of Mixing Zone Depth, d
(m) |
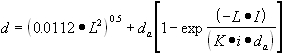
|
S25 |
|
| Mass-Limit Equations for Inhalation Exposure Route and Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route | Mass-Limit Volatilization Factor for the Inhalation Exposure Route - Residential, Industrial/ Commercial, VF (m3/kg) | 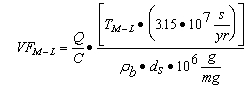
NOTE: This equation may be used when area and depth of contaminant source are known or can be estimated reliably. |
S26 |
| Mass-Limit Volatilization Factor for Inhalation Exposure Route - Construction Worker, VF ¢ - (m3/kg) |
|
S27 |
| Mass-Limit Remediation Objective for Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route (mg/kg)
|
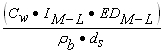
NOTE: This equation may be used when area and depth of contaminant source are known or can be estimated reliably. |
S28 | |
|
Equation for Derivation of the Soil Saturation Limit, Csat
|
S29 |
||
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| AT | Averaging Time for Noncarcinogens in Ingestion Equation | yr | Residential = 6
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 0.115 |
|
| AT | Averaging Time for Noncarcinogens in Inhalation Equation | yr | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 0.115 |
|
| ATc | Averaging Time for Carcinogens | yr | SSL | 70 |
| BW | Body Weight | kg | Residential = 15, noncarcinogens
70, carcinogens Industrial/Commercial = 70 Construction Worker = 70 |
|
| Csat | Soil Saturation Concentration | mg/kg | Appendix A, Table A or
Equation S29 in Appendix C, Table A |
Chemical-Specific or
Calculated Value |
| Cw | Target Soil Leachate Concentration | mg/L | Equation S18 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Groundwater Standard, Health Advisory concentration, or
Calculated Value |
| d | Mixing Zone Depth | m | SSL or
Equation S25 in Appendix C, Table A |
2 m or
Calculated Value |
| da | Aquifer Thickness | m | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| ds | Depth of Source | m | Field Measurement or Estimation | Site-Specific |
| DA | Apparent Diffusivity | cm2/s | Equation S10 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| Di | Diffusivity in Air | cm2/s | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| Dw | Diffusivity in Water | cm2/s | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| DF | Dilution Factor | unitless | Equation S22 in
Appendix C, Table A |
20 or Calculated Value |
| ED | Exposure Duration for Ingestion of Carcinogens | yr | Industrial/Commercial = 25
Construction Worker = 1 |
|
| ED | Exposure Duration for Inhalation of Carcinogens | yr | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 1 |
|
| ED | Exposure Duration for Ingestion of Noncarcinogens | yr | Residential = 6
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 1 |
|
| ED | Exposure Duration for Inhalation of Noncarcinogens | yr | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 1 |
|
| ED | Exposure Duration for the Direct Ingestion of Groundwater | yr | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 1 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| EDM-L | Exposure Duration for Migration to Groundwater Mass-Limit Equation S28 | yr | SSL | 70 |
| EF | Exposure Frequency | d/yr | Residential = 350
Industrial/Commercial = 250 Construction Worker = 30 |
|
| F(x) | Function dependent on Um/Ut | unitless | SSL | 0.194 |
| foc | Organic Carbon Content of Soil | g/g | SSL or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
Surface Soil = 0.006
Subsurface soil = 0.002, or Site-Specific |
| GWobj | Groundwater Remediation Remediation Objective | mg/L | Appendix B, Table E,
35 IAC 620.Subpart F, or Equation S23 in Appendix C, Table A |
Chemical-Specific or Calculated |
| H' | Henry's Law Constant | unitless | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| i | Hydraulic Gradient | m/m | Field Measurement
(See Appendix C, Table F) |
Site-Specific |
| I | Infiltration Rate | m/yr | SSL | 0.3 |
| IM-L | Infiltration Rate for Migration to Groundwater Mass-Limit Equation S28 | m/yr | SSL | 0.18 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| IFsoil-adj
(residential) |
Age Adjusted Soil Ingestion Factor for Carcinogens | (mg-yr)/(kg-d) | SSL | 114 |
| IRsoil | Soil Ingestion Rate | mg/d | Residential = 200
Industrial/Commercial = 50 Construction Worker = 480 |
|
| IRW | Daily Water Ingestion Rate | L/d | Residential = 2
Industrial/Commercial = 1 |
|
| K | Aquifer Hydraulic Conductivity | m/yr | Field Measurement
(See Appendix C, Table F) |
Site-Specific |
| Kd | Soil-Water Partition Coefficient | cm3/g or L/kg | Equation S19 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| Koc | Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient | cm3/g or L/kg | Appendix C, Table E
or Appendix C, Table I |
Chemical-Specific |
| Ks | Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity | m/yr | Appendix C, Table K
Appendix C, Illustration C |
Site-Specific |
| L | Source Length Parallel to Groundwater Flow | m | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| PEF | Particulate Emission
Factor |
m3/kg | SSL or Equation S15 in Appendix C, Table A | Residential = 1.32
·
109 or Site-Specific
Industrial/Commercial = 1.24 · 109 or Site-Specific |
| PEF ¢ | Particulate Emission Factor adjusted for Agitation (construction worker) | m3/kg | Equation S16 in Appendix C, Table A using PEF (industrial/commercial) | 1.24 · 108 or Site-Specific |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| Q/C
(used in VF equations) |
