TITLE35:
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
SUBTITLE
C:
WATER POLLUTION
CHAPTERII:
ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTIONAGENCY
PART
355
DETERMINATION OF
AMMONIA
NITROGEN WATER QUALITY BASED EFFLUENT
LIMITS FOR DISCHARGES TO GENERAL USE WATERS
SUBPART A:
INTRODUCTION
Section
355.101
Purpose, Scope and Application
355.103
Definitions
SUBPART B:
AMMONIA
NITROGEN (as N) WATER QUALITY
STANDARDS
AND WQBELs
Introduction
Calculation Convercion of Total Ammonia and Un ionized Ammonia Nitrogen
____________
Quality Standards Regarding NPDES Permit Limits
Estimation ofProjected Effluent Quality
Mixing Allowance
Calculation ofPreliminaryEffluent Limitation
Summary ofthe Results for a Reasonable Potential Analysis
and the Determination of
Ammonia Nitrogen WQBELs
SUBPART C:
EFFLUENT MODIFIED WATERS
Section
~C~~1i1
T.
355.303
EMW Application Requirements
355.305
Evaluation ofEMW Applications
355.307
Determination ofEMW Designation
355.309
355.311
Procedures for Delineating an EMW
Ammonia Nitrogen Decay Equation
-
-
.
.
with EMWs
355.315
Publication.ofEMViTs
AUTHORITY:
Implementing and authorized by Section
39 of the Illinois Environmental Protection Act
415
ILCS
5/39.
SOURCE:
Adopted at 23
Ill. Reg. 7267, effective June 9,
1999.
NOTE:
In
this
Part,
unless
the
context clearly
indicates
otherwise,
superscript
numbers
or
letters
are
denoted by parentheses; subscript are denoted by brackets.
Section
355.201
355.203
355.205
355.207
355.209
355.211
Numeric
Water
SUBPART A:
INTRODUCTION
Section 355.101
Purpose, Scope and
Application
a)
This
Part
contains
procedures
to
determine
water
quality
based
effluent
limits
for
ammonia
nitrogen
(as N) (ammonia
nitrogen WQBELs)
that
are
necessary to
prevent waters of the
State
from exceeding
water quality
standards pursuant to 40 CFR
122.44(d)(1) and
35
Ill.
Adm. Code
309.14 1(d)(3).
Ammonia nitrogen
WQBELs
must be
sufficient to
ensure compliance
with
the
water quality
standards
for ammonia nitrogen found
in the Illinois Pollution Control Board (IPCB)
regulations at
35
Ill. Adm. Code 302.202,
302.212,
3-02.213
and 304.122.
b)
Ammonia nitrogen WQBELs
are applicableto the general use waters ofthe State.
c)
There shall
be
an opportunity for compliance with the
ammonia nitrogen water quality
standards
as provided
by the IPCB
regulations
through•
application of allowed
mixing, mixing zones
and
zones ofinitial
dilution at35
Ill. Adm. Code
302.102 and 302.213.
d)
In
addition
to
water
quality
based
effluent
limits,
the
discharge
of ammonia
nitrogen
from
a
facility may be
limited
based
on
other provisions
in the Environmental Protection Act 415
ILCS
5
(Act) and regulations adopted thereunder
or the Federal Water Pollution Control Act, 33
USC
1251-1387
(FWPCA) and
regulations
adopted thereunder.
Section 355.103
Definitions
All
terms in this Part shall
have the meanings
set forth
in the Environmental Protection Act
and
in the
IPCB regulations under
35
Ill. Adm. Code 301
and 302
except,
for purposes of this
Part, the
following
definitions apply:
“7Q10” means the average daily flow ofthe lowest total
flow for a seven day neriod that occurs
once ma loyearperiod.
“AWQMN”
or “Ambient
Water Quality Monitoring Network”
means the network of sampling
stations maintained by the Agency and located on streams throughout the State.
“Agency” means the Illinois Environmental
Protection Agency.
“Ammonia decay” refers to the cumulative
effect ofnitrification, volatilixmtion,
plant uptake, and
other-processes that reducethe concentration ofammonia nitrogen in waters by natural
muss.
“cfc” means cubic feetper second.
“DAF” means decign average flow.
“DMR” means discharge monitoring report.
“EMW” or “Effluent Modified Water”
means those waters
or portions ofwaters that
the
Agency
has determined, pursuant to 35 Ill. Mm.
Code
302.213,
are
not subject to the chronic
ammonia
nitrogen ctandards of35 Ill. Adm.
Code 302.212(b).
“IPCB” means the Illinois Pollution Control Board.
“ISWS”
means the Illinoic
State
Water
Survey, a part of the
Office
Of
Scientific
Research and
Analysic in the Illinois Department ofNatural
Resources.
“Kjeldahl” means the total oforganic nitrogen
and
ammonia nitrogen.
“MGD”
“NPDES”
means National Pollutant Discharge Elimination Systems.
“PEL”
or
“Preliminary
Effluent
Limitation”
is
an
estimate
of
an
allowable
discharge
concentration taking into
consideration allowed mixing or dilution.
“PEQ” or “Projected Effluent Quality”
is
the maximum
contaminant concentrationestimated to
be
discharged by a facility or activity taking
into
account
statistical analysis ofthe discharge or
activity.
