| 830.101 | Purpose, Scope and Applicability |
| 830.102 | Definitions |
| 830.103 | Incorporations by Reference |
| 830.104 | Exempt Operations and Activities |
| 830.105 | Permit-Exempt Facilities and Activities |
| 830.106 | On-Farm Landscape Waste Compost Facility |
| 830.107 | Compliance Dates |
| 830.108 | Severability |
| 830.201 | Scope and Applicability |
| 830.202 | Minimum Performance Standards and Reporting Requirements for Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.203 | Location Standards for Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.204 | Additional Stormwater and Landscape Waste Leachate Controls at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.205 | Additional Operating Standards for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.206 | Operating Plan for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.207 | Salvaging at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.208 | Access Control at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.209 | Load Checking at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.210 | Personnel Training for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.211 | Recordkeeping for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.212 | Contingency Plan for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.213 | Closure Plan for Permitted Landscapse Waste Compost Facilities |
| 830.501 | Scope and Applicability |
| 830.502 | Compost Classes |
| 830.503 | Performance Standards for General Use Compost |
| 830.504 | Testing Requirements for End-Product Compost Derived from Landscape Waste |
| 830.507 | Sampling Methods |
| 830.508 | Off-Specification Compost |
| 830.601 | Scope and Applicability |
| 830.602 | Financial Assurance Plan |
| 830.603 | Written Cost Estimate |
| 830.604 | Financial Assurance Fund |
| 830.605 | Financial Assurance Mechanism |
| 830.606 | Financial Assurance Certification |
| Appendix A | Early Detection and Groundwater Monitoring Program |
| Appendix B | Performance Test Methods |
| Table A | Inorganic Concentration Limits for General Use Compost |
| Table B | Sampling and Handling Requirements |
| Table C | Seed Germination Record Sheet |
| a) | The purpose of this Part is to establish: |
| 1) | Performance standards for landscape waste compost facilities operating in the State of Illinois; and |
| 2) | Testing procedures and standards for end-product compost offered, by a facility, for sale or use in the State of Illinois. |
| b) | General applicability. |
| 1) | The provisions of this Part apply to all landscape waste compost facilities operating in the State of Illinois, except those expressly exempted pursuant to Section 830.104 and those regulated pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 391 and 40 CFR Part 503. |
| 2) | Facilities regulated pursuant to this Part are not subject to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 807 or 810 through 815, except that any accumulation of materials meeting the 35 Ill. Adm. Code 810 definition of a waste pile shall be subject to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 810 through 815. |
| 3) | Facilities regulated pursuant to Subpart B shall accept only landscape waste for composting. |
| c) | Specific applicability. |
| 1) | The provisions of this Subpart apply to all facilities subject to this Part; the definitions set forth in Section 830.102 apply for purposes of this Part, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831, and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 832. |
| 2) | The performance standards set forth in Subpart B are applicable to landscape waste composting facilities subject to this Part. |
| 3) | The performance standards set forth in Subpart E are applicable to all general use compost offered for sale or use in Illinois; the testing requirements set forth in Subpart E are applicable to facilities offering general use compost for sale or use in Illinois. |
| 4) | The financial assurance requirements set forth in Subpart F are applicable to all facilities subject to this Part that are required to have a permit pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831. |
| "Act" means the Environmental Protection Act [415 ILCS 5]. | |
| "Additive" means components, other than landscape waste, added to composting material to maximize the decomposition process by adjusting any of the following: moisture, temperature, oxygen transfer, pH, carbon to nitrogen ratio, biology or biochemistry of the composting material. | |
| "Aerated static pile" means a composting system that uses a series of perforated pipes or equivalent air distribution systems running underneath a compost pile and connected to a blower that either draws or blows air through the piles. Little or no pile agitation or turning is performed. | |
| "Aerobic composting" means a process managed and maintained to promote maturation of organic materials by microbial action in the presence of free oxygen contained within the gas in the composting material. | |
| "Aerobic" means done in the presence of free oxygen. | |
| "Agency" means the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency. | |
| "Agronomic Rates" means the application of not more than 20 tons per acre per year, except that the Agency may allow a higher rate for individual sites where the owner or operator has demonstrated to the Agency that the site's soil characteristics or crop needs require a higher rate. (Section 21(q) of the Act.) | |
| "Anaerobic composting" means a process managed and maintained to promote maturation of organic materials by microbial action in the absence of free oxygen within the gas in the composting material. | |
| "Bad Load" means a load of material that would, if accepted, cause or contribute to a violation of the Act, even if managed in accordance with these regulations and any facility permit conditions. | |
| "Batch" means material used to fill the vessel of a contained composting system. | |
| "Board" means the Illinois Pollution Control Board. | |
| "Bulking agent" means a material used to increase porosity, to improve aeration, or to absorb moisture from decomposing waste. | |
| "Closure" means the process of terminating composting facility operations pursuant to applicable Sections in this Part, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831 and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 832, beginning upon permit expiration without filing for renewal, intentional cessation of waste acceptance or cessation of waste acceptance for greater than 180 consecutive days, unless an alternative time frame is approved in a closure plan. | |
| "Commercial activity" means any activity involving the transfer of money. | |
| "Compost" means the humus-like product of the process of composting waste, which may be used as a soil conditioner. (Section 3.70 of the Act.) | |
| "Composting" means the biological treatment process by which microorganisms decompose the organic fraction of the waste, producing compost. (Section 3.70 of the Act.) Land application is not composting. | |
| "Composting area" means the area of a composting facility in which waste, composting material or undistributed end-product compost is unloaded, stored, staged, stockpiled, treated or otherwise managed. | |
| "Composting material" means solid wastes that are in the process of being composted. | |
| "Composting operation" means an enterprise engaged in the production and distribution of end-product compost. | |
| "Contained composting process" means a method of producing compost in which the composting material is confined or contained in a vessel or structure which both protects the material from the elements and controls the moisture and air flow. | |
| "Designated use compost" means end-product compost which does not meet the standards set forth in Section 830.503 of this Part. | |
| "Dewar flask" means an insulated container used especially to store liquefied gases, having a double wall, an evacuated space between the walls and silvered surfaces. | |
| "Domestic sewage" means waste water derived principally from dwellings, business or office buildings, institutions, food service establishments, and similar facilities. | |
| "End-product compost" means organic material that has been processed to maturity and classified as general use compost or designated use compost in accordance with this Part. | |
| "Facility" means any landscape waste compost facility. | |
| "Garbage" is waste resulting from the handling, processing, preparation, cooking, and consumption of food, and wastes from the handling, processing, storage, and sale of produce. (Section 3.11 of the Act.) | |
| "Garden compost operation" means an operation which (1) has no more than 25 cubic yards of landscape waste, composting material or end-product compost on-site at any one time and (2) is not engaging in commercial activity. | |
| "General use compost" means end-product compost which meets the standards set forth in Section 830.503 of this Part. | |
| "Groundwater" means underground water which occurs within the saturated zone and geologic materials where the fluid pressure in the pore space is equal to or greater than atmospheric pressure. (Section 3(b) of the Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55].) | |
| "In-vessel composting" means a diverse group of composting methods in which composting materials are contained in a building, reactor, or vessel. | |
| "In-vessel continuous feed system" means a method of producing compost in which the raw composting material is delivered on a continuous basis to a reactor. | |
| "Insulating material" means material used for the purpose of preventing the passage of heat out of a windrow or other pile. Insulating material includes, but is not limited to, end-product compost, foam, or soil. Insulating material does not include composting material that has not reached maturity. | |