Inverse of the mean concentration at the center of a square source | (g/m2-s)/(kg/m3) | Appendix C, Table H | Residential = 68.81
Industrial/Commercial = 85.81 Construction Worker = 85.81 |
| Q/C
(used in PEF equations) |
Inverse of the mean concentration at the center of a square source | (g/m2-s)/(kg/m3) | SSL or Appendix C, Table H | Residential = 90.80
Industrial/Commercial = 85.81 Construction Worker = 85.81 |
| RfC | Inhalation Reference Concentration | mg/m3 | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific
(Note: for Construction Workers use subchronic reference concentrations) |
| RfDo | Oral Reference Dose | mg/(kg-d) | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific
(Note: for Construction Worker use subchronic reference doses) |
| S | Solubility in Water | mg/L | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| SFo | Oral Slope Factor | (mg/kg-d)-1 | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific |
| T | Exposure Interval | s | Residential = 9.5
·
108
Industrial/Commercial = 7.9 · 108 Construction Worker = 3.6 · 106 |
|
| TM-L | Exposure Interval for Mass-Limit Volatilization Factor Equation S26 | yr | SSL | 30 |
| THQ | Target Hazard Quotient | unitless | SSL | 1 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| TR | Target Cancer Risk | unitless | Residential = 10-6 at the point of human exposure
Industrial/Commercial = 10-6 at the point of human exposure Construction Worker = 10-6 at the point of human exposure |
|
| Um | Mean Annual Windspeed | m/s | SSL | 4.69 |
| URF | Inhalation Unit Risk Factor | ( m g/m3)-1 | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific |
| Ut | Equivalent Threshold Value of Windspeed at 7 m | m/s | SSL | 11.32 |
| V | Fraction of Vegetative Cover | unitless | SSL or Field Measurement | 0.5 or Site-Specific |
| VF | Volatilization Factor | m3/kg | Equation S8 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| VF ¢ | Volatilization Factor adjusted for Agitation | m3/kg | Equation S9 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| VFM-L | Mass-Limit Volatilization Factor | m3/kg | Equation S26 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| VF ¢ M-L | Mass-Limit Volatilization Factor adjusted for Agitation | m3/kg | Equation S27 in
Appendix C, Table A |
Calculated Value |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| h | Total Soil Porosity | Lpore/Lsoil | SSL or
Equation S24 in Appendix C, Table A |
0.43, or
Gravel = 0.25 Sand = 0.32 Silt = 0.40 Clay = 0.36, or Calculated Value |
| q a | Air-Filled Soil Porosity | Lair/Lsoil | SSL or
Equation S21 in Appendix C, Table A |
Surface Soil (top 1 meter) = 0.28
Subsurface Soil (below 1 meter) = 0.13, or Gravel = 0.05 Sand = 0.14 Silt - 0.24 Clay = 0.19, or Calculated Value |
| q w | Water-Filled Soil Porosity | Lwater/Lsoil | SSL or
Equation S20 in Appendix C, Table A |
Surface Soil (top 1 meter) = 0.15
Subsurface Soil (below 1 meter) = 0.30, or Gravel = 0.20 Sand = 0.18 Silt = 0.16 Clay = 0.17, or Calculated Value |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| r b | Dry Soil Bulk Density | kg/L or g/cm3 | SSL or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
1.5, or
Gravel = 2.0
Site-Specific |
| r s | Soil Particle Density | g/cm3 | SSL or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
2.65, or
Site-Specific |
| r w | Water Density | g/cm3 | SSL | 1 |
| 1/(2b+3) | Exponential in Equation S20 | unitless | Appendix C, Table K
Appendix C, Illustration C |
Site-Specific |
| a | HEAST = Health Effects Assessment Summary Tables. USEPA, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. EPA/SQO/R-95/036. Updated Quarterly. |
| Equations for the combined exposures routes of soil ingestion | Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants (mg/kg) | 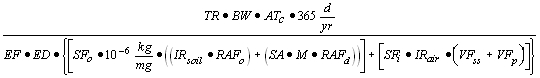
|
R1 |
| inhalation of vapors and particulates, and dermal contact with soil | Remediation Objectives for Non-carcinogenic Contaminants (mg/kg) | 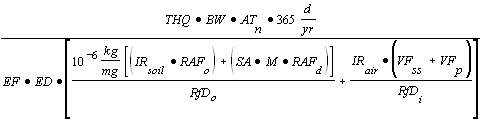
|
R2 |
| Volatilization Factor for Surficial Soils, VFss
(kg/m3) Whichever is less between R3 and R4 |
|
R3 |
|
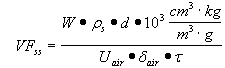
|
R4 |
| Volatilization Factor for Surficial Soils Regarding Particulates, VFp
(kg/m3) |
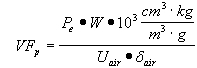
|
R5 |
|
| Effective Diffusion Coefficient in Soil Based on Vapor-Phase Concentration Dseff
(cm2/s) |
|
R6 |
|
| Equations for the ambient vapor inhalation (outdoor) | Remediation Objectives for Carcinogenic Contaminants (mg/kg) |
R7 |
|
| route from subsurface soils | Remediation Objectives for Non-carcinogenic Contaminants (mg/kg) |
|
R8 |
| Carcinogenic Risk-Based Screening Level for Air, RBSLair
(ug/m3) |
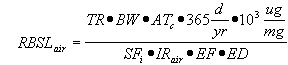
|
R9 |
|
| Noncarcinogenic Risk-Based Screening Level for Air, RBSLair
(ug/m3) |
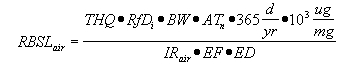
|
R10 |
|
| Volatilization Factor - Subsurface Soil to Ambient Air, VFsamb
|
|
R11 |
| Equations for the Soil Component of the Groundwater | Remediation Objective
(mg/kg) |
NOTE: This equation can only be used to model contaminant migration not in the water bearing unit. |
R12 |
| Ingestion Exposure Route | Groundwater at the source, GWsource
(mg/L) |
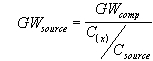
|
R13 |
| Leaching Factor,
LFsw (mg/Lwater)/(mg/kgsoil) |
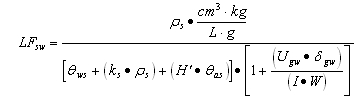
|
R14 |
|
| Steady-State Attenuation Along the Centerline of a Dissolved Plume,
C(x)/Csource |
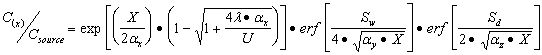
