SUBPART B: GENERAL FACILITY STANDARDS
Section 725.110 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart B apply to owners and operators of all hazardous waste facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.111 USEPA Identification Number
Every facility owner or operator must apply to the Agency for a USEPA identification number using Notification of RCRA Subtitle C Activities (Site Identification Form) (USEPA Form 8700-12).
BOARD NOTE: USEPA Form 8700-12 is available from the Agency, Bureau of Land (217-782-6762). It is also available on-line for download in PDF file format: www.epa.gov/hwgenerators/instructions-and-form-hazardous-waste-generators-transporters-and-treatment-storage-and .
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
Section 725.112 Required Notices
a) Receipt from a Foreign Source. The owner or operator of a facility that has arranged to receive hazardous waste subject to Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722, from a foreign source must submit the following required notices:
1) As required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(b), for imports where the competent authority of the country of export does not require the foreign exporter to submit to it a notification proposing export and obtain consent from USEPA and the competent authorities for the countries of transit, the owner or operator of the facility, if acting as the importer, must provide notification of the proposed transboundary movement in English to USEPA using the methods listed in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(b)(1) at least 60 days before the first shipment is expected to depart the country of export. The notification may cover up to one year of shipments of wastes having similar physical and chemical characteristics; the same United Nations/USDOT identification number from the Hazardous Materials Table in 49 CFR 172.101, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111; the same USEPA hazardous waste numbers; and the same applicable OECD waste codes from the lists in the OECD Guidance Manual, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111; and being sent from the same foreign exporter.
2) As required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(d)(2)(O), a copy of the movement document with all the required signatures within three working days after receiving the shipment to the foreign exporter; to the competent authorities of the countries of export and transit that control the shipment as an export and transit shipment of hazardous waste respectively; and on or after the electronic import-export reporting compliance date, to EPA electronically using USEPA’s Waste Import Export Tracking System (WIETS). The original of the signed movement document must be maintained at the facility for at least three years. The owner or operator of a facility may satisfy this recordkeeping requirement by retaining electronically submitted documents in the facility’s account on USEPA’s WIETS, if copies are readily available for viewing and production upon request by any USEPA or Agency inspector. An owner or operator of a facility may be held liable for the inability to produce the documents for inspection under this section if the owner or operator of a facility can demonstrate that the inability to produce the document is due exclusively to technical difficulty with USEPA’s WIETS for which the owner or operator of a facility bears no responsibility.
3) As required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(f)(4), if the facility has physical control of the waste and it must be sent to an alternate facility or returned to the country of export, the owner or operator of the facility must inform USEPA, using the methods listed in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(b)(1) of the need to return or arrange alternate management of the shipment.
4) As required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.184(g), the owner or operator must:
A) Send copies of the signed and dated confirmation of recovery or disposal, as soon as possible, but within thirty days after completing recovery or disposal on the waste in the shipment and within one calendar year after receiving the waste, to the foreign exporter, to the competent authority of the country of export that controls the shipment as an export of hazardous waste. For shipments recycled or disposed of on or after the electronic import-export reporting compliance date, to USEPA electronically using USEPA’s WIETS.
B) If the facility performed any of recovery operations R12, R13, or RC3 or disposal operations D13 through D15, promptly send copies of the confirmation of recovery or disposal that it receives from the final recovery or disposal facility within one year of shipment delivery to the final recovery or disposal facility that performed one of recovery operations R1 through R11 or RC1 or one of disposal operations D1 through D12, or DC1 to DC2, to the competent authority of the country of export that controls the shipment as an export of hazardous waste; on or after the electronic import-export reporting compliance date, to USEPA electronically using USEPA’s WIETS, or its successor system. The recovery and disposal operations in this subsection are defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.181.
b) Before transferring ownership or operation of a facility during its operating life, or of a disposal facility during the post-closure care period, the owner or operator must notify the new owner or operator in writing of the requirements of this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 703 (also see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.155).
BOARD NOTE: An owner’s or operator’s failure to notify the new owner or operator of the requirements of this Part in no way relieves the new owner or operator of his obligation to comply with all applicable requirements.
(Source: Amended at 48 Ill. Reg. 9911, effective June 20, 2024)
Section 725.113 General Waste Analysis
a) Waste Analysis
1) Before an owner or operator treats, stores, or disposes of any hazardous wastes, or non-hazardous wastes if applicable under Section 725.213(d), the owner or operator must obtain a detailed chemical and physical analysis of a representative sample of the wastes. At a minimum, the analysis must contain all the information that must be known to treat, store, or dispose of the waste in accordance with this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.
2) The analysis may include data developed under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721 and existing published or documented data on the hazardous waste or on waste generated from similar processes.
BOARD NOTE: For example, the facility’s record of analyses performed on the waste before the effective date of these regulations or studies conducted on hazardous waste generated from processes similar to that which generated the waste to be managed at the facility may be included in the data base required to comply with subsection (a)(1), except as otherwise specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107(b) and (c). The owner or operator of an off-site facility may arrange for the generator of the hazardous waste to supply part or all of the information required by subsection (a)(1). If the generator does not supply the information and the owner or operator chooses to accept a hazardous waste, the owner or operator is responsible for obtaining the information required to comply with this Section.
3) The analysis must be repeated as necessary to ensure that it is accurate and up to date. At a minimum, the analysis must be repeated as follows:
A) When the owner or operator is notified or has reason to believe that the process or operation generating the hazardous waste, or non-hazardous waste if applicable under Section 725.213(d), has changed; and
B) For off-site facilities, when the results of the inspection required in subsection (a)(4) indicate that the hazardous waste received at the facility does not match the waste designated on the accompanying manifest or shipping paper.
4) The owner or operator of an off-site facility must inspect and, if necessary, analyze each hazardous waste movement received at the facility to determine whether it matches the identity of the waste specified on the accompanying manifest or shipping paper.
b) The owner or operator must develop and follow a written waste analysis plan that describes the procedures that the owner or operator will carry out to comply with subsection (a). The owner or operator must keep this plan at the facility. At a minimum, the plan must specify the following:
1) The parameters for which each hazardous waste, or non-hazardous waste if applicable under Section 725.213(d), will be analyzed and the rationale for the selection of these parameters (i.e., how analysis for these parameters will provide sufficient information on the waste’s properties to comply with subsection (a)).
2) The test methods that will be used to test for these parameters.
3) The sampling method that will be used to obtain a representative sample of the waste to be analyzed. A representative sample may be obtained using either of the following methods:
A) One of the sampling methods described in Appendix A to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721, or
B) An equivalent sampling method.
BOARD NOTE: See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.120(c) for related discussion.
4) The frequency with which the initial analysis of the waste will be reviewed or repeated to ensure that the analysis is accurate and up-to-date.
5) For off-site facilities, the waste analyses that hazardous waste generators have agreed to supply.
6) Where applicable, the methods that will be used to meet the additional waste analysis requirements for specific waste management methods, as specified in Sections 725.300, 725.325, 725.352, 725.373, 725.414, 725.441, 725.475, 725.502, 725.934(d), 725.963(d), and 725.984 and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107.
7) For surface impoundments exempted from land disposal restrictions under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.104(a), the procedures and schedules for the following:
A) The sampling of impoundment contents;
B) The analysis of test data; and
C) The annual removal of residues that are not delisted under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.122 or that exhibit a characteristic of hazardous waste and either of the following is true:
i) The waste residues do not meet the applicable treatment standards of Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, or
ii) Where no treatment standards have been established, the waste residues are prohibited from land disposal under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.132 or 728.139.
8) For an owner or operator seeking an exemption to the air emission standards of Subpart CC of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 in accordance with Section 725.983:
A) If direct measurement is used for the waste determination, the procedures and schedules for waste sampling and analysis, and the analysis of test data to verify the exemption.
B) If knowledge of the waste is used for the waste determination, any information prepared by the facility owner or operator, or by the generator of the waste if the waste is received from off-site, that is used as the basis for knowledge of the waste.
c) For off-site facilities, the waste analysis plan required in subsection (b) must also specify the procedures that will be used to inspect and, if necessary, analyze each movement of hazardous waste received at the facility to ensure that it matches the identity of the waste designated on the accompanying manifest or shipping paper. At a minimum, the plan must describe the following:
1) The procedures that will be used to determine the identity of each movement of waste managed at the facility;
2) The sampling method that will be used to obtain a representative sample of the waste to be identified if the identification method includes sampling; and
3) The procedures that the owner or operator of an off-site landfill receiving containerized hazardous waste will use to determine whether a hazardous waste generator or treater has added a biodegradable sorbent to the waste in the container.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.114 Security
a) The owner or operator must prevent the unknowing entry and minimize the possibility for the unauthorized entry of persons or livestock onto the active portion of his facility, unless the following are true:
1) Physical contact with the waste, structures, or equipment of the active portion of the facility will not injure unknowing or unauthorized persons or livestock that may enter the active portion of the facility; and
2) Disturbance of the waste or equipment by the unknowing or unauthorized entry of persons or livestock onto the active portion of a facility will not cause a violation of the requirements of this Part.
b) Unless exempt under subsections (a)(1) and (a)(2), a facility must have the following:
1) A 24-hour surveillance system (e.g., television monitoring or surveillance by guards or facility personnel) that continuously monitors and controls entry into the active portion of the facility; or
2) Controlled access, including the following minimum elements:
A) An artificial or natural barrier (e.g., a fence in good repair or a fence combined with a cliff) that completely surrounds the active portion of the facility; and
B) A means to control entry at all times through the gates or other entrances to the active portion of the facility (e.g., an attendant, television monitors, locked entrance, or controlled roadway access to the facility).
BOARD NOTE: The requirements of subsection (b) are satisfied if the facility or plant within which the active portion is located itself has a surveillance system or a barrier and a means to control entry that complies with the requirements of subsection (b)(1) or (b)(2).
c) Unless exempt under subsection (a)(1) or (a)(2), a sign with the legend, “Danger—Unauthorized Personnel Keep Out”, must be posted at each entrance to the active portion of a facility and at other locations in sufficient numbers to be seen from any approach to this active portion. The sign must be legible from a distance of at least 25 feet. Existing signs with a legend other than “Danger—Unauthorized Personnel Keep Out” may be used if the legend on the sign indicates that only authorized personnel are allowed to enter the active portion and that entry onto the active portion can be dangerous.
BOARD NOTE: See Section 725.217(b) for discussion of security requirements at disposal facilities during the post-closure care period.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.115 General Inspection Requirements
a) The owner or operator must inspect the facility for malfunctions and deterioration, operator errors and discharges that may be causing—or which may lead to—the conditions listed below. The owner or operator must conduct these inspections often enough to identify problems in time to correct them before they harm human health or the environment.
1) Release of hazardous waste constituents to the environment, or
2) A threat to human health.
b) Written schedule.
1) The owner or operator must develop and follow a written schedule for inspecting all monitoring equipment, safety and emergency equipment, security devices, and operating and structural equipment (such as dikes and sump pumps) that are important to preventing, detecting, or responding to environmental or human health hazards.
2) The owner or operator must keep this schedule at the facility.
3) The schedule must identify the types of problems (e.g., malfunctions or deterioration) that are to be looked for during the inspection (e.g., inoperative sump pump, leaking fitting, eroding dike, etc.).
4) The frequency of inspection may vary for the items on the schedule. However, the frequency should be based on the rate of deterioration of the equipment and the probability of an environmental or human health incident if the deterioration, malfunction, or operator error goes undetected between inspections. Areas subject to spills, such as loading and unloading areas, must be inspected daily when in use. At a minimum, the inspection schedule must include the items and frequencies called for in Sections 725.274, 725.293, 725.295, 725.326, 725.360, 725.378, 725.404, 725.447, 725.477, 725.503, 725.933, 725.952, 725.953, 725.958, and 725.984 through 725.990, where applicable.
5) This subsection (b)(5) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.15(b)(5), which became obsolete when USEPA terminated the Performance Track Program at 74 Fed. Reg. 22741 (May 14, 2009). USEPA has recognized that program-related rules are no longer effective at 75 Fed. Reg. 12989, 12992, note 1 (Mar. 18, 2010). This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal requirements.
c) The owner or operator must remedy any deterioration or malfunction of equipment or structure that the inspection reveals on a schedule that ensures that the problem does not lead to an environmental or human health hazard. Where a hazard is imminent or has already occurred, remedial action must be taken immediately.
d) The owner or operator must record inspections in an inspection log or summary. The owner or operator must keep these records for at least three years from the date of inspection. At a minimum, these records must include the date and time of the inspection, the name of the inspector, a notation of the observations made and the date, and nature of any repairs or other remedial actions.
(Source: Amended at 35 Ill. Reg. 18052, effective October 14, 2011)
Section 725.116 Personnel Training
a) Personnel Training Program
1) Facility personnel must successfully complete a program of classroom instruction or on-the-job training that teaches them to perform their duties in a way that ensures the facility’s compliance with the requirements of this part. The owner or operator must ensure that this program includes all the elements described in the document required under subsection (d)(3).
2) This program must be directed by a person trained in hazardous waste management procedures, and must include instruction that teaches facility personnel hazardous waste management procedures (including contingency plan implementation) relevant to the positions in which they are employed.
3) At a minimum, the training program must be designed to ensure that facility personnel are able to respond effectively to emergencies by familiarizing them with emergency procedures, emergency equipment and emergency systems, including the following where applicable:
A) Procedures for using, inspecting, repairing and replacing facility emergency and monitoring equipment;
B) Key parameters for automatic waste feed cut-off systems;
C) Communications or alarm systems;
D) Response to fires or explosions;
E) Response to groundwater contamination incidents; and
F) Shutdown of operations.
4) For facility employees that receive emergency response training pursuant to the federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations at 29 CFR 1910.120(p)(8) and 1910.120(q), the facility is not required to provide separate emergency response training pursuant to this section, provided that the overall facility OSHA emergency response training meets all the requirements of this Section.
b) Facility personnel must successfully complete the program required in subsection (a) upon the effective date of these regulations or six months after the date of their employment or assignment to a facility or to a new position at a facility, whichever is later. Employees hired after the effective date of these regulations must not work in unsupervised positions until they have completed the training requirements of subsection (a).
c) Facility personnel must take part in an annual review of the initial training required in subsection (a).
d) The owner or operator must maintain the following documents and records at the facility:
1) The job title for each position at the facility related to hazardous waste management and the name of the employee filling each job;
2) A written job description for each position listed under subsection (d)(1). This description may be consistent in its degree of specificity with descriptions for other similar positions in the same company location or bargaining unit, but must include the requisite skill, education, or other qualifications and duties of facility personnel assigned to each position;
3) A written description of the type and amount of both introductory and continuing training that will be given to each person filling a position listed under subsection (d)(1);
4) Records that document that the training or job experience required under subsections (a), (b), and (c) has been given to and completed by facility personnel.
e) Training records on current personnel must be kept until closure of the facility. Training records on former employees must be kept for at least three years from the date the employee last worked at the facility. Personnel training records may accompany personnel transferred within the same company.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.117 General Requirements for Ignitable, Reactive, or Incompatible Wastes
a) The owner or operator must take precautions to prevent accidental ignition or reaction of ignitable or reactive waste. This waste must be separated and protected from sources of ignition or reaction, including, but not limited to, open flames, smoking, cutting and welding, hot surfaces, frictional heat, sparks (static, electrical or mechanical), spontaneous ignition (e.g., from heat-producing chemical reactions), and radiant heat. While ignitable or reactive waste is being handled, the owner or operator must confine smoking and open flame to specially designated locations. “No Smoking” signs must be conspicuously placed wherever there is a hazard from ignitable or reactive waste.
b) Where specifically required by other Sections of this Part, the treatment, storage, or disposal of ignitable or reactive waste and the mixture or commingling of incompatible waste or incompatible wastes and materials, must be conducted so that it does not do any of the following:
1) It does not generate extreme heat or pressure, fire or explosion, or violent reaction;
2) It does not produce uncontrolled toxic mists, fumes, dusts, or gases in sufficient quantities to threaten human health;
3) It does not produce uncontrolled flammable fumes or gases in sufficient quantities to pose a risk of fire or explosions;
4) It does not damage the structural integrity of the device or facility containing the waste; or
5) Through other like means, it does not threaten human health or the environment.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.118 Location Standards
The placement of any hazardous waste in a salt dome, salt bed formation, underground mine, or cave is prohibited.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.119 Construction Quality Assurance Program
a) CQA Program
1) A construction quality assurance (CQA) program is required for all surface impoundment, waste pile and landfill units that are required to comply with Sections 725.321(a), 725.354, and 725.401(a). The program must ensure that the constructed unit meets or exceeds all design criteria and specifications in this Part. The program must be developed and implemented under the direction of a CQA officer that is a registered professional engineer.
2) The CQA program must address the following physical components, where applicable:
A) Foundations;
B) Dikes;
C) Low-permeability soil liners;
D) Geomembranes (flexible membrane liners);
E) Leachate collection and removal systems and leak detection systems; and
F) Final cover systems.
b) Written CQA plan. Before construction begins on a unit subject to the CQA program under subsection (a), the owner or operator must develop a written CQA plan. The plan must identify steps that will be used to monitor and document the quality of materials and the condition and manner of their installation. The CQA plan must include the following:
1) Identification of applicable units and a description of how they will be constructed.
2) Identification of key personnel in the development and implementation of the CQA plan, and CQA officer qualifications.
3) A description of inspection and sampling activities for all unit components identified in subsection (a)(2), including observations and tests that will be used before, during and after construction to ensure that the construction materials and the installed unit components meet the design specifications. The description must cover: Sampling size and locations; frequency of testing; data evaluation procedures; acceptance and rejection criteria for construction materials; plans for implementing corrective measures; and data or other information to be recorded and retained in the operating record under Section 725.173.
c) Contents of Program
1) The CQA program must include observations, inspections, tests and measurements sufficient to ensure the following:
A) Structural stability and integrity of all components of the unit identified in subsection (a)(2);
B) Proper construction of all components of the liners, leachate collection and removal system, leak detection system, and final cover system, according to permit specifications and good engineering practices, and proper installation of all components (e.g., pipes) according to design specifications;
C) Conformity of all materials used with design and other material specifications under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321, 724.351, and 724.401.