| "Land application" means the spreading of waste, at an agronomic rate, as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and crop productivity. | |
| "Landscape Waste" means all accumulations of grass or shrubbery cuttings, leaves, tree limbs and other materials accumulated as the result of the care of lawns, shrubbery, vines and trees. (Section 3.20 of the Act.) | |
| "Landscape waste compost facility" means an entire landscape waste composting operation, with the exception of a garden compost operation. | |
| "Landscape waste leachate" means a liquid containing any of the following: waste constituents originating in landscape waste; landscape waste composting material; additives; and end-product compost. | |
| "Maturity" means a state which is characteristically: generally dark in color; humus-like; crumbly in texture; not objectionable in odor; resembling rich topsoil; and bearing little resemblance in physical form to the waste from which it is derived. | |
| "Modification" means a permit revision authorizing either an extension of the current permit term or a physical or operational change at a composting facility which involves different or additional processes, increases the capacity of the operation, requires construction, or alters a requirement set forth as a special condition in the existing permit. | |
| "MPN" means most probable number, a mathematical inference of the viable count from the fraction of cultures that fail to show growth in a series of tubes containing a suitable medium. | |
| "Nearest residence" means an occupied dwelling and adjacent property commonly used by inhabitants of the dwelling. | |
| "Non-compostable material" means items not subject to microbial decomposition under conditions used to compost waste. | |
| "Off-site" means not on-site. | |
| "On-farm landscape waste compost facility" means a landscape compost facility which satisfies all of the criteria set forth in Section 830.106. | |
| "On-site" means on the same or geographically contiguous property which may be divided by public or private right-of-way, provided the entrance and exit between the properties is at a crossroads intersection and access is by crossing as opposed to going along the right-of-way. Noncontiguous properties owned by the same person but connected by a right-of-way which the owner controls and to which the public does not have access are also considered on-site property. | |
| "On-site commercial facility" means a landscape waste compost facility at which the landscape waste composted is generated only on-site and the end-product is offered for off-site sale or use. | |
| "On-site facility" means a landscape waste compost facility at which the landscape waste composted is generated only on-site and the end-product is not offered for off-site sale or use. | |
| "Open composting process" means a method of producing compost without protecting the compost from weather conditions. | |
| "Operator" means the individual, partnership, co-partnership, firm, company, corporation, association, joint stock company, trust, estate, political subdivision, State agency, or any other legal entity that is responsible for the operation of the facility. The property owner, if different from the operator, shall be deemed the operator in the event that the operator abandons the facility. | |
| "Origin" means the legal entity from which a substance has been obtained. | |
| "Processing into windrows or other piles" means placement of waste materials into windrows or other piles of a size, structure, and mixture adequate to begin the composting process. | |
| "Property owner" means the owner of the land on which the composting operation is located or proposed to be located, except that if the operator has obtained a lease for at least the duration of the proposed facility permit plus one year, then "property owner" shall mean the operator of the composting operation. "Registered professional engineer" means a person registered under the Illinois Professional Engineering Practice Act [225 ILCS 325]. | |
| "Relatively impermeable soil" means a soil located above the water table that has a hydraulic conductivity no greater than 1 x 10(-5) centimeters per second for a thickness of at least one foot. | |
| "Runoff" means water resulting from precipitation that flows overland before it enters a defined stream channel, excluding any portion of such overland flow that infiltrates into the ground before it reaches the stream channel, and any precipitation that falls directly into a stream channel. | |
| "Runon" means any rainwater, leachate or other liquid that drains over land onto any part of a facility. | |
| "Salvaging" means the return of waste materials to beneficial use. | |
| "Salvaging operations" means those activities that recover waste for beneficial use, so long as the activity is done under the supervision of the compost facility's operator, does not interfere with or otherwise delay the operations of the compost facility, and results in the removal of all materials for salvaging from the compost facility daily or separation by type and storage in a manner that does not create a nuisance, harbor vectors, or cause an unsightly appearance. | |
| "Septage" means the liquid portions and sludge residues removed from septic tanks. | |
| "Sewage" means water-carried human and related waste from any source. | |
| "Site" means any location, place, tract of land, and facilities, including but not limited to buildings, and improvements used for purposes subject to regulation or control by the Act and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 830, 831 and 832. (Section 3.43 of the Act.) | |
| "Sludge" means any solid, semisolid, or liquid waste generated from a municipal, commercial, or industrial wastewater treatment plant, water supply treatment plant, or air pollution control facility, or any other such waste having similar characteristics and effects. (Section 3.44 of the Act.) | |
| "Special waste" means any industrial process waste, pollution control waste or hazardous waste, except as determined pursuant to Section 22.9 of the Act and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 808. (Section 3.45 of the Act.) | |
| "Stability" means a state in which the compost decomposes slowly even under conditions favorable for microbial activity. | |
| "Staging area" means an area within a facility where raw material for composting is processed, temporarily stored in accordance with the standards set forth in 830.205(a)(1)(A), loaded or unloaded. | |
| "Surface water" means all tributary streams and drainage basins, including natural lakes and artificial reservoirs, which may affect a specific water supply above the point of water supply intake. Such term does not include treatment works (such as a retention basin). | |
| "Ten (10) year, 24 hour precipitation event" means a precipitation event of 24 hour duration with a probable recurrence interval of once in 10 years. | |
| "20-20-20 NPK" means a fertilizer containing 20 percent total nitrogen (N), 20 percent available phosphoric acid (P[2]O[5]) and 20 percent soluble potash (K[2]O). | |
| "Unacceptable load" means a load containing waste a facility is not authorized to accept. | |
| "Underground water" means all water beneath the land surface. | |
| "Vector" means any living agent, other than human, capable of transmitting, directly or indirectly, an infectious disease. | |
| "Water table" means the boundary between the unsaturated and saturated zones of geologic materials or the surface on which the fluid pressure in the pores of a porous medium is exactly at atmospheric pressure. | |
| "Windrow" means an elongated pile of solid waste or composting material constructed to promote composting. | |
| "Woody landscape waste" means plant material greater than two inches in diameter. |
| a) | American Public Health Association et al., 1015 Fifteenth Street, N.W., Washington, D.C. 20005, "Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater," 18th Edition, 1992. |
| b) | "Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods," Third Edition (September, 1986), as amended by Revision I (December, 1987), Final Update I (November, 1992) and Proposed Update II (July, 1992), United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., EPA Publication Number SW-846. |
| c) | North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, North Dakota State University, Fargo, North Dakota 58105, "Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region," North Central Regional Publication No. 221 (Revised), Bulletin No. 499 (Revised), October, 1988. |
| a) | The requirements of this Part shall not apply to a garden compost operation as defined at Section 830.102. |
| b) | The testing requirements set forth in Subpart E of this Part shall not apply to end-product compost used as a daily cover or vegetative amendment in the final layer of a landfill. (Section 22.33(c) of the Act.) |
| c) | Notwithstanding subsection (b) of this Section, end-product compost shall not be used as daily cover or vegetative amendments in the final layer of a landfill unless such use is approved in the landfill's permit. |
| Section 830.105 | |
| Permit-Exempt Facilities and Activities | |
| a) | A landscape waste composting operation for landscape wastes generated by such facility's own activities which are stored, treated or disposed of within the site where such wastes are generated (Section 21(q)(1) of the Act); |
| b) | Applying landscape waste or composted landscape waste at agronomic rates (Section 21(q)(2) of the Act); or |
| c) | A landscape waste composting facility on a farm which meets all of the criteria set forth at Section 830.106 (Section 21(q)(3) of the Act). |
| a) | A landscape compost operation on a farm must satisfy all of the following criteria: |