NOTE: 1. This equation does not predict the contaminant flow within bedrock. 2. If the value of the First Order Degradation Constant ( l ) is not readily available, then set l = 0. |
R15 |
|
| Longitudinal Dispersivity,
a
x
(cm) |
R16 |
| Transverse Dispersivity,
a
y
(cm) |
R17 |
||
| Vertical Dispersivity,
a
z
(cm) |
R18 |
||
| Specific Discharge, U
(cm/d) |
R19 |
||
| Soil-Water Sorption Coefficient, ks |
R20 |
||
| Volumetric Air Content in Vadose Zone Soils,
q
as
(cm3air/cm3soil) |
R21 |
||
| Volumetric Water Content in Vadose Zone Soils,
q
ws
(cm3water/cm3soil) |
R22 |
||
| Total Soil Porosity,
q
T
(cm3/cm3soil) |
R23 |
| Groundwater Darcy Velocity, Ugw
(cm/yr) |
R24 |
||
| Equations for the Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route | Remediation Objective for Carcinogenic Contaminants
(mg/L) |
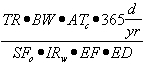
|
R25 |
| Dissolved Hydrocarbon Concentration along Centerline, C(x)
(g/cm3water) |
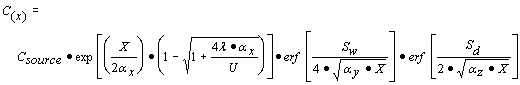
1. This equation does not predict the contaminant flow within bedrock. 2. If the value of the First Order Degradation Constant ( l ) is not readily available, then set l = 0. |
R26 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| ATc | Averaging Time for Carcinogens | yr | RBCA | 70 |
| ATn | Averaging Time for Noncarcinogens | yr | RBCA | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 0.115 |
| BW | Adult Body Weight | kg | RBCA | 70 |
| Csource | The greatest potential concentration of the contaminant of concern in the groundwater at the source of the contamination, based on the concentrations of contaminants in groundwater due to the release and the projected concentration of the contaminant migrating from the soil to the groundwater. | mg/L | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| C(x) | Concentration of Contaminant in Groundwater at Distance X from the source | mg/L | Equation R26 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| C(x)/Csource | Steady-State Attenuation Along the Centerline of a Dissolved Plume | unitless | Equation R15 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| d | Lower Depth of Surficial Soil Zone | cm | Field Measurement | 100 or
Site-Specific (not to exceed 100) |
| Dair | Diffusion Coefficient in Air | cm2/s | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| Dwater | Diffusion Coefficient in Water | cm2/s | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| Dseff | Effective Diffusion Coefficient in Soil Based on Vapor-Phase Concentration | cm2/s | Equation R6 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| ED | Exposure Duration | yr | RBCA | Residential = 30
Industrial/Commercial = 25 Construction Worker = 1 |
| EF | Exposure Frequency | d/yr | RBCA | Residential = 350
Industrial/Commercial = 250 Construction Worker = 30 |
| erf | Error Function | unitless | Appendix C, Table G | Mathematical Function |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| foc | Organic Carbon Content of Soil | g/g | RBCA or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
Surface Soil = 0.006
Subsurface Soil = 0.002 or Site-Specific |
| GWcomp | Groundwater Objective at the Compliance Point | mg/L | Appendix B, Table E,
35 IAC 620.Subpart F, or Equation R25 in Appendix C, Table C |
Site-Specific |
| GWsource | Groundwater Concentration at the Source | mg/L | Equation R13 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| H’ | Henry’s Law Constant | cm3water/cm3air | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| i | Hydraulic Gradient | cm/cm (unitless) | Field Measurement
(See Appendix C, Table F) |
Site-Specific |
| I | Infiltration Rate | cm/yr | RBCA | 30 |
| IRair | Daily Outdoor Inhalation Rate | m3/d | RBCA | 20 |
| IRsoil | Soil Ingestion Rate | mg/d | RBCA | Residential = 100
Industrial/Commercial = 50 Construction Worker = 480 |
| IRw | Daily Water Ingestion Rate | L/d | RBCA | Residential = 2
Industrial/Commercial = 1 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| K | Aquifer Hydraulic Conductivity | cm/d for Equations R15, R19 and R26
cm/yr for Equation R24 |
Field Measurement
(See Appendix C, Table F) |
Site-Specific |
| Koc | Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient | cm3/g or L/kg | Appendix C, Table E or
Appendix C, Table I |
Chemical-Specific |
| ks
(non-ionizing organics) |
Soil Water Sorption Coefficient | cm3water/gsoil | Equation R20 in
Appendix C,Table C |
Calculated Value |
| ks
(ionizing organics) |
Soil Water Sorption Coefficient | cm3water/gsoil | Equation R20 in Appendix C, Table C | Chemical-Specific |
| ks
(inorganics) |
Soil Water Sorption Coefficient | cm3water/gsoil | Appendix C, Table J | Chemical-Specific |
| Ls | Depth to Subsurface Soil Sources | cm | RBCA | 100 |
| LF sw | Leaching Factor | (mg/Lwater)/
(mg/kgsoil) |
Equation R14 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| M | Soil to Skin Adherence Factor | mg/cm2 | RBCA | 0.5 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| Pe | Particulate Emission Rate | g/cm2-s | RBCA | 6.9 · 10-14 |
| RAFd
|
Dermal Relative Absorption Factor | unitless | RBCA | 0.5 |
| RAFd
(PNAs) |
Dermal Relative Absorption Factor | unitless | RBCA | 0.05 |
| RAFd
(inorganics) |
Dermal Relative Absorption Factor | unitless | RBCA | 0 |
| RAFo | Oral Relative Absorption Factor | unitless | RBCA | 1.0 |
| RBSLair | Carcinogenic
Risk-Based Screening Level for Air |
m g/m3 | Equation R9 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Chemical-, Media-, and Exposure Route-Specific |
| RBSLair | Noncarcinogenic
Risk-Based Screening Level for Air |