2) The CQA program must include test fills for compacted soil liners, using the same compaction methods as in the full-scale unit, to ensure that the liners are constructed to meet the hydraulic conductivity requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(c)(1), 724.351(c)(1), or 724.401(c)(1) in the field. Compliance with the hydraulic conductivity requirements must be verified by using in-situ testing on the constructed test fill. The test fill requirement is waived where data are sufficient to show that a constructed soil liner meets the hydraulic conductivity requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(c)(1), 724.351(c)(1), or 724.401(c)(1) in the field.
d) Certification. The owner or operator of units subject to this Section must submit to the Agency by certified mail or hand delivery, at least 30 days prior to receiving waste, a certification signed by the CQA officer that the CQA plan has been successfully carried out and that the unit meets the requirements of Sections 725.321(a), 725.354, or 725.401(a). The owner or operator may receive waste in the unit after 30 days from the Agency’s receipt of the CQA certification unless the Agency determines in writing that the construction is not acceptable, or extends the review period for a maximum of 30 more days, or seeks additional information from the owner or operator during this period. Documentation supporting the CQA officer’s certification must be furnished to the Agency upon request.
e) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART C: PREPAREDNESS AND PREVENTION
Section 725.130 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart C apply to owners and operators of all hazardous waste facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.131 Maintenance and Operation of Facility
Facilities must be maintained and operated to minimize the possibility of a fire, explosion or any unplanned sudden or non-sudden release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents to air, soil, or surface water that could threaten human health or the environment.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.132 Required Equipment
All facilities must be equipped with the following, unless none of the hazards posed by waste handled at the facility could require a particular kind of equipment specified below:
a) An internal communications or alarm system capable of providing immediate emergency instruction (voice or signal) to facility personnel;
b) A device, such as a telephone (immediately available at the scene of operations) or a hand-held two-way radio, capable of summoning emergency assistance from local police departments, fire departments, or State or local emergency response teams;
c) Portable fire extinguishers, fire control equipment (including special extinguishing equipment, such as that using foam, inert gas, or dry chemicals), spill control equipment and decontamination equipment; and
d) Water at adequate volume and pressure to supply water hose streams or foam producing equipment or automatic sprinklers or water spray systems.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.133 Testing and Maintenance of Equipment
All facility communications or alarm systems, fire protection equipment, spill control equipment, and decontamination equipment, where required, must be tested and maintained as necessary to assure its proper operation in time of emergency.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.134 Access to Communications or Alarm System
a) Whenever hazardous waste is being poured, mixed, spread, or otherwise handled, all personnel involved in the operation must have immediate access to an internal alarm or emergency communication device, either directly or through visual or voice contact with another employee, unless such a device is not required under Section 725.132.
b) If there is ever just one employee on the premises while the facility is operating, he must have immediate access to a device, such as a telephone (immediately available at the scene of operation) or a hand-held two-way radio, capable of summoning external emergency assistance, unless such a device is not required under Section 725.132.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.135 Required Aisle Space
The owner or operator must maintain aisle space to allow the unobstructed movement of personnel, fire protection equipment, spill control equipment, and decontamination equipment to any area of facility operation in an emergency, unless aisle space is not needed for any of these purposes.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.137 Arrangements with Local Authorities
a) The owner or operator must attempt to make the following arrangements, as appropriate for the type of waste handled at his facility and the potential need for the services of the following organizations:
1) Arrangements to familiarize police, fire departments, and emergency response teams with the layout of the facility, properties of hazardous waste handled at the facility and associated hazards, places where facility personnel would normally be working, entrances to roads inside the facility and possible evacuation routes;
2) Where more than one police and fire department might respond to an emergency, agreements designating primary emergency authority to a specific police and a specific fire department and agreements with any others to provide support to the primary emergency authority;
3) Agreements with State emergency response teams, emergency response contractors, and equipment suppliers; and
4) Arrangements to familiarize local hospitals with the properties of hazardous waste handled at the facility and the types of injuries or illnesses that could result from fires, explosions, or releases at the facility.
b) Where State or local authorities decline to enter into such arrangements, the owner or operator must document the refusal in the operating record.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART D: CONTINGENCY PLAN AND EMERGENCY PROCEDURES
Section 725.150 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart D apply to owners and operators of all hazardous waste facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.151 Purpose and Implementation of Contingency Plan
a) Each owner or operator must have a contingency plan for his facility. The contingency plan must be designed to minimize hazards to human health or the environment from fires, explosions, or any unplanned sudden or non-sudden release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents to air, soil, or surface water.
b) The provisions of the plan must be carried out immediately whenever there is a fire, explosion, or release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that could threaten human health or the environment.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.152 Content of Contingency Plan
a) The contingency plan must describe the actions facility personnel must take to comply with Sections 725.151 and 725.156 in response to fires, explosions, or any unplanned sudden or non-sudden release of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents to air, soil, or surface water at the facility.
b) If the owner or operator has already prepared a federal Spill Prevention Control and Countermeasures (SPCC) Plan in accordance with 40 CFR Part 112, or some other emergency or contingency plan, it needs only amend that plan to incorporate hazardous waste management provisions that are sufficient to comply with the requirements of this Part. The owner or operator may develop one contingency plan that meets all regulatory requirements. USEPA has recommended that the plan be based on the National Response Team’s Integrated Contingency Plan Guidance (One Plan). When modifications are made to non-RCRA provisions in an integrated contingency plan, the changes do not trigger the need for a RCRA permit modification.
BOARD NOTE: The federal One Plan guidance appeared in the Federal Register at 61 Fed. Reg. 28642 (June 5, 1996), and was corrected at 61 Fed. Reg. 31103 (June 19, 1996). USEPA, Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery, Chemical Emergency Preparedness and Prevention Office, has made these documents available on-line for examination and download at yosemite.epa.gov/oswer/Ceppoweb.nsf/content/serc-lepc-publications.htm.
c) The plan must describe arrangements agreed to by local police department, fire departments, hospitals, contractors, and State and local emergency response teams to coordinate emergency services, pursuant to Section 725.137.
d) The plan must list names, addresses, and phone numbers (office and home) of all persons qualified to act as emergency coordinator (see Section 725.155), and this list must be kept up to date. Where more than one person is listed one must be named as primary emergency coordinator and others must be listed in the order in which they will assume responsibility as alternates.
e) The plan must include a list of all emergency equipment at the facility (such as fire extinguishing systems, spill control equipment, communications and alarm systems (internal and external), and decontamination equipment) where this equipment is required. This list must be kept up to date. In addition, the plan must include the location and a physical description of each item on the list and a brief outline of its capabilities.
f) The plan must include an evacuation plan for facility personnel where there is a possibility that evacuation could be necessary. This plan must describe signals to be used to begin evacuation, evacuation routes, and alternate evacuation routes (in cases where the primary routes could be blocked by releases of hazardous waste or fires).
(Source: Amended at 35 Ill. Reg. 18052, effective October 14, 2011)
Section 725.153 Copies of Contingency Plan
The facility owner or operator must undertake each of the following actions with regard to copies of the contingency plan and all revisions to the plan:
a) It must maintain a copy at the facility; and
b) It must submit a copy to each local police department, fire department, hospital, and State and local emergency response team that may be called upon to provide emergency services at the facility.
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 1031, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 725.154 Amendment of Contingency Plan
The contingency plan must be reviewed and immediately amended, if necessary, whenever any of the following occurs:
a) Applicable regulations are revised;
b) The plan fails in an emergency;
c) The facility changes—in its design, construction, operation, maintenance, or other circumstances—in a way that materially increases the potential for fires, explosions, or releases of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents or changes the response necessary in an emergency;
d) The list of emergency coordinators changes; or
e) The list of emergency equipment changes.
(Source: Amended at 33 Ill. Reg. 1155, effective December 30, 2008)
Section 725.155 Emergency Coordinator
At all times, there must be at least one employee either on the facility premises or on call (i.e., available to respond to an emergency by reaching the facility within a short period of time) with the responsibility for coordinating all emergency response measures. This emergency coordinator must be thoroughly familiar with all aspects of the facility’s contingency plan, all operations and activities at the facility, the location and characteristics of waste handled, the location of all records within the facility and the facility layout. In addition, this person must have the authority to commit the resources needed to carry out the contingency plan.
BOARD NOTE: The emergency coordinator’s responsibilities are more fully spelled out in Section 725.156. Applicable responsibilities for the emergency coordinator vary, depending on factors such as type and variety of wastes handled by the facility and type and complexity of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.156 Emergency Procedures
a) Whenever there is an imminent or actual emergency situation, the emergency coordinator (or his designee when the emergency coordinator is on call) must immediately do the following:
1) He or she must activate internal facility alarms or communication systems, where applicable, to notify all facility personnel; and
2) He or she must notify appropriate State or local agencies with designated response roles if their help is needed.
b) Whenever there is a release, fire, or explosion, the emergency coordinator must immediately identify the character, exact source, amount, and areal extent of any released materials. He or she may do this by observation or review of facility records or manifests and, if necessary, by chemical analysis.
c) Concurrently, the emergency coordinator must assess possible hazards to human health or the environment that may result from the release, fire, or explosion. This assessment must consider both direct and indirect effects of the release, fire, or explosion (e.g., the effects of any toxic, irritating, or asphyxiating gases that are generated, or the effects of any hazardous surface water run-off from water or chemical agents used to control fire and heat-induced explosions).
d) If the emergency coordinator determines that the facility has had a release, fire, or explosion that could threaten human health or the environment outside the facility, the emergency coordinator must report those findings as follows:
1) If the assessment indicates that evacuation of local areas may be advisable, the emergency coordinator must immediately notify appropriate local authorities. The emergency coordinator must be available to help appropriate officials decide whether local areas should be evacuated; and
2) The emergency coordinator must immediately notify either the government official designated as the on-scene coordinator for that geographical area or the National Response Center (using their 24-hour toll free number 800-424-8802). The report must include the following:
A) The name and telephone number of the reporter;
B) The name and address of facility;
C) The time and type of incident (e.g., release, fire, etc.);
D) The name and quantity of materials involved, to the extent known;
E) The extent of injuries, if any; and
F) The possible hazards to human health or the environment outside the facility.
e) During an emergency the emergency coordinator must take all reasonable measures necessary to ensure that fires, explosions, and releases do not occur, recur, or spread to other hazardous waste at the facility. These measures must include, where applicable, stopping processes and operations, collecting and containing released waste, and removing or isolating containers.
f) If the facility stops operations in response to a fire, explosion or release, the emergency coordinator must monitor for leaks, pressure buildup, gas generation, or ruptures in valves, pipes, or other equipment, wherever this is appropriate.
g) Immediately after an emergency, the emergency coordinator must provide for treating, storing, or disposing of recovered waste, contaminated soil, or surface water, or any other material that results from a release, fire, or explosion at the facility.
BOARD NOTE: Unless the owner or operator can demonstrate in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(d) or (e) that the recovered material is not a hazardous waste, the owner or operator becomes a generator of hazardous waste and must manage it in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722, 723, and 725.
h) The emergency coordinator must ensure that, in the affected areas of the facility, the following occur:
1) No waste that may be incompatible with the released material is treated, stored, or disposed of until cleanup procedures are completed; and
2) All emergency equipment listed in the contingency plan is cleaned and fit for its intended use before operations are resumed.
i) The owner or operator must note in the operating record the time, date, and details of any incident that requires implementing the contingency plan. Within 15 days after the incident, it must submit a written report on the incident to the Agency. The report must include the following information:
1) The name, address, and telephone number of the owner or operator;
2) The name, address, and telephone number of the facility;
3) The date, time, and type of incident (e.g., fire, explosion, etc.);
4) The name and quantity of materials involved;
5) The extent of injuries, if any;
6) An assessment of actual or potential hazards to human health or the environment, where this is applicable; and
7) The estimated quantity and disposition of recovered material that resulted from the incident.
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
SUBPART E: MANIFEST SYSTEM, RECORDKEEPING, AND REPORTING
Section 725.170 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart E apply to owners and operators of both on-site and off-site facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise. Sections 725.171, 725.172, and 725.176 do not apply to owners and operators of on-site facilities that do not receive any hazardous waste from off-site sources, nor do they apply to owners and operators of off-site facilities with respect to waste military munitions exempted from manifest requirements under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726.303(a).
(Source: Amended at 35 Ill. Reg. 18052, effective October 14, 2011)
Section 725.171 Use of Manifest System
a) Receipt of Manifested Hazardous Waste
1) If a facility receives hazardous waste accompanied by a manifest, the owner, operator, or its agent must sign and date the manifest, as indicated in subsection (a)(2), to certify that the hazardous waste covered by the manifest was received, that the hazardous waste was received except as noted in the discrepancy space of the manifest, or that the hazardous waste was rejected as noted in the manifest discrepancy space.
2) If a facility receives a hazardous waste shipment accompanied by a manifest, the owner, operator, or its agent must do the following:
A) The owner, operator, or agent must sign and date, by hand, each copy of the manifest;
B) The owner, operator, or agent must note any discrepancies (as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.172) on each copy of the manifest;
C) The owner, operator, or agent must immediately give the transporter at least one copy of the manifest;
D) The owner, operator, or agent must send a copy (Page 3) of the manifest to the generator within 30 days after delivery;
E) Paper manifest submission requirements are the following:
i) The owner, operator, or agent must send the top copy (Page 1) of any paper manifest and any paper continuation sheet to the e-Manifest System for purposes of data entry and processing. In lieu of submitting the paper copy to the e-Manifest System operator, the owner or operator may transmit to the e-Manifest System operator an image file of Page 1 of the manifest and any continuation sheet, or both a data string file and the image file corresponding to Page 1 of the manifest and any continuation sheet, within 30 days after the date of delivery. Submissions of copies to the e-Manifest System must be made at the mailing address or electronic mail/submission address specified at the e-Manifest program website’s directory of services. Beginning on June 30, 2021, USEPA will not accept mailed paper manifests from facilities for processing in the e-Manifest System; and
ii) Options for Compliance on June 30, 2021. Beginning on June 30, 2021, the requirement to submit the top copy (Page 1) of the paper manifest and any paper continuation sheet to the e-Manifest System for purposes of data entry and processing may be met by the owner or operator only by transmitting to the e-Manifest System an image file of Page 1 of the manifest and any continuation sheet, or by transmitting to the e-Manifest System both a data file and the image file corresponding to Page 1 of the manifest and any continuation sheet, within 30 days after the date of delivery. Submissions of copies to the e-Manifest System must be made to the electronic mail/submission address specified at the e-Manifest program website’s directory of services. Beginning on June 30, 2021, USEPA will not accept mailed paper manifests from facilities for processing in the e-Manifest System; andF) The owner, operator, or agent must retain at the facility a copy of each manifest for at least three years after the date of delivery.
3) The owner or operator of a facility that receives hazardous waste subject to Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722 from a foreign source must:
A) Additionally list the relevant consent number from consent documentation supplied by USEPA to the facility for each waste listed on the hazardous waste manifest (USEPA Form 8700-22), matched to the relevant list number for the waste from block 9b. If additional space is needed, the owner or operator should use Continuation Sheets (USEPA Form 8700–22A); and
B) Send a copy of the manifest to USEPA using the addresses listed in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.182(e) within 30 days of delivery until the facility can submit such a copy to the e-Manifest system per subsection (a)(2)(E).
b) If a facility receives from a rail or water (bulk shipment) transporter hazardous waste that is accompanied by a shipping paper containing all the information required on the manifest (excluding the USEPA identification numbers, generator certification, and signatures), the owner or operator or its agent must do each of the following:
1) It must sign and date each copy of the manifest or shipping paper (if the manifest has not been received) to certify that the hazardous waste covered by the manifest or shipping paper was received;
2) It must note any significant discrepancies, as defined in Section 725.172(a), in the manifest or shipping paper (if the manifest has not been received) on each copy of the manifest or shipping paper;
BOARD NOTE: The owner or operator of a facility whose procedures under Section 725.113(c) include waste analysis need not perform that analysis before signing the shipping paper and giving it to the transporter. Section 725.172(b), however, requires reporting an unreconciled discrepancy discovered during later analysis.
3) It must immediately give the rail or water (bulk shipment) transporter at least one copy of the manifest or shipping paper (if the manifest has not been received);
4) The owner or operator must send a copy of the signed and dated manifest or a signed and dated copy of the shipping paper (if the manifest has not been received within 30 days after delivery) to the generator within 30 days after the delivery; and
BOARD NOTE: 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.123(c) requires the generator to send three copies of the manifest to the facility when hazardous waste is sent by rail or water (bulk shipment).
5) Retain at the facility a copy of the manifest and shipping paper (if signed in lieu of the manifest at the time of delivery) for at least three years from the date of delivery.
c) Whenever a shipment of hazardous waste is initiated from a facility, the owner or operator of that facility must comply with the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722. The provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.115, 722.116, and 722.117 apply to the on-site accumulation of hazardous wastes by generators. Therefore, the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.115, 722.116, and 722.117 only apply to an owner or operator that ships hazardous waste that it generated at that facility or operating as an LQG consolidating hazardous waste from VSQGs under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.117(f).
d) As required by 40 CFR 262.84(d)(2)(O), within three working days after the receipt of a shipment subject to Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722, the owner or operator of a facility must provide a copy of the movement document bearing all required signatures to the foreign exporter and to the competent authorities of the countries of export and transit that control the shipment as an export or transit of hazardous waste. On or after the electronic import-export reporting compliance date, to USEPA electronically using USEPA’s WIETS. The original copy of the tracking document must be maintained at the facility for at least three years from the date of signature. The owner or operator of a facility may satisfy this recordkeeping requirement by retaining electronically submitted documents in the facility’s account on USEPA’s WIETS, provided that copies are readily available for viewing and production if requested by any USEPA or authorized state inspector. No owner or operator of a facility may be held liable for the inability to produce the documents for inspection under this section if the owner or operator of a facility can demonstrate that the inability to produce the document is due exclusively to technical difficulty with USEPA’s WIETS, for which the owner or operator of a facility bears no responsibility.
e) A facility must determine whether the consignment state for a shipment regulates any additional wastes (beyond those regulated federally) as hazardous wastes under its state hazardous waste program. A facility must also determine whether the consignment state or generator state requires the facility to submit any copies of the manifest to that state.f) Legal Equivalence to Paper Manifests. E-Manifests that are obtained, completed, transmitted in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.120(a)(3), and used in accordance with this Section in lieu of the paper manifest form are the legal equivalent of paper manifest forms bearing handwritten signatures, and satisfy for all purposes any requirement in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728 to obtain, complete, sign, provide, use, or retain a manifest.
1) Any requirement in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728 for the owner or operator of a facility to sign a manifest or manifest certification by hand, or to obtain a handwritten signature, is satisfied by signing with or obtaining a valid and enforceable electronic signature within the meaning of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.125.
2) Any requirement in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728 to give, provide, send, forward, or to return to another person a copy of the manifest is satisfied when a copy of an e-Manifest is transmitted to the other person.
3) Any requirement in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728 for a manifest to accompany a hazardous waste shipment is satisfied when a copy of an e-Manifest is accessible during transportation and forwarded to the person or persons who are scheduled to receive delivery of the hazardous waste shipment.
4) Any requirement in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728 for an owner or operator to keep or retain a copy of each manifest is satisfied by the retention of the facility’s e-Manifest copies in its account on the e-Manifest System, provided that such copies are readily available for viewing and production if requested by any USEPA or Agency inspector.
5) No owner or operator may be held liable for the inability to produce an e-Manifest for inspection under this Section if the owner or operator can demonstrate that the inability to produce the e-Manifest is due exclusively to a technical difficulty with the e-Manifest System for which the owner or operator bears no responsibility.
g) An owner or operator may participate in the e-Manifest System either by accessing the e-Manifest System from the owner’s or operator’s electronic equipment, or by accessing the e-Manifest System from portable equipment brought to the owner’s or operator’s site by the transporter that delivers the waste shipment to the facility.
h) Special Procedures Applicable to Replacement Manifests. If a facility receives hazardous waste that is accompanied by a paper replacement manifest for a manifest that was originated electronically, the following procedures apply to the delivery of the hazardous waste by the final transporter:
1) Upon delivery of the hazardous waste to the designated facility, the owner or operator must sign and date each copy of the paper replacement manifest by hand in Item 20 (Designated Facility Certification of Receipt) and note any discrepancies in Item 18 (Discrepancy Indication Space) of the paper replacement manifest;
2) The owner or operator of the facility must give back to the final transporter one copy of the paper replacement manifest;
3) Within 30 days after delivery of the hazardous waste to the designated facility, the owner or operator of the facility must send one signed and dated copy of the paper replacement manifest to the generator and send an additional signed and dated copy of the paper replacement manifest to the e-Manifest System; and
4) The owner or operator of the facility must retain at the facility one copy of the paper replacement manifest for at least three years after the date of delivery.
i) Special Procedures Applicable to Electronic Signature Methods Undergoing Tests. If an owner or operator using an e-Manifest signs this manifest electronically using an electronic signature method that is undergoing pilot or demonstration tests aimed at demonstrating the practicality or legal dependability of the signature method, the owner or operator must also sign with an ink signature the facility’s certification of receipt or discrepancies on the printed copy of the manifest provided by the transporter. Upon executing its ink signature on this printed copy, the owner or operator must retain this original copy among its records for at least three years after the date of delivery of the waste.
j) Imposition of User Fee for e-Manifest Use
1) As prescribed in 40 CFR 265.1311, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, and determined in 40 CFR 265.1312, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, an owner or operator that is a user of the e-Manifest System must be assessed a user fee by USEPA for the submission and processing of each e-Manifest and paper manifest. USEPA has stated that it would update the schedule of user fees and publish them to the user community, as provided in 40 CFR 265.1313, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111.
2) An owner or operator subject to user fees under this Section must make user fee payments in accordance with the requirements of 40 CFR 265.1314, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, subject to the informal fee dispute resolution process of 40 CFR 265.1316, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, and subject to the sanctions for delinquent payments under 40 CFR 265.1315, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111.k) E-Manifest Signatures. E-Manifest signatures must meet the criteria described in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.125.
l) Post-Receipt Manifest Data Corrections. After a facility has certified to the receipt of hazardous wastes by signing Item 20 of the manifest, any interested person (i.e., any waste handler shown on the manifest or the Agency) may submit any post-receipt data corrections at any time.