| 1) | The composting facility is operated by the farmer on property on which the composting material is utilized, and the composting facility constitutes no more than 2% of the property's total acreage, except that the Agency may allow a higher percentage for individual sites where the owner or operator has demonstrated to the Agency that the site's soil characteristics or crop needs require a higher rate; |
| 2) | The property on which the composting facility is located, and any associated property on which the compost is used, is principally and diligently devoted to the production of agricultural crops and is not owned, leased or otherwise controlled by any waste hauler or generator of nonagricultural compost materials, and the operator of the composting facility is not an employee, partner, shareholder, or in any way connected with or controlled by any such waste hauler or generator; |
| 3) | All compost generated by the composting facility is applied at agronomic rates and used as mulch, fertilizer or soil conditioner on land actually farmed by the person operating the composting facility, and the finished compost is not stored at the composting site for a period longer than 18 months prior to its application as mulch, fertilizer, or soil conditioner; and |
| 4) | All composting material was placed more than 200 feet from the nearest potable water supply well, was placed outside the boundary of the 10-year floodplain or on a part of the site that is floodproofed, was placed at least 1/4 mile from the nearest residence (other than a residence located on the same property as the facility) and there are not more than 10 occupied non-farm residences within 1/2 mile of the boundaries of the site on the date of application, and was placed more than 5 feet above the water table. |
| b) | The owner or operator, by January 1, 1991 (or the January 1 following commencement of operation, whichever is later) and January 1 of each year thereafter shall: |
| 1) | register the site with the Agency, by obtaining an Illinois Inventory Identification Number from the Agency; |
| 2) | File a report with the Agency, on a form provided by the Agency, certifying at a minimum: |
| A) | The volume of composting material received and used at the site during the previous calendar year; and |
| B) | The volume of compost produced during the previous calendar year; |
| C) | That the facility is in compliance with the requirements set forth in subsection (a) of this Section. (Section 21 of the Act) |
| a) | All operators of existing facilities shall comply with the applicable minimum performance standards and recordkeeping requirements set forth in Section 830.202 of this Part by the effective date of these regulations. (Section 21(q) of the Act.) |
| b) | By November 10, 1995, all operators of existing facilities shall certify compliance with the applicable provisions set forth in Sections 830.206, 830.210, 830.211, 830.504 and 830.507. Certification of compliance with Sections 830.206, 830.210, 830.211, 830.504 and 830.507 shall be done by completing and filing with the Agency a form provided by the Agency. |
| c) | By November 10, 1995, all operators of existing permitted facilities shall certify compliance with Subpart F of this Part. Such certification of compliance shall be done as specified in Section 830.606. |
| d) | Each existing permitted facility shall, in addition, remain in compliance with all conditions set forth in its current facility permit, pending permit expiration or modification authorizing construction, resulting in an increase in capacity, transferring ownership or extending the current permit term. |
| e) | Upon application either for permit renewal or for modification authorizing construction, resulting in an increase in capacity, extending the current permit term or initiated by the Agency pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 832.201, an existing permitted facility shall demonstrate, as part of the permit application, compliance with all provisions of this Part applicable to permitted facilities. |
| a) | Garden compost facilities are exempt from all the requirements of Part 830. |
| b) | On-site landscape waste compost facilities are subject to the location standards in Section 830.203. |
| c) | On-site commercial landscape waste compost facilities are subject to the minimum performance standards in Section 830.202, the location standards in Section 830.203, and the end-product quality standards in Subpart E of this Part. |
| d) | On-farm landscape waste compost facilities which satisfy all the requirements in Section 830.106(a) are subject to the minimum performance standards in Section 830.202. |
| e) | Permitted landscape waste compost facilities are subject to the minimum performance standards in Section 830.202, the location standards in Section 830.203, the additional operating standards and requirements in Sections 830.204 through 830.213, the end-product quality standards of Subpart E of this Part and the financial assurance requirements of Subpart F of this Part. |
| Section 830.202 | Minimum Performance Standards and Reporting Requirements for Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | The composting material shall not contain any domestic sewage, sewage sludge or septage. |
| b) | Any bulking agent used which is otherwise a waste as defined at Section 3.53 of the Act, other than landscape waste, may only be used as authorized by the Agency in writing or by permit. |
| c) | The operator shall take specific measures to control odors and other sources of nuisance so as not to cause or contribute to a violation of the Act. Specific measures an operator should take to control odor include but are not limited to: adherence to the contents of the odor minimization plan required at subsection (e). Specific measures an operator should take to control other sources of nuisance include preventative measures to control litter, vectors, and dust and noise generated from truck or equipment operation. |
| d) | The operator shall have available for inspection a plan for the intended purposes of end-product compost and a contingency plan for handling end-product compost and composting material that does not meet the general use compost standards set forth in Section 830.503 of this Part. Such a plan may include, but is not limited to, consideration of the following: on-site usage; identification of potential buyers including but not limited to gardeners, landscapers, vegetable farmers, turf growers, operators of golf courses, and ornamental crop growers; maintaining consistent product quality for such factors as stability, color, texture, odor, pH, and man-made inerts; and removal of end-product compost that cannot be used in the expected manner because it does not meet the general use compost standards. (Section 22.33(a)(4) of the Act.) |
| e) | The operator shall have a plan for minimizing odors. The plan must include: |
| 1) | Specifications of a readily-available supply of bulking agents, additives or odor control agents; |
| 2) | Procedures for avoiding delay in processing and managing landscape waste during all weather conditions; |
| 3) | Methods for taking into consideration the following factors prior to turning or moving composting material: |
| A) | Time of day; |
| B) | Wind direction; |
| C) | Percent moisture; |
| D) | Estimated odor potential; and |
| E) | Degree of maturity. |
| f) | Landscape waste must be processed within five days after receipt into windrows or other piles which promote proper conditions for composting. Incoming leaves, brush or woody landscape waste may be stored in designated areas for use as a carbon source and bulking agent, rather than being processed into windrows or other piles. |
| g) | The facility must be designed and constructed so that runon is diverted around the composting area. The runoff from the facility resulting from precipitation less than or equal to the 10 year, 24 hour precipitation event must be controlled so as not to cause or contribute to a violation of the Act. |
| h) | The facility must be constructed and maintained to have an accessible clear space between windrows or other piles, suitable for housekeeping operations, visual inspection of piling areas and fire fighting operations. |
| i) | Except for on-farm landscape waste compost facilities, the operator shall post permanent signs at each entrance, the text of which specifies in letters not less than three inches high: |
| 1) | The name and mailing address of the operation; |
| 2) | The operating hours; |
| 3) | Materials which can be accepted; and |
| 4) | The statement, "COMPLAINTS CONCERNING THIS FACILITY CAN BE MADE TO THE FOLLOWING PERSONS, followed by the name and telephone number of the operator, and the name and telephone number of the Bureau of Land, Illinois Environmental Protection Agency, Springfield, Illinois. |
| j) | General use compost, if offered for sale or use, must meet the performance standards set forth in Section 830.503. |
| k) | Reporting Requirements. |
| 1) | The operator of any facility required, pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831, to have a permit shall submit a written annual statement to the Agency, on a form provided by the Agency, on or before April 1 of each year that includes: |
| A) | An estimate of the amount of material, in tons, received for composting in the previous calendar year (Section 39(m) of the Act); |
| B) | An estimate of the amount and disposition of compost material (i.e., end-product compost, chipped/shredded brush) in the previous calendar year; and |
| C) | A Composting Facility Financial Assurance Plan Compliance Certification in accordance with the requirements set forth in Section 830.606. |
| 2) | For any permit-exempt facility with over 100 cubic yards of composting material on-site at one time, a report must be filed by April 1 of each year with the Agency, on a form provided by the Agency, stating, at a minimum, the facility location, an estimate of the amount of material, in cubic yards or tons, received for composting in the previous calendar year, and the total amount of end-product compost still on-site, used or sold during the previous calendar year. |