“Reasonable
Potential
Analysis”
or
“Reasonable
Potential
to
Exceed”
means
the procedure
to
predict whether
an existing
or
future
discharge may
cause or contribute
to
a violation of water
quality standards, criteria or values.
“Summer” means the months
of
March
A~.psi4through
October,
inclusive.
If early life stages of
sensitive organisms are present in a water body during othermonths, these months are
included as
summermonths.
“USEPA” means the United States Environmental
Protection Agency.
“USGS” means theUnited States Geological
Survey.
“WQBEL”
or
“Water Quality Based Effluent Limit” means
an NPDES permit limit
that ensures
that applicable water quality
standards and criteria
are
met
in
waters
where
such
standards
and
criteria apply.
“Winter” means the months ofNovember through February
March,
inclusive.
If
early life stages
of organisms
for a
water
body
exist
in
any
of these
months,
these
months
will
be
considered
summer months.
SUBPART
B:
AMMONIA
NITROGEN
(as N) WATER QUALITY
STANDARDS AND
WQBELs
Section 355.201
Introduction
The need for an ammonia nitrogen (as N)
WQBEL is based on the reasonable potential ofa discharge to
cause
or contribute to a violation ofthe applicable ammonia nitrogen water quality standard.
During the
NPDES
permit
review
process, the
Agency
shall
conduct an
analysis
of the
reasonable potential
for
ammonia to
exceed
or contribute to excursions
above the ammonia
nitrogen water
quality
standard
that
may
occur
in
the receiving water.
This
analysis
shall
be
conducted
for,
both
acute,
and
chronic
and
subchronic
winter and summer
ammonia nitrogen water quality standards.
The Agency may subdivide
summer
or
winter
periods
into
quarterly
or
monthly
segments
with
analysis
of reasonable,
potential
corresponding to those smaller time
segments in individual permit applications.
a)
The
first step
in the reasonable
potential
analysis
is to
compare
the
Projected Effluent
Quality
(PEQ),
as provided
in
Section
3
55.205,
to
the total ammonia nitrogen water
quality
standard as
converted to total
ammonia nitrogen
as provided
in
Section 355.203.
If the PEQ is less
than or
equal to the water quality standard as converted to total ammonia nitrogen as provided
in
Section
355.203,
then no reasonable potential
to exceed the standard exists and no effluent limitation will
be established in the permit unless otherwise warranted under subsection (c) ofthis Section~
b)
Ifthe PEQ exceeds the applicable total ammonia nitrogen water quality standard as
converted to
total ammonia nitrogen as provided in Section 355.203, the analysis
shall proceed to the second
step asprovided in Section
355.207.
c)
If the
wastewater prior
to
treatment
contains
total Kjeldahl
nitrogen
at
levels
in
which
a
reasonable potential
to exceed total ammonia nitrogen water quality standards as converted4o as
provided in Section 355.203 exists, then the discharge ofammonia nitrogen shall be limited in the
NPDES permit by an ammonia nitrogen WQBEL.
Reasonable potential to exceed, water quality
standards will be determined consistent with Sections 355.203 through 355.211 ofthis Part.
Even
if there appears to
be no
potential to exceed ‘the
water
quality
standards based
on
the
effluent
quality analysis in subsection (a) or (b), an ammonia nitrogen WQBEL shall be established.
Section 355.203
Calculation Conversion ofTotal Ammonia and Un-ionized Ammonia Nitrogen
Numeric Water Quality Standards Regarding NPDES Permit Limits
The numeric water quality standards for ammonia nitrogen in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.212
are established
as the
un
ionized
fraction ofthe total
ammonia nitrogen present,
since the un ionized
component m~ere
closely relates to the toxicology informationutilized in
deriving
the-ammonia
nitrogen
standard.
However,
most discharge monitoring data used -in
deriving-a
PEQ will be in the form
of total
ammonia
nitrogen.
WQBELC
will
be
set
as
total
ammonia
nitrogen
concentrations-.
The
conversion
formula contained in 35 Ill. Mm. Code 302.212 shall be used to estimate the portion oftotal
ammonia nitronen that
exists
in
the un ionized condition.
The
nrimarv
variables affecting
~
eQuilibrium
between
ionmiecl
mU
un
ioniaecI
tractions
are
temperature
and
pH.
Temperature
and
pH
affect
the
numeric
total
ammonia
nitrogen standard.
Both
stream
temperature
and
pH
can
be
expected
to
be
different than
discharge temperature
and pH; therefore,
the conversion calculation of the
water
quality
standardwill be based on conditions
expected to exist downstream ofthe discharge.
a)
Where receiving stream
specific data is
available, that data shall be the basis for the
selection of
temperature and pH values to be used in calculating converting total ammonia nitrogenstandards
with which
an NPDES permit limit will
be based.
A data collection
station
downstream ofthe
discharge at or beyond the point where complete mixing has occurred
is preferred.to
un
ionized
ammonia nitrogen.
When, receiving
stream
specific
data is not
available, data from the
closest
representative Agency water quality monitoring station during the
most recent five years will be
used in this conversion formula.
The temperature will be set at the 75th percentile
(75
percent of
the values are less than).
The pH valuewill be set at the 75th percentile
(75
percent ofthe values
are less than) for determination of both acute, aa4 chronic and subchronic conditions.