1) An interested person must make all corrections to manifest data by electronic submission, either by directly entering corrected data to the web-based service provided in the e-Manifest System for such corrections, or by an upload of a data file containing data corrections relating to one or more previously submitted manifests.
2) Each correction submission must include the following information:
A) The Manifest Tracking Number and date of receipt by the facility of the original manifests for which data are being corrected;
B) The item numbers of the original manifest that is the subject of the submitted corrections; and
C) For each item number with corrected data, the data previously entered and the corresponding data as corrected by the correction submission.
3) Each correction submission must include a statement that the person submitting the corrections certifies that, to the best of his or her knowledge or belief, the corrections that are included in the submission will cause the information reported about the previously received hazardous wastes to be true, accurate, and complete:
A) The person must execute the certification statement with a valid electronic signature; and
B) The person may submit a batch upload of data corrections under one certification statement.
4) Upon receipt by the e-Manifest System of any correction submission, other interested persons shown on the manifest will be provided electronic notice of the submitter’s corrections.
5) Other interested persons shown on the manifest may respond to the submitter’s corrections with comments to the submitter, or by submitting another correction to the e-Manifest System, certified by the respondent as specified in subsection (l)(3), and with notice of the corrections to other interested persons shown on the manifest.
(Source: Amended at 44 Ill. Reg. 15374, effective September 3, 2020)
Section 725.172 Manifest Discrepancies
a) "Manifest discrepancies" are defined as any one of the following:
1) Significant differences (as defined by subsection (b) between the quantity or type of hazardous waste designated on the manifest or shipping paper, and the quantity and type of hazardous waste a facility actually receives;
2) Rejected wastes, which may be a full or partial shipment of hazardous waste that the treatment, storage, or disposal facility cannot accept; or
3) Container residues, which are residues that exceed the quantity limits for empty containers in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b) and 726.607.
b) "Significant differences in quantity" are defined as the appropriate of the following: for bulk waste, variations greater than 10 percent in weight; or, for batch waste, any variation in piece count, such as a discrepancy of one drum in a truckload. "Significant differences in type" are defined as obvious differences that can be discovered by inspection or waste analysis, such as waste solvent substituted for waste acid, or as toxic constituents not reported on the manifest or shipping paper.
c) Upon discovering a significant difference in quantity or type, the owner or operator must attempt to reconcile the discrepancy with the waste generator or transporter (e.g., with telephone conversations). If the discrepancy is not resolved within 15 days after receiving the waste, the owner or operator must immediately submit to the Agency a letter describing the discrepancy and attempts to reconcile it, and a copy of the manifest or shipping paper at issue.
d) Rejection of Hazardous Waste
1) Upon rejecting waste or identifying a container residue that exceeds the quantity limits for empty containers in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b), the facility owner or operator must consult with the generator before sending the waste to another facility that can manage the waste. If it is impossible to locate an alternative facility that can receive the waste, the facility owner or operator may return the rejected waste or residue to the generator. The facility owner or operator must send the waste to the alternative facility or to the generator within 60 days after the rejection or the container residue identification.
2) While the facility owner or operator is making arrangements for sending rejected wastes or residues to another facility under this Section, it must ensure that either the delivering transporter retains custody of the waste, or the facility owner or operator must provide for secure, temporary custody of the waste, pending delivery of the waste to the first transporter designated on the manifest prepared under subsection (e) or (f).
e) Except as provided in subsection (e)(7), for full or partial load rejections and residues that are to be sent off-site to an alternate facility, the facility owner or operator must prepare a new manifest in compliance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.120(a) and the instructions in subsections (e)(1) through (e)(6):
1) The facility owner or operator must write the generator’s USEPA identification number in Item 1 of the new manifest. The facility owner or operator must write the generator’s name and mailing address in Item 5 of the new manifest. If the mailing address is different from the generator’s site address, then the facility owner or operator must write the generator’s site address in the designated space in Item 5.
2) The facility owner or operator must write the name of the alternate designated facility and the facility’s USEPA identification number in the designated facility block (Item 8) of the new manifest.
3) The facility owner or operator must copy the manifest tracking number found in Item 4 of the old manifest to the Special Handling and Additional Information Block of the new manifest, and indicate that the shipment is a residue or rejected waste from the previous shipment.
4) The facility owner or operator must copy the manifest tracking number found in Item 4 of the new manifest to the manifest reference number line in the Discrepancy Block of the old manifest (Item 18a).
5) The facility owner or operator must write the USDOT description for the rejected load or the residue in Item 9 (USDOT Description) of the new manifest and write the container types, quantity, and volumes of waste.
6) The facility owner or operator must sign the Generator’s/Offeror’s Certification to certify, as the offeror of the shipment, that the waste has been properly packaged, marked and labeled and is in proper condition for transportation, and mail a signed copy of the manifest to the generator identified in Item 5 of the new manifest.
7) For full load rejections that are made while the transporter remains present at the facility, the facility owner or operator may send the rejected shipment to the alternate facility by completing Item 18b of the original manifest and supplying the information on the next destination facility in the Alternate Facility space. The facility owner or operator must retain a copy of this manifest for its records, and then give the remaining copies of the manifest to the transporter to accompany the shipment. If the original manifest is not used, then the facility owner or operator must use a new manifest and comply with subsections (e)(1) through (e)(6).
f) Except as provided in subsection (f)(7), for rejected wastes and residues that must be sent back to the generator, the facility owner or operator must prepare a new manifest in compliance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.120(a) and the instructions in subsections (f)(1) through (f)(6) and (f)(8):
1) The facility owner or operator must write the facility’s USEPA identification number in Item 1 of the new manifest. The facility owner or operator must write the facility’s name and mailing address in Item 5 of the new manifest. If the mailing address is different from the facility’s site address, then the facility owner or operator must write the facility’s site address in the designated space for Item 5 of the new manifest.
2) The facility owner or operator must write the name of the initial generator and the generator’s USEPA identification number in the designated facility block (Item 8) of the new manifest.
3) The facility owner or operator must copy the manifest tracking number found in Item 4 of the old manifest to the Special Handling and Additional Information Block of the new manifest, and indicate that the shipment is a residue or rejected waste from the previous shipment.
4) The facility owner or operator must copy the manifest tracking number found in Item 4 of the new manifest to the manifest reference number line in the Discrepancy Block of the old manifest (Item 18a).
5) The facility owner or operator must write the USDOT description for the rejected load or the residue in Item 9 (USDOT Description) of the new manifest and write the container types, quantity, and volumes of waste.
6) The facility owner or operator must sign the Generator’s/Offeror’s Certification to certify, as offeror of the shipment, that the waste has been properly packaged, marked and labeled and is in proper condition for transportation.
7) For full load rejections that are made while the transporter remains at the facility, the facility owner or operator may return the shipment to the generator with the original manifest by completing Item 18b of the manifest and supplying the generator’s information in the Alternate Facility space. The facility owner or operator must retain a copy for its records and then give the remaining copies of the manifest to the transporter to accompany the shipment. If the original manifest is not used, then the facility owner or operator must use a new manifest and comply with subsections (f)(1) through (f)(6) and (f)(8).
8) For full or partial load rejections and container residues contained in non-empty containers that are returned to the generator, the facility owner or operator must also comply with the exception reporting requirements in Section 722.142(a).
g) If a facility owner or operator rejects a waste or identifies a container residue that exceeds the quantity limits for empty containers in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b) after it has signed, dated, and returned a copy of the manifest to the delivering transporter or to the generator, the facility owner or operator must amend its copy of the manifest to indicate the rejected wastes or residues in the discrepancy space of the amended manifest. The facility owner or operator must also copy the manifest tracking number from Item 4 of the new manifest to the Discrepancy space of the amended manifest, and must re-sign and date the manifest to certify to the information as amended. The facility owner or operator must retain the amended manifest for at least three years from the date of amendment, and must, within 30 days, send a copy of the amended manifest to the transporter and generator that received copies before being amended.
(Source: Amended at 48 Ill. Reg. 17086, effective November 7, 2024)Section 725.173 Operating Record
a) The owner or operator must keep a written operating record at the facility.
b) The following information must be recorded as it becomes available and maintained in the operating record for three years unless otherwise provided as follows:
1) A description and the quantity of each hazardous waste received and the methods and dates of its treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility, as required by Appendix A. This information must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility;
2) The location of each hazardous waste within the facility and the quantity at each location. For disposal facilities the location and quantity of each hazardous waste must be recorded on a map or diagram that shows each cell or disposal area. For all facilities this information must include cross-references to manifest document numbers if the waste was accompanied by a manifest. This information must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility;
BOARD NOTE: See Sections 725.219, 725.379, and 725.409 for related requirements.
3) Records and results of waste analysis, waste determinations, and trial tests performed, as specified in Sections 725.113, 725.300, 725.325, 725.352, 725.373, 725.414, 725.441, 725.475, 725.502, 725.934, 725.963, and 725.984 and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.104(a) and 728.107;
4) Summary reports and details of all incidents that require implementing the contingency plan, as specified in Section 725.156(j);
5) Records and results of inspections, as required by Section 725.115(d) (except these data need be kept only three years);
6) Monitoring, testing, or analytical data, where required by Subpart F or Sections 725.119, 725.194, 725.291, 725.293, 725.295, 725.324, 725.326, 725.355, 725.360, 725.376, 725.378, 725.380(d)(1), 725.402, 725.404, 725.447, 725.477, 725.934(c) through (f), 725.935, 725.963(d) through (i), 725.964, and 725.983 through 725.990. Maintain in the operating record for three years, except for records and results pertaining to groundwater monitoring and cleanup, and response action plans for surface impoundments, waste piles, and landfills, which must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility;
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.194, monitoring data at disposal facilities must be kept throughout the post-closure period.
7) All closure cost estimates under Section 725.242 and, for disposal facilities, all post-closure cost estimates under Section 725.244 must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility;
8) Records of the quantities (and date of placement) for each shipment of hazardous waste placed in land disposal units under an extension of the effective date of any land disposal restriction granted pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.105, a petition pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.106, or a certification under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.108 and the applicable notice required of a generator under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107(a). All of this information must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility;
9) For an off-site treatment facility, a copy of the notice and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required of the generator or the owner or operator under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108;
10) For an on-site treatment facility, the information contained in the notice (except the manifest number) and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required of the generator or the owner or operator under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108;
11) For an off-site land disposal facility, a copy of the notice and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required of the generator or the owner or operator of a treatment facility under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108;
12) For an on-site land disposal facility, the information contained in the notice required of the generator or owner or operator of a treatment facility under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107, except for the manifest number, and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108;
13) For an off-site storage facility, a copy of the notice and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required of the generator or the owner or operator under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108;
14) For an on-site storage facility, the information contained in the notice (except the manifest number) and the certification and demonstration, if applicable, required of the generator or the owner or operator under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.107 or 728.108; and
15) Monitoring, testing or analytical data, and corrective action, where required by Sections 725.190 and 725.193(d)(2) and (d)(5), and the certification, as required by Section 725.296(f), must be maintained in the operating record until closure of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.174 Availability, Retention, and Disposition of Records
a) All records, including plans, required under this Part must be furnished upon request and made available at all reasonable times for inspection by any officer, employee, or representative of the Agency that is duly designated by the Agency.
b) The retention period for all records required under this Part is extended automatically during the course of any unresolved enforcement action regarding the facility or as requested by the Agency.
c) A copy of records of waste disposal locations and quantities under Section 725.173(b)(2) must be submitted to the Agency and local land authority upon closure of the facility (see Section 725.219).
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.175 Annual Report
The owner and operator must complete and submit a Hazardous Waste Report (USEPA Form 8700–13 A/B) to the Agency by March 1 of the following year and must cover facility activities during the previous calendar year.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.176 Unmanifested Waste Report
a) If a facility accepts for treatment, storage, or disposal any hazardous waste from an off-site source without an accompanying manifest, or without an accompanying shipping paper, as described by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 723.120(e), and if the waste is not excluded from the manifest requirement by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 260 through 265, then the owner or operator must prepare and submit a letter to the Agency within 15 days after receiving the waste. The unmanifested waste report must contain the following information:
1) The USEPA identification number, name, and address of the facility;
2) The date the facility received the waste;
3) The USEPA identification number, name, and address of the generator and the transporter, if available;
4) A description and the quantity of each unmanifested hazardous waste the facility received;
5) The method of treatment, storage, or disposal for each hazardous waste;
6) The certification signed by the owner or operator of the facility or its authorized representative; and
7) A brief explanation of why the waste was unmanifested, if known.
b) This subsection (b) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.76(b), which USEPA has marked “reserved”. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal regulations.
BOARD NOTE: Small quantities of hazardous waste are excluded from regulation under this Part and do not require a manifest. Where a facility received unmanifested hazardous waste, USEPA has suggested that the owner or operator obtain from each generator a certification that the waste qualifies for exclusion. Otherwise, USEPA has suggested that the owner or operator file an unmanifested waste report for the hazardous waste movement.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.177 Additional Reports
In addition to submitting the annual report and unmanifested waste reports described in Sections 725.175 and 725.176, the owner or operator must also report the following information to the Agency:
a) Releases, fires, and explosions, as specified in Section 725.156(j);
b) Groundwater contamination and monitoring data, as specified in Section 725.193 and 725.194;
c) Facility closure, as specified in Section 725.215; and
d) As otherwise required by Subparts AA, BB, and CC.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART F: GROUNDWATER MONITORING
Section 725.190 Applicability
a) The owner or operator of a surface impoundment, landfill, or land treatment facility that is used to manage hazardous waste must implement a groundwater monitoring program capable of determining the facility’s impact on the quality of groundwater in the uppermost aquifer underlying the facility, except as Section 725.101 and subsection (c) provide otherwise.
b) Except as subsections (c) and (d) provide otherwise, the owner or operator must install, operate, and maintain a groundwater monitoring system that meets the requirements of Section 725.191 and must comply with Sections 725.192 through 725.194. This groundwater monitoring program must be carried out during the active life of the facility and for disposal facilities during the post-closure care period as well.
c) All or part of the groundwater monitoring requirements of this Subpart F may be waived if the owner or operator can demonstrate that there is a low potential for migration of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents from the facility via the uppermost aquifer to water supply wells (domestic, industrial, or agricultural) or to surface water. This demonstration must be in writing and must be kept at the facility. This demonstration must be certified by a qualified geologist or geotechnical engineer and must establish the following:
1) The potential for migration of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents from the facility to the uppermost aquifer by an evaluation of the following information:
A) A water balance of precipitation, evapotranspiration, run-off, and infiltration; and
B) Unsaturated zone characteristics (i.e., geologic materials, physical properties, and depth to ground water); and
2) The potential for hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that enter the uppermost aquifer to migrate to a water supply well or surface water by an evaluation of the following information:
A) Saturated zone characteristics (i.e., geologic materials, physical properties, and rate of groundwater flow); and
B) The proximity of the facility to water supply wells or surface water.
d) If an owner or operator assumes (or knows) that groundwater monitoring of indicator parameters in accordance with Sections 725.191 and 725.192 would show statistically significant increases (or decreases in the case of pH) when evaluated pursuant to Section 725.193(b), it may install, operate, and maintain an alternate groundwater monitoring system (other than the one described in Sections 725.191 and 725.192). If the owner or operator decides to use an alternate groundwater monitoring system, it must have done as follows:
1) The owner or operator must develop a specific plan, certified by a qualified geologist or geotechnical engineer, that satisfies the requirements of federal 40 CFR 265.93(d)(3) for an alternate groundwater monitoring system. This plan is to be placed in the facility’s operating record and maintained until closure of the facility;
2) The owner or operator must have initiated the determinations specified in federal 40 CFR 265.93(d)(4);
3) The owner or operator must prepare a written report in accordance with Section 725.193(d)(5) and place it in the facility’s operating record and maintain until closure of the facility;
4) The owner or operator must continue to make the determinations specified in Section 725.193(d)(4) on a quarterly basis until final closure of the facility; and
5) The owner or operator must comply with the recordkeeping and reporting requirements in Section 725.194(b).
e) The groundwater monitoring requirements of this Subpart F may be waived with respect to any surface impoundment of which the following is true:
1) The impoundment is used to neutralize wastes that are hazardous solely because they exhibit the corrosivity characteristic pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.122 or which are listed as hazardous wastes in Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721 only for this reason; and
2) The impoundment contains no other hazardous wastes, if the owner or operator can demonstrate that there is no potential for migration of hazardous wastes from the impoundment. The demonstration must establish, based upon consideration of the characteristics of the wastes and the impoundment, that the corrosive wastes will be neutralized to the extent that they no longer meet the corrosivity characteristic before they can migrate out of the impoundment. The demonstration must be in writing and must be certified by a qualified professional.
f) A permit or enforceable document can contain alternative requirements for groundwater monitoring that replace all or part of the requirements of this Subpart F applicable to a regulated unit (as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.190), as provided pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, where the Board has determined by an adjusted standard granted pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104 the following:
1) The regulated unit is situated among solid waste management units (or areas of concern), a release has occurred, and both the regulated unit and one or more solid waste management units (or areas of concern) are likely to have contributed to the release; and
2) It is not necessary to apply the groundwater monitoring requirements of this Subpart F because the alternative requirements will adequately protect human health and the environment. The alternative standards for the regulated unit must meet the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.201(a).
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
Section 725.191 Groundwater Monitoring System
a) A groundwater monitoring system must be capable of yielding groundwater samples for analysis and must consist of the following components:
1) Monitoring wells (at least one) installed hydraulically upgradient (i.e., in the direction of increasing static head) from the limit of the waste management area. Their number, locations, and depths must be sufficient to yield groundwater samples that fulfill both of the following requirements:
A) The samples are representative of background groundwater quality in the uppermost aquifer near the facility; and
B) The samples are not affected by the facility; and
2) Monitoring wells (at least three) installed hydraulically downgradient (i.e., in the direction of decreasing static head) at the limit of the waste management area. Their number, locations, and depths must ensure that they immediately detect any statistically significant amounts of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that migrate from the waste management area to the uppermost aquifer.
b) Separate monitoring systems for each waste management component of a facility are not required provided that provisions for sampling upgradient and downgradient water quality will detect any discharge from the waste management area.
1) In the case of a facility consisting of only one surface impoundment, landfill, or land treatment area, the waste management area is described by the waste boundary (perimeter).
2) In the case of a facility consisting of more than one surface impoundment, landfill, or land treatment area, the waste management area is described by the imaginary boundary line that circumscribes the several waste management components.
3) The facility owner or operator may demonstrate that an alternate hydraulically downgradient monitoring well location will meet the criteria outlined below. The demonstration must be in writing and kept at the facility. The demonstration must be certified by a qualified groundwater scientist and establish each of the following:
A) That an existing physical obstacle prevents monitoring well installation at the hydraulically downgradient limit of the waste management area;
B) That the selected alternate downgradient location is as close to the limit of the waste management area as practical; and
C) That the alternate location ensures detection as early as possible of any statistically significant amounts of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that migrate from the waste management area to the uppermost aquifer.
D) Lateral expansion, new, or replacement units are not eligible for an alternate downgradient location under this subsection (b)(3).
c) All monitoring wells must be cased in a manner that maintains the integrity of the monitoring well bore hole. This casing must be screened or perforated and packed with gravel or sand where necessary to enable sample collection at depths where appropriate aquifer flow zones exist. The annular space (i.e., the space between the bore hole and well casing) above the sampling depth must be sealed with a suitable material (e.g., cement grout or bentonite slurry) to prevent contamination of samples and the groundwater.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.192 Sampling and Analysis
a) The owner or operator must obtain and analyze samples from the installed groundwater monitoring system. The owner or operator must develop and follow a groundwater sampling and analysis plan. The owner or operator must keep this plan at the facility. The plan must include procedures and techniques for each of the following:
1) Sample collection;
2) Sample preservation and shipment;
3) Analytical procedures; and
4) Chain of custody control.