m g/m3 | Equation R10 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Chemical-, Media-, and Exposure Route-Specific |
| RfDi | Inhalation Reference Dose | mg/kg-d | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific |
| RfDo | Oral Reference Dose | mg/(kg-d) | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific
(Note: for Construction Worker use subchronic reference doses) |
| SA | Skin Surface Area | cm2/d | RBCA | 3,160 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| Sd | Source Width Perpendicular to Groundwater Flow Direction in Vertical Plane | cm | Field Measurement | For Migration to Groundwater Route:
Use 200 or Site-Specific For Groundwater remediation objective: Use Site-Specific |
| Sw | Source Width Perpendicular to Groundwater Flow Direction in Horizontal Plane | cm | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| SFi | Inhalation Cancer Slope Factor | (mg/kg-d)-1 | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific |
| SFo | Oral Slope Factor | (mg/kg-d)-1 | IEPA (IRIS/HEASTa) | Toxicological-Specific |
| THQ | Target Hazard Quotient | unitless | RBCA | 1 |
| TR | Target Cancer Risk | unitless | RBCA | Residential = 10-6 at the point of human exposure
Industrial/Commercial = 10-6 at the point of human exposure Construction Worker = 10-6 at the point of human exposure |
| U | Specific Discharge | cm/d | Equation R19 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| Uair | Average Wind Speed Above Ground Surface in Ambient Mixing Zone | cm/s | RBCA | 225 |
| Ugw | Groundwater Darcy Velocity | cm/yr | Equation R24 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| VF p | Volatilization Factor for Surficial Soils Regarding Particulates | kg/m3 | Equation R5 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| VFsamb | Volatilization Factor (Subsurface Soils to Ambient Air) | (mg/m3air)/(mg/
kgsoil) or kg/m3 |
Equation R11 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| VFss | Volatilization Factor for Surficial Soils | kg/m3 | Use Equations R3 and R4 in Appendix C, Table C | Calculated Value from Equation R3 or R4 (whichever is less) |
| W | Width of Source Area Parallel to Direction to Wind or Groundwater Movement | cm | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| w | Average Soil Moisture Content | gwater/gsoil | RBCA or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
0.1, or
Surface Soil (top 1 meter) = 0.1 Subsurface Soil (below 1 meter) = 0.2, or Site-Specific |
| X | Distance along the Centerline of the Groundwater Plume Emanating from a Source. The x direction is the direction of groundwater flow | cm | Field Measurement | Site-Specific |
| a x | Longitudinal Dispersitivity | cm | Equation R16 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| a y | Transverse Dispersitivity | cm | Equation R17 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| a z | Vertical Dispersitivity | cm | Equation R18 in
Appendix C, Table C |
Calculated Value |
| d air | Ambient Air Mixing Zone Height | cm | RBCA | 200 |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| d gw | Groundwater Mixing Zone Thickness | cm | RBCA | 200 |
| q as | Volumetric Air Content in Vadose Zone Soils | cm3air/cm3soil | RBCA or
Equation R21 in Appendix C, Table C |
Surface Soil (top 1 meter) = 0.28
Subsurface Soil (below 1 meter)= 0.13, or Gravel = 0.05 Sand = 0.14 Silt = 0.16 Clay = 0.17, or Calculated Value |
| q ws | Volumetric Water Content in Vadose Zone Soils | cm3water/cm3soil | RBCA or
Equation R22 in Appendix C, Table C |
Surface Soil (top 1 meter) = 0.15
Subsurface Soil (below 1 meter) = 0.30, or Gravel = 0.20 Sand = 0.18 Silt = 0.16 Clay = 0.17, or Calculated Value |
| Symbol | Parameter | Units | Source | Parameter Value(s) |
| q T | Total Soil Porosity | cm3/cm3soil | RBCA or
Equation R23 in Appendix C, Table C |
0.43, or
Gravel = 0.25 Sand = 0.32 Silt = 0.40 Clay = 0.36, or Calculated Value |
| l | First Order Degradation Constant | d-1 | Appendix C, Table E | Chemical-Specific |
| p | pi | 3.1416 | ||
| r s | Soil Bulk Density | g/cm3 | RBCA or
Field Measurement (See Appendix C, Table F) |
1.5, or
Gravel = 2.0 Sand = 1.8 Silt = 1.6 Clay = 1.7, or Site-Specific |
| r w | Water Density | g/cm3 | RBCA | 1 |
| t | Averaging Time for Vapor Flux | s | RBCA | 9.46 · 108 |
| a | HEAST = Health Effects Assessment Summary Tables. USEPA, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. EPA/540/R-95/036. Updated Quarterly. |
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| Neutral Organics | |||||||
| 83-32-9 | Acenaphthene | 4.24 | 0.0421 | 7.69E-6 | 0.00636 | 7,080 | 0.0034 |
| 67-64-1 | Acetone | 1,000,000 | 0.124 | 1.14E-5 | 0.00159 | 0.575 | 0.0495 |
| 15972-60-8 | Alachlor | 242 | 0.0198 | 5.69E-6 | 0.00000132 | 394 | No Data |
| 116-06-3 | Aldicarb | 6,000 | 0.0305 | 7.19E-6 | 0.0000000574 | 12 | 0.00109 |
| 309-00-2 | Aldrin | 0.18 | 0.0132 | 4.86E-6 | 0.00697 | 2,450,000 | 0.00059 |
| 120-12-7 | Anthracene | 0.0434 | 0.0324 | 7.74E-6 | 0.00267 | 29,500 | 0.00075 |
| 1912-24-9 | Atrazine | 70 | 0.0258 | 6.69E-6 | 0.00000005 | 451 | No Data |
| 71-43-2 | Benzene | 1,750 | 0.088 | 9.80E-6 | 0.228 | 58.9 | 0.0009 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 56-55-3 | Benzo(a)anthracene | 0.0094 | 0.0510 | 9.00E-6 | 0.000137 | 398,000 | 0.00051 |
| 205-99-2 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 0.0015 | 0.0226 | 5.56E-6 | 0.00455 | 1,230,000 | 0.00057 |
| 207-08-9 | Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 0.0008 | 0.0226 | 5.56E-6 | 0.000034 | 1,230,000 | 0.00016 |
| 65-85-0 | Benzoic Acid | 3,500 | 0.0536 | 7.97E-6 | 0.0000631 | 0.600 | No Data |