Ifthe 75th
percentile pH value results in
a permit limit for chronic exposure conditions
(monthly
average
ammonia permit limit) less than
1.5
mg/L summer limit or 4.0
mgIL
winter limit, the values will
be recalculated based on
a 50th
percentile pH value (half the
values are
less than).
The permit
limit will then be set atthe value derived with
a 50th percentile pH as long as that value does not
exceed
1.5
mgfL
for summer months and
4.0
mgfL
for winter months.
If a
50th
percentile pH
value would allow a higher summer limit than
1.5
mg(L, the limit will be
set at
1.5
mg/L.
If a
50th percentile pH would allow a higher winter limit than 4.0 mg/L, the winter limit would be set
at 4.0 mg/L.
Limits based on the subchronic ammonia standard will be 2.5 times the chronic limit
established by the aboveprocedure.
b)
When sufficient stream
specific information is available with simultaneous measurements oftotal
ammonia,
pH,
and
temperature,
a Gonvercion
relationship
reflecting
the
dynamic
interaction
between pH, temperature
and
ammonia equilibrium may
be developed
instead of the
approach
presented in subsection (a) above.
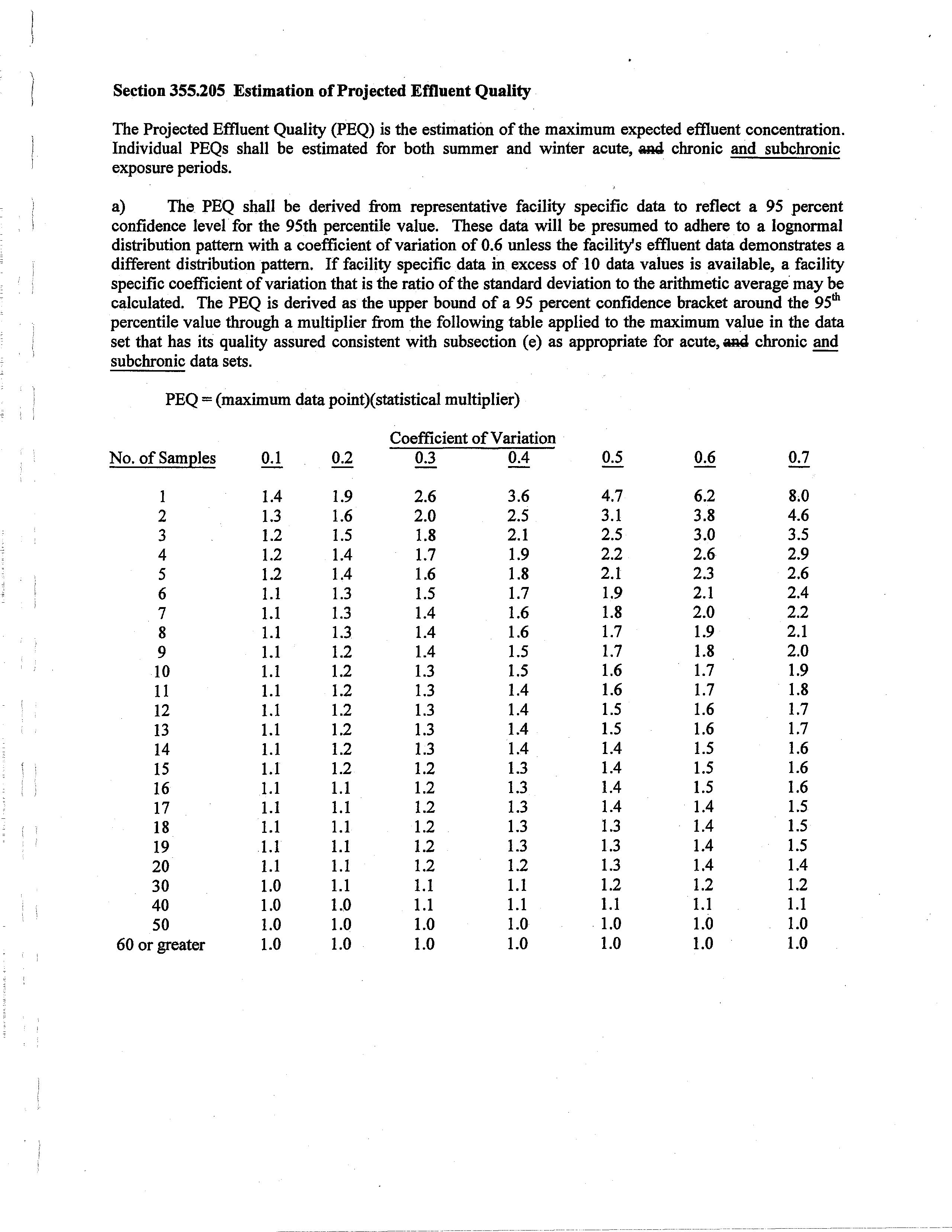
Section
355.205
Estimation ofProjected Effluent Quality~
The Projected Effluent Quality (PEQ)
is the estimation of the maximum expected effluent concentration.
Individual
PEQs
shall
be
estimated
for both
summer
and
winter
acute, w~4chronic and
subchronic
exposure periods.
a)
The
PEQ
shall
be
derived
from
representative
facility
specific
data
to
reflect a
95
percent
confidence
level for the 95th percentile
value.