BOARD NOTE: See “Procedures Manual For Ground Water Monitoring At Solid Waste Disposal Facilities”, USEPA document number EPA-530/SW-611, and “Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes”, USEPA document number EPA-600/4-79-020, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), for discussions of sampling and analysis procedures.
b) The owner or operator must determine the concentration or value of the following parameters in groundwater samples in accordance with subsections (c) and (d):
1) Parameters characterizing the suitability of the groundwater as a drinking water supply, as specified in Appendix C.
2) The following parameters establishing groundwater quality:
A) Chloride,
B) Iron,
C) Manganese,
D) Phenols,
E) Sodium, and
F) Sulfate.
BOARD NOTE: These parameters are to be used as a basis for comparison in the event a groundwater quality assessment is required under Section 725.193(d).
3) The following parameters used as indicators of groundwater contamination:
A) pH,
B) Specific Conductance,
C) Total Organic Carbon, and
D) Total Organic Halogen.
c) Establishing Background Concentrations
1) For all monitoring wells, the owner or operator must establish initial background concentrations or values of all parameters specified in subsection (b). The owner or operator must do this quarterly for one year.
2) For each of the indicator parameters specified in subsection (b)(3), the owner or operator must obtain at least four replicate measurements for each sample and determine the initial background arithmetic mean and variance by pooling the replicate measurements for the respective parameter concentrations or values in samples obtained from upgradient wells during the first year.
d) After the first year, the owner or operator must sample all monitoring wells and analyze the samples with the following frequencies:
1) Samples collected to establish groundwater quality must be obtained and analyzed for the parameters specified in subsection (b)(2) at least annually.
2) Samples collected to indicate groundwater contamination must be obtained and analyzed for the parameters specified in subsection (b)(3) at least semi-annually.
e) The owner or operator must determine the elevation of the groundwater surface at each monitoring well each time a sample is obtained.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.193 Preparation, Evaluation, and Response
a) The owner or operator must prepare an outline of a groundwater quality assessment program. The outline must describe a more comprehensive groundwater monitoring program (than that described in Sections 725.191 and 725.192) capable of determining each of the following:
1) Whether hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents have entered the groundwater;
2) The rate and extent of migration of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents in the groundwater; and
3) The concentrations of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents in the groundwater.
b) For each indicator parameter specified in Section 725.192(b)(3), the owner or operator must calculate the arithmetic mean and variance, based on at least four replicate measurements on each sample, for each well monitored in accordance with Section 725.192(d)(2) and compare these results with its initial background arithmetic mean. The comparison must consider individually each of the wells in the monitoring system and must use the Student’s t-test at the 0.01 level of significance (see Appendix D) to determine statistically significant increases (and decreases, in the case of pH) over initial background.
c) Well Comparisons
1) If the comparisons for the upgradient wells made under subsection (b) show a significant increase (or pH decrease) the owner or operator must submit this information in accordance with Section 725.194(a)(2)(B).
2) If the comparisons for downgradient wells made under subsection (b) show a significant increase (or pH decrease) the owner or operator must then immediately obtain additional groundwater samples for those downgradient wells where a significant difference was detected, split the samples in two and obtain analyses of all additional samples to determine whether the significant difference was a result of laboratory error.
d) Notice to the Agency
1) If the analyses performed under subsection (c)(2) confirm the significant increase (or pH decrease) the owner or operator must provide written notice to the Agency—within seven days after the date of such confirmation—that the facility may be affecting groundwater quality.
2) Within 15 days after the notification under subsection (d)(1), the owner or operator must develop a specific plan, based on the outline required under subsection (a) and certified by a qualified geologist or geotechnical engineer for a groundwater quality assessment at the facility. This plan must be placed in the facility operating record and be maintained until closure of the facility.
3) The plan to be submitted under Section 725.190(d)(1) or subsection (d)(2) must specify all of the following:
A) The number, location, and depth of wells;
B) Sampling and analytical methods for those hazardous wastes or hazardous waste constituents in the facility;
C) Evaluation procedures, including any use of previously gathered groundwater quality information; and
D) A schedule of implementation.
4) The owner or operator must implement the groundwater quality assessment plan that satisfies the requirements of subsection (d)(3) and, at a minimum, determine each of the following:
A) The rate and extent of migration of the hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents in the groundwater; and
B) The concentrations of the hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents in the groundwater.
5) The owner or operator must make his first determination under subsection (d)(4), as soon as technically feasible, and prepare a report containing an assessment of the groundwater quality. This report must be placed in the facility operating record and be maintained until closure of the facility.
6) If the owner or operator determines, based on the results of the first determination under subsection (d)(4), that no hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents from the facility have entered the groundwater, then he may reinstate the indicator evaluation program described in Section 725.192 and subsection (b). If the owner or operator reinstates the indicator evaluation program, he must so notify the Agency in the report submitted under subsection (d)(5).
7) If the owner or operator determines, based on the first determination under subsection (d)(4), that hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents from the facility have entered the groundwater, then the owner or operator must do either of the following:
A) It must continue to make the determinations required under subsection (d)(4) on a quarterly basis until final closure of the facility if the groundwater quality assessment plan was implemented prior to final closure of the facility; or
B) It may cease to make the determinations required under subsection (d)(4) if the groundwater quality assessment plan was implemented during the post-closure care period.
e) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Subpart F, any groundwater quality assessment to satisfy the requirements of subsection (d)(4) that is initiated prior to final closure of the facility must be completed and reported in accordance with subsection (d)(5).
f) Unless the groundwater is monitored to satisfy the requirements of subsection (d)(4) at least annually the owner or operator must evaluate the data on groundwater surface elevations obtained under Section 725.192(e) to determine whether the requirements under Section 725.191(a) for locating the monitoring wells continues to be satisfied. If the evaluation shows that Section 725.191(a) is no longer satisfied, the owner or operator must immediately modify the number, location, or depth of the monitoring wells to bring the groundwater monitoring system into compliance with this requirement.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.194 Recordkeeping and Reporting
a) Unless the groundwater is monitored to satisfy the requirements of Section 725.193(d)(4), the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Keep records of the analyses required in Section 725.192(c) and (d), the associated groundwater surface elevations required in Section 725.192(e), and the evaluations required in Section 725.193(b) throughout the active life of the facility and, for disposal facilities, also throughout the post-closure care period; and
2) Report the following groundwater monitoring information to the Agency:
A) During the first year when initial background concentrations are being established for the facility: concentrations or values of the parameters listed in Section 725.192(b)(1) for each groundwater monitoring well, within 15 days after completing each quarterly analysis. The owner or operator must separately identify for each monitoring well any parameters whose concentration or value has been found to exceed the maximum contaminant levels listed in Appendix C to this Part;
B) Annually: concentrations or values of the parameters listed in Section 725.192(b)(3) for each groundwater monitoring well, along with the required evaluations for these parameters under Section 725.193(b). The owner or operator must separately identify any significant differences from initial background found in the upgradient wells, in accordance with Section 725.193(c)(1). During the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must submit this information as part of the annual report required under Section 725.175; and
C) As part of the annual report required under Section 725.175: results of the evaluation of groundwater surface elevations under Section 725.193(f) and a description of the response to the evaluation, where applicable.
b) If the groundwater is monitored to satisfy the requirements of Section 725.193(d)(4), the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Keep records of the analyses and evaluations specified in the plan that satisfy the requirements of Section 725.193(d)(3) throughout the active life of the facility and, for disposal facilities, also throughout the post-closure care period; and
2) Annually, until final closure of the facility, submit to the Agency a report containing the results of the groundwater quality assessment program that includes, but is not limited to, the calculated (or measured) rate of migration of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents in the groundwater during the reporting period. The owner or operator must submit this report as part of the annual report required under Section 725.175.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART G: CLOSURE AND POST-CLOSURE CARE
Section 725.210 Applicability
Except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise, the following requirements apply as indicated:
a) Sections 725.211 through 725.215 (which concern closure) apply to the owners and operators of all hazardous waste management facilities; and
b) Sections 725.216 through 725.220 (which concern post-closure care) apply to the owners and operators of the following:
1) All hazardous waste disposal facilities;
2) Waste piles and surface impoundments from which the owner or operator intends to remove the wastes at closure to the extent that these Sections are made applicable to such facilities in Section 725.328 or 725.358;
3) Tank systems that are required pursuant to Section 725.297 to meet requirements for landfills; or
4) Containment buildings that are required pursuant to Section 725.1102 to meet the requirement for landfills.
c) Section 725.221 applies to owners and operators of units that are subject to the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161 and which are regulated under an enforceable document (as established pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161).
d) A permit or enforceable document can contain alternative requirements that replace all or part of the closure and post-closure care requirements of this Subpart G (and the unit-specific standards in Section 725.211(c)) applying to a regulated unit (as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.190), as provided in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, where the Board has determined by an adjusted standard granted pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104 the following:
1) The regulated unit is situated among solid waste management units (or areas of concern), a release has occurred, and both the regulated unit and one or more solid waste management units (or areas of concern) are likely to have contributed to the release; and
2) It is not necessary to apply the closure requirements of this Subpart G (and those referenced herein) because the alternative requirements will adequately protect human health and the environment, and will satisfy the closure performance standard of Section 725.211 (a) and (b).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.211 Closure Performance Standard
The owner or operator must close the facility in a manner that does the following:
a) The closure minimizes the need for further maintenance;
b) The closure controls, minimizes, or eliminates, to the extent necessary to adequately protect human health and the environment, post-closure escape of hazardous waste, hazardous constituents, leachate, contaminated run-off, or hazardous waste decomposition products to the ground or surface waters or to the atmosphere; and
c) The closure complies with the closure requirements of this Part, including, but not limited to, the requirements of Sections 725.297, 725.328, 725.358, 725.380, 725.410, 725.451, 725.481, 725.504, and 725.1102.
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 1031, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 725.212 Closure Plan; Amendment of Plan
a) Written Plan. Within six months after the effective date of the rule that first subjects a facility to provisions of this Section, the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management facility must have a written closure plan. Until final closure is completed and certified in accordance with Section 725.215, a copy of the most current plan must be furnished to the Agency upon request including request by mail. In addition, for facilities without approved plans, it must also be provided during site inspections on the day of inspection to any officer, employee, or representative of the Agency.
b) Content of Plan. The plan must identify the steps necessary to perform partial or final closure of the facility at any point during its active life. The closure plan must include the following minimal information:
1) A description of how each hazardous waste management unit at the facility will be closed in accordance with Section 725.211;
2) A description of how final closure of the facility will be conducted in accordance with Section 725.211. The description must identify the maximum extent of the operation that will be unclosed during the active life of the facility;
3) An estimate of the maximum inventory of hazardous wastes ever on-site over the active life of the facility and a detailed description of the methods to be used during partial and final closure, including, but not limited to methods for removing, transporting, treating, storing, or disposing of all hazardous waste, and identification of and the types of off-site hazardous waste management units to be used, if applicable;
4) A detailed description of the steps needed to remove or decontaminate all hazardous waste residues and contaminated containment system components, equipment, structures, and soils during partial and final closure including, but not limited to, procedures for cleaning equipment and removing contaminated soils, methods for sampling and testing surrounding soils, and criteria for determining the extent of decontamination necessary to satisfy the closure performance standard;
5) A detailed description of other activities necessary during the partial and final closure periods to ensure that all partial closures and final closure satisfy the closure performance standards, including, but not limited to, groundwater monitoring, leachate collection, and run-on and run-off control;
6) A schedule for closure of each hazardous waste management unit and for final closure of the facility. The schedule must include, at a minimum, the total time required to close each hazardous waste management unit and the time required for intervening closure activities that will allow tracking of the progress of partial and final closure. (For example, in the case of a landfill unit, estimates of the time required to treat or dispose of all hazardous waste inventory and of the time required to place a final cover must be included.);
7) An estimate of the expected year of final closure for facilities that use trust funds to demonstrate financial assurance under Section 725.243 or 725.245 and whose remaining operating life is less than twenty years, and for facilities without approved closure plans; and
8) For a facility where alternative requirements are established at a regulated unit under Section 725.190(f), 725.210(d), or 725.240(d), as provided under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, either the alternative requirements applying to the regulated unit or a reference to the enforceable document containing those alternative requirements.
c) Amendment of Plan. The owner or operator may amend the closure plan at any time prior to the notification of partial or final closure of the facility. An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must submit a written request to the Agency to authorize a change to the approved closure plan. The written request must include a copy of the amended closure plan for approval by the Agency.
1) The owner or operator must amend the closure plan whenever any of the following occurs:
A) Changes in the operating plans or facility design affect the closure plan;
B) Whenever there is a change in the expected year of closure, if applicable;
C) In conducting partial or final closure activities, unexpected events require a modification of the closure plan; or
D) The owner or operator requests the establishment of alternative requirements, as provided under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, to a regulated unit under Section 725.190(f), 725.210(c), or 725.240(d).
2) The owner or operator must amend the closure plan at least 60 days prior to the proposed change in facility design or operation, or no later than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred that has affected the closure plan. If an unexpected event occurs during the partial or final closure period, the owner or operator must amend the closure plan no later than 30 days after the unexpected event. These provisions also apply to owners or operators of surface impoundments and waste piles that intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure but are required to close as landfills in accordance with Section 725.410.
3) An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must submit the modified plan to the Agency at least 60 days prior to the proposed change in facility design or operation, or no more than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred that has affected the closure plan. If an unexpected event has occurred during the partial or final closure period, the owner or operator must submit the modified plan no more than 30 days after the unexpected event. These provisions also apply to owners or operators of surface impoundments and waste piles that intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure but are required to close as landfills in accordance with Section 725.410. If the amendment to the plan is a Class 2 or 3 modification according to the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.280, the modification to the plan must be approved according to the procedures in subsection (d)(4).
4) The Agency may request modifications to the plan under the conditions described in subsection (c)(1). An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must submit the modified plan within 60 days after the request from the Agency, or within 30 days if the unexpected event occurs during partial or final closure. If the amendment is considered a Class 2 or 3 modification according to the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.280, the modification to the plan must be approved in accordance with the procedures in subsection (d)(4).
d) Notification of Partial Closure and Final Closure
1) When Notice is Required
A) The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Agency at least 180 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin closure of the first surface impoundment, waste pile, land treatment, or landfill unit, or final closure if it involves such a unit, whichever is earlier.
B) The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Agency at least 45 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin partial or final closure of a boiler or industrial furnace.
C) The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Agency at least 45 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin final closure of a facility with only tanks, container storage, or incinerator units.
D) An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must notify the Agency in writing at least 60 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin closure of a surface impoundment, waste pile, landfill, or land treatment unit, or final closure of a facility involving such a unit.
E) An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must notify the Agency in writing at least 45 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin partial or final closure of a boiler or industrial furnace.
F) An owner or operator with an approved closure plan must notify the Agency in writing at least 45 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator expects to begin final closure of a facility with only tanks, container storage, or incinerator units.
2) The date when the owner or operator “expects to begin closure” must be either of the following dates:
A) Within 30 days after the date on which any hazardous waste management unit receives the known final volume of hazardous wastes or, if there is a reasonable possibility that the hazardous waste management unit will receive additional hazardous wastes, no later than one year after the date on which the unit received the most recent volume of hazardous waste. If the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management unit demonstrates to the Agency that the hazardous waste management unit or facility has the capacity to receive additional hazardous wastes and that the owner or operator has taken and will continue to take, all steps to prevent threats to human health and the environment, including compliance with all interim status requirements, the Agency must approve an extension to this one-year limit; or
B) For units meeting the requirements of Section 725.213(d), no later than 30 days after the date on which the hazardous waste management unit receives the known final volume of non-hazardous wastes or, if there is a reasonable possibility that the hazardous waste management unit will receive additional non-hazardous wastes, no later than one year after the date on which the unit received the most recent volume of non-hazardous wastes. If the owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that the hazardous waste management unit has the capacity to receive additional non-hazardous wastes and that the owner and operator have taken, and will continue to take, all steps to prevent threats to human health and the environment, including compliance with all applicable interim status requirements, the Agency must approve an extension to this one-year limit.
3) The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Agency no later than 15 days after occurrence of either of the following events:
A) Termination of interim status (except when a permit is issued to the facility simultaneously with termination of interim status); or
B) Issuance of a judicial decree or Board order to cease receiving hazardous wastes or to close the facility or unit.
4) The Agency must provide the owner or operator and the public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments on the plan and request modifications of the plan no later than 30 days from the date of the notice. The Agency must also, in response to a request or at its own discretion, hold a public hearing whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues concerning a closure plan. The Agency must give public notice of the hearing at least 30 days before it occurs. (Public notice of the hearing may be given at the same time as notice of the opportunity for the public to submit written comments and the two notices may be combined.) The Agency must approve, modify, or disapprove the plan within 90 days after its receipt. If the Agency does not approve the plan, the Agency must provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons for the refusal, and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statement. The Agency must approve or modify this plan in writing within 60 days. If the Agency modifies the plan, this modified plan becomes the approved closure plan. The Agency must assure that the approved plan is consistent with Sections 725.211 through 725.215 and the applicable requirements of Sections 725.190 et seq., 725.297, 725.328, 725.358, 725.380, 725.410, 725.451, 725.481, 725.504, and 725.1102. A copy of this modified plan with a detailed statement of reasons for the modifications must be mailed to the owner or operator.
e) Removal of Wastes and Decontamination or Dismantling of Equipment. Nothing in this Section precludes the owner or operator from removing hazardous wastes and decontaminating or dismantling equipment in accordance with the approved partial or final closure plan at any time before or after notification of partial or final closure.
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
Section 725.213 Closure; Time Allowed for Closure
a) Within 90 days after receiving the final volume of hazardous wastes, or the final volume of non-hazardous wastes, if the owner or operator complies with all the applicable requirements of subsections (d) and (e) at a hazardous waste management unit or facility, or 90 days after approval of the closure plan, whichever is later, the owner or operator must treat, remove from the unit or facility, or dispose of on-site all hazardous wastes in accordance with the approved closure plan. The Agency must approve a longer period if the owner or operator demonstrates the following:
1) The need to remain in operation by showing either of the following conditions exists:
A) The activities required to comply with this subsection (a) will, of necessity, take longer than 90 days to complete; or
B) All of the following conditions are true:
i) The hazardous waste management unit or facility has the capacity to receive additional hazardous wastes, or has the capacity to receive non-hazardous wastes, if the owner or operator complies with subsections (d) and (e);
ii) There is a reasonable likelihood that the owner or operator, or another person will recommence operation of the hazardous waste management unit or facility within one year; and
iii) Closure of the hazardous waste management unit or facility would be incompatible with continued operation of the site; and
2) The owner or operator has taken and will continue to take all steps to prevent threats to human health and the environment including compliance with all applicable interim status requirements.
b) The owner or operator must complete partial and final closure activities in accordance with the approved closure plan and within 180 days after receiving the final volume of hazardous wastes, or the final volume of non-hazardous wastes, if the owner or operator complies with all applicable requirements of subsections (d) and (e) at the hazardous waste management unit or facility, or 180 days after approval of the closure plan, if that is later. The Agency must approve an extension to the closure period if the owner or operator demonstrates the following:
1) The need to remain in operation by showing either of the following conditions exists:
A) The partial or final closure activities will, of necessity, take longer than 180 days to complete; or
B) All of the following conditions are true:
i) The hazardous waste management unit or facility has the capacity to receive additional hazardous wastes, or the final volume of non-hazardous wastes, if the owner or operator complies with all the applicable requirements of subsections (d) and (e); and
ii) There is a reasonable likelihood that the owner or operator or another person will recommence operation of the hazardous waste management unit or facility within one year; and
iii) Closure of the hazardous waste management unit or facility would be incompatible with continued operation of the site; and
2) The owner or operator has taken and will continue to take all steps to prevent threats to human health and the environment from the unclosed but not operating hazardous waste management unit or facility, including compliance with all applicable interim status requirements.
c) The demonstration referred to in subsections (a)(1) and (b)(1) must be made as follows:
1) The demonstration in subsection (a)(1) must be made at least 30 days prior to the expiration of the 90-day period in subsection (a); and
2) The demonstrations in subsection (b)(1) must be made at least 30 days prior to the expiration of the 180-day period in subsection (b), unless the owner or operator is otherwise subject to deadlines in subsection (d).
d) Continued Receipt of Non-Hazardous Waste. The Agency must permit an owner or operator to receive non-hazardous wastes in a landfill, land treatment unit or surface impoundment unit after the final receipt of hazardous wastes at that unit if the following are true:
1) The owner or operator submits an amended Part B application, or a new Part B application if none was previously submitted, and demonstrates the following:
A) The unit has the existing design capacity as indicated on the Part A application to receive non-hazardous wastes;
B) There is a reasonable likelihood that the owner or operator or another person will receive non-hazardous waste in the unit within one year after the final receipt of hazardous wastes;
C) The non-hazardous wastes will not be incompatible with any remaining wastes in the unit, or with the facility design and operating requirements of the unit or facility pursuant to this Part;
D) Closure of the hazardous waste management unit would be incompatible with continued operation of the unit or facility; and
E) The owner or operator is operating and will continue to operate in compliance with all applicable interim status requirements;
2) The Part B application includes an amended waste analysis plan, groundwater monitoring and response program, human exposure assessment required pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.186, closure and post-closure care plans, updated cost estimates, and demonstrations of financial assurance for closure and post-closure care, as necessary and appropriate, to reflect any changes due to the presence of hazardous constituents in the non-hazardous wastes and changes in closure activities, including the expected year of closure, if applicable pursuant to Section 725.212(b)(7), as a result of the receipt of non-hazardous wastes following the final receipt of hazardous wastes;
3) The Part B application is amended, as necessary and appropriate, to account for the receipt of non-hazardous wastes following receipt of the final volume of hazardous wastes; and
4) The Part B application and the demonstrations referred to in subsections (d)(1) and (d)(2) are submitted to the Agency no later than 180 days prior to the date on which the owner or operator of the facility receives the known final volume of hazardous wastes or no later than 90 days after this Section applies to the facility, whichever is later.
e) Surface Impoundments. In addition to the requirements in subsection (d), an owner or operator of a hazardous waste surface impoundment that is not in compliance with the liner and leachate collection system requirements in Section 725.321(a) must receive non-hazardous wastes only as authorized by an adjusted standard pursuant to this subsection (e).