| 50-32-8 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.00162 | 0.043 | 9.00E-6 | 0.0000463 | 1,020,000 | 0.00065 |
| 111-44-4 | Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 17,200 | 0.0692 | 7.53E-6 | 0.000738 | 15.5 | 0.0019 |
| 117-81-7 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate | 0.34 | 0.0351 | 3.66E-6 | 0.00000418 | 15,100,000 | 0.0018 |
| 75-27-4 | Bromodichloromethane | 6,740 | 0.0298 | 1.06E-5 | 0.0656 | 55.0 | No Data |
| 75-25-2 | Bromoform | 3,100 | 0.0149 | 1.03E-5 | 0.0219 | 87.1 | 0.0019 |
| 71-36-3 | Butanol | 74,000 | 0.0800 | 9.30E-6 | 0.000361 | 6.92 | 0.01283 |
| 85-68-7 | Butyl Benzyl Phthalate | 2.69 | 0.0174 | 4.83E-6 | 0.0000517 | 57,500 | 0.00385 |
| 86-74-8 | Carbazole | 7.48 | 0.0390 | 7.03E-6 | 0.000000626 | 3,390 | No Data |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 1563-66-2 | Carbofuran | 320 | 0.0249 | 6.63E-6 | .00377 | 37 | No Data |
| 75-15-0 | Carbon Disulfide | 1,190 | 0.104 | 1.00E-5 | 1.24 | 45.7 | No Data |
| 56-23-5 | Carbon Tetrachloride | 793 | 0.0780 | 8.80E-6 | 1.25 | 174 | 0.0019 |
| 57-74-9 | Chlordane | 0.056 | 0.0118 | 4.37E-6 | 0.00199 | 120,000 | 0.00025 |
| 106-47-8 | p-Chloroaniline | 5,300 | 0.0483 | 1.01E-5 | 0.0000136 | 66.1 | No Data |
| 108-09-7 | Chlorobenzene | 472 | 0.0730 | 8.70E-6 | 0.152 | 219 | 0.0023 |
| 124-48-1 | Chlorodibromomethane | 2,600 | 0.0196 | 1.05E-5 | 0.0321 | 63.1 | 0.00385 |
| 67-66-3 | Chloroform | 7,920 | 0.104 | 1.00E-5 | 0.15 | 39.8 | 0.00039 |
| 95-57-8 | 2-Chlorophenol | 22,000 | 0.0501 | 9.46E-6 | 0.016 | 388 | No Data |
| 218-01-9 | Chrysene | 0.0016 | 0.0248 | 6.21E-6 | 0.00388 | 398,000 | 0.00035 |
| 94-75-7 | 2,4-D | 680 | 0.0231 | 7.31E-6 | 0.00000041 | 451 | 0.00385 |
| 72-54-8 | 4,4'-DDD | 0.09 | 0.0169 | 4.76E-6 | 0.000164 | 1,000,000 | 0.000062 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 72-55-9 | 4,4'-DDE | 0.12 | 0.0144 | 5.87E-6 | 0.000861 | 4,470,000 | 0.000062 |
| 50-29-3 | 4,4'-DDT | 0.025 | 0.0137 | 4.95E-6 | 0.000332 | 2,630,000 | 0.000062 |
| 75-99-0 | Dalapon | 900,000 | 0.0414 | 9.46E-6 | 0.00000264 | 5.8 | 0.005775 |
| 53-70-3 | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | 0.00249 | 0.0202 | 5.18E-6 | 0.000000603 | 3,800,000 | 0.00037 |
| 96-12-8 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane | 1,200 | 0.0212 | 7.02E-6 | 0.00615 | 182 | 0.001925 |
| 106-93-4 | 1,2-Dibromoethane | 4,200 | 0.0287 | 8.06E-6 | 0.0303 | 93 | 0.005775 |
| 84-74-2 | Di-n-butyl Phthalate | 11.2 | 0.0438 | 7.86E-6 | 0.0000000385 | 33,900 | 0.03013 |
| 95-50-1 | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | 156 | 0.0690 | 7.90E-6 | 0.0779 | 617 | 0.0019 |
| 106-46-7 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | 73.8 | 0.0690 | 7.90E-6 | 0.0996 | 617 | 0.0019 |
| 91-94-1 | 3,3-Dichlorobenzidine | 3.11 | 0.0194 | 6.74E-6 | 0.000000164 | 724 | 0.0019 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 75-34-3 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 5,060 | 0.0742 | 1.05E-5 | 0.23 | 31.6 | 0.0019 |
| 107-06-2 | 1,2-Dichloroethane | 8,520 | 0.104 | 9.90E-6 | 0.0401 | 17.4 | 0.0019 |
| 75-35-4 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | 2,250 | 0.0900 | 1.04E-5 | 1.07 | 58.9 | 0.0053 |
| 156-59-2 | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 3,500 | 0.0736 | 1.13E-5 | 0.167 | 35.5 | 0.00024 |
| 156-60-5 | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | 6,300 | 0.0707 | 1.19E-5 | 0.385 | 52.5 | 0.00024 |
| 120-83-2 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 4,500 | 0.0346 | 8.77E-6 | 0.00013 | 147 | 0.00027 |
| 78-87-5 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 2,800 | 0.0782 | 8.73E-6 | 0.115 | 43.7 | 0.00027 |
| 542-75-6 | 1,3-Dichloropropylene
(cis + trans) |
2,800 | 0.0626 | 1.00E-5 | 0.726 | 45.7 | 0.061 |
| 60-57-1 | Dieldrin | 0.195 | 0.0125 | 4.74E-6 | 0.000619 | 21,400 | 0.00032 |
| 84-66-2 | Diethyl Phthalate | 1,080 | 0.0256 | 6.35E-6 | 0.0000185 | 288 | 0.00619 |
| 105-67-9 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 7,870 | 0.0584 | 8.69E-6 | 0.000082 | 209 | 0.0495 |
| 51-28-5 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 2,790 | 0.0273 | 9.06E-6 | 0.0000182 | 0.01 | 0.00132 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 121-14-2 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 270 | 0.203 | 7.06E-6 | 0.0000038 | 95.5 | 0.00192 |
| 606-20-2 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene | 182 | 0.0327 | 7.26E-6 | 0.0000306 | 69.2 | 0.00192 |
| 88-85-7 | Dinoseb | 52 | 0.0215 | 6.62E-6 | 0.0000189 | 1,120 | 0.002817 |
| 117-84-0 | Di-n-octyl Phthalate | 0.02 | 0.0151 | 3.58E-6 | 0.00274 | 83,200,000 | 0.0019 |
| 115-29-7 | Endosulfan | 0.51 | 0.0115 | 4.55E-6 | 0.000459 | 2,140 | 0.07629 |
| 145-73-3 | Endothall | 21,000 | 0.0291 | 8.07E-6 | 0.0000000107 | 0.29 | No Data |
| 72-20-8 | Endrin | 0.25 | 0.0125 | 4.74E-6 | 0.000308 | 12,300 | 0.00032 |
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | 169 | 0.0750 | 7.80E-6 | 0.323 | 363 | 0.003 |
| 206-44-0 | Fluoranthene | 0.206 | 0.0302 | 6.35E-6 | 0.00066 | 107,000 | 0.00019 |
| 86-73-7 | Fluorene | 1.98 | 0.0363 | 7.88E-6 | 0.00261 | 13,800 | 0.000691 |
| 76-44-8 | Heptachlor | 0.18 | 0.0112 | 5.69E-6 | 60.7 | 1,410,000 | 0.13 |
| 1024-57-3 | Heptachlor epoxide | 0.2 | 0.0132 | 4.23E-6 | 0.00039 | 83,200 | 0.00063 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 118-74-1 | Hexachlorobenzene | 6.2 | 0.0542 | 5.91E-6 | 0.0541 | 55,000 | 0.00017 |