These
data will
be
presumed
to
adhere to
a
lognonnal
distribution pattern with a coefficient ofvariation of0.6 unless the facility’s effluent data demonstrates a
different distribution pattern.
If facility specific data in
excess of 10
data values
is available,
a facility
specific coefficient ofvariation that
is the ratio ofthe standard deviation to the arithmetic average may be
calculated.
The PEQ
is derived as the
upper bound ofa
95
percent confidence bracket around the
95th
percentile value through a multiplier from the following table
applied to the
maximum value
in the data
set that has
its
quality assured consistent with subsection
(e)
as appropriate
for acute, w4
chronic and
subchronic data sets.
PEQ
=
(maximum datapoint)(statistical multiplier)
CoefficientofVariation
No. of Samples
0A
0.2
03
0~4
0.5
(~6
03
1
1.4
1.9
2.6
3.6
4.7
6.2
8.0
2
1.3
1.6
2.0
2.5
3.1
3.8
4.6
3
1.2
1.5
1.8
2.1
2.5
3.0
3.5
4
1.2
1.4
1.7
1.9
2.2
2.6
2.9
5
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.1
2.3
2.6
6
1.1
1.3
1.5
1.7
1.9
2.1
2.4
7
1.1
1.3
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
8
1.1
1.3
1.4
1.6
1.7
1.9
2.1
9
1.1
1.2
1.4
1.5
1.7
1.8
2.0
10
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.9
11
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.6
1.7
1.8
12
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
13
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
14
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.4
1.5
1.6
15
1.1
1.2
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
16
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
17
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.4
1.5
18
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.3
1.4
1.5
19
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.3
1.4
1.5
20
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.4
30
1.0
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.2
1.2
1.2
40
1.0
1.0
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.1
50
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
60 or greater
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
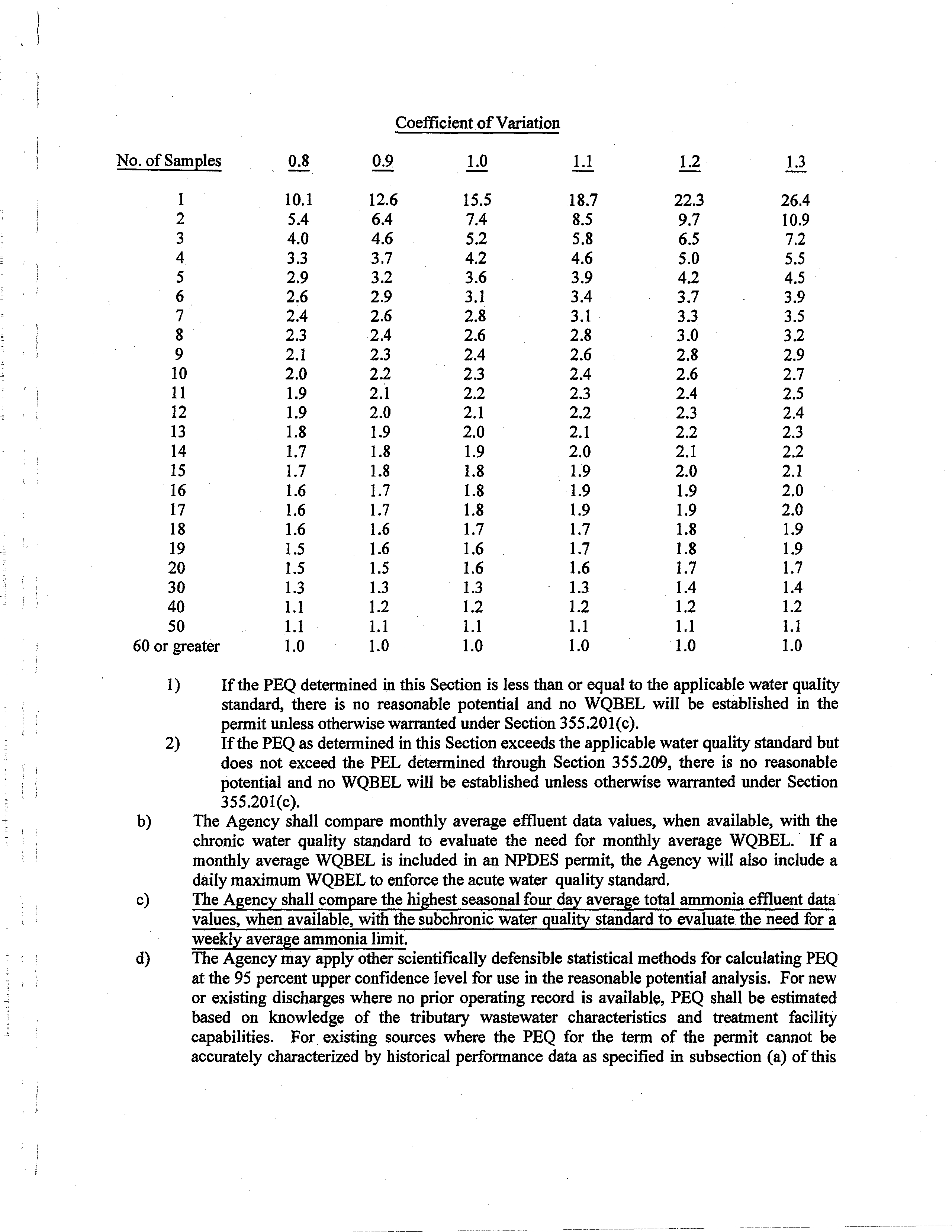
Coefficient ofVariation
No. ofSamples
0~
0.9
LO
Li
12
1.3
1
10.1
12.6
15.5
18.7
22.3
26.4
2
5.4
6.4
7.4
8.5
9.7
10.9
3
4.0
4.6
5.2
5.8
6.5
7.2
4
3.3
3.7
4.2
4.6
5.0
5.5
5
2.9
3.2
3.6
3.9
4.2
4.5
6
2.6
2.9
3.1
3.4
3.7
3.9
7
2.4
2.6
2.8
3.1
3.3
3.5
8
2.3
2.4
2.6
2.8
3.0
3.2
9
2.1
2.3
2.4
2.6
2.8
2.9
10
2.0
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.6
2.7
11
1.9
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
12
,
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
13
1.8
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
14
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
15
1.7
1.8
1.8
,
1.9
2.0
2.1
16
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
1.9
2.0
17
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
1.9
2.0
18
1.6
1.6
1.7
1.7
1.8
,
1.9
19
1.5
1.6
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
20
1.5
1.5
1.6
1.6
1.7
1.7
30
1.3
1.3
1.3
‘
1.3
1.4
1.4
40
1.1
1.2
1.2
1.2
1.2
1.2
50
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.1
1.1
60orgreater
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1)
Ifthe PEQ determined in this Section is
less than or equal to the applicable water quality
standard, there
is no reasonable potential
and
no WQBEL will be established in the
permit unless otherwisewarrantedunder Section 355.201(c).