| l) | Closure. |
| 1) | Unless otherwise authorized in a facility permit, all landscape waste, composting material, end-product compost, and additives must be removed from the facility within 180 days following the beginning of closure. |
| 2) | An operator of a facility regulated under this Subpart shall close the facility in a manner which: |
| A) | Minimizes the need for further maintenance; and |
| B) | Controls, minimizes or eliminates the release of landscape waste, landscape waste constituents, landscape waste leachate, and composting constituents to the groundwater or surface waters or to the atmosphere to the extent necessary to prevent threats to human health or the environment. |
| 3) | By April 1 of the year following completion of closure, the operator of a facility required to report pursuant to subsection (k)(2) of this Section shall file a report with the Agency verifying that closure was completed in accordance with this Section in the previous calendar year. |
| m) | Odor complaints. |
| 1) | Except for on-farm landscape waste compost facilities, for every odor complaint received, the operator shall: |
| A) | Record and report to the Agency within 24 hours after receiving the complaint, the date and time received, the name of complainant, the address and phone number of complainant, if volunteered upon request, and the name of the personnel receiving the complaint. |
| B) | Record the date, time, and nature of any action taken in response to an odor complaint, and report such information to the Agency within 7 days after the complaint. |
| a) | With the exception of on-farm landscape waste operations, all landscape waste compost facilities subject to this Part shall comply with the following: |
| 1) | The composting area of the facility must include a setback of at least 200 feet from the nearest potable water supply well. (Section 39(m) of the Act) |
| 2) | The composting area of the facility must be located outside the boundary of the 10-year floodplain or the site shall be floodproofed. (Section 39(m) of the Act) |
| 3) | The composting area of the facility must be located so as to minimize incompatibility with the character of the surrounding area, including at least a 200 foot setback from any residence, and in the case of a facility that is developed or the permitted composting area of which is expanded after November 17, 1991, the composting area shall be located at least 1/8 mile from the nearest residence (other than a residence located on the same property as the facility). (Section 39(m) of the Act) In addition, in the case of a facility that is developed or the permitted composting area of which is expanded after January 1, 1999, the composting area shall be located at least 1/8 mile from the property line of each of the following: |
| A) | Facilities that primarily serve to house or treat people that are immunocompromised or immunosuppressed, such as cancer or AIDS patients; people with asthma, cystic fibrosis, or bioaerosol allergies; or children under the age of one year; |
| B) | Primary and secondary schools and adjacent areas that the school uses for recreation; and |
| C) | Any facility for child care licensed under Section 3 of the Child Care Act of 1969 [225 ILCS 10/3]; preschools; and adjacent areas that the facility or preschool uses for recreation. |
| 4) | If, at the time the facility permit application is deemed complete by the Agency pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 832, the composting area of the facility is located within 1/4 mile of the nearest off-site residence or within 1/2 mile of the nearest platted subdivision containing a residence, or if more than 10 residences are located within 1/2 mile of the boundaries of the facility, in order to minimize incompatibility with the character of the surrounding area, landscape waste must be processed by the end of the operating day on which the landscape waste is received into windrows, other piles or a contained composting system providing proper conditions for composting. |
| 5) | The composting area of the facility must be designed to prevent any compost material from being placed within 5 feet of the water table, to adequately control runoff from the site, and to collect and manage any landscape waste leachate that is generated on the site. (Section 39(m) of the Act) Compliance with the water table distance requirement may be demonstrated by either of the following means: |
| A) | Using published water table maps or other published documentation to establish the location of the water table in relation to site elevation; or |
| B) | Actual measuring of the water table elevation at least once per month for three consecutive months. |
| 6) | The facility must meet all requirements under the Wild and Scenic Rivers Act (16 USC 1271 et seq.). |
| 7) | The facility must not restrict the flow of a 100-year flood, result in washout of landscape waste from a 100-year flood, or reduce the temporary water storage capacity of the 100-year floodplain, unless measures are undertaken to provide alternative storage capacity, such as lagoons, holding tanks, or provision of drainage around structures at the facility. |
| 8) | The facility must not be located in any area where it may pose a threat of harm or destruction to the features for which: |
| A) | An irreplaceable historic or archaeological site has been listed pursuant to the National Historic Preservation Act (16 USC 470 et seq.) or the Illinois Historic Preservation Act [20 ILCS 3410]; |
| B) | A natural landmark has been designated by the National Park Service or the Illinois State Historic Preservation Office; or |
| C) | A natural area has been designated as a Dedicated Illinois Nature Preserve pursuant to the Illinois Natural Areas Preservation Act [525 ILCS 30]. |
| 9) | The facility must not be located in any area where it may jeopardize the continued existence of any designated endangered species, result in the destruction or adverse modification of the critical habitat for such species, or cause or contribute to the taking of any endangered or threatened species of plant, fish or wildlife listed pursuant to the Endangered Species Act (16 USC 1531 et seq.) or the Illinois Endangered Species Protection Act [520 ILCS 10]. |
| b) | A facility’s compliance with the location standards set forth in subsection (a) of this Section shall be determined at the time described below: |
| 1) | For a facility that is required to obtain a permit under Section 21(d) of the Act, at the time that a complete permit application for a new or expanded facility is filed with the Agency under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 832; or |
| 2) | For a facility that is not required to obtain a permit under Section 21(d) of the Act, at the time that construction of the new or expanded facility begins. |
| (Source: Amended at 22 Ill. Reg. 21052, effective November 23, 1998) |
| Section 830.204 | Additional Stormwater and Landscape Waste Leachate Controls at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | Stormwater or other water which comes into contact with landscape waste received, stored, processed or composted, or which mixes with landscape waste leachate, must be considered landscape waste leachate and must be collected and reused in the process, properly disposed of off-site, or treated as necessary prior to discharge off-site to meet applicable standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code Subtitle C. |
| b) | Ponding of landscape waste leachate within the facility must be prevented, except to the extent done by design and approved in the facility permit. |
| c) | Soil surfaces used for composting must be allowed to dry periodically in order to promote aerobic conditions in the soil subsurface. |
| Section 830.205 | Additional Operating Standards for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | Composting Process |
| 1) | All permitted landscape waste compost facilities must meet the following composting process standards: |
| A) | Landscape waste must be processed within 24 hours after receipt at the facility into windrows, other piles or a contained composting system providing proper conditions for composting. Incoming leaves, and brush or woody landscape waste, may be stored in designated areas for use as a carbon source and bulking agent, if so provided as a permit condition, rather than being processed in windrows or other piles. |
| B) | Unless the facility is designed for anaerobic composting, the operator shall take measures to adjust the oxygen level, as necessary, to promote aerobic composting. Aeration intensity must be altered to suit the varying oxygen requirements that different landscape wastes may have. |
| C) | The operator shall take measures to maintain the moisture level of the composting material within a range of 40% to 60% on a dry weight basis. |
| D) | The staging area must be adequate in size and design to facilitate the unloading of landscape waste from delivery vehicles and the unobstructed maneuvering of vehicles and other equipment. |
| E) | Neither landscape waste nor composting material may be mixed with end-product compost ready to be sold or offered for use. This prohibition shall not apply to the use of end-product compost as an amendment to composting material. |
| F) | The facility must have sufficient equipment and personnel to process incoming volumes of landscape waste accepted within the time frames required in this Section, and sufficient capacity to handle projected incoming volumes of landscape waste. |