| 319-84-6 | alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC) | 2.0 | 0.0142 | 7.34E-6 | 0.000435 | 1,230 | 0.0025 |
| 58-89-9 | gamma-HCH (Lindane) | 6.8 | 0.0142 | 7.34E-6 | 0.000574 | 1,070 | 0.0029 |
| 77-47-4 | Hexachlorocyclo-
pentadiene |
1.8 | 0.0161 | 7.21E-6 | 1.11 | 200,000 | 0.012 |
| 67-72-1 | Hexachloroethane | 50 | 0.0025 | 6.80E-6 | 0.159 | 1,780 | 0.00192 |
| 193-39-5 | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 0.000022 | 0.0190 | 5.66E-6 | 0.0000656 | 3,470,000 | 0.00047 |
| 78-59-1 | Isophorone | 12,000 | 0.0623 | 6.76E-6 | 0.000272 | 46.8 | 0.01238 |
| 7439-97-6 | Mercury | --- | 0.0307 | 6.30E-6 | 0.467 | --- | No Data |
| 72-43-5 | Methoxychlor | 0.045 | 0.0156 | 4.46E-6 | 0.000648 | 97,700 | 0.0019 |
| 74-83-9 | Methyl Bromide | 15,200 | 0.0728 | 1.21E-5 | 0.256 | 10.5 | 0.01824 |
| 75-09-2 | Methylene Chloride | 13,000 | 0.101 | 1.17E-5 | 0.0898 | 11.7 | 0.012 |
| 95-48-7 | 2-Methylphenol | 26,000 | 0.0740 | 8.30E-6 | 0.0000492 | 91.2 | 0.0495 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 91-20-3 | Naphthalene | 31.0 | 0.0590 | 7.50E-6 | 0.0198 | 2,000 | 0.0027 |
| 98-95-3 | Nitrobenzene | 2,090 | 0.0760 | 8.60E-6 | 0.000984 | 64.6 | 0.00176 |
| 86-30-6 | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine | 35.1 | 0.0312 | 6.35E-6 | 0.000205 | 1,290 | 0.01 |
| 621-64-7 | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine | 9,890 | 0.0545 | 8.17E-6 | 0.0000923 | 24.0 | 0.0019 |
| 87-86-5 | Pentachlorophenol | 1,950 | 0.0560 | 6.10E-6 | 0.000001 | 592 | 0.00045 |
| 108-95-2 | Phenol | 82,800 | 0.0820 | 9.10E-6 | 0.0000163 | 28.8 | 0.099 |
| 1918-02-1 | Picloram | 430 | 0.0255 | 5.28E-6 | 0.00000000166 | 1.98 | No Data |
| 1336-36-3 | Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) | 0.7 | -------a | -------a | -------a | 309,000 | No Data |
| 129-00-0 | Pyrene | 0.135 | 0.0272 | 7.24E-6 | 0.000451 | 105,000 | 0.00018 |
| 122-34-9 | Simazine | 5 | 0.027 | 7.36E-6 | 0.0000000133 | 133 | No Data |
| 100-42-5 | Styrene | 310 | 0.0710 | 8.00E-6 | 0.113 | 776 | 0.0033 |
| 93-72-1 | 2,4,5-TP (Silvex) | 31 | 0.0194 | 5.83E-6 | 0.0000000032 | 5,440 | No Data |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 127-18-4 | Tetrachloroethylene | 200 | 0.0720 | 8.20E-6 | 0.754 | 155 | 0.00096 |
| 108-88-3 | Toluene | 526 | 0.0870 | 8.60E-6 | 0.272 | 182 | 0.011 |
| 8001-35-2 | Toxaphene | 0.74 | 0.0116 | 4.34E-6 | 0.000246 | 257,000 | No Data |
| 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 300 | 0.0300 | 8.23E-6 | 0.0582 | 1,780 | 0.0019 |
| 71-55-6 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | 1,330 | 0.0780 | 8.80E-6 | 0.705 | 110 | 0.0013 |
| 79-00-5 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane | 4,420 | 0.0780 | 8.80E-6 | 0.0374 | 50.1 | 0.00095 |
| 79-01-6 | Trichloroethylene | 1,100 | 0.0790 | 9.10E-6 | 0.422 | 166 | 0.00042 |
| 95-95-4 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 1,200 | 0.0291 | 7.03E-6 | 0.000178 | 1,600 | 0.00038 |
| 88-06-2 | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 800 | 0.0318 | 6.25E-6 | 0.000319 | 381 | 0.00038 |
| 108-05-4 | Vinyl Acetate | 20,000 | 0.0850 | 9.20E-6 | 0.021 | 5.25 | No Data |
| 57-01-4 | Vinyl Chloride | 2,760 | 0.106 | 1.23E-6 | 1.11 | 18.6 | 0.00024 |
| 108-38-3 | m-Xylene | 161 | 0.070 | 7.80E-6 | 0.301 | 407 | 0.0019 |
|
CAS No. |
Chemical |
Solubility in Water (S) (mg/L) |
Diffusivity in Air (Di) (cm2/s) |
Diffusivity in Water (Dw) (cm2/s) |
Dimensionless
Henry's Law Constant (H') (25oC) |
Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc)
(L/kg) |
First
Order Degradation Constant ( l ) (d-1) |
| 95-47-6 | o-Xylene | 178 | 0.087 | 1.00E-5 | 0.213 | 363 | 0.0019 |
| 106-42-3 | p-Xylene | 185 | 0.0769 | 8.44E-6 | 0.314 | 389 | 0.0019 |
| 1330-20-7 | Xylenes (total) | 186 | 0.0720 | 9.34E-6 | 0.25 | 260 | 0.0019 |
| Methods for Determining Physical Soil Parameters |
| Parameter | Sampling Locationa | Method |
|
r b (soil bulk density) |
Surface |
ASTM - D 1556-90
Sand Cone Methodb |
| ASTM - D 2167-94
Rubber Balloon Methodb |
||
| ASTM - D 2922-91
Nuclear Methodb |
||
| Subsurface | ASTM - D 2937-94
Drive Cylinder Methodb |
|
| r s (soil particle density) | Surface or Subsurface | ASTM - D 854-92
Specific Gravity of Soilb |
|
w (moisture content) |
Surface or Subsurface |
ASTM - D 4959-89
(Reapproved 1994) Standardb |
| ASTM - D 4643-93
Microwave Ovenb |
||
| ASTM - D2216-92
Laboratory Determinationb |
||
| ASTM - D3017-88
(Reapproved 1993) Nuclear Methodb |
||
| Equivalent USEPA Method (e.g., sample preparation procedures described in methods 3541 or 3550) | ||
|
foc (organic carbon content) |
Surface or Subsurface |
Nelson and Sommers (1982) |
| ASTM - D 2974-87
(Reapproved 1995) Moisture, Ash, and Organic Matterb |
||
| USEPA Method 9060A
Total Organic Content |
| Methods for Determining Physical Soil Parameters |
| Parameter | Sampling Locationa | Method |
| h or q T (total soil porosity) | Surface or Subsurface (calculated) | Equation S24 in Appendix C, Table A for SSL Model, or Equation R23 in Appendix C, Table C for RBCA Model |
| q a or q as (air-filled soil porosity) | Surface or Subsurface (calculated) | Equation S21 in Appendix C, Table A for SSL Model, or Equation R21 in Appendix C, Table C for RBCA Model |
| q w or q ws (water-filled soil porosity) | Surface or Subsurface (calculated) | Equation S20 in Appendix C, Table A for SSL Model, or Equation R22 in Appendix C, Table C for RBCA Model |
|
|
|
ASTM - D 5084-90
Flexible Wall Permeameter |
| K (hydraulic conductivity) | Surface or Subsurface | Pump Test |
| Slug Test | ||