2)
IfthePEQ as determined inthis Section exceeds the applicable water quality
standard but
does not exceed the PEL determined through
Section
355209,
there
is no reasonable
potential and no WQBEL will be
established unless otherwise
warranted under
Section
355.201(c).
b)
The Agency shall compare
monthly average
effluent data values,
when available,
with the
chronic water quality
standard
to
evaluate the
need
for monthly
average
WQBEL.
If a
monthly average WQBEL
is
included in
an NPDES
permit, the
Agency will also include a
dailymaximumWQBEL to enforce the acute water quality standard.
c)
The Agency shall compare the highest seasonal four
day average total ammonia effluent data’
values,when available, with the subchronic water quality standard to evaluate the need for a
weekly averageammonia limit.
d)
TheAgencymay apply other scientifically defensible
statistical methods for calculating PEQ
at the
95
percent upper confidence level for use
in the reasonable potential analysis.
For
new
or existing discharges where no prior operatingrecord is available, PEQ shall be
estimated
based on knowledge of the
tributary wastewater
characteristics
and
treatment
facility
capabilities.
For, existing sources where the PEQ
for the term of the permit cannot be
accurately characterized by historical performance data as
specified
in subsection (a) of
this
Section
due to
significant changes
in tributary
loading, plant
operating parameters or other
factors
affecting
treatment
efficiency
during
the
term
covered
by
the
permit,
a
PEQ
representative of the future permit term may be estimated by analysis of the
historical data
consistent with
subsection (a) with
adjustment of the historical
value
to
reflect the
change
expected from the anticipated loading or operating changes.
e)
Regardless ofthe
statistical procedure used,
if the PEQ for
ammonia nitrogen (as N)
is
less
than or equal to
the water quality standard, the Agency shall deem the discharge not to have a
reasonable potential
to exceed and a
WQBEL shall
not
be required unless
otherwise required
under Section 355.201.
f)
Data Requirements the derivation of PEQ is based
on the
effluent
quality
demonstrated by
self-monitoring data as required by the NPDES permit or
Agency-generated data,
such
as
effluent sampling or facility-related
stream
studies.
Effluent data used in the
derivation of
PEQ shall be representative of the concentration
and
variability ofammonia nitrogen in the
discharge anticipated for the applicable periodoftheNPDES permit. Data shall be collected
and
analyzed
in
accordance
with
USEPA
or Agency
approved
sampling
and
analytical
methods (40 CFR 136).
The following criteria shall be followed in data selection:
1)
the most recent five years of data shall
be used unless
the
Agency determines
that an
alternative period
better represents
the
time period for which
effluent quality
is
being
projected.
Such
alternative
time
periods
may include,
but
are not
limited
to,
shorter
periods
that
reflect
changed
discharge
characteristics
resulting
from
changes
in
manufacturing activities or wastewatertreatment systems;
and
2)
data anomalies
resulting
from
collection,
analysis or recording errors or atypical plant
operating conditions may be eliminated from the data.
Section
355.207
Mixing Allowance
IfthePEQforammonia nitrogen (asN) is greaterthan the water
quality standard, the Agency shall assess
the level of treatment being
provided
by
the
discharger.
If
the
discharger
is
providing
(or
will
be
providing) a level oftreatment consistent with the best degree oftreatment required by
35 Ill. Adm. Code
304.102(a), the PEQ derived under Section 355205 shall be compared to the PEL determined by applying
alloweddilution to the discharge consistent with Section
355.209.