1) The petition for adjusted standard must include the following:
A) A plan for removing hazardous wastes; and
B) A contingent corrective measures plan.
2) The removal plan must provide for the following:
A) Removing all hazardous liquids;
B) Removing all hazardous sludges to the extent practicable without impairing the integrity of the liner or liners, if any; and
C) Removal of hazardous wastes no later than 90 days after the final receipt of hazardous wastes. The Board will allow a longer time, if the owner or operator demonstrates the following:
i) That the removal of hazardous wastes will, of necessity, take longer than the allotted period to complete; and
ii) That an extension will not pose a threat to human health and the environment.
3) The following is required of contingent corrective measures plan:
A) It must meet the requirements of a corrective action plan pursuant to Section 724.199, based upon the assumption that a release has been detected from the unit.
B) It may be a portion of a corrective action plan previously submitted pursuant to Section 724.199.
C) It may provide for continued receipt of non-hazardous wastes at the unit following a release only if the owner or operator demonstrates that continued receipt of wastes will not impede corrective action.
D) It must provide for implementation within one year after a release, or within one year after the grant of the adjusted standard, whichever is later.
4) Release. A release is a statistically significant increase (or decrease in the case of pH) in hazardous constituents over background levels, detected in accordance with the requirements in Subpart F.
5) In the event of a release, the owner or operator of the unit must perform the following actions:
A) Within 35 days, the owner or operator must file with the Board a petition for adjusted standard pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104. If the Board finds that it is necessary to do so in order to adequately protect human health and the environment, the Board will modify the adjusted standard to require the owner or operator to perform either of the following actions:
i) Begin to implement the corrective measures plan in less than one year; or
ii) Cease the receipt of wastes until the plan has been implemented.
iii) The Board will retain jurisdiction or condition the adjusted standard so as to require the filing of a new petition to address any required closure pursuant to subsection (e)(7);
B) The owner or operator must implement the contingent corrective measures plan; and
C) The owner or operator may continue to receive wastes at the unit if authorized by the approved contingent measures plan.
6) Annual Report. During the period of corrective action, the owner or operator must provide annual reports to the Agency that fulfill the following requirements:
A) They must describe the progress of the corrective action program;
B) They must compile all groundwater monitoring data; and
C) They must evaluate the effect of the continued receipt of non-hazardous wastes on the effectiveness of the corrective action.
7) Required Closure. The owner or operator must commence closure of the unit in accordance with the closure plan and the requirements of this Part if the Board terminates the adjusted standard, or if the adjusted standard terminates pursuant to its terms.
A) The Board will terminate the adjusted standard if the owner or operator failed to implement corrective action measures in accordance with the approved contingent corrective measures plan.
B) The Board will terminate the adjusted standard if the owner or operator fails to make substantial progress in implementing the corrective measures plan and achieving the facility’s groundwater protection standard, or background levels if the facility has not yet established a groundwater protection standard.
C) The adjusted standard will automatically terminate if the owner or operator fails to implement the removal plan.
D) The adjusted standard will automatically terminate if the owner or operator fails to timely file a required petition for adjusted standard.
8) Adjusted Standard Procedures. The following procedures must be used in granting, modifying or terminating an adjusted standard pursuant to this subsection.
A) Except as otherwise provided, the owner or operator must follow the procedures of Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104 to petition the Board for an adjusted standard.
B) Initial Justification. The Board will grant an adjusted standard, pursuant to subsection (e)(1), if the owner or operator demonstrates that the removal plan and contingent corrective measures plans meet the requirements of subsections (e)(2) and (e)(3).
C) The Board will include the following conditions in granting an adjusted standard pursuant to subsection (e)(1):
i) A plan for removing hazardous wastes;
ii) A requirement that the owner or operator remove hazardous wastes in accordance with the plan;
iii) A contingent corrective measures plan;
iv) A requirement that, in the event of a release, the owner or operator must, within 35 days, file with the Board a petition for adjusted standard, implement the corrective measures plan, and file semi-annual reports with the Agency;
v) A condition that the adjusted standard will terminate if the owner or operator fails to implement the removal plan or timely file a required petition for adjusted standard; and
vi) A requirement that, in the event the adjusted standard is terminated, the owner or operator must commence closure of the unit in accordance with the requirements of the closure plan and this Part.
D) Justification in the Event of a Release. The Board will modify or terminate the adjusted standard pursuant to a petition filed pursuant to subsection (e)(5)(A), as provided in that subsection or in subsection (e)(7).
9) The owner or operator may file a revised closure plan within 15 days after an adjusted standard is terminated.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.214 Disposal or Decontamination of Equipment, Structures, and Soils
During the partial and final closure periods, all contaminated equipment, structures, and soil must be properly disposed of, or decontaminated unless specified otherwise in Section 725.297, 725.328, 725.358, 725.380, or 725.410. By removing all hazardous wastes or hazardous constituents during partial and final closure, the owner or operator may become a generator of hazardous waste and must handle that hazardous waste in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.215 Certification of Closure
Within 60 days after completion of closure of each hazardous waste surface impoundment, waste pile, land treatment, and landfill unit, and within 60 days after completion of final closure, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency, by registered mail, a certification that the hazardous waste management unit or facility, as applicable, has been closed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan. The certification must be signed by the owner or operator and by a qualified Professional Engineer. Documentation supporting Professional Engineer’s certification must be furnished to the Agency upon request until the Agency releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for closure under Section 725.243(h).
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.216 Survey Plat
No later than the submission of the certification of closure of each hazardous waste disposal unit, an owner or operator must submit to any local zoning authority, or authority with jurisdiction over local land use, to the County Recorder and to the Agency, a survey plat indicating the location and dimensions of landfill cells or other hazardous waste disposal units with respect to permanently surveyed benchmarks. This plat must be prepared and certified by a professional land surveyor. The plat filed with any local zoning authority, or authority with jurisdiction over local land use, and the County Recorder must contain a note, prominently displayed, that states the owner’s and operator’s obligation to restrict disturbance of the hazardous waste disposal unit in accordance with the applicable regulations of this Subpart G.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.217 Post-Closure Care and Use of Property
a) Post-Closure Care
1) Post-closure care for each hazardous waste management unit subject to the requirements of Sections 725.217 through 725.220 must begin after completion of closure of the unit and continue for 30 years after that date. It must consist of at least the following:
A) Monitoring and reporting in accordance with the requirements of Subparts F, K, L, M, and N; and
B) Maintenance and monitoring of waste containment systems in accordance with the requirements of Subparts F, K, L, M, and N.
2) Any time preceding closure of a hazardous waste management unit subject to post-closure care requirements or final closure, or any time during the post-closure period for a particular hazardous waste disposal unit, the Board will, by an adjusted standard granted pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104 or by an order in some other appropriate type of proceeding (e.g., an enforcement proceeding), do the following:
A) Shorten the post-closure care period applicable to the hazardous waste management unit, or facility, if all disposal units have been closed, if the Board finds that the reduced period is sufficient to adequately protect human health and the environment (e.g., leachate or groundwater monitoring results; characteristics of the hazardous waste; application of advanced technology; or alternative disposal, treatment, or re-use techniques indicate that the hazardous waste management unit or facility is secure); or
B) Extend the post-closure care period applicable to the hazardous waste management unit or facility, if the Board finds that the extended period is necessary to adequately protect human health and the environment (e.g., leachate or groundwater monitoring results indicate a potential for migration of hazardous wastes at levels that may be harmful to human health and the environment).
3) As provided by Section 725.218(i), the Board will utilize site-specific rulemaking to adjust the length of the post-closure care period.
b) The Agency must require, at partial or final closure, continuation of any of the security requirements of Section 725.214 during part or all of the post-closure period when either of the following occurs:
1) Hazardous wastes may remain exposed after completion of partial or final closure; or
2) Access by the public or domestic livestock may pose a hazard to human health.
c) Post-closure use of property on or in which hazardous wastes remain after partial or final closure must never be allowed to disturb the integrity of the final cover, liners, or any other components of any containment system or the function of the facility’s monitoring systems, unless the Agency determines either of the following with respect to the disturbance:
1) It is necessary to the proposed use of the property, and will not increase the potential hazard to human health or the environment; or
2) It is necessary to reduce a threat to human health or the environment.
d) All post-closure care activities must be performed in accordance with the provisions of the approved post-closure plan, as specified in Section 725.218.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.218 Post-Closure Care Plan; Amendment of Plan
a) Written Plan. The owner or operator of a hazardous waste disposal unit must have a written post-closure care plan. An owner or operator of a surface impoundment or waste pile that intends to remove all hazardous wastes at closure must prepare a post-closure care plan and submit it to the Agency within 90 days after the date that the owner or operator or Agency determines that the hazardous waste management unit or facility must be closed as a landfill, subject to the requirements of Sections 725.217 through 725.220.
b) Until final closure of the facility, a copy of the most current post-closure care plan must be furnished to the Agency upon request, including request by mail. In addition, for facilities without approved post-closure care plans, it must also be provided during site inspections, on the day of inspection, to any officer, employee, or representative of the Agency. After final closure has been certified, the person or office specified in subsection (c)(3) must keep the approved post-closure care plan during the post-closure care period.
c) For each hazardous waste management unit subject to the requirements of this Section, the post-closure care plan must identify the activities that will be carried on after closure of each disposal unit and the frequency of these activities and include the following minimal information:
1) A description of the planned monitoring activities and frequencies at which they will be performed to comply with Subparts F, K, L, M, and N during the post-closure care period;
2) A description of the planned maintenance activities and frequencies at which they will be performed to ensure the following:
A) The integrity of the cap and final cover or other containment systems in accordance with the requirements of Subparts K, L, M, and N; and
B) The function of the monitoring equipment in accordance with the requirements of Subparts F, K, L, M, and N;
3) The name, address, and phone number of the person or office to contact about the hazardous waste disposal unit or facility during the post-closure care period;
4) For a facility subject to Section 725.221, provisions that satisfy the requirements of Section 725.221(a)(1) and (a)(3); and
5) For a facility where alternative requirements are established at a regulated unit under Section 725.190(f), 725.210(d), or 725.240(d), as provided under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, either the alternative requirements that apply to the regulated unit, or a reference to the enforceable document containing those requirements.
d) Amendment of Plan. The owner or operator may amend the post-closure care plan at any time during the active life of the facility or during the post-closure care period. An owner or operator with an approved post-closure care plan must submit a written request to the Agency to authorize a change to the approved plan. The written request must include a copy of the amended post-closure care plan for approval by the Agency.
1) The owner or operator must amend the post-closure care plan whenever the following occur:
A) Changes in operating plans or facility design affect the post-closure care plan; or
B) Events occur during the active life of the facility, including partial and final closures, that affect the post-closure care plan; and
C) The owner or operator requests the establishment of alternative requirements to a regulated unit under Section 725.190(f), 725.210(d), or 725.240(d).
2) The owner or operator must amend the post-closure care plan at least 60 days prior to the proposed changes in facility design or operation, or no later than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred that has affected the post-closure care plan.
3) An owner or operator with an approved post-closure care plan must submit the modified plan to the Agency at least 60 days prior to the proposed change in facility design or operation, or no more than 60 days after an unexpected event has occurred that has affected the post-closure care plan. If an owner or operator of a surface impoundment or a waste pile that intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure in accordance with Section 725.328(b) or 725.358(a) is required to close as a landfill in accordance with Section 725.410, the owner or operator must submit a post-closure care plan within 90 days after the determination by the owner or operator or Agency that the unit must be closed as a landfill. If the amendment to the post-closure care plan is a Class 2 or 3 modification according to the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.280, the modification to the plan must be approved according to the procedures in subsection (f).
4) The Agency may request modifications to the plan under the conditions described in subsection (d)(1). An owner or operator with an approved post-closure care plan must submit the modified plan no later than 60 days after the request from the Agency. If the amendment to the plan is considered a Class 2 or 3 modification according to the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.280 the modifications to the post-closure care plan must be approved in accordance with the procedures in subsection (f). If the Agency determines that an owner or operator of a surface impoundment or waste pile that intended to remove all hazardous wastes at closure must close the facility as a landfill, the owner or operator must submit a post-closure care plan for approval to the Agency within 90 days after the determination.
e) The owner or operator of a facility with hazardous waste management units subject to these requirements must submit the post-closure care plan to the Agency at least 180 days before the date the owner or operator expects to begin partial or final closure of the first hazardous waste disposal unit. The date when the owner or operator “expects to begin closure” of the first hazardous waste disposal unit must be either within 30 days after the date on which the hazardous waste management unit receives the known final volume of hazardous waste or, if there is a reasonable possibility that the hazardous waste management unit will receive additional hazardous wastes, no later than one year after the date on which the unit received the most recent volume of hazardous wastes. The owner or operator must submit the closure plan to the Agency no later than 15 days after either of the following:
1) Termination of interim status (except when a permit is issued to the facility simultaneously with termination of interim status); or
2) Issuance of a judicial decree or Board order to cease receiving wastes or close.
f) Procedures
1) Except as provided in subsection (f)(2), the Agency must provide the owner or operator and the public through a newspaper notice the opportunity to submit written comments on the post-closure care plan and request modifications to the plan, no later than 30 days after the date of the notice. The Agency may also, in response to a request or at its own discretion, hold a public hearing whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues concerning the post-closure care plan. The Agency must give public notice of the hearing at least 30 days before it occurs. (Public notice of the hearing may be given at the same time as notice of the opportunity for written public comments and the two notices may be combined.) The Agency must approve, modify, or disapprove the plan within 90 days after its receipt. If the Agency determines not to approve the plan, the Agency must provide the owner or operator with a detailed statement of reasons for the refusal and the owner or operator must modify the plan or submit a new plan for approval within 30 days after receiving such written statements. The Agency must approve or modify this plan in writing within 60 days. If the Agency modifies the plan, this modified plan becomes the approved post-closure care plan. Any final Agency determination must ensure that the approved post-closure care plan is consistent with Sections 725.217 through 725.220. A copy of this modified plan with a detailed statement of reasons for the modifications must be mailed to the owner or operator.
2) The Agency must not provide notice or the opportunity for public comment if, in a prior proceeding, the Board has ordered the modifications to the plan.
g) The post-closure care plan and length of the post-closure care period may be modified at any time prior to the end of the post-closure care period in either of the following two ways:
1) The owner or operator or any member of the public may petition to extend or reduce the post-closure care period applicable to a hazardous waste management unit or facility based on cause, or alter the requirements of the post-closure care period based on cause.
A) The petition must include evidence demonstrating either of the following:
i) The secure nature of the hazardous waste management unit or facility makes the post-closure care requirements unnecessary or supports reduction of the post-closure care period specified in the current post-closure care plan (e.g., leachate or groundwater monitoring results; characteristics of the waste; application of advanced technology; or alternative disposal, treatment, or re-use techniques indicate that the facility is secure), or
ii) The requested extension in the post-closure care period or alteration of post-closure care requirements is necessary to prevent threats to human health and the environment (e.g., leachate or groundwater monitoring results indicate a potential for migration of hazardous wastes at levels that may be harmful to human health and the environment).
B) These petitions must be considered only when they present new and relevant information not previously considered.
i) Except as provided in subsection (g)(1)(B)(ii), whenever the Agency is considering a petition, it must provide the owner or operator and the public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments within 30 days after the date of the notice. The Agency must also, in response to a request or at its own discretion, hold a public hearing whenever a hearing might clarify one or more issues concerning the post-closure care plan. The Agency must give the public notice of the hearing at least 30 days before it occurs. (Public notice of the hearing may be given at the same time as notice of the opportunity for written public comments and the two notices may be combined.) After considering the comments, the Agency must issue a final determination, based upon the criteria set forth in subsection (g)(1).
ii) The Agency must not provide notice or the opportunity for public comment if, in a prior proceeding, the Board has ordered the modifications to the plan.
C) If the Agency denies the petition, it must send the petitioner a brief written response giving a reason for the denial.
2) The Agency must tentatively decide to modify the post-closure care plan if the Agency determines that it is necessary to prevent threats to human health and the environment. The Agency may propose to extend or reduce the post-closure care period applicable to a hazardous waste management unit or facility based on cause or alter the requirements of the post-closure care period based on cause.
A) The Agency must provide the owner or operator and the affected public, through a newspaper notice, the opportunity to submit written comments within 30 days after the date of the notice and the opportunity for a public hearing as in subsection (g)(1)(B). After considering the comments, the Agency must issue a final determination.