| i (hydraulic gradient) | Surface or Subsurface | Field Measurement |
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.Table G: | Error Function (erf) | ||||||||||||
b
|
erf (
b
)
|
| 0 | 0 |
| 0.05 | 0.056372 |
| 0.1 | 0.112463 |
| 0.15 | 0.167996 |
| 0.2 | 0.222703 |
| 0.25 | 0.276326 |
| 0.3 | 0.328627 |
| 0.35 | 0.379382 |
| 0.4 | 0.428392 |
| 0.45 | 0.475482 |
| 0.5 | 0.520500 |
| 0.55 | 0.563323 |
| 0.6 | 0.603856 |
| 0.65 | 0.642029 |
| 0.7 | 0.677801 |
| 0.75 | 0.711156 |
| 0.8 | 0.742101 |
| 0.85 | 0.770668 |
| 0.9 | 0.796908 |
| 0.95 | 0.820891 |
| 1.0 | 0.842701 |
| 1.1 | 0.880205 |
| 1.2 | 0.910314 |
| 1.3 | 0.934008 |
| 1.4 | 0.952285 |
| 1.5 | 0.966105 |
| 1.6 | 0.976348 |
| 1.7 | 0.983790 |
| 1.8 | 0.989091 |
| 1.9 | 0.992790 |
| 2.0 | 0.995322 |
| 2.1 | 0.997021 |
| 2.2 | 0.998137 |
| 2.3 | 0.998857 |
| 2.4 | 0.999311 |
| 2.5 | 0.999593 |
| 2.6 | 0.999764 |
| 2.7 | 0.999866 |
| 2.8 | 0.999925 |
| 2.9 | 0.999959 |
| 3.0 | 0.999978 |
| Section 742.Table H: | |
| Q/C Values by Source Area |
Source
(Acres) |
Area Q/C Value
(g/m2-s per kg/m3) |
0.5
|
97.78
|
1
|
85.81
|
2
|
76.08
|
5
|
65.75
|
10
|
59.16
|
30
|
50.60
|
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.TABLE I: | |
| Koc Values for Ionizing Organics as a Function of pH (cm3/g or L/kg) |
|
pH |
Benzoic Acid |
2-Chloro- phenol |
2,4-
Dichloro-phenol |
Pentachloro-phenol |
2,4,5-Trichloro-phenol | 2,4,6-Trichloro-phenol |
Dinoseb |
2,3,5-TP (Silvex) |
| 4.5 | 1.07E+01 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 1.34E+04 | 2.37E+03 | 1.06E+03 | 3.00E+03 | 1.28E+04 |
| 4.6 | 9.16E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 1.24E+04 | 2.37E+03 | 1.05E+03 | 2.71E+03 | 1.13E+04 |
| 4.7 | 7.79E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 1.13E+04 | 2.37E+03 | 1.05E+03 | 2.41E+03 | 1.01E+04 |
| 4.8 | 6.58E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 1.02E+04 | 2.37E+03 | 1.05E+03 | 2.12E+03 | 9.16E+03 |
| 4.9 | 5.54E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 9.05E+03 | 2.37E+03 | 1.04E+03 | 1.85E+04 | 8.40E+03 |
| 5.0 | 4.64E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 7.96E+03 | 2.36E+03 | 1.03E+03 | 1.59E+04 | 7.76E+03 |
| 5.1 | 3.88E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 6.93E+03 | 2.36E+03 | 1.02E+03 | 1.36E+04 | 7.30E+03 |
| 5.2 | 3.25E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 5.97E+03 | 2.35E+03 | 1.01E+03 | 1.15E+04 | 6.91E+03 |
| 5.3 | 2.72E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.59E+02 | 5.10E+03 | 2.34E+03 | 9.99E+02 | 9.66E+03 | 6.60E+03 |
| 5.4 | 2.29E+00 | 3.98E+02 | 1.58E+02 | 4.32E+03 | 2.33E+03 | 9.82E+02 | 8.10E+03 | 6.36E+03 |
| 5.5 | 1.94E+00 | 3.97E+02 | 1.58E+02 | 3.65E+03 | 2.32E+03 | 9.62E+02 | 6.77E+03 | 6.16E+03 |
| 5.6 | 1.65E+00 | 3.97E+02 | 1.58E+02 | 3.07E+03 | 2.31E+03 | 9.38E+02 | 5.65E+03 | 6.00E+03 |
| 5.7 | 1.42E+00 | 3.97E+02 | 1.58E+02 | 2.58E+03 | 2.29E+03 | 9.10E+02 | 4.73E+03 | 5.88E+03 |
| 5.8 | 1.24E+00 | 3.97E+02 | 1.58E+02 | 2.18E+03 | 2.27E+03 | 8.77E+02 | 3.97E+03 | 5.78E+03 |
| 5.9 | 1.09E+00 | 3.97E+02 | 1.57E+02 | 1.84E+03 | 2.24E+03 | 8.39E+02 | 3.35E+03 | 5.70E+03 |
|
pH |
Benzoic Acid |
2-Chloro- phenol |
2,4-
Dichloro-phenol |
Pentachloro-phenol |
2,4,5-Trichloro-phenol | 2,4,6-Trichloro-phenol |
Dinoseb |
2,3,5-TP (Silvex) |
| 6.0 | 9.69E-01 | 3.96E+02 | 1.57E+02 | 1.56E+03 | 2.21E+03 | 7.96E+02 | 2.84E+03 | 5.64E+03 |
| 6.1 | 8.75E-01 | 3.96E+02 | 1.57E+02 | 1.33E+03 | 2.17E+03 | 7.48E+02 | 2.43E+03 | 5.59E+03 |
| 6.2 | 7.99E-01 | 3.96E+02 | 1.56E+02 | 1.15E+03 | 2.12E+03 | 6.97E+02 | 2.10E+03 | 5.55E+03 |
| 6.3 | 7.36E-01 | 3.95E+02 | 1.55E+02 | 9.98E+02 | 2.06E+03 | 6.44E+02 | 1.83E+03 | 5.52E+03 |
| 6.4 | 6.89E-01 | 3.94E+02 | 1.54E+02 | 8.77E+02 | 1.99E+03 | 5.89E+02 | 1.62E+03 | 5.50E+03 |
| 6.5 | 6.51E-01 | 3.93E+02 | 1.53E+02 | 7.81E+02 | 1.91E+03 | 5.33E+02 | 1.45E+03 | 5.48E+03 |
| 6.6 | 6.20E-01 | 3.92E+02 | 1.52E+02 | 7.03E+02 | 1.82E+03 | 4.80E+02 | 1.32E+03 | 5.46E+03 |
| 6.7 | 5.95E-01 | 3.90E+02 | 1.50E+02 | 6.40E+02 | 1.71E+03 | 4.29E+02 | 1.21E+03 | 5.45E+03 |
| 6.8 | 5.76E-01 | 3.88E+02 | 1.47E+02 | 5.92E+02 | 1.60E+03 | 3.81E+02 | 1.12E+03 | 5.44E+03 |
| 6.9 | 5.60E-01 | 3.86E+02 | 1.45E+02 | 5.52E+02 | 1.47E+03 | 3.38E+02 | 1.05E+03 | 5.43E+03 |
| 7.0 | 5.47E-01 | 3.83E+02 | 1.41E+02 | 5.21E+02 | 1.34E+03 | 3.00E+02 | 9.96E+02 | 5.43E+03 |
| 7.1 | 5.38E-01 | 3.79E+02 | 1.38E+02 | 4.96E+02 | 1.21E+03 | 2.67E+02 | 9.52E+02 | 5.42E+03 |
| 7.2 | 5.32E-01 | 3.75E+02 | 1.33E+02 | 4.76E+02 | 1.07E+03 | 2.39E+02 | 9.18E+02 | 5.42E+03 |
| 7.3 | 5.25E-01 | 3.69E+02 | 1.28E+02 | 4.61E+02 | 9.43E+02 | 2.15E+02 | 8.90E+02 | 5.42E+03 |
| 7.4 | 5.19E-01 | 3.62E+02 | 1.21E+02 | 4.47E+02 | 8.19E+02 | 1.95E+02 | 8.68E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| 7.5 | 5.16E-01 | 3.54E+02 | 1.14E+02 | 4.37E+02 | 7.03E+02 | 1.78E+02 | 8.50E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| 7.6 | 5.13E-01 | 3.44E+02 | 1.07E+02 | 4.29E+02 | 5.99E+02 | 1.64E+02 | 8.36E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
|
pH |
Benzoic Acid |
2-Chloro- phenol |
2,4-
Dichloro-phenol |
Pentachloro-phenol |
2,4,5-Trichloro-phenol | 2,4,6-Trichloro-phenol |
Dinoseb |
2,3,5-TP (Silvex) |
| 7.7 | 5.09E-01 | 3.33E+02 | 9.84E+01 | 4.23E+02 | 5.07E+02 | 1.53E+02 | 8.25E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| 7.8 | 5.06E-01 | 3.19E+02 | 8.97E+01 | 4.18E+02 | 4.26E+02 | 1.44E+02 | 8.17E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| 7.9 | 5.06E-01 | 3.04E+02 | 8.07E+01 | 4.14E+02 | 3.57E+02 | 1.37E+02 | 8.10E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| 8.0 | 5.06E-01 | 2.86E+02 | 7.17E+01 | 4.10E+02 | 2.98E+02 | 1.31E+02 | 8.04E+02 | 5.41E+03 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| pH | As | Ba | Be | Cd | Cr (+3) | Cr (+6) | Hg | Ni | Ag | Se | Tl | Zn |