Section 355.209
Calculation ofPreliminary Effluent Limitation
a)
The
preliminary
effluent
limitation
(PEL)
is
calculated
in
a
mass balance
approach
reflecting
allowed
dilution as referenced
in Section
355.207:
WQS
=
(Q~eJ)(PEL)
+
(Q~dJ)(C~dJ)/(Q~e
+
Q~dJ)
or
PEL
WQS(Q~eJ
+
Q~d)
-
(Q~dJ)(C~d)IQ~eJ
where:
WQS
=
applicable total ammonia
nitrogen water quality
standard
as
converted to total
ammonia
nitrogen pursuant to Section
355.203
Q~eJ
effluent flow rate
Q~d
=
allowed mixing flow rate
as determined in accordance with the mixing zone provisions of
35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.102
and
implementation procedures adopted
thereunder
C~d
=
background ammonia nitrogen (as N)concentration in mixing-water
Effluent flow
rate shall
be
selected
to
coincide,with the
critical
stream
flow condition used to
quanti~allowed
dilution.
Typically this will be estimated to be the average of the
lowest three
months average flow
rate during the previous year
for
domestic
wastewater
sources.
For
industrial
and
other wastewater
sources where flow
rates
are
not directly
correlated to
climatic
patterns,
Q~e
will be estimated as the average of the highest three monthly average flow rates.
With either
approach, Q~e
shall be modifled when future
flows
are
expected to
vary
significantly
from historical data.
b)
The reasonable
potential
analysis
shall
be
completed separately
for
the
winter
and
summer
seasons and for acute, and chronic and subchronic water quality
standards.
The Agency may
subdivide summer or winter periods
into quarterly
or monthly
segments
with
analysis
of
reasonable
potential
corresponding
to
those
smaller
time
segments
in
individual
permit
applications.WQBELs based on the acute water quality standard shall be expressed as a daily
maximum. WQBELs based on the chronic waterquality standard shall be
expressed as a monthly
average. WQBELs based on thesubchronicWQS shall be expressed as aweekly
average.
Section 355.211 Summary of theResults foraReasonable Potential Analysis
and theDetermination ofAmmonia NitrogenWQBELs
a)
If the PEQ determined in Section 3
55.205
is less than or equal to the applicable water quality
standard, there is.no reasonable potential andno WQBEL will be established in thepermit unless
otherwise warranted under Section 355.201(c).
b)
IfthePEQexceedsthe applicable water qUality
standardbut does not exceed the PEL determined
through Section 355.209, there is no
reasonable potential
and no WQBEL
shall
be
established
unless otherwise warranted under
Section 355.201(c).
c)
Ifthe PEQ exceeds the PEL
determined through Section
3
55.209,
there is
reasonable potential
to
exceed the standard
and
the PEL shall be established as theWQBEL.
d)
If aWQBEL
is warranted under
Section
355.201(c),
the
WQBEL
shall
be
set
at the
PEL as
determined through Section
355.209.
SUBPART
C:
EFFLUENT
MODIFIED WATERS
IP~B
regulationc at 35
111.
Adm.
Code
302.202,
302.212,
302.213,
and
301.122 establish provicions fur
designating waters
as EMVtTs.
EMWc
are-subject
to
all general use
water quality standards
except
for
the
chronic
ammonia
nitrogen
water
quality
standards
of 302.212(b).
This
Section
provides
for
the
designation ofan
EMW
wherein the chronic portion ofthe un
ionized
standard
is
inapplicable.
In lieu of
the chronic standard, the IPCB
has established discharge restrictions
at
35
III. Adin.
Code 301.122(d)
for-any discharge tributary
to an
EMW.
These restrictions
include limits
-on discharges
at 1.5
mg!L
total
ammonia nitrogen during the April
through October
summer season
and
Ii)
mgfL
total ammonia nitrogen
during NQvember through March
as monthly
averages.
Beyond these
monthly
average
limits, there is
also
a
provision
to
assure
continuation
of the
existing
level
of performance
and
adherence
to
the
nondegradation provision of35
Ill.
Adm~
Code 302.105.
The criteria fordesignation ofan
EMW
include
two
specific provisions:
the water body
must have the potential
to exceed the chronic
standard
due to a
permitted
discharge; and the elevated chronic ammonia nitrogen concentration will not advereely
impact
designated uses ofthe affected stretch ofthe water body.
EMW status
shalLbe designated in the
receivingwater body if:
-a)
aquatic
life
expected
to
exist
in
the
receiving
waters
is
known
to
be
tolarant of .the
projected
ammonia nitrogen concentrations resulting
from the treatment plant effluent in conjunction with
ambient
conditions.
Determination of the
aquatic
community expected to
inhabit the receiving waters
shall be
Section
355.301
Introduction
consistent
with
stream
morphology, particularly physical
features and
hydrologic regimes
of the
water
body;
b)
the receiving stream does not exceed the acute water quality standard of
35
Ill. Adm. Code
302i12(b);
and
~c)
the discharger demonstrates a
reasonable
potential
to
exceed
the
chronic
ammonia
nitrogen
standard pursuant to SubpartB ofthis Past.
IfanEMW
cannot
be granted, then monthly average effluent
limits in the
NPDUS
permit shall be determined from-the
procedures for establishing ammonia nitrogen
WQBELs
pursuant
to SubpartS ofthis Part.
If necessary, a schedule to
attain
compliance
with
these
limits
shall also be included in the discharge?s
NPDES
permit.
Section355303
EMW
Application Reguirementi
TheAgency shall consider designating a portion ofthe
receivingwaterbody
as anEMW upon receiptofa
valid application foran
E~W
and when the provisions-ofthis Subpart
are met.