| G) | The operator shall obtain written authorization from the Agency to use any additive, other than water, prior to its use. Unless otherwise authorized any additive, or combination of additives, other than water, must not exceed 10%, by volume, of the composting material. |
| 2) | An operator of a permitted landscape waste compost facility using an open composting process shall turn each windrow or other pile at least four times per year and not less than once every six months. This provision does not apply to composting systems designed for anaerobic conditions. |
| 3) | An operator of a permitted landscape waste compost facility using a contained composting process shall have mechanisms to control moisture, air flow and air emissions. These mechanisms must be operated and maintained throughout the landscape waste composting process as specified in any permit required pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831. |
| 4) | Operators of permitted facilities required to process composting material to further reduce pathogens shall comply with the applicable thermal processing requirement among the following: |
| A) | If the facility uses a windrow composting process, during a 15 consecutive day period the temperature throughout each windrow must be maintained at 55C or greater and, during the same period, each windrow must be turned a minimum of 5 times; |
| B) | If the facility uses an aerated static pile composting process, the composting material must be covered with 6 to 12 inches of insulating material, and the temperature throughout each pile material must be maintained at 55oC or greater for 3 consecutive days; and |
| C) | If the facility uses an in-vessel composting process, the temperature of the composting material throughout the mixture must be maintained at 55C or greater for 3 consecutive days. |
| b) | Composting Surface |
| 1) | Open Composting Processes |
| A) | Composting areas must be: |
| i) | located on relatively impermeable soils, as demonstrated by actual measurement; |
| ii) | located on a base with resistance to saturated flow equivalent to the resistance of relatively impermeable soil; or |
| iii) | subject to an early detection and monitoring program, pursuant to subsection (m)(3) of this Section. |
| B) | The composting surface must be constructed and maintained to allow: |
| i) | Diversion of runon waters away from the landscape waste and compost; |
| ii) | Management of runoff waters and landscape waste leachate in accordance with Section 830.204; and |
| iii) | Facility operation during all weather conditions. |
| C) | The surface of the landscape waste composting area of the facility must be sloped at two percent or greater unless an alternative water management system to promote drainage and to prevent surface water ponding is approved in the facility permit. |
| 2) | Contained Composting Processes |
| A) | Composting areas at facilities at which composting material or leachate comes into contact with an open surface must be: |
| i) | Located on relatively impermeable soils, as demonstrated by actual measurement; |
| ii) | located on a base with resistance to saturated flow equivalent to the resistance of relatively impermeable soil; or |
| iii) | Subject to an early detection and groundwater monitoring program, pursuant to subsection (m)(4) of this Section. |
| B) | The composting surface must support all structures and equipment. |
| c) | Utilities. All utilities necessary for safe operation in compliance with the requirements of this Part, including, but not limited to, lights, power, water supply and communications equipment, must be available at the facility at all times. |
| d) | Maintenance. The operator shall maintain and operate all systems and related appurtenances and structures in a manner that facilitates proper operations in compliance with the requirements of this Part. If a breakdown of equipment occurs, standby equipment must be used or additional equipment brought on site as necessary to comply with the requirements of this Part and any pertinent permit conditions. |
| e) | Open Burning. Open burning is prohibited except in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 200 through 245. |
| f) | Dust Control. The operator shall implement methods for controlling dust in accordance with Subparts B and K of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 212. |
| g) | Noise Control. The facility must be designed, constructed, operated and maintained so as not to cause or contribute to a violation of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 900 through 905 or of Section 24 of the Act. |
| h) | Vector Control. Insects, rodents, and other vectors must be controlled so as not to cause or contribute to a violation of the Act. |
| i) | Fire Protection. The operator shall institute fire protection measures including, but not limited to, maintaining a supply of water and radio or telephone access to the nearest fire department. Fire extinguishers must be provided at two separate locations within the facility. |
| j) | Litter Control. The operator shall control litter at the facility. At a minimum: |
| 1) | The operator shall patrol the facility daily to check for litter accumulation. All litter must be collected in a secure container for later disposal; and |
| 2) | Litter must be confined to the property on which the facility is located. At the conclusion of each day of operation, any litter strewn beyond the confines of the facility must be collected and disposed of at a facility approved to receive such waste in accordance with the applicable Board regulations. |
| k) | Management of Non-compostable Wastes. The operator shall develop management procedures for collection, containment and disposal of non-compostable wastes received at the facility. Disposal must be at a facility approved to receive such waste in accordance with applicable Board regulations at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 810 through 815. |
| l) | Mud Tracking. The operator shall implement measures, such as the use of wheel washing units or rumble strips, to prevent tracking of mud by delivery vehicles onto public roadways. |
| m) | Monitoring |
| 1) | At a minimum, for batch, windrow and pile systems: |
| A) | The temperature of each batch, windrow or pile of composting material must be monitored on a weekly basis; |
| B) | The moisture level in each batch, windrow or pile of composting material must be monitored once every two weeks; and |
| C) | For aerobic composting, the oxygen level of each batch, windrow or pile of composting material must be monitored weekly. |
| 2) | At a minimum, for in-vessel continuous feed systems: |
| A) | The temperature of the composting material must be monitored daily; |
| B) | The moisture of the composting material must be monitored daily, unless otherwise authorized by the Agency in a facility permit; and |
| C) | For aerobic composting by means of an in-vessel continuous feed system, the oxygen level of the composting material must be monitored daily. |
| 3) | Early detection and groundwater monitoring, if required pursuant to Section 830.205(b)(1)(A) or Section 830.205(b)(2)(A), shall be done in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 830.Appendix A. |
| Section 830.206 | Operating Plan for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | Designation of personnel, by title, responsible for operation, control and maintenance of the facility; |
| b) | A description of the anticipated quantity and variation throughout the year of waste to be received; |
| c) | Methods for measuring incoming waste; |
| d) | Methods to control the types of waste received, in accordance with Section 830.209, and methods for removing, recovering and disposing of non-compostables, in accordance with Sections 830.205(k), 830.207 and 830.209; |
| e) | Methods to control traffic and to expedite unloading in accordance with Section 830.205(a)(1)(D); |
| f) | Management procedures that will be used in composting, which must include: |
| 1) | A description of any treatment the wastes will receive prior to windrowing (e.g., chipping, shredding) and the maximum length of time required to process each day's receipt of waste into windrows; |
| 2) | The specifications to which the windrows will be constructed (width, height, and length) and calculation of the capacity of the facility; |
| 3) | A list of additives, including the type, amount and origin, that will be used to adjust moisture, temperature, oxygen transfer, pH, carbon to nitrogen ratio, or biological characteristics of the composting material, and rates and methods of application of such additives; and |
| 4) | An estimate of the length of time necessary to complete the composting process. |
| g) | Methods to minimize odors. In addition to the requirements specified in 830.202(e), the operating plan must include: |
| 1) | A management plan for bad loads; |
| 2) | A demonstration that the processing and management of anticipated quantities of landscape waste can be accomplished during all weather conditions; |
| 3) | Procedures for receiving and recording odor complaints, investigating immediately in response to any odor complaints to determine the cause of odor emissions, and remedying promptly any odor problem at the facility; |
| 4) | Additional odor-minimizing measures, which may include the following: |
| A) | Avoidance of anaerobic conditions in the composting material; |
| B) | Use of mixing for favorable composting conditions; |
| C) | Formation of windrows or other piles into a size and shape favorable to minimizing odors; and |
| D) | Use of end-product compost as cover to act as a filter during early stages of composting. |
| h) | Methods to control stormwater and landscape waste leachate, in accordance with Section 830.204; |
| i) | Methods to control noise, vectors and litter, in accordance with Section 830.205; |
| j) | Methods to control dust emissions, in accordance with Section 830.205(f), which must include: |