| 4.9 | 2.5E+01 | 1.1E+01 | 2.3E+01 | 1.5E+01 | 1.2E+03 | 3.1E+01 | 4.0E-02 | 1.6E+01 | 1.0E-01 | 1.8E+01 | 4.4E+01 | 1.6E+01 |
| 5.0 | 2.5E+01 | 1.2E+01 | 2.6E+01 | 1.7E+01 | 1.9E+03 | 3.1E+01 | 6.0E-02 | 1.8E+01 | 1.3E-01 | 1.7E+01 | 4.5E+01 | 1.8E+01 |
| 5.1 | 2.5E+01 | 1.4E+01 | 2.8E+01 | 1.9E+01 | 3.0E+03 | 3.0E+01 | 9.0E-02 | 2.0E+01 | 1.6E-01 | 1.6E+01 | 4.6E+01 | 1.9E+01 |
| 5.2 | 2.6E+01 | 1.5E+01 | 3.1E+01 | 2.1E+01 | 4.9E+03 | 2.9E+01 | 1.4E-01 | 2.2E+01 | 2.1E-01 | 1.5E+01 | 4.7E+01 | 2.1E+01 |
| 5.3 | 2.6E+01 | 1.7E+01 | 3.5E+01 | 2.3E+01 | 8.1E+03 | 2.8E+01 | 2.0E-01 | 2.4E+01 | 2.6E-01 | 1.4E+01 | 4.8E+01 | 2.3E+01 |
| 5.4 | 2.6E+01 | 1.9E+01 | 3.8E+01 | 2.5E+01 | 1.3E+04 | 2.7E+01 | 3.0E-01 | 2.6E+01 | 3.3E-01 | 1.3E+01 | 5.0E+01 | 2.5E+01 |
| 5.5 | 2.6E+01 | 2.1E+01 | 4.2E+01 | 2.7E+01 | 2.1E+04 | 2.7E+01 | 4.6E-01 | 2.8E+01 | 4.2E-01 | 1.2E+01 | 5.1E+01 | 2.6E+01 |
| 5.6 | 2.6E+01 | 2.2E+01 | 4.7E+01 | 2.9E+01 | 3.5E+04 | 2.6E+01 | 6.9E-01 | 3.0E+01 | 5.3E-01 | 1.1E+01 | 5.2E+01 | 2.8E+01 |
| 5.7 | 2.7E+01 | 2.4E+01 | 5.3E+01 | 3.1E+01 | 5.5E+04 | 2.5E+01 | 1.0E-00 | 3.2E+01 | 6.7E-01 | 1.1E+01 | 5.4E+01 | 3.0E+01 |
| 5.8 | 2.7E+01 | 2.6E+01 | 6.0E+01 | 3.3E+01 | 8.7E+04 | 2.5E+01 | 1.6E-00 | 3.4E+01 | 8.4E-01 | 9.8E+00 | 5.5E+01 | 3.2E+01 |
| 5.9 | 2.7E+01 | 2.8E+01 | 6.9E+01 | 3.5E+01 | 1.3E+05 | 2.4E+01 | 2.3E-00 | 3.6E+01 | 1.1E+00 | 9.2E+00 | 5.6E+01 | 3.4E+01 |
| 6.0 | 2.7E+01 | 3.0E+01 | 8.2E+01 | 3.7E+01 | 2.0E+05 | 2.3E+01 | 3.5E-00 | 3.8E+01 | 1.3E+00 | 8.6E+00 | 5.8E+01 | 3.6E+01 |
| 6.1 | 2.7E+01 | 3.1E+01 | 9.9E+01 | 4.0E+01 | 3.0E+05 | 2.3E+01 | 5.1E-00 | 4.0E+01 | 1.7E+00 | 8.0E+00 | 5.9E+01 | 3.9E+01 |
| 6.2 | 2.8E+01 | 3.3E+01 | 1.2E+02 | 4.2E+01 | 4.2E+05 | 2.2E+01 | 7.5E-00 | 4.2E+01 | 2.1E+00 | 7.5E+00 | 6.1E+01 | 4.2E+01 |
| 6.3 | 2.8E+01 | 3.5E+01 | 1.6E+02 | 4.4E+01 | 5.8E+05 | 2.2E+01 | 1.1E+01 | 4.5E+01 | 2.7E+00 | 7.0E+00 | 6.2E+01 | 4.4E+01 |
| 6.4 | 2.8E+01 | 3.6E+01 | 2.1E+02 | 4.8E+01 | 7.7E+05 | 2.1E+01 | 1.6E+01 | 4.7E+01 | 3.4E+00 | 6.5E+00 | 6.4E+01 | 4.7E+01 |
| 6.5 | 2.8E+01 | 3.7E+01 | 2.8E+02 | 5.2E+01 | 9.9E+05 | 2.0E+01 | 2.2E+01 | 5.0E+01 | 4.2E+00 | 6.1E+00 | 6.6E+01 | 5.1E+01 |
| 6.6 | 2.8E+01 | 3.9E+01 | 3.9E+02 | 5.7E+01 | 1.2E+06 | 2.0E+01 | 3.0E+01 | 5.4E+01 | 5.3E+00 | 5.7E+00 | 6.7E+01 | 5.4E+01 |
| pH | As | Ba | Be | Cd | Cr (+3) | Cr (+6) | Hg | Ni | Ag | Se | Tl | Zn |
| 6.7 | 2.9E+01 | 4.0E+01 | 5.5E+02 | 6.4E+01 | 1.5E+06 | 1.9E+01 | 4.0E+01 | 5.8E+01 | 6.6E+00 | 5.3E+00 | 6.9E+01 | 5.8E+01 |
| 6.8 | 2.9E+01 | 4.1E+01 | 7.9E+02 | 7.5E+01 | 1.8E+06 | 1.9E+01 | 5.2E+01 | 6.5E+01 | 8.3E+00 | 5.0E+00 | 7.1E+01 | 6.2E+01 |
| 6.9 | 2.9E+01 | 4.2E+01 | 1.1E+03 | 9.1E+01 | 2.1E+06 | 1.8E+01 | 6.6E+01 | 7.4E+01 | 1.0E+01 | 4.7E+00 | 7.3E+01 | 6.8E+01 |
| 7.0 | 2.9E+01 | 4.2E+01 | 1.7E+03 | 1.1E+02 | 2.5E+06 | 1.8E+01 | 8.2E+01 | 8.8E+01 | 1.3E+01 | 4.3E+00 | 7.4E+01 | 7.5E+01 |
| 7.1 | 2.9E+01 | 4.3E+01 | 2.5E+03 | 1.5E+02 | 2.8E+06 | 1.7E+01 | 9.9E+01 | 1.1E+02 | 1.6E+01 | 4.1E+00 | 7.6E+01 | 8.3E+01 |
| 7.2 | 3.0E+01 | 4.4E+01 | 3.8E+03 | 2.0E+02 | 3.1E+06 | 1.7E+01 | 1.2E+02 | 1.4E+02 | 2.0E+01 | 3.8E+00 | 7.8E+01 | 9.5E+01 |
| 7.3 | 3.0E+01 | 4.4E+01 | 5.7E+03 | 2.8E+02 | 3.4E+06 | 1.6E+01 | 1.3E+02 | 1.8E+02 | 2.5E+01 | 3.5E+00 | 8.0E+01 | 1.1E+02 |
| 7.4 | 3.0E+01 | 4.5E+01 | 8.6E+03 | 4.0E+02 | 3.7E+06 | 1.6E+01 | 1.5E+02 | 2.5E+02 | 3.1E+01 | 3.3E+00 | 8.2E+01 | 1.3E+02 |
| 7.5 | 3.0E+01 | 4.6E+01 | 1.3E+04 | 5.9E+02 | 3.9E+06 | 1.6E+01 | 1.6E+02 | 3.5E+02 | 3.9E+01 | 3.1E+00 | 8.5E+01 | 1.6E+02 |
| 7.6 | 3.1E+01 | 4.6E+01 | 2.0E+04 | 8.7E+02 | 4.1E+06 | 1.5E+01 | 1.7E+02 | 4.9E+02 | 4.8E+01 | 2.9E+00 | 8.7E+01 | 1.9E+02 |
| 7.7 | 3.1E+01 | 4.7E+01 | 3.0E+04 | 1.3E+03 | 4.2E+06 | 1.5E+01 | 1.8E+02 | 7.0E+02 | 5.9E+01 | 2.7E+00 | 8.9E+01 | 2.4E+02 |
| 7.8 | 3.1E+01 | 4.9E+01 | 4.6E+04 | 1.9E+03 | 4.3E+06 | 1.4E+01 | 1.9E+02 | 9.9E+02 | 7.3E+01 | 2.5E+00 | 9.1E+01 | 3.1E+02 |
| 7.9 | 3.1E+01 | 5.0E+01 | 6.9E+04 | 2.9E+03 | 4.3E+06 | 1.4E+01 | 1.9E+02 | 1.4E+03 | 8.9E+01 | 2.4E+00 | 9.4E+01 | 4.0E+02 |
| 8.0 | 3.1E+01 | 5.2E+01 | 1.0E+05 | 4.3E+03 | 4.3E+06 | 1.4E+01 | 2.0E+02 | 1.9E+03 | 1.1E+02 | 2.2E+00 | 9.6E+01 | 5.3E+02 |
| Section 742.APPENDIX C: | |
| Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations |
| Section 742.TABLE K: | Parameter Estimates for Calculating Water-Filled Soil Porosity (q w) |
Soil Texturea
|
Saturated Hydraulic
Conductivity, Ks (m/yr) |
1/(2b+3)b
|
| Sand | 1,830 | 0.090 |
| Loamy Sand | 540 | 0.085 |
| Sandy Loam | 230 | 0.080 |
| Silt Loam | 120 | 0.074 |
| Loam | 60 | 0.073 |
| Sandy Clay Loam | 40 | 0.058 |
| Silt Clay Loam | 13 | 0.054 |
| Clay Loam | 20 | 0.050 |
| Sandy Clay | 10 | 0.042 |
| Silt Clay | 8 | 0.042 |
| Clay | 5 | 0.039 |
| a | The appropriate texture classification is determined by a particle size analysis by ASTM D2488-93 as incorporated by reference in Section 742.210 and the U.S. Department of Agriculture Soil Textural Triangle shown in Appendix C, Illustration C. |
| Section 41 of the Environmental Protection Act (415 ILCS 5/41(1994)) provides for the appeal of final Board opinions and orders to the Illinois Appellate Court within 35 days of the date of service of this order. The Rules of the Supreme Court of Illinois establish filing requirement. (See also 35 Ill.Adm. Code 101.246 “Motions for Reconsideration.”) |