—a)
All applicants shall provide:
1) the name, address
and design average flow ofthe facility;
2)
all instream ammonia nitrogen, pH
and
water temperature data
collected by
or available to the
applicant;
3)
a
physical
description
of the
receiving
stream
including
information
on
depth,
substrate,
instream-cover, average width, percent
canopy, riffle poe1
sequence, stream gradient and
other pertinent
factors that the discharger wishes to be considered; and
1)
any other information conóerning the receiving waterbody that the applicant believes is
relevant.
Receiving
stream
information
must-
be
collected
from
the
reach
anticipated
to
constitute
the
requested
EMW
and continuing downstream for an additional
distance comprising
33
of the
requested
EMW
length.
b)
Applicants having one or more of the
following
characteristics
shall
supply,
in addition to the
information in
subsection (a), information required under subsection (c)
below:
1)
aDAF larger
than
0.25MOD
-2)-
~
~
permanent flow
constituting 7Qi 0-flow; of
greater
than zero
(excluding the applicant’s discharge), upstream orwithin the
reach of
the
anticipated
EMW; or
3)
a discharge location on a receiving stream evaluated under
the
Agoncy’i
‘iologi
il Stream Ch
~~~n~SC)
and Ii ~4a;
-
-
“
~
——
~
—
.per~de~4he
liach
~
islocat-’d.
4tan1ourstrr~~
.g~4J~
~‘--it~p
BSC
~
-
4in
EWstatusand~aiu~
I
.
‘~
ntnj”-
4)ni~~aninn+n1~
4...
aree
ka
‘4
UI
U~Iani
C
c)
;~
•1
aractenzan
.~
.-.-......
.....
.~
ntmg,
w mnnvt
iscnargers ant
cnaracte
1Cs
C
-ITLJJ
I11UL~
~iream-
eSe
cicecties
“a
Eli
•aiii
ttssiwt
unstrearn
utort_
in
one or more ofthe
toiiowmg mtormation:
1) Stream
cun’ev
data
that assesses ammonia nitrogen
imnact-to
the aquatic life ofthereceivmg stream.
uenerally, data
collected within the
pact
five
years
that are reflective of
current loading, stream flow’,
and-physical conditions
are
preferred. ifnone ofthese factors have significantly
changed, older data may suffice.
However,
any
additional
data concerning the aquatic life community ofthe receiving
stream must be included in the application as it becomes
known
to the discharger. The Agencymayhave previously
-conducted
tuch
studies
and
theseinay satisfythis
requirementand
r
2) Data concerning thepresence ofsensitive species including
threatened
andendangered federallyor State listed aquatic
species,
self sustaining
populationsofcold
waterspecies-or
species ofspecial significanceregardmg their-sensiti fly
to ammonia nitrogen.
Such
data
may be available from one or
more ofthe
following sources or other local or regional
souroes-
A)
the Illinois Department ofNatural
Resources Divisioti of
Natural Resources Review & Coordination
B)
the report “Biologically Significant Illinois Streams”,
a publication ofthe INHS
(Center forBiological
Diversity Teclmical Repert 1992(1)); or
C)
local colleges
and universities.
Section
355305
Evaluation of
EMW
Applications
TheAgency shall evaluate
EMW
applications based on all
information
providedpursuant to Section 355.303, as well as information
available from
the Agency’s monitoring programs.
Additionally, the Agency shall seek
and
obtain information from
otherIllinois natural resourceagencies.
Such
information shall include the following:
a)
biological
studies conducted on the receivingwater~
b)
ammonia nitrogen, pH, and temperature data from
ambient, intensive
basin, or facility related stream surveys
c)
ammonia nitrogen, pH and temperature
effluent data;
d)
physical instream habitatdata; or
e)
total ammonia nitrogen loading and-related informationattributed
to other sources in the affected reach~
Section
355.307
Determination of
EMW Designation
Upon evaluating
the
EMW
application and any additional
information
available, the Agency shall determine whether the receiving stream can be
designated
as an EMW
based on the provisions of35 Ill. Adm.
Code 302.213,
301.122, and 3
55.305.
Existing EMW designations
are-subject to review’ as
to whether requirements for
such
designations continue to be met atthe
time of an NPDES permit renewal or modification.
a) Ifthe-Agency determines that a receiving
stream
cannot be
designated as an
EMV1T,
th
Agency shall notify the applicantin
writing
as to its decision and the basis forthat decision.
b)
If areceiving stream can be designated
as an EMW,
the-Agency
shall issue a
public notice that contains:
1) determination ofthe length ofthe
EMW,
and
2)
summary of the ecological analysis
uëed in the
EMW
designation process.
Section
355309
ProcedurefiL forDelineating an EMW
The methodology for determiningthe length ofa water body to be designated
as
BMW shall be based
on the tonic
total ammonia nitrogen (asN) water
quality standard for winter conditions-and a decay coefficient representing
rr
~ii
flT~s._.
conditions depictthe
“worst case” ammonianitregen aecay rates and are to
be used when calculating the reach ofa water body to be designated as
EMW.
This modeling shall be performed-in
the following
manner:
a)
Downstream waters shall be subdivided into segments where
stream cross sectional
area are
uniform. Senments
dischargt.
on/I
will ~pically begir
a44~”ial
point
çnitrt~ao
-the-
nLr-
b) TheDAF~--~
flow for industrial plants and outer point sources ox ammoma
nitrogen (as N) downstream will be used as effluent flow rates in
the analysis.
A 7Q10 flow rate shall be determined for each
segment.
Discharge rates under YQ1O conditions are
to be obtained
frommaps generated
by the ISWS unless the
Agincy has previously
approvedan alternate 7Q11) discharge rate.
c) The average velocity
for each segment shall be derived for 7Q1O
discharge conditions. In
the absence
offield measurements,
velocity shall be determined from hydraulic geome~’equations
derived by the ISWS.
These equations are published in the
University of Illinois Water Resources Center publication, “\~~C
Research Report
No.
15,
Hydraulic Geometry of Illinois Streams”
(July
1968), which is hereby inco~orated
by
reference
and
includes no further editions or amendments.
A minimum
velocity of
0.2 ft’sec will be used unless field measurements
indicatethat a
different velocity exists during 7QIO conditions.
d)
The
chronic
water quality standard shall be converted to total
ammonia nitrogen (as N) as outiined in Section
355.201.
e)
The concentrations of ammonia nitrogen in the effluents shall be
the same as the monthly-average winter ammonia nitrogen permit
limitfor the point source.
If no monthly average w’inter ammonia
nitrogen permit limit exists, then avalue of 1.0 mg/L
shall be
used.
f)
The ammonia nitrogen concentration at the end of each segment
shall be calculated using the equations contained in Section
355.311.
The point at which the w’ater quality standard will be
met shall be the
downstream
terminus ofthe
RMMT.
The length of
the
EMW
shall equal the sum of all segment lengths, but in no case
shall be less than 100 yards in length.
g)
The permittee has
the
opportunity to submit field measurements to
be used in this
analysis.
Section 355.311
Ammonia Nitrogen Decay Equation
A decayquation
shall be used ta-predict
instream
ammonia nitrogen
concentrations at locations
downstream ofthe outfall, thereby determining
the linear extent of the EMW.
a)
Modeling of the decay (conversion to nitrite!nitrate) of ammonia
nitrogen from adischarge
and predicting the levels
tef ammonia
nitrogen at points downstream from the discharge shall follow’ the
decay equation:
n~
eca
z
LI SI.
confluences with
other
~tream~
o- wtiere
.
ammonia nitrogen (as N) enter
4~”
uomwwc w’asuew’ater treatment
plants
andthe maximum
Cnfj
—
(Q~nC~n
-~
Qn
1
C~n l~(Qn
fl
~-
Q~n)
xe
(kt)
where
the parameters used inthe decay equation
are
defined as
follow’s:
C~nfj-
ammonia nitrogen concentration atthe end ofsegment
“n”
—
travel time to point “n” (days)
Q~n
=
additional flow introduced into segment “n” (cfs) (see
Section
355.309(b)
for initial segment)
C~nJ
=
ammonia nitrogen concentration introduced into segment
“n”-(monthly
average effluent limit for initial
segment)
-
Q~n
11
=
upstream 7Q 10
flow’
rate orflow rate entering sagment
“n”
from previous segment (cfs)
C~n l-=
upstream ammonianitrogen concentration entering
segment “n” from previous segment
—
first order decay coefficient used in determining the
natural biological, physical, and chemical degradation
of ammonia
nitrogen that
occurs.
The value of“k” may
vary
as a finction ofthe receiving stream
characteristics.
In the absence of stream specific
data,
arepresentative
value shall be selected from
studies ofstreams
with
similar characteristicsand
shall be used in calculations as a default value
representative ofw’inter ammonia nitrogen decay.
b)
Where no upstream flow-is available for mixing and no additional
sources of ammonia nitrogen
are present downstream, the equation
reduces to the following:
C~nfC~nje( kt)
where:
Cnfj
~the
applicable w’inter chronic water quality standard
Sec
-C~n
—
monthly average w’inter effluent limit
tion 355.313
Restrictions Applicable to Discharges with EMWt
When the Agency issues a
publication ofa draft
NPDES permit designating an
EMW, effluent limits for ammonianitrogen shall be protective ofthe
aquatic community expected to exist
in the
EMW as
orovided in 35
III. Adm.
Code 301.122.
~u
instance shall these effluent limits exceed 30 day average
concentrations of
1.5
mg!L total ammonia nitrogen (asN) during
themonths of
April
through October,
and
1.0
mgfL
totalammonia
nitrogen (asN) during themonths ofNovemberthrough
March.
b) When uses
are
at risk of
impact due to increased concentrations of
ammonia nitrogen,more stringent 30 day averageeffluent
limits
shall be-incorporated.
c)
The draftpermit shall also include daily maximum
effluent limits
for total ammonia nitrogen (as N) and thsse shall be determined by
applying the acute
w’ater quality standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code
302.212(b)
pursuant
to Section 355203.
d)
The Agency shall take final action as to the designation of an EMW
concurrent with final NPDES permit issuance.
Section 355.315
Publication
of EMWs
The Agency shall compile the number and length of EMWs and
report the
information
in each edition of the Illinois Water Quality Report pursuant
to Section 305(b) ofthe Federal Clean
Water Act, as
amended,
33 USC
1315(b), and in the Illinois Register on a semi annual basis.
CR02/22142509.1