| 1) | Consideration of the following factors prior to turning or moving the composting material: |
| A) | Time of day; |
| B) | Wind direction; |
| C) | Percent moisture; |
| D) | Estimated emission potential; and |
| E) | Degree of maturity; and |
| 2) | Maintenance of roads, wetting of roads, use of dust control agents, or any combination of these methods; |
| k) | Methods for monitoring temperature, oxygen level and moisture level of the composting material, in accordance with Section 830.205(m); |
| l) | Methods for adjusting temperature, oxygen level and moisture level of the composting material, in accordance with Section 830.205(a); |
| m) | Recordkeeping and reporting procedures required pursuant to Section 830.211; and |
| n) | Methods to obtain composite samples and test end-product compost to demonstrate compliance with Subpart E of this Part. |
| a) | Salvaging operations at permitted landscape waste compost facilities must not interfere with the operation of the landscape waste facility or result in a violation of any standard in this Part. |
| b) | All salvaging operations must be performed in a safe and sanitary manner in compliance with the requirements of this Part. |
| c) | Salvageable materials: |
| 1) | May be accumulated on-site by the operator, provided they are managed so as not to create a nuisance, harbor vectors, cause malodors, or create an unsightly appearance; and |
| 2) | Must not be accumulated in a manner meeting the definition of a waste pile. |
| Section 830.208 | Access Control at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| Section 830.209 | Load Checking at Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | Each load received at a permitted landscape waste compost facility must be inspected, upon receipt, for its acceptability at the facility and must be visually checked, prior to processing, for noncompostable waste. |
| b) | The facility must reject unacceptable loads. |
| Section 830.210 | Personnel Training for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | The operator of a permitted landscape waste compost facility shall provide training to all personnel prior to initial operation of a composting facility. In addition, annual personnel training shall be provided, which must include, at a minimum, a thorough explanation of the operating procedures for both normal and emergency situations. |
| b) | New employees shall be trained, prior to participating in operations at the facility, in facility operations, maintenance procedures, and safety and emergency procedures relevant to their employment. |
| c) | The operator shall have personnel sign an acknowledgement stating that they have received the training required pursuant to this Section. |
| d) | The facility operating plan required pursuant to Section 830.206 must be made available and explained to all employees. |
| Section 830.211 | Recordkeeping for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | Copies of the facility permit, design plans, operating plan, and any required reports must be kept at the facility, or at a definite location specified in the operating plan or permit, so as to be available during inspection of the facility. |
| b) | The operator shall record the following information: |
| 1) | The quantity of each load of landscape waste received; |
| 2) | The origin, type and quantity of any additive accepted, when received at the facility; |
| 3) | The type and quantity of any additive used in the composting process (water added during composting need not be quantified), as quantified based on a monthly review of additives remaining; |
| 4) | The dates of turning of each windrow or other pile; |
| 5) | All monitoring data required pursuant to a facility permit; |
| 6) | Conditions evaluated pursuant to Section 830.206; |
| 7) | For any odor complaint received, the information collected pursuant to Section 830.202(m); |
| 8) | Details of all incidents that require implementation of the facility's contingency plan, in accordance with Section 830.212, and methods used to resolve them; |
| 9) | Records pertaining to sampling and testing, as follows: |
| A) | Locations in the composting area from which samples are obtained; |
| B) | Number of samples taken; |
| C) | Volume of each sample taken; |
| D) | Date and time of collection of samples; |
| E) | Name and signature of person responsible for sampling; |
| F) | Name and address of the laboratory receiving samples, if applicable; and |
| G) | Signature of the person responsible for sample analysis. |
| 10) | The daily quantity of each type of end-product compost removed from the facility, according to the end-product compost classifications provided in Subpart E of this Part; and |
| 11) | Verification that requisite personnel training has been done, in accordance with Section 830.210. |
| c) | The operator shall keep dated copies of the end-product compost analyses required pursuant to Section 830.504. |
| d) | The records required pursuant to this Section shall be made available during normal business hours for inspection and photocopying by the Agency. Such records must be kept for a period of three years, subject to extension upon written request by the Agency and automatic extension during the course of any enforcement action relating to the facility. Records must be sent to the Agency upon request. |
| Section 830.212 | Contingency Plan for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | A contingency plan must be established, addressing the contingencies set forth in Section 830.202(c) and the following additional contingencies: |
| 1) | Equipment breakdown; |
| 2) | Odors; |
| 3) | Unacceptable waste delivered to the facility; |
| 4) | Groundwater contamination; |
| 5) | Any accidental release of special waste; and |
| 6) | Conditions such as fires, dust, noise, vectors, power outages and unusual traffic conditions. |
| b) | The facility contingency plan must be available on-site and implemented as necessary. |
| Section 830.213 | Closure Plan for Permitted Landscape Waste Compost Facilities |
| a) | A written closure plan must be developed which contains, at a minimum, the following: |
| 1) | Steps necessary for the premature final closure of the facility under circumstances during its intended operating permit term when the cost of closure would be the greatest; |
| 2) | Steps necessary for, and a schedule for the completion of, the routine final closure of the facility at the end of its intended operating life; and |
| 3) | Steps necessary to prevent damage to the environment during temporary suspension of landscape waste acceptance if the facility permit allows temporary suspension of landscape waste acceptance at the facility without initiating final closure. |
| b) | Until completion of closure has been certified, the operator shall maintain a copy of the closure plan at the facility or at a definite location, specified in the facility permit, so as to be available during inspection of the facility. |
| c) | An operator of a facility shall develop and file a revised closure plan upon modification of the operations of the facility which affect the cost of closure of the facility or any portion thereof, which include, but are not limited to: |
| 1) | A temporary suspension of landscape waste acceptance at the facility; or |
| 2) | An increase in the design capacity at the facility to process landscape waste. |
| d) | The operator shall initiate implementation of the closure plan within 30 days following the beginning of closure. |
| e) | Not later than 30 days following the beginning of closure, the operator shall post signs, easily visible at all access gates leading into the facility. The text of such signs must read, in letters not less than three inches high: "This facility is closed for all composting activities and all receipt of landscape waste materials. No dumping allowed. Violators will be prosecuted." Such signs must be maintained in legible condition until certification of completion of closure is issued for the facility by the Agency. |
| f) | Notice of Closure. The operator shall send notice of closure to the Agency within 30 days following the beginning of closure. A compost closure report must be submitted to the Agency, on a form provided by the Agency, which must cover the time elapsed since the end of the last annual report period. |
| g) | Certificate of Completion of Closure. |
| 1) | Upon completion of closure, the operator shall prepare and submit to the Agency an affidavit, on a form provided by the Agency, stating that the facility has been closed in accordance with the closure plan. |
| 2) | Upon finding that the facility has been closed in accordance with the closure plan, the Agency shall issue a certificate of completion of closure and shall terminate the facility permit. |
| h) | The operator of a permitted facility shall maintain financial assurance as provided in Subpart F. |
| a) | End-product compost used as daily cover or vegetative amendment in the final layer of a landfill is exempt from the requirements set forth in this Subpart. (Section 22.33(c) of the Act.) |
| b) | The provisions set forth in Sections 830.502, 830.503, and 830.507 of this Subpart apply to all end-product compost subject to this Part. |
| c) | In addition, the provisions set forth in Sections 830.504 and 830.508 apply to all end-product compost derived from landscape waste and subject to this Part. |
| a) | General Use Compost: End-product compost which meets the standards set forth in Section 830.503. |
| b) | Designated Use Compost: End-product compost which does not qualify as general use end-product compost. Designated use compost must be used only as daily cover or vegetative amendment in the final layer at a landfill. (Section 22.33(c) of the Act.) |
| a) | Must be free of any materials which pose a definite hazard to human health due to physical characteristics, such as glass or metal shards; |
| b) | Must not contain man-made materials larger than four millimeters in size exceeding 1% of the end-product compost, on a dry weight basis; |
| c) | Must have a pH between 6.5 and 8.5; |
| d) | Must have reached stability, as demonstrated by one of the methods prescribed in Section 830.Appendix B; |
| e) | Must not exceed, on a dry weight basis, the inorganic concentrations set forth in Section 830.Table A; and |
| f) | Must not contain fecal coliform populations that exceed 1000 MPN per gram of total solids (dry weight basis), or Salmonella species populations that exceed 3 MPN per 4 grams of total solids (dry weight basis). |
| Section 830.504 | Testing Requirements for End-Product Compost Derived from Landscape Waste |
| a) | Operators shall perform testing to demonstrate compliance with the standards set forth in subsections (b) - (e) of Section 830.503. Such testing must be done in accordance with the methods set forth in Section 830.Appendix B, except that an alternative method or methods may be used to demonstrate compliance with any of these standards, if approved in writing by the Agency. |
| b) | Operators of facilities which are authorized to use an additive pursuant to Section 830.205(a)(1)(G) which may cause an exceedence of Section 830.503(f) shall test for pathogens using the method set forth in Section 830.Appendix B, except that an alternative method or methods may be used to demonstrate compliance with any of these standards, if approved in writing by the Agency. |
| c) | For any facility not required to have a permit, no testing need be done to demonstrate compliance with the inorganics standards set forth in Section 830.Table A for general use compost derived from landscape waste. |
| d) | End-product compost derived from landscape waste must be tested for the parameters set forth in Section 830.503 at a frequency of: |
| 1) | Once every 5,000 cubic yards of end-product compost transported off-site; or |
| 2) | Once per year, if less than 5,000 cubic yards of end-product compost are transported off-site per year. |
| a) | Twelve grab samples, each 550 milliliters in size, must be taken from the end-product compost at the facility, in the following manner: |
| 1) | Four grab samples from points both equidistant throughout the length and at the center of the windrow or other pile, at a depth not less than one meter from the surface of the windrow or other pile; |
| 2) | Four grab samples from points both equidistant throughout the length and one quarter the width of the windrow or other pile, at a depth not less than half the distance between the surface and the bottom of the windrow or other pile; and |
| 3) | Four grab samples from points both equidistant throughout the length and one eighth the width of the windrow or other pile, at a depth not less than half the distance between the surface and the bottom of the windrow or other pile. |
| 4) | The twelve grab samples must be thoroughly mixed to form a homogenous composite sample. Analyses must be of a representative subsample. The sample holding times, sample container types and minimum collection volumes listed in Section 830.Table B shall apply; or |
| b) | Sampling methods set forth in Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods (SW-846), incorporated by reference at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 830.103. |
| a) | This Subpart provides procedures by which the operator of any composting facility required, pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 831, to have a permit shall demonstrate compliance with the financial assurance plan requirement set forth in Sections 22.33 of the Act. |
| b) | The operator is not required to comply with the provisions of this Subpart if the operator demonstrates that: |
| 1) | Closure and post-closure care plans filed pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724, 725, 807 or 811 will result in closure of the facility in accordance with the requirements of this Part; and |
| 2) | The operator has provided financial assurance adequate to provide for such closure and post-closure care pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724, 725, 807 or 811. |
| a) | A written cost estimate, determined pursuant to Section 830.603, covering the maximum cost of premature final closure; and |
| b) | The financial mechanism chosen by the operator to comply with the requirement set forth in Section 830.604(a). |
| a) | The written cost estimate required pursuant to Section 830.602(a) must be based on the steps necessary to complete closure in accordance with Section 830.213, and must include an itemization of the cost to complete each step. |
| b) | The operator shall revise the current cost estimate whenever a change in the closure plan increases the cost estimate. |
| a) | The operator must maintain financial assurance equal to or greater than the amount provided as a written cost estimate in the financial assurance plan. |
| b) | The funds comprising financial assurance must be used to cover the cost of closure. |
| c) | Upon certification of completion of closure, any financial assurance funds remaining will be made available for unrestricted use. |
| a) | The operator may utilize either of the following mechanisms to comply with Section 830.604: |
| 1) | A cash reserve fund; or |
| 2) | Self-insurance. |
| b) | An operator choosing to use a cash reserve account as the mechanism by which to comply with Section 830.604 shall: |
| 1) | Fully fund the account within one year after the initial receipt of waste, except that facilities in operation on the November 10, 1994 shall fully fund the account by November 10, 1995; and |
| 2) | Thereafter maintain full funding pending the expenditure of such funds to cover the costs of closure. |
| c) | An operator choosing to use self-insurance as the mechanism by which to comply with subsection (a) of this Section shall have: |
| 1) | Net working capital and tangible net worth each at least six times the current cost estimate; |
| 2) | Tangible net worth of at least $10 million; |
| 3) | Assets in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of the operator's total assets and at least six times the current cost estimate; and |
| 4) | Either: |
| A) | Two of the following three ratios: a ratio of total liabilities to net worth of less than 2.0; a ratio of the sum of net income plus depreciation, depletion and amortization to total liabilities of greater than 0.1; or a ratio of current assets to current liabilities of greater than 1.5; or |
| B) | A current rating of AAA, AA, A or BBB for its most recent bond issuance, as issued by Standard and Poor, or a rating of Aaa, Aa, A or Bbb, as issued by Moody. |
| a) | Operator name; |
| b) | Illinois Inventory Identification Number and Permit Number assigned by the Agency; |
| c) | Facility name; |
| d) | Address and county in which the facility is located; and |
| e) | A statement certifying compliance with the provisions of this Subpart. |
| Section 830.APPENDIX A: | Early Detection and Groundwater Monitoring Program |
| a) | Program. |
| 1) | The operator shall perform a hydrogeologic site investigation pursuant to subsection (b) of this Appendix to characterize the subsurface and determine the location and quality of groundwater beneath the facility. |
| 2) | An appropriate monitoring system must be designed, capable of determining the compost facility's impact or potential impact on the quality of groundwater beneath the facility. |
| 3) | If the water table is located greater than ten (10) feet below ground surface and the soil has been classified as a soil exhibiting moderate or poor drainage by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Soil Conservation Service on a published county soil survey map, the owner of operator shall install either an early detection system, pursuant to subsection (d)(1) of this Section, or a groundwater monitoring system, pursuant to subsection (d)(2) of this Section. Otherwise, a groundwater monitoring system must be installed, pursuant to subsection (d)(2) of this Section. |
| 4) | If either early detection monitoring or groundwater monitoring indicates an impact on underground water beneath the facility, a site evaluation must be performed, using the procedures set forth in subsection (e) of this Section, and remedial action implemented, if appropriate. |
| 5) | The results of the hydrogeologic site investigation and the proposed monitoring system design must be submitted to the Agency as part of an application for a facility permit. |
| b) | Hydrogeologic Site Investigation. The operator shall conduct a hydrogeologic site investigation to obtain the following information: |
| 1) | The regional hydrogeologic setting of the facility, using material available from Illinois scientific surveys, state and federal organizations, water well drilling logs and previous investigations. A complete list of references and any well logs utilized must be submitted to the Agency with the results of the hydrogeologic site investigation; |
| 2) | The site-specific hydrogeologic setting of the facility, using continuously sampled borings of the site and information collected from on-site piezometers or monitoring wells. At a minimum, borings must be to a depth of ten (10) feet; |
| 3) | Soil characteristics, including soil types and physical properties of the underlying strata, including the potential pathways for contaminant migration. Any confining unit relative to waste constituents expected to be present must be identified; |
| 4) | Water-bearing sediments or geologic units beneath the facility, their classification pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620 and the direction and rate of groundwater flow. Also, regional and local areas of groundwater discharge and recharge affecting groundwater at the facility must be identified; and |
| 5) | Water quality beneath the facility, including any potential impact on groundwater. The groundwater quality analysis must take into account the type of compost facility and its expected leachate constituents. |
| c) | All drill holes, including exploration borings that are not converted into monitoring wells, monitoring wells that are no longer necessary to the operation of the facility, and other holes that may cause or facilitate contamination of groundwater, must be sealed in accordance with the standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 811.316. |
| d) | Monitoring System |
| 1) | Early Detection System |
| A) | Monitoring device(s) must be installed: |
| i) | Hydraulically upgradient from the facility or at sufficient distance from the composting area so as not to be affected by it, to establish representative background water quality in the waters beneath (or near) the facility; and |
| ii) | Beneath and around the composting area, sufficient to enable early detection of the downward migration of constituents related to the composting activities at the facility. |
| B) | The parameters monitored must be those expected to be in the leachate, taking into consideration the type of compost facility. |
| C) | If lysimeters are utilized, the following requirements must be used in designing an adequate monitoring system; |
| i) | Lysimeters must be located, when possible, in a depression in the path of site runoff in each direction of flow and topographically low areas associated with the unit(s). |
| ii) | At a minimum, each lysimeter must be sampled within 48 hours after each rain event exceeding 0.5 inches, provided that the rain event is not within two weeks after the date previous samples were successfully collected. |
| iii) | Any lysimeter placed around the perimeter must be installed at an angle so that the cup of the lysimeter is beneath the unit(s). |
| 2) | Groundwater Monitoring System |
| A) | Monitoring well(s) must be installed: |
| i) | Hydraulically upgradient from the facility, to establish representative background water quality in the groundwater beneath (or near) the facility; and |
| ii) | Hydraulically downgradient (i.e., in the direction of decreasing static head) from the compost facility. Locations and depths of monitoring wells must ensure detection of waste constituents that migrate from the waste management unit to the groundwater. |
| B) | The parameters monitored must be those expected to be in the leachate, taking into consideration the type of compost facility. |
| C) | The groundwater monitoring system must be installed at the closest practicable distance from the composting area boundary, or at an alternative distance specified by permit. |
| 3) | Approval of any early detection monitoring system or groundwater monitoring system must be obtained from the Agency prior to operation. |
| e) | Evaluation |
| 1) | Further evaluation of an impact to underground water shall be required if: |
| A) | An exceedence of the appropriate standard as stated in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620 is confirmed; |
| B) | A progressive increase in measured parameters other than pH is observed over two consecutive sampling events; or |
| C) | Where groundwater monitoring wells are used, a statistical increase over background or upgradient concentrations, calculated in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 811.320(e), is observed. |
| 2) | An impact as described in subsection (e)(1)(A) or (e)(1)(C) of this Section must be confirmed by resampling the underground water within 30 days after the date on which the first sample analyses are received. The operator shall provide notification to the Agency of the results of the resampling analysis within 30 days after the date on which the sample analyses are received, but no later than 90 days after the first samples were taken. |
| 3) | Within 60 days after the confirmation of impact but no later than 120 days after the date on which the first sample was taken, the operator shall propose as a permit modification a plan to address the impact, which may include further evaluation of data, including the use of appropriate statistical methods, groundwater monitoring or remedial action. |
| a) | Man-made materials |
| 1) | Take four 250 gram samples. |
| 2) | Dry samples at 70 C for 24 hours. Let sample cool to room temperature (20 to 25 C). |
| 3) | Weigh each sample and pass through a four millimeter screen. Inspect material remaining on the screen, and separate and weigh man-made materials. Calculate percent man-made materials relative to the total dry weight of the sample prior to screening. |
| b) | Pathogens |
| c) | pH |
| d) | Stability The operator shall demonstrate that the composite sample has reached stability by showing either: |
| 1) | That the compost does not reheat, upon standing, to greater than 20o C above room temperature (20 to 25o C). The degree of reheating must be measured using the following method: |
| A) | Take 4 liters of composite sample and adjust the moisture of the end-product compost so it falls within the range of 45 to 55% water on a dry weight basis; |
| B) | Fill a 2 liter Dewar flask (100 millimeters, inside diameter) loosely with sample within the acceptable moisture range and gently tap to simulate natural settling. Keep at room temperature (20 to 25o C). |
| C) | Insert thermometer into Dewar flask to a point 5 centimeters from bottom of flask. Do not push thermometer against bottom of flask. |
| D) | Record time and temperature each day for 15 days to determine when the highest point is reached. After each reading, shake down the thermometer; or |
| 2) | That the end-product compost supports a germination rate of 70% for annual ryegrass and radish using the following protocol: |
| A) | Mix 4 liters vermiculite with 4 grams of air-dried soil. |
| B) | Take 1 liter of the composite sample with a moisture level within the range of 45 to 55 percent, on a dry weight basis; if necessary, adjust the moisture level until within such range. |
| C) | In three 2-liter containers, combine the vermiculite-soil mix with the compost sample at the following ratios: |
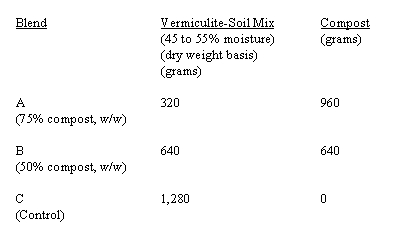
| D) | Break up lumps of compost with a spatula or trowel. Moisten the blend with water. |
| E) | Cover each container with plastic wrap and mix well by inverting each container 20 times. |
| F) | Transfer each blend into four 4-inch pots. Fill the pots to the brim and firm the surface by pressing down with the bottom of another 4-inch pot. Leave about 2 to 5 centimeters of space between surface of the blend and the top of the pot. |
| G) | Add approximately 50 milliliters of water soluble fertilizer (e.g., 20-20-20 NPK, fish emulsion) diluted to half-strength to each pot. |
| H) | Place 10 seeds of annual ryegrass and 10 radish seeds onto the surface of the moistened blend. Cover the seeds with about 1 centimeter dry vermiculite. |
| I) | Set the pots in a tray of warm water and let them remain there until capillary action has drawn water up and moistened the surface of the blend. Remove the pots from the tray when moisture from the bottom-watering is observed. |
| J) | Put pots in an environment suitable for plant growth (e.g., 8 to 12 hours of light daily, 30 to 60% humidity, 20 to 25 C). Check pots daily to determine if watering is needed. Blends should be kept evenly moist. If necessary, cover each pot with plastic wrap until the seedlings emerge. Remove plastic wrap at the first sign of emergence. |
| K) | Seven days after planting the seeds, count emergent seedlings in each pot and record visual observations of relative plant conditions identified in Section 830.Table C. |
| L) | Calculate the percent germination of plants in each blend relative to the control pot, using the formula set forth in Section 830.Table C. |
| Section 830.TABLE A: | Inorganic Concentration Limits for General Use Compost |
| Maximum | Test Method | |
| Concentration Limit | (SW-846) | |
| (mg/kg dry weight basis) | ||
| Arsenic | 41 | 7060 or 7061 |
| Cadmium | 21 | 7130 or 7131 or 6010 |
| Chromium | 1,200 | 7190 or 7191 or 6010 |
| Copper | 1,500 | 7210 or 7211 or 6010 |
| Lead | 300 | 7420 or 7421 or 6010 |
| Mercury | 17 | 7471 |
| Nickel | 420 | 7520 or 6010 |
| Selenium | 36 | 7740 or 7741 |
| Zinc | 2,800 | 7950 or 7951 or 6010 |
| Parameter | Container Type | Minimum Sample Size (ml) | Preservation | Maximum Storage Time |
| Man-made materials | P, G | 1,000 | Do not freeze | 28 days |
| pH | P, G | 50 | Analyze immediately | |
| Seed Germination | P, G | 1,000 | Analyze immediately | |
| Self-heating | P, G | 4,000 | Analyze immediately | |
| Pathogens | P, G | 500 | Cool to 4 C | 2 weeks |
| Inorganic | P(A), G(A) | 500 | Cool to 4 C | 6 months |
| Blend | Pot ID | Number of Annual Ryegrass Seedlings | Number of Radish Seedlings |
| A | A1 | ||
| A | A2 | ||
| A | A3 | ||
| A | A4 | ||
| B | B1 | ||
| B | B2 | ||
| B | B3 | ||
| B | B4 | ||
| C | C1 | ||
| C | C2 | ||
| C | C3 | ||
| C | C4 |
| (C1 + C2 + C3 + C4)/4 |
| (C1 + C2 + C3 + C4)/4 |
| (C1 + C2 + C3 + C4)/4 |
| (C1 + C2 + C3 + C4)/4 |
| Pots | Seedling | Parameter | None | Slight | Moderate | High |
| A1 - A4 | Ryegrass | Wilting | ||||
| A1 - A4 | Ryegrass | Chlorosis | ||||
| A1 - A4 | Ryegrass | Discoloration | ||||
| A1 - A4 | Ryegrass | Malodorous | ||||
| A1 - A4 | Ryegrass | Fungal Growth |
| Pots | Seedling | Parameter | None | Slight | Moderate | High |
| B1 - B4 | Ryegrass | Wilting | ||||
| B1 - B4 | Ryegrass | Chlorosis | ||||
| B1 - B4 | Ryegrass | Discoloration | ||||
| B1 - B4 | Ryegrass | Malodorous | ||||
| B1 - B4 | Ryegrass | Fungal Growth |
| Pots | Seedling | Parameter | None | Slight | Moderate | High |
| C1 - C4 | Ryegrass | Wilting | ||||
| C1 - C4 | Ryegrass | Chlorosis | ||||
| C1 - C4 | Ryegrass | Discoloration | ||||
| C1 - C4 | Ryegrass | Malodorous | ||||
| C1 - C4 | Ryegrass | Fungal Growth |