B) The Agency must base its final determination upon the same criteria as required for petitions under subsection (g)(1)(A). A modification of the post-closure care plan may include, where appropriate, the temporary suspension rather than permanent deletion of one or more post-closure care requirements. At the end of the specified period of suspension, the Agency would then determine whether the requirements should be permanently discontinued or reinstated to prevent threats to human health and the environment.
h) The Agency procedures described in Sections 725.212 through 725.219 are in the nature of permit amendments. Amendment of refusal to amend the plan is a permit denial for purposes of appeal pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 105. The Agency must not amend permits in such a manner so that the permit would not conform with Board regulations.
i) If any person seeks a closure or post-closure care plan that would not conform with Board regulations, such person must file a site-specific rulemaking petition pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 102 or a variance petition pursuant to Sections 35 through 38 of the Act and Subpart B of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.219 Post-Closure Notices
Within 90 days after closure is completed, the owner or operator of a disposal facility must submit to the County Recorder and to the Agency a survey plat indicating the location and dimensions of landfill cells or other disposal areas with respect to permanently surveyed benchmarks. This plat must be prepared and certified by a professional land surveyor. The plat filed with the County Recorder must contain a note, prominently displayed, that states the owner’s or operator’s obligation to restrict disturbance of the site as specified in Section 725.217(c). In addition, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency and to the County Recorder a record of the type, location, and quantity of hazardous waste disposed of within each cell or area of the facility. The owner or operator must identify the type, location, and quantity of hazardous wastes disposed of within each cell or area of the facility. For wastes disposed of before these regulations were promulgated, the owner or operator must identify the type, location, and quantity of the wastes to the best of his knowledge and in accordance with any records the owner or operator has kept.
a) No later than 60 days after certification of closure of each hazardous waste disposal unit, the owner or operator must submit to the County Recorder, to any local zoning authority, or any authority with jurisdiction over local land use, and to the Agency, a record of the type, location, and quantity of hazardous wastes disposed of within each cell or other disposal unit of the facility. For hazardous wastes disposed of before January 12, 1981, the owner or operator must identify the type, location, and quantity of the hazardous wastes to the best of the owner or operator’s knowledge and in accordance with any records the owner or operator has kept.
b) Within 60 days after certification of closure of the first hazardous waste disposal unit and within 60 days after certification of closure of the last hazardous waste disposal unit, the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Record, in accordance with Illinois law, a notation on the deed to the facility property, or on some other instrument that is normally examined during title search, that will in perpetuity notify any potential purchaser of the property of the following:
A) The land has been used to manage hazardous wastes;
B) Its use is restricted pursuant to Subpart G; and
C) The survey plat and record of the type, location, and quantity of hazardous wastes disposed of within each cell or other hazardous waste disposal unit of the facility required by Sections 725.216 and 725.219(a) have been filed with the County Recorder, any local zoning authority, or any authority with jurisdiction over local land use, and with the Agency; and
2) Submit to the Agency a certification signed by the owner or operator that the owner or operator has recorded the notation specified in subsection (b)(1), together with a copy of the document in which the notation has been placed.
c) If the owner or operator or any subsequent owner of the land upon which a hazardous waste disposal unit was located wishes to remove hazardous wastes and hazardous waste residues; the liner, if any; and all contaminated structures, equipment, and soils, such person must request a modification to the approved post-closure plan in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.218(g). The owner or operator must demonstrate that the removal of hazardous wastes will satisfy the criteria of Section 725.217(c). By removing hazardous waste, the owner or operator may become a generator of hazardous waste and must manage it in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, 720 through 728, and 738. If the owner or operator is granted approval to conduct the removal activities, the owner or operator may request that the Agency approve either of the following:
1) Removal of the notation on the deed to the facility property or other instrument normally examined during title search, or
2) Addition of a notation to the deed or instrument indicating the removal of the hazardous waste.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.220 Certification of Completion of Post-Closure Care
No later than 60 days after the completion of the established post-closure care period for each hazardous waste disposal unit, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency, by registered mail, a certification that the post-closure care period for the hazardous waste disposal unit was performed in accordance with the specifications in the approved post-closure plan. The certification must be signed by the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer. Documentation supporting the Professional Engineer’s certification must be furnished to the Agency upon request until the Agency releases the owner or operator from the financial assurance requirements for post-closure care under Section 725.245(h).
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.221 Alternative Post-Closure Care Requirements
a) An owner or operator that is subject to the requirement to obtain a post-closure care permit under Subpart B of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703 but which obtains an enforceable document in lieu of a post-closure permit, as provided in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, must comply with the following requirements:
1) The requirements to submit information about the facility in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.214;
2) The requirements for facility-wide corrective action in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.201; and
3) The requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.191 through 724.200.
b) Implementation of Alternative Requirements
1) Public Notice, Public Comments, and Public Hearing.
A) In establishing alternative requirements in an enforceable document in lieu of a permit under this Section, the Board will assure a meaningful opportunity for public involvement that, at a minimum, includes public notice and opportunity for public comment, as provided under the relevant provisions of the Act:
i) For a site-specific rulemaking, in Sections 27 and 28 of the Act.
ii) For an adjusted standard, in Section 28.1 of the Act.
iii) For a variance, in Sections 35 through 38 of the Act.
iv) For an order issued pursuant to Section 33(a) of the Act, in Sections 31, 32, and 33 of the Act.
B) When an owner or operator submits a plan to the Agency pursuant to an appropriate statutory or regulatory authority, the Agency must provide public notice and an opportunity for public hearing on the plan according to the requirements of Subparts D and E of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705 as follows:
i) When the Agency becomes involved in remedial action at the facility under regulations or in an enforcement action;
ii) On the proposed preferred remedy and on the assumptions on which the remedy is based, especially those relating to land use and site characterization; and
iii) At the time of a proposed decision that remedial action is complete at the facility.
C) The requirements of subsection (b)(1)(B) must be met before the Agency may consider that the facility owner or operator has met the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, unless the facility qualifies for a modification to these public participation requirements under either of subsection (b)(2) or (b)(3).
2) If the Agency determines that even a short delay in the implementation of a remedy would adversely affect human health or the environment, the Agency may delay compliance with the requirements of subsection (b)(1)(B) and immediately implement the remedy. However, the Agency must assure involvement of the public at the earliest opportunity and, in all cases, upon making the decision that additional remedial action is not needed at the facility.
3) The Agency may allow a remediation initiated prior to August 6, 1999 to substitute for corrective action required under a post-closure care permit.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART H: FINANCIAL REQUIREMENTS
Section 725.240 Applicability
a) The requirements of Sections 725.242, 725.243, and 725.247 through 725.250 apply to owners and operators of all hazardous waste facilities, except as provided otherwise in this Section or in Section 725.101.
b) The requirements of Sections 725.244 and 725.245 apply only to owners and operators of any of the following:
1) Disposal facilities;
2) Tank systems that are required pursuant to Section 725.297 to meet the requirements for landfills; or
3) Containment buildings that are required pursuant to Section 725.1102 to meet the requirements for landfills.
c) States and the federal government are exempt from the requirements of this Subpart H.
d) A permit or enforceable document can contain alternative requirements that replace all or part of the financial assurance requirements of this Subpart H applying to a regulated unit, as provided in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.161, where the Board or Agency has done the following:
1) The Board, by an adjusted standard granted pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104, has established alternative requirements for the regulated unit established pursuant to Section 725.190(f) or Section 724.210(d); and
2) The Board has determined that it is not necessary to apply the financial assurance requirements of this Subpart H because the alternative financial assurance requirements will adequately protect human health and the environment.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.241 Definitions of Terms as Used in this Subpart H
a) “Closure plan” means the plan for closure prepared in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.212.
b) “Current closure cost estimate” means the most recent of the estimates prepared in accordance with Sections 725.242(a), (b), and (c).
c) “Current post-closure cost estimate” means the most recent of the estimates prepared in accordance with Sections 725.244(a), (b), and (c).
d) “Parent corporation” means a corporation that directly owns at least 50 percent of the voting stock of the corporation that is the facility owner or operator; the latter corporation is deemed a “subsidiary” of the parent corporation.
e) “Post-closure plan” means the plan for post-closure care prepared in accordance with the requirements of Sections 725.217 through 725.220.
f) The following terms are used in the specifications for the financial tests for closure, post-closure care, and liability coverage. The definitions are intended to assist in the understanding of these regulations and are not intended to limit the meanings of terms in a way that conflicts with generally accepted accounting practices.
“Assets” mean all existing and all probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity.
“Current assets” mean cash or other assets or resources commonly identified as those that are reasonably expected to be realized in cash or sold or consumed during the normal operating cycle of the business.
“Current liabilities” means obligations whose liquidation is reasonably expected to require the use of existing resources properly classifiable as current assets or the creation of other current liabilities.
“Current plugging and abandonment cost estimate” means the most recent of the estimates prepared in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.212(a), (b), and (c).
“Independently audited” refers to an audit performed by an independent certified public accountant in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards.
“Liabilities” means probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events.
“Net working capital” means current assets minus current liabilities.
“Net worth” means total assets minus total liabilities and is equivalent to owner’s equity.
“Tangible net worth” means the tangible assets that remain after deducting liabilities; such assets would not include intangibles, such as goodwill and rights to patents or royalties.
g) In the liability insurance requirements the terms “bodily injury” and “property damage” have the meanings given below. The Board intends the meanings of other terms used in the liability insurance requirements to be consistent with their common meanings within the insurance industry. The definitions given below of several of the terms are intended to assist in the understanding of these regulations and are not intended to limit their meanings in a way that conflicts with general insurance industry usage.
“Accidental occurrence” means an accident, including continuous or repeated exposure to conditions, that results in bodily injury or property damage neither expected nor intended from the standpoint of the insured.
“Bodily injury” means bodily injury, sickness, or disease sustained by a person, including death resulting from any of these at any time. However, this term does not include those liabilities that, consistent with standard insurance industry practices, are excluded from coverage in liability insurance policies for bodily injury.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from the Insurance Services Office, Inc. definition of this term.
“Environmental damage” means the injurious presence in or upon land, the atmosphere or any watercourse or body of water of solid, liquid, gaseous, or thermal contaminants, irritants, or pollutants.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from the Insurance Services Office, Inc. definition of this term. This term is used in the definition of “pollution incident”.
“Legal defense costs” means any expenses that an insurer incurs in defending against claims of third parties brought under the terms and conditions of an insurance policy.
“Nonsudden accidental occurrence” means an occurrence that takes place over time and involves continuous or repeated exposure.
“Pollutant” means any solid, liquid, gaseous, or thermal irritant or contaminant, including smoke, vapor, soot, fumes, acids, alkalis, chemicals, and waste.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from the Insurance Services Office, Inc. definition of this term. This definition is used in the definition of “pollution incident”.
“Pollution incident” means emission, discharge, release or escape of pollutants into or upon land, the atmosphere, or any watercourse or body of water, provided that such emission, discharge, release, or escape results in “environmental damage”. The entirety of any such emission, discharge, release, or escape must be deemed to be one “pollution incident”. “Waste” includes materials to be recycled, reconditioned, or reclaimed. The term “pollution incident” includes an “occurrence”.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from the Insurance Services Office, Inc. definition of this term. This definition is used in the definition of “property damage”.
“Property damage” means as follows:
Either of the following:
Physical injury to, destruction of, or contamination of tangible property, including all resulting loss of use of that property; or
Loss of use of tangible property that is not physically injured, destroyed, or contaminated, but has been evacuated, withdrawn from use, or rendered inaccessible because of a “pollution incident”.
This term does not include those liabilities that, consistent with standard insurance industry practices, are excluded from coverage in liability insurance policies for property damage.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from the Insurance Services Office, Inc. definition of this term.
“Sudden accidental occurrence” means an occurrence that is not continuous or repeated in nature.
h) “Substantial business relationship” means the extent of a business relationship necessary under applicable state law to make a guarantee contract issued incident to that relationship valid and enforceable. A “substantial business relationship” must arise from a pattern of recent or ongoing business transactions, in addition to the guarantee itself, such that the Agency can reasonably determine that a substantial business relationship currently exists between the guarantor and the owner or operator that is adequate consideration to support the obligation of the guarantee relating to any liability towards a third-party. “Applicable state law”, as used in this subsection (h), means the laws of the State of Illinois and those of any sister state that govern the guarantee and the adequacy of the consideration.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 265.141(h) (2017) and the discussion at 53 Fed. Reg. 33938, 33941-33943 (Sep. 1, 1988). This term is also independently defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.141(h) and 727.240(b)(8). Any Agency determination that a substantial business relationship exists is subject to Board review pursuant to Section 40 of the Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.242 Cost Estimate for Closure
a) The owner or operator must have a detailed written estimate, in current dollars, of the cost of closing the facility in accordance with the requirements in Sections 725.211 through 725.215 and applicable closure requirements of Sections 725.297, 725.328, 725.358, 725.380, 725.410, 725.451, 725.481, 725.504, and 725.1102.
1) The estimate must equal the cost of final closure at the point in the facility’s active life when the extent and manner of its operation would make closure the most expensive, as indicated by its closure plan (see Section 725.212(b)); and
2) The closure cost estimate must be based on the costs to the owner or operator of hiring a third party to close the facility. A third party is a party that is neither a parent nor a subsidiary of the owner or operator. (See definition of “parent corporation” in Section 725.241(d).) The owner or operator may use costs for on-site disposal if the owner or operator demonstrates that on-site disposal capacity will exist at all times over the life of the facility.
3) The closure cost estimate must not incorporate any salvage value that may be realized by the sale of hazardous wastes, or non-hazardous wastes if permitted by the Agency pursuant to Section 725.213(d), facility structures or equipment, land or other facility assets at the time of partial or final closure.
4) The owner or operator must not incorporate a zero cost for hazardous waste, or non-hazardous waste if permitted by the Agency pursuant to Section 725.213(d), that may have economic value.
b) During the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must adjust the closure cost estimate for inflation within 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instruments used to comply with Section 725.243. For an owner or operator using the financial test or corporate guarantee, the closure cost estimate must be updated for inflation within 30 days after the close of the firm’s fiscal year and before submission of updated information to the Agency, as specified in Section 725.243(e)(5). The adjustment may be made by recalculating the closure cost estimate in current dollars, or by using an inflation factor derived from the most recent annual Implicit Price Deflator for Gross National Product (Deflator), as published by the U.S. Department of Commerce in its Survey of Current Business, as specified in subsections (b)(1) and (b)(2). The inflation factor is the result of dividing the latest published annual Deflator by the Deflator for the previous year.
1) The first adjustment is made by multiplying the closure cost estimate by the inflation factor. The result is the adjusted closure cost estimate.
2) Subsequent adjustments are made by multiplying the latest adjusted closure cost estimate by the latest inflation factor.
BOARD NOTE: The table of Deflators is available as Table 1.1.9., “Implicit Price Deflators for Gross Domestic Product”, in the National Income and Product Account Tables, published by U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, National Economic Accounts, available on-line at the following web address: www.bea.gov/national/nipaweb/TableView.asp?SelectedTable=13&FirstYear=2002&LastYear=2004&Freq=Qtr .
c) During the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must revise the closure cost estimate no later than 30 days after a revision has been made to the closure plan that increases the cost of closure. If the owner or operator has an approved closure plan, the closure cost estimate must be revised no later than 30 days after the Agency has approved the request to modify the closure plan if the change in the closure plan increases the cost of closure. The revised closure cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as specified in subsection (b).
d) The owner or operator must keep the following at the facility during the operating life of the facility: the latest closure cost estimate prepared in accordance with subsections (a) and (c), and, when this estimate has been adjusted in accordance with subsection (b), the latest adjusted closure cost estimate.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.243 Financial Assurance for Closure
An owner or operator of each facility must establish financial assurance for closure of the facility. The owner or operator must choose from the options specified in subsections (a) through (e).
a) Closure Trust Fund
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by establishing a closure trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this subsection and submitting an original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Agency. The trustee must be an entity that has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a federal or State agency.
2) The wording of the trust agreement must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251, and the trust agreement must be accompanied by a formal certification of acknowledgment, as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. Schedule A of the trust agreement must be updated within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current closure cost estimate covered by the agreement.
3) Payments into the trust fund must be made annually by the owner or operator over the remaining operating life of the facility as estimated in the closure plan; this period is hereafter referred to as the “pay-in period”. The payments into the closure trust fund must be made as follows:
A) The first payment must be at least equal to the current closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f), divided by the number of years in the pay-in period.
B) Subsequent payments must be made no later than 30 days after each anniversary date of the first payment. The amount of each subsequent payment must be determined by this formula:
Next Payment = ( CE - CV )Y
Where:
CE = the current closure cost estimate
CV= the current value of the trust fundY = the number of years remaining in the pay-in period
4) The owner or operator may accelerate payments into the trust fund or may deposit the full amount of the current closure cost estimate at the time the fund is established. However, the owner or operator must maintain the value of the fund at no less than the value that the fund would have if annual payments were made as specified in subsection (a)(3).
5) If the owner or operator establishes a closure trust fund after having used one or more alternate mechanisms specified in this Section, the owner or operator’s first payment must be in at least the amount that the fund would contain if the trust fund were established initially and annual payments made as specified in subsection (a)(3).
6) After the pay-in period is completed, whenever the current closure cost estimate changes, the owner or operator must compare the new estimate with the trustee’s most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, must either deposit an amount into the fund so that its value after this deposit at least equals the amount of the current closure cost estimate, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the difference.
7) If the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current closure cost estimate, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current closure cost estimate.
8) If an owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, for all or part of the trust fund, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current closure cost estimate covered by the trust fund.
9) Within 60 days after receiving a request from the owner or operator for release of funds as specified in subsection (a)(7) or (a)(8), the Agency must instruct the trustee to release to the owner or operator such funds as the Agency specifies in writing.
10) After beginning partial or final closure, an owner or operator or another person authorized to conduct partial or final closure may request reimbursement for closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. The owner or operator may request reimbursement for partial closure only if sufficient funds are remaining in the trust fund to cover the maximum costs of closing the facility over its remaining operating life. Within 60 days after receiving bills for partial or final closure activities, the Agency must instruct the trustee to make reimbursement in those amounts as the Agency specifies in writing if the Agency determines that the partial or final closure expenditures are in accordance with the approved closure plan, or otherwise justified. If the Agency determines that the maximum cost of closure over the remaining life of the facility will be significantly greater than the value of the trust fund, it must withhold reimbursement of such amounts as it deems prudent until it determines, in accordance with subsection (h), that the owner or operator is no longer required to maintain financial assurance for final closure of the facility. If the Agency does not instruct the trustee to make such reimbursements, the Agency must provide the owner or operator a detailed written statement of reasons.
11) The Agency must agree to termination of the trust when either of the following occurs:
A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or
B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h).
b) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Closure Trust Fund
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this subsection (b) and submitting the bond to the Agency. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
BOARD NOTE: The U.S. Department of the Treasury updates Circular 570, “Companies Holding Certificates of Authority as Acceptable Sureties on Federal Bonds and as Acceptable Reinsuring Companies”, on an annual basis pursuant to 31 CFR 223.16. Circular 570 is available on the Internet from the following website: http://www.fms.treas.gov/c570/ . 2) The wording of the surety bond must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) The owner or operator that uses a surety bond to satisfy the requirements of this Section must also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of the bond, all payments made thereunder will be deposited by the surety directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in subsection (a), except as follows: A) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the surety bond; and B) Until the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to the requirements of this Section, the following are not required by these regulations: i) Payments into the trust fund, as specified in subsection (a); ii) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251(a)) to show current closure cost estimates; iii) Annual valuations, as required by the trust agreement; and iv) Notices of nonpayment, as required by the trust agreement. 4) The bond must guarantee that the owner or operator will: A) Fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum of the bond before the beginning of final closure of the facility; B) Fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum within 15 days after an order to begin final closure is issued by the Board or a court of competent jurisdiction; or C) Provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain the Agency’s written approval of the assurance provided, within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the bond from the surety. 5) Under the terms of the bond, the surety will become liable on the bond obligation when the owner or operator fails to perform as guaranteed by the bond. 6) The penal sum of the bond must be in an amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). 7) Whenever the current closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the increase. Whenever the current closure cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 8) Under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts. 9) The owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Agency has given prior written consent based on its receipt of evidence of alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section. c) Closure Letter of Credit 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to the requirements of this subsection (c) and submitting the letter to the Agency. The issuing institution must be an entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter-of-credit operations are regulated and examined by a federal or State agency. 2) The wording of the letter of credit must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) An owner or operator that uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this Section must also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of the letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the Agency must be deposited by the issuing institution directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements of the trust fund specified in subsection (a), except as follows: A) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the letter of credit; and B) Unless the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to the requirements of this Section, the following are not required by these regulations: i) Payments into the trust fund, as specified in subsection (a); ii) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement (as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251) to show current closure cost estimates; iii) Annual valuations, as required by the trust agreement; and iv) Notices of nonpayment as required by the trust agreement. 4) The letter of credit must be accompanied by a letter from the owner or operator referring to the letter of credit by number, issuing institution, and date and providing the following information: the USEPA identification number, name, and address of the facility, and the amount of funds assured for closure of the facility by the letter of credit. 5) The letter of credit must be irrevocable and issued for a period of at least one year. The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least one year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Agency by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date. Under the terms of the letter of credit, the 120 days will begin on the date when both the owner or operator and the Agency have received the notice, as evidenced by the return receipts. 6) The letter of credit must be issued in an amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). 7) Whenever the current closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the increase. Whenever the current closure cost estimate decreases, the amount of the credit may be reduced to the amount of the current closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 8) Following a final judicial determination or Board order finding that the owner or operator has failed to perform final closure in accordance with the approved closure plan when required to do so, the Agency may draw on the letter of credit. 9) If the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice from issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the Agency must draw on the letter of credit. The Agency may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days of any such extension the Agency must draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Agency. 10) The Agency must return the letter of credit to the issuing institution for termination when one of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). d) Closure Insurance 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining closure insurance that conforms to the requirements of this subsection and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the Agency. At a minimum, the insurer must be licensed to transact the business of insurance, or eligible to provide insurance as an excess or surplus lines insurer, in one or more States. 2) The wording of the certificate of insurance must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) The closure insurance policy must be issued for a face amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). The term “face amount” means the total amount the insurer is obligated to pay under the policy. Actual payments by the insurer will not change the face amount, although the insurer’s future liability will be lowered by the amount of the payments. 4) The closure insurance policy must guarantee that funds will be available to close the facility whenever final closure occurs. The policy must also guarantee that, once final closure begins, the insurer will be responsible for paying out funds, up to an amount equal to the face amount of the policy, upon the direction of the Agency to such party or parties as the Agency specifies. 5) After beginning partial or final closure, an owner or operator or any other person authorized to conduct closure may request reimbursement for closure expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. The owner or operator may request reimbursement for partial closure only if the remaining value of the policy is sufficient to cover the maximum costs of closing the facility over its remaining operating life. Within 60 days after receiving bills for closure activities, the Agency must instruct the insurer to make reimbursement in such amounts as the Agency specifies in writing if the Agency determines that the partial or final closure expenditures are in accordance with the approved closure plan or otherwise justified. If the Agency determines that the maximum cost of closure over the remaining life of the facility will be significantly greater than the face amount of the policy, it must withhold reimbursement of such amounts as it deems prudent until it determines, in accordance with subsection (h), that the owner or operator is no longer required to maintain financial assurance for final closure of the particular facility. If the Agency does not instruct the insurer to make such reimbursements, the Agency must provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons. 6) The owner or operator must maintain the policy in full force and effect until the Agency consents to termination of the policy by the owner or operator as specified in subsection (d)(10). Failure to pay the premium, without substitution of alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section, will constitute a significant violation of these regulations, warranting such remedy as the Board may impose pursuant to the Environmental Protection Act. Such violation will be deemed to begin upon receipt by the Agency of a notice of future cancellation, termination, or failure to renew due to nonpayment of the premium, rather than upon the date of expiration. 7) Each policy must contain a provision allowing assignment of the policy to a successor owner or operator. Such assignment may be conditional upon consent of the insurer, provided such consent is not unreasonably refused. 8) The policy must provide that the insurer may not cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy except for failure to pay the premium. The automatic renewal of the policy must, at a minimum, provide the insured with the option of renewal at the face amount of the expiring policy. If there is a failure to pay the premium, the insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Agency. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Agency and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur and the policy will remain in full force and effect in the event that, on or before the date of expiration, one of the following occurs: A) The Agency deems the facility abandoned; B) Interim status is terminated or revoked; C) Closure is ordered by the Board or a court of competent jurisdiction; D) The owner or operator is named as debtor in a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under 11 USC (Bankruptcy); or E) The premium due is paid. 9) Whenever the current closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this Section to cover the increase. Whenever the current closure cost estimate decreases, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 10) The Agency must give written consent to the owner or operator that the owner or operator may terminate the insurance policy when either of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). e) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee for Closure 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by demonstrating that the owner or operator passes a financial test as specified in this subsection. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of either subsection (e)(1)(A) or (e)(1)(B): A) The owner or operator must have all of the following: i) Two of the following three ratios: a ratio of total liabilities to net worth less than 2.0; a ratio of the sum of net income plus depreciation, depletion and amortization to total liabilities greater than 0.1; and a ratio of current assets to current liabilities greater than 1.5; ii) Net working capital and tangible net worth each at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates; iii) Tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and iv) Assets located in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of total assets or at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates. B) The owner or operator must have all of the following: i) A current rating for its most recent bond issuance of AAA, AA, A, or BBB, as issued by Standard and Poor’s, or Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa, as issued by Moody’s; ii) Tangible net worth at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates; iii) Tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and iv) Assets located in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of total assets or at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates. 2) The phrase “current closure and post-closure cost estimates”, as used in subsection (e)(1), refers to the cost estimates required to be shown in subsections 1 through 4 of the letter from the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251). The phrase “current plugging and abandonment cost estimates”, as used in subsection (e)(1), refers to the cost estimates required to be shown in subsections 1 through 4 of the letter from the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.240). 3) To demonstrate that the owner or operator meets this test, the owner or operator must submit each of the following items to the Agency: A) A letter signed by the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer and worded as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251; B) A copy of the independent certified public accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year; and C) A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator stating the following: i) That the accountant has compared the data that the letter from the chief financial officer specifies as having been derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements; and ii) In connection with that procedure, that no matters came to the accountant’s attention which caused the accountant to believe that the specified data should be adjusted. 4) This subsection (e)(4) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.143(e)(4), a federal provision relating to an extension of the time to file the proofs of financial assurance required by this subsection (e) granted by USEPA. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal regulations. 5) After the initial submission of items specified in subsection (e)(3), the owner or operator must send updated information to the Agency within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in subsection (e)(3). 6) If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (e)(1), the owner or operator must send notice to the Agency of intent to establish alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year. 7) The Agency may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the requirements of subsection (e)(1), require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in subsection (e)(3). If the Agency finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (e)(1), the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section within 30 days after notification of such a finding. 8) The Agency may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in the accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements (see subsection (e)(3)(B)). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Agency must evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section within 30 days after notification of the disallowance. 9) The owner or operator is no longer required to submit the items specified in subsection (e)(3) when either of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). 10) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a written guarantee, hereafter referred to as “corporate guarantee”. The guarantor must be the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in subsections (e)(1) through (e)(8), and must comply with the terms of the corporate guarantee. The wording of the corporate guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. The corporate guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Agency as specified in subsection (e)(3). One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor’s chief financial officer. If the guarantor’s parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, the letter must describe the value received in consideration of the guarantee. If the guarantor is a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator, this letter must describe this substantial business relationship” and the value received in consideration of the guarantee. The terms of the corporate guarantee must provide the following: A) That, if the owner or operator fails to perform final closure of a facility covered by the corporate guarantee in accordance with the closure plan and other interim status requirements whenever required to do so, the guarantor will do so or establish a trust fund as specified in subsection (a), in the name of the owner or operator. B) That the corporate guarantee will remain in force unless the guarantor sends notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts. C) That, if the owner or operator fails to provide alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section and obtain the written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the corporate guarantee from the guarantor, the guarantor will provide such alternate financial assurance in the name of the owner or operator. f) Use of Multiple Financial Mechanisms. An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by establishing more than one financial mechanism per facility. These mechanisms are limited to trust funds, surety bonds, letters of credit, and insurance. The mechanisms must be as specified in subsections (a) through (d), respectively, except that it is the combination of mechanisms, rather than the single mechanism, that must provide financial assurance for an amount at least equal to the current closure cost estimate. If an owner or operator uses a trust fund in combination with a surety bond or a letter of credit, the owner or operator may use the trust fund as the standby trust fund for the other mechanisms. A single standby trust fund may be established for two or more mechanisms. The Agency may use any or all of the mechanisms to provide for closure of the facility. g) Use of a Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities. An owner or operator may use a financial assurance mechanism specified in this Section to meet the requirements of this Section for more than one facility. Evidence of financial assurance submitted to the Agency must include a list showing, for each facility, the USEPA identification number, name, address, and the amount of funds for closure assured by the mechanism. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and maintained for each facility. The amount of funds available to the Agency must be sufficient to close all of the owner or operator’s facilities. In directing funds available through the mechanism for closure of any of the facilities covered by the mechanism, the Agency may direct only the amount of funds designated for that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional funds available under the mechanism. h) Release of the Owner or Operator from the Requirements of This Section. Within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer that final closure has been completed in accordance with the approved closure plan, the Agency must notify the owner or operator in writing that the owner or operator is no longer required by this Section to maintain financial assurance for closure of the facility, unless the Agency determines that closure has not been in accordance with the approved closure plan. The Agency must provide the owner or operator a detailed written statement of any such determination that closure has not been in accordance with the approved closure plan. i) Appeal. The following Agency actions are deemed to be permit modifications or refusals to modify for purposes of appeal to the Board (35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.184(e)(3)): 1) An increase in, or a refusal to decrease the amount of, a bond, letter of credit, or insurance; or 2) Requiring alternate assurance upon a finding that an owner or operator or parent corporation no longer meets a financial test. (Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018) Section 725.244 Cost Estimate for Post-Closure Care
a) The owner or operator of a hazardous waste disposal unit must have a detailed written estimate, in current dollars, of the annual cost of post-closure monitoring and maintenance of the facility in accordance with the applicable post-closure regulations in Section 725.217 through 725.220, 725.328, 725.358, 725.380, and 725.410.
1) The post-closure cost estimate must be based on the costs to the owner or operator of hiring a third party to conduct post-closure care activities. A third party is a party that is neither a parent nor a subsidiary of the owner or operator. (See the definition of “parent corporation” in Section 725.241(d).)
2) The post-closure cost estimate is calculated by multiplying the annual post-closure cost estimate by the number of years of post-closure care required under Section 725.217.
b) During the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must adjust the post-closure cost estimate for inflation within 30 days after each anniversary of the date on which the first post-closure cost estimate was prepared. The adjustment must be made 60 days prior to the anniversary date of the establishment of the financial instruments used to comply with Section 725.245. For an owner or operator using the financial test or corporate guarantee, the closure cost estimate must be updated for inflation within 30 days after the close of the firm’s fiscal year and before submission of updated information to the Agency as specified in Section 725.245(e)(5). The adjustment may be made by recalculating the post-closure cost estimate in current dollars, or by using an inflation factor derived from the annual Implicit Price Deflator for Gross National Product as published by the U.S. Department of Commerce in its Survey of Current Business as specified in subsections (b)(1) and (b)(2). The inflation factor is the result of dividing the latest published annual Deflator by the Deflator for the previous year.
1) The first adjustment is made by multiplying the post-closure estimate by the inflation factor. The result is the adjusted post-closure cost estimate.
2) Subsequent adjustments are made by multiplying the latest adjusted post-closure cost estimate by the latest inflation factor.
c) During the active life of the facility, the owner or operator must revise the post-closure cost estimate whenever a change in the post-closure plan no later than 30 days after a revision to the post-closure plan that increases the cost of post-closure care. If the owner or operator has an approved post-closure plan, the post-closure cost estimate must be revised no later than 30 days after the Agency has approved the request to modify the plan if the change in the post-closure plan increases the cost of post-closure care. The revised post-closure cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as specified in subsection (b).
d) The owner or operator must keep the following at the facility during the operating life of the facility: the latest post-closure cost estimate prepared in accordance with subsections (a) and (c) and, when this estimate has been adjusted in accordance with subsection (b), the latest adjusted post-closure cost estimate.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.245 Financial Assurance for Post-Closure Monitoring and Maintenance
An owner or operator of a facility with a hazardous waste disposal unit must establish financial assurance for post-closure care of the disposal units. The owner or operator must choose from the following options:
a) Post-Closure Trust Fund
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by establishing a post-closure trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this subsection and submitting an original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Agency. The trustee must be an entity that has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a federal or State agency.
2) The wording of the trust agreement must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251 and the trust agreement must be accompanied by a formal certification of acknowledgment (as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251). Schedule A of the trust agreement must be updated within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current post-closure cost estimate covered by the agreement.
3) Payments into the trust fund must be made annually by the owner or operator over the remaining operating life of the facility as estimated in the closure plan; this period is hereafter referred to as the “pay-in period”. The payments into the post-closure trust fund must be made as follows:
A) The first payment must be at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f), divided by the number of years in the pay-in period.
B) Subsequent payments must be made no later than 30 days after each anniversary date of the first payment. The amount of each subsequent payment must be determined by this formula:
Next Payment = ( CE - CV )Y
Where:
CE = the current closure cost estimate
CV= the current value of the trust fundY = the number of years remaining in the pay-in period
4) The owner or operator may accelerate payments into the trust fund or may deposit the full amount of the current post-closure cost estimate at the time the fund is established. However, the owner or operator must maintain the value of the fund at no less than the value that the fund would have if annual payments were made as specified in subsection (a)(3).
5) If the owner or operator establishes a post-closure trust fund after having used one or more alternate mechanisms specified in this Section, the owner or operator’s first payment must be in at least the amount that the fund would contain if the trust fund were established initially and annual payments made as specified in subsection (a)(3).
6) After the pay-in period is completed, whenever the current post-closure cost estimate changes during the operating life of the facility, the owner or operator must compare the new estimate with the trustee’s most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, must either deposit an amount into the fund so that its value after this deposit at least equals the amount of the current post-closure cost estimate, or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this Section to cover the difference.
7) During the operating life of the facility, if the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current post-closure cost estimate, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current post-closure cost estimate.
8) If an owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance as specified in this Section for all or part of the trust fund, owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current post-closure cost estimate covered by the trust fund.
9) Within 60 days after receiving a request from the owner or operator for release of funds as specified in subsection (a)(7) or (a)(8), the Agency must instruct the trustee to release to the owner or operator such funds as the Agency specifies in writing.
10) During the period of post-closure care, the Agency must approve a release of funds if the owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that the value of the trust fund exceeds the remaining cost of post-closure care.
11) An owner or operator or any other person authorized to perform post-closure care may request reimbursement for post-closure care expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. Within 60 days after receiving bills for post-closure activities, the Agency must instruct the trustee to make reimbursement in those amounts as the Agency specifies in writing if the Agency determines that the post-closure care expenditures are in accordance with the approved post-closure plan or otherwise justified. If the Agency does not instruct the trustee to make such reimbursements, the Agency must provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons.
12) The Agency must agree to termination of a trust when either of the following occurs:
A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or
B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h).
b) Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment into a Post-Closure Trust Fund
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this subsection (b) and submitting the bond to the Agency. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
BOARD NOTE: The U.S. Department of the Treasury updates Circular 570, “Companies Holding Certificates of Authority as Acceptable Sureties on Federal Bonds and as Acceptable Reinsuring Companies”, on an annual basis pursuant to 31 CFR 223.16. Circular 570 is available on the Internet from the following website: http://www.fms.treas.gov/c570/ . 2) The wording of the surety bond must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) The owner or operator that uses a surety bond to satisfy the requirements of this Section must also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of the bond, all payments made thereunder will be deposited by the surety directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in subsection (a), except as follows: A) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the surety bond; and B) Until the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to the requirements of this Section, the following are not required by these regulations: i) Payments into the trust fund, as specified in subsection (a); ii) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement (as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251) to show current post-closure cost estimates; iii) Annual valuations, as required by the trust agreement; and iv) Notices of nonpayment, as required by the trust agreement. 4) The bond must guarantee that the owner or operator will perform the following acts: A) Fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum of the bond before the beginning of final closure of the facility; or B) Fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum within 15 days after an order to begin closure is issued by the Board or a court of competent jurisdiction; or C) Provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain the Agency’s written approval of the assurance provided, within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the bond from the surety. 5) Under the terms of the bond, the surety will become liable on the bond obligation when the owner or operator fails to perform as guaranteed by the bond. 6) The penal sum of the bond must be in an amount at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). 7) Whenever the current post-closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency or obtain other financial assurance as specified in this Section to cover the increase. Whenever the current post-closure cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current post-closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 8) Under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts. 9) The owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Agency has given prior written consent based on its receipt of evidence of alternate financial assurance as specified in this Section. c) Post-Closure Letter of Credit 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to the requirements of this subsection (c) and submitting the letter to the Agency. The issuing institution must be an entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter-of-credit operations are regulated and examined by a federal or State agency. 2) The wording of the letter of credit must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) An owner or operator that uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this Section must also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of the letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the Agency must be deposited by the issuing institution directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements of the trust fund specified in subsection (a), except as follows: A) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the letter of credit; and B) Unless the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to the requirements of this Section, the following are not required by these regulations: i) Payments into the trust fund, as specified in subsection (a); ii) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement (as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.151) to show current post-closure cost estimates; iii) Annual valuations, as required by the trust agreement; and iv) Notices of nonpayment, as required by the trust agreement. 4) The letter of credit must be accompanied by a letter from the owner or operator referring to the letter of credit by number, issuing institution, and date and providing the following information: the USEPA identification number, name, and address of the facility, and the amount of funds assured for post-closure care of the facility by the letter of credit. 5) The letter of credit must be irrevocable and issued for a period of at least one year. The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least one year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Agency by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date. Under the terms of the letter of credit, the 120 days will begin on the date when both the owner or operator and the Agency have received the notice, as evidenced by the return receipts. 6) The letter of credit must be issued in an amount at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). 7) Whenever the current post-closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit during the operating life of the facility, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current post-closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases during the operating life of the facility, the amount of the credit may be reduced to the amount of the current post-closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 8) During the period of post-closure care, the Agency must approve a decrease in the amount of the letter of credit if the owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that the amount exceeds the remaining cost of post-closure care. 9) Following a final judicial determination or Board order finding that the owner or operator has failed to perform post-closure care in accordance with the approved post-closure plan and other interim status requirements, the Agency may draw on the letter of credit. 10) If the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice from the issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the Agency must draw on the letter of credit. The Agency may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days after any such extension the Agency must draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Agency. 11) The Agency must return the letter of credit to the issuing institution for termination when either of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). d) Post-Closure Insurance 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining post-closure insurance that conforms to the requirements of this subsection and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the Agency. At a minimum, the insurer must be licensed to transact the business of insurance, or eligible to provide insurance as an excess or surplus lines insurer, in one or more states. 2) The wording of the certificate of insurance must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. 3) The post-closure insurance policy must be issued for a face amount at least equal to the current post-closure estimate, except as provided in subsection (f). The term “face amount” means the total amount the insurer is obligated to pay under the policy. Actual payments by the insurer will not change the face amount, although the insurer’s future liability will be lowered by the amount of the payments. 4) The post-closure insurance policy must guarantee that funds will be available to provide post-closure care of facility whenever the post-closure period begins. The policy must also guarantee that, once post-closure care begins, the insurer will be responsible for paying out funds, up to an amount equal to the face amount of the policy, upon the direction of the Agency, to such party or parties as the Agency specifies. 5) An owner or operator or any other person authorized to perform post-closure care may request reimbursement for post-closure care expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. Within 60 days after receiving bills for post-closure activities, the Agency must instruct the insurer to make reimbursement in such amounts as the Agency specifies in writing, if the Agency determines that the post-closure care expenditures are in accordance with the approved post-closure plan or otherwise justified. If the Agency does not instruct the insurer to make such reimbursements, the Agency must provide the owner or operator with a detailed written statement of reasons. 6) The owner or operator must maintain the policy in full force and effect until the Agency consents to termination of the policy by the owner or operator, as specified in subsection (d)(11). Failure to pay the premium, without substitution of alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, will constitute a significant violation of these regulations, warranting such remedy as the Board may impose pursuant to the Environmental Protection Act. Such violation will be deemed to begin upon receipt by the Agency of a notice of future cancellation, termination, or failure to renew due to nonpayment of the premium, rather than upon the date of expiration. 7) Each policy must contain a provision allowing assignment of the policy to a successor owner or operator. Such assignment may be conditional upon consent of the insurer, provided such consent is not unreasonably refused. 8) The policy must provide that the insurer may not cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy except for failure to pay the premium. The automatic renewal of the policy must, at a minimum, provide the insured with the option of renewal at the face amount of the expiring policy. If there is a failure to pay the premium, the insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Agency. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Agency and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return receipts. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, and the policy will remain in full force and effect in the event that, on or before the date of expiration, one of the following occurs: A) The Agency deems the facility abandoned; B) Interim status is terminated or revoked; C) Closure is ordered by the Board or a court of competent jurisdiction; D) The owner or operator is named as debtor in a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under 11 USC (Bankruptcy); or E) The premium due is paid. 9) Whenever the current post-closure cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy during the operating life of the facility, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the increase. Whenever the current post-closure cost estimate decreases during the operating life of the facility, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current post-closure cost estimate following written approval by the Agency. 10) Commencing on the date that liability to make payments pursuant to the policy accrues, the insurer must thereafter annually increase the face amount of the policy. Such increase must be equivalent to the face amount of the policy, less any payments made, multiplied by an amount equivalent to 85 percent of the most recent investment rate or of the equivalent coupon-issue yield announced by the U.S. Treasury for 26-week Treasury securities. 11) The Agency must give written consent to the owner or operator that the owner or operator may terminate the insurance policy when either of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). e) Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee for Post-Closure Care 1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by demonstrating that the owner or operator passes a financial test, as specified in this subsection (e). To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of either subsection (e)(1)(A) or (e)(1)(B): A) The owner or operator must have each of the following: i) Two of the following three ratios: a ratio of total liabilities to net worth less than 2.0; a ratio of the sum of net income plus depreciation, depletion and amortization to total liabilities greater than 0.1; and a ratio of current assets to current liabilities greater than 1.5; ii) Net working capital and tangible net worth each at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates; iii) Tangible new worth of at least $10 million; and iv) Assets in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of total assets or at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the plugging and abandonment cost estimates. B) The owner or operator must have each of the following: i) A current rating for its most recent bond issuance of AAA, AA, A, or BBB, as issued by Standard and Poor’s, or Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa, as issued by Moody’s; ii) Tangible net worth at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates; iii) Tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and iv) Assets located in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of its total assets or at least six times the sum of the current closure and post-closure cost estimates and the current plugging and abandonment cost estimates. 2) The phrase “current closure and post-closure cost estimates”, as used in subsection (e)(1), refers to the cost estimates required to be shown in subsections 1 through 4 of the letter from the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251). The phrases “current plugging and abandonment cost estimates”, as used in subsection (e)(1), refers to the cost estimates required to be shown in subsections 1 through 4 of the letter from the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.240). 3) To demonstrate that it meets this test, the owner or operator must submit each of the following items to the Agency: A) A letter signed by the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer and worded as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251; B) A copy of the independent certified public accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year; and C) A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator stating both of the following: i) That the accountant has compared the data that the letter from the chief financial officer specifies as having been derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements; and ii) In connection with that procedure, that no matters came to the accountant’s attention that caused the accountant to believe that the specified data should be adjusted. 4) This subsection (e)(4) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.143(e)(4), a federal provision relating to an extension of the time to file the proofs of financial assurance required by this subsection (e) granted by USEPA. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal regulations. 5) After the initial submission of items specified in subsection (e)(3), the owner or operator must send updated information to the Agency within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in subsection (e)(3). 6) If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (e)(1), the owner or operator must send notice to the Agency of intent to establish alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year. 7) The Agency may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the requirements of subsection (e)(1), require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in subsection (e)(3). If the Agency finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (e)(1), the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, within 30 days after notification of such a finding. 8) The Agency may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in the accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements (see subsection (e)(3)(B)). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Agency must evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, within 30 days after notification of the disallowance. 9) During the period of post-closure care, the Agency must approve a decrease in the current post-closure cost estimate for which this test demonstrates financial assurance if the owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that the amount of the cost estimate exceeds the remaining cost of post-closure care. 10) The owner or operator is no longer required to submit the items specified in subsection (e)(3) when either of the following occurs: A) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section; or B) The Agency releases the owner or operator from the requirements of this Section in accordance with subsection (h). 11) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a written guarantee, hereafter referred to as “corporate guarantee”. The guarantor must be the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in subsections (e)(1) through (e)(9), and must comply with the terms of the corporate guarantee. The wording of the corporate guarantee must be identical to the wording specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. The corporate guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Agency as specified in subsection (e)(3). One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor’s chief financial officer. If the guarantor’s parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, the letter must describe the value received in consideration of the guarantee. If the guarantor is a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator, this letter must describe this substantial business relationship” and the value received in consideration of the guarantee. The terms of the corporate guarantee must provide as follows: A) That, if the owner or operator fails to perform post-closure care of a facility covered by the corporate guarantee in accordance with the post-closure plan and other interim status requirements whenever required to do so, the guarantor will do so or establish a trust fund as specified in subsection (a), in the name of the owner or operator. B) That the corporate guarantee will remain in force unless the guarantor sends notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts. C) That, if the owner or operator fails to provide alternate financial assurance, as specified in this Section, and obtain the written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the corporate guarantee from the guarantor, the guarantor will provide such alternate financial assurance in the name of the owner or operator. f) Use of Multiple Financial Mechanisms. An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by establishing more than one financial mechanism per facility. These mechanisms are limited to trust funds, surety bonds, letters of credit, and insurance. The mechanisms must be as specified in subsections (a) through (d), respectively, except that it is the combination of mechanisms, rather than the single mechanism, that must provide financial assurance for an amount at least equal to the current post-closure cost estimate. If an owner or operator uses a trust fund in combination with a surety bond or a letter of credit, it may use the trust fund as the standby trust fund for the other mechanisms. A single standby trust fund may be established for two or more mechanisms. The Agency may use any or all of the mechanisms to provide for post-closure care of the facility. g) Use of a Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities. An owner or operator may use a financial assurance mechanism specified in this Section to meet the requirements of this Section for more than one facility. Evidence of financial assurance submitted to the Agency must include a list showing, for each facility, the USEPA Identification Number, name, address, and the amount of funds for post-closure care assured by the mechanism. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and maintained for each facility. The amount of funds available to the Agency must be sufficient to provide post-closure care for all of the owner or operator’s facilities. In directing funds available through the mechanism for post-closure care of any of the facilities covered by the mechanism, the Agency may direct only the amount of funds designated for that facility, unless the owner or operator agrees to the use of additional funds available under the mechanism. h) Release of the Owner or Operator from the Requirements of This Section. Within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer that the post-closure care period has been completed in accordance with the approved post-closure plan, the Agency must notify the owner or operator in writing that the owner or operator is no longer required by this Section to maintain financial assurance for post-closure care of that unit, unless the Agency determines that post-closure care has not been in accordance with the approved plan. The Agency must provide the owner or operator a detailed written statement of any such determination that post-closure care has not been in accordance with the approved post-closure plan. i) Appeal. The following Agency actions are deemed to be permit modifications or refusals to modify for purposes of appeal to the Board (35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.184(e)(3)): 1) An increase in, or a refusal to decrease the amount of, a bond, letter of credit, or insurance; or 2) Requiring alternate assurance upon a finding that an owner or operator or parent corporation no longer meets a financial test. (Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018) Section 725.246 Use of a Mechanism for Financial Assurance of Both Closure and Post-Closure Care
An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements for financial assurance for both closure and post-closure care for one or more facilities by using a trust fund, surety bond, letter of credit, insurance, financial test, or corporate guarantee that meets the specifications for the mechanism in both Sections 725.243 and 725.245. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism had been established and maintained for financial assurance of closure and of post-closure care.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.247 Liability Requirements
a) Coverage for Sudden Accidental Occurrences. An owner or operator of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility, or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by sudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. The owner or operator must have and maintain liability coverage for sudden accidental occurrences in the amount of at least $1 million per occurrence with an annual aggregate of at least $2 million, exclusive of legal defense costs. This liability coverage may be demonstrated, as specified in subsections (a)(1) through (a)(6):
1) An owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage by having liability insurance, as specified in this subsection (a)(1).
A) Each insurance policy must be amended by attachment of the Hazardous Waste Facility Liability Endorsement or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance. The wording of the endorsement and of the certificate of insurance must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. The owner or operator must submit a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Agency. If requested by the Agency, the owner or operator must provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy.
B) Each insurance policy must be issued by an insurer that is licensed by the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, Division of Insurance.
2) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by passing a financial test or using the guarantee for liability coverage, as specified in subsections (f) and (g).
3) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a letter of credit for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (h).
4) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a surety bond for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (i).
5) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a trust fund for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (j).
6) An owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage through the use of combinations of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, and trust fund, except that the owner or operator may not combine a financial test covering part of the liability coverage requirement with a guarantee unless the financial statement of the owner or operator is not consolidated with the financial statement of the guarantor. The amounts of coverage demonstrated must total at least the minimum amounts required by this Section. If the owner or operator demonstrates the required coverage through the use of a combination of financial assurances pursuant to this subsection (a)(6), the owner or operator must specify at least one such assurance as “primary” coverage, and must specify other such assurance as “excess” coverage.
7) An owner or operator must notify the Agency within 30 days whenever one of the following occurs:
A) A claim results in a reduction in the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage provided by a financial instrument authorized in subsections (a)(1) through (a)(6);
B) A Certification of Valid Claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is entered between the owner or operator and third-party claimant for liability coverage pursuant to subsections (a)(1) through (a)(6); or
C) A final court order establishing a judgment for bodily injury or property damage caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is issued against the owner or operator or an instrument that is providing financial assurance for liability coverage pursuant to subsections (a)(1) through (a)(6).
b) Coverage for Nonsudden Accidental Occurrences. An owner or operator of a surface impoundment, landfill, or land treatment facility that is used to manage hazardous waste, or a group of such facilities, must demonstrate financial responsibility for bodily injury and property damage to third parties caused by nonsudden accidental occurrences arising from operations of the facility or group of facilities. The owner or operator must have and maintain liability coverage for nonsudden accidental occurrences in the amount of at least $3 million per occurrence with an annual aggregate of at least $6 million, exclusive of legal defense costs. An owner or operator meeting the requirements of this Section may combine the required per-occurrence coverage levels for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences into a single per-occurrence level, and combine the required annual aggregate coverage levels for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences into a single annual aggregate level. An owner or operator that combines coverage levels for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences must maintain liability coverage in the amount of at least $4 million per occurrence and $8 million annual aggregate. This liability coverage may be demonstrated, as specified in subsections (b)(1) through (b)(6):
1) An owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage by having liability insurance, as specified in this subsection (b)(1).
A) Each insurance policy must be amended by attachment of the Hazardous Waste Facility Liability Endorsement or evidenced by a Certificate of Liability Insurance. The wording of the endorsement must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. The wording of the certificate of insurance must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. The owner or operator must submit a signed duplicate original of the endorsement or the certificate of insurance to the Agency. If requested by the Agency, the owner or operator must provide a signed duplicate original of the insurance policy.
B) Each insurance policy must be issued by an insurer that is licensed by the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, Division of Insurance.
2) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by passing a financial test or using the guarantee for liability coverage, as specified in subsections (f) and (g).
3) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a letter of credit for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (h).
4) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a surety bond for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (i).
5) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a trust fund for liability coverage, as specified in subsection (j).
6) An owner or operator may demonstrate the required liability coverage through the use of combinations of insurance, financial test, guarantee, letter of credit, surety bond, and trust fund, except that the owner or operator may not combine a financial test covering part of the liability coverage requirement with a guarantee unless the financial statement of the owner or operator is not consolidated with the financial statement of the guarantor. The amounts of coverage demonstrated must total at least the minimum amounts required by this Section. If the owner or operator demonstrates the required coverage through the use of a combination of financial assurances pursuant to this subsection (b)(6), the owner or operator must specify at least one such assurance as “primary” coverage, and must specify other such assurance as “excess” coverage.
7) An owner or operator must notify the Agency within 30 days whenever one of the following occurs:
A) A claim results in a reduction in the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage provided by a financial instrument authorized in subsections (b)(1) through (b)(6);
B) A Certification of Valid Claim for bodily injury or property damages caused by sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is entered between the owner or operator and third-party claimant for liability coverage pursuant to subsections (b)(1) through (b)(6); or
C) A final court order establishing a judgment for bodily injury or property damage caused by a sudden or non-sudden accidental occurrence arising from the operation of a hazardous waste treatment, storage, or disposal facility is issued against the owner or operator or an instrument that is providing financial assurance for liability coverage pursuant to subsections (b)(1) through (b)(6).
c) Request for Adjusted Level of Required Liability Coverage. If an owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that the levels of financial responsibility required by subsection (a) or (b) are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility or group of facilities, the owner or operator may obtain an adjusted level of required liability coverage from the Agency. The request for an adjusted level of required liability coverage must be submitted in writing to the Agency. If granted, the Agency’s action must take the form of an adjusted level of required liability coverage, such level to be based on the Agency assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. The Agency may require an owner or operator that requests an adjusted level of required liability coverage to provide such technical and engineering information as is necessary to determine a level of financial responsibility other than that required by subsection (a) or (b). The Agency must process any request for an adjusted level of required liability coverage as if it were a permit modification request pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.271(e)(3) and 705.128. Notwithstanding any other provision, the Agency must hold a public hearing whenever it finds, on the basis of requests, a significant degree of public interest in a tentative decision to grant an adjusted level of required liability insurance. The Agency may also hold a public hearing at its discretion whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues involved in the tentative decision.
d) Adjustments by the Agency. If the Agency determines that the levels of financial responsibility required by subsection (a) or (b) are not consistent with the degree and duration of risk associated with treatment, storage, or disposal at the facility or group of facilities, the Agency must adjust the level of financial responsibility required pursuant to subsection (a) or (b) as may be necessary to adequately protect human health and the environment. This adjusted level must be based on the Agency’s assessment of the degree and duration of risk associated with the ownership or operation of the facility or group of facilities. In addition, if the Agency determines that there is a significant risk to human health and the environment from non-sudden accidental occurrences resulting from the operations of a facility that is not a surface impoundment, landfill or land treatment facility, the Agency may require that an owner or operator of the facility comply with subsection (b). An owner or operator must furnish to the Agency, within a time specified by the Agency in the request, which must not be less than 30 days, any information that the Agency requests to determine whether cause exists for such adjustments of level or type of coverage. The Agency must process any request for an adjusted level of required liability coverage as if it were a permit modification request pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.271(e)(3) and 705.128. Notwithstanding any other provision, the Agency must hold a public hearing whenever it finds, on the basis of requests, a significant degree of public interest in a tentative decision to grant an adjusted level of required liability insurance. The Agency may also hold a public hearing at its discretion whenever such a hearing might clarify one or more issues involved in the tentative decision.
e) Period of Coverage. Within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and a qualified Professional Engineer that final closure has been completed in accordance with the approved closure plan, the Agency must notify the owner or operator in writing that the owner or operator is no longer required by this Section to maintain liability coverage for that facility, unless the Agency determines that closure has not been in accordance with the approved closure plan.
f) Financial Test for Liability Coverage
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by demonstrating that the owner or operator passes a financial test, as specified in this subsection (f)(1). To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of subsection (f)(1)(A) or (f)(1)(B):
A) The owner or operator must have each of the following:
i) Net working capital and tangible net worth each at least six times the amount of liability coverage to be demonstrated by this test;
ii) Tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and
iii) Assets in the United States amounting to either: at least 90 percent of total assets; or at least six times the amount of liability coverage to be demonstrated by this test.
B) The owner or operator must have each of the following:
i) A current rating for the owner or operator’s most recent bond issuance of AAA, AA, A, or BBB, as issued by Standard and Poor’s, or Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa, as issued by Moody’s;
ii) Tangible net worth of at least $10 million;
iii) Tangible net worth at least six times the amount of liability coverage to be demonstrated by this test; and
iv) Assets in the United States amounting to either of the following: at least 90 percent of total assets or at least six times the amount of liability coverage to be demonstrated by this test.
2) The phrase “amount of liability coverage”, as used in subsection (f)(1), refers to the annual aggregate amounts for which coverage is required pursuant to subsections (a) and (b).
3) To demonstrate that the owner or operator meets this test, the owner or operator must submit each of the following three items to the Agency:
A) A letter signed by the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer and worded as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. If an owner or operator is using the financial test to demonstrate both assurance for closure or post-closure care, as specified by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.243(f) and 724.245(f), or by Sections 725.243(e) and 725.245(e), and liability coverage, it must submit the letter specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251 to cover both forms of financial responsibility; a separate letter, as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251 is not required.
B) A copy of the independent certified public accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year.
C) A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator stating as follows:
i) That the accountant has compared the data that the letter from the chief financial officer specifies as having been derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements; and
ii) In connection with that procedure, that no matters came to the accountant’s attention that caused the accountant to believe that the specified data should be adjusted.
5) After the initial submission of items specified in subsection (f)(3), the owner or operator must send updated information to the Agency within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in subsection (f)(3).
6) If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (f)(1), the owner or operator must obtain insurance, a letter of credit, a surety bond, a trust fund, or a guarantee for the entire amount of required liability coverage, as specified in this Section. Evidence of insurance must be submitted to the Agency within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the test requirements.
7) The Agency may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in the accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements (see subsection (f)(3)(B)). An adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion is cause for disallowance. The Agency must evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide evidence of insurance for the entire amount of required liability coverage, as specified in this Section, within 30 days after notification of disallowance.
g) Guarantee for Liability Coverage
1) Subject to subsection (g)(2), an owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a written guarantee, referred to as a “guarantee”. The guarantor must be the direct or higher-tier parent corporation of the owner or operator, a firm whose parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, or a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners and operators in subsections (f)(1) through (f)(6). The wording of the guarantee must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251. A certified copy of the guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Agency as specified in subsection (f)(3). One of these items must be the letter from the guarantor’s chief financial officer. If the guarantor’s parent corporation is also the parent corporation of the owner or operator, this letter must describe the value received in consideration of the guarantee. If the guarantor is a firm with a “substantial business relationship” with the owner or operator, this letter must describe this “substantial business relationship” and the value received in consideration of the guarantee. The terms of the guarantee must provide as follows:
A) If the owner or operator fails to satisfy a judgment based on a determination of liability for bodily injury or property damage to third parties caused by sudden or nonsudden accidental occurrences (or both as the case may be), arising from the operation of facilities covered by this guarantee, or fails to pay an amount agreed to in settlement of claims arising from or alleged to arise from such injury or damage, the guarantor will do so up to the limits of coverage.
B) The guarantee remains in force unless the guarantor sends notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. The guarantee must not be terminated unless and until the Agency approves alternate liability coverage complying with Section 725.247 or 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.247.
2) The guarantor must execute the guarantee in Illinois. The guarantee must be accompanied by a letter signed by the guarantor that states as follows:
A) The guarantee was signed in Illinois by an authorized agent of the guarantor;
B) The guarantee is governed by Illinois law; and
C) The name and address of the guarantor’s registered agent for service of process.
3) The guarantor must have a registered agent pursuant to Section 5.05 of the Business Corporation Act of 1983 [805 ILCS 5/5.05] or Section 105.05 of the General Not-for-Profit Corporation Act of 1986 [805 ILCS 105/105.05].
h) Letter of Credit for Liability Coverage
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to the requirements of this subsection, and submitting a copy of the letter of credit to the Agency.
2) The financial institution issuing the letter of credit must be an entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter of credit operations are regulated and examined by the Illinois Commissioner of Banks and Trust Companies.
3) The wording of the letter of credit must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251.
4) An owner or operator that uses a letter of credit to satisfy the requirements of this Section may also establish a trust fund. Under the terms of such a letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the trustee of the standby trust will be deposited by the issuing institution into the standby trust in accordance with instructions from the trustee. The trustee of the standby trust fund must be an entity that has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by the Illinois Commissioner of Banks and Trust Companies, or that complies with the Corporate Fiduciary Act [205 ILCS 620].
5) The wording of the standby trust fund must be identical to the wording specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251(n).
i) Surety Bond for Liability Coverage
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this subsection (i) and submitting a copy of the bond to the Agency.
2) The surety company issuing the bond must be licensed by the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, Division of Insurance.
3) The wording of the surety bond must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251.
j) Trust Fund for Liability Coverage
1) An owner or operator may satisfy the requirements of this Section by establishing a trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this subsection and submitting a signed, duplicate original of the trust agreement to the Agency.
2) The trustee must be an entity that has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by the Illinois Commissioner of Banks and Trust Companies, or that complies with the Corporate Fiduciary Act [205 ILCS 620].
3) The trust fund for liability coverage must be funded for the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided by the trust fund before it may be relied upon to satisfy the requirements of this Section. If at any time after the trust fund is created the amount of funds in the trust fund is reduced below the full amount of liability coverage to be provided, the owner or operator, by the anniversary of the date of establishment of the fund, must either add sufficient funds to the trust fund to cause its value to equal the full amount of liability coverage to be provided, or obtain other financial assurance, as specified in this Section, to cover the difference. For purposes of this subsection, “the full amount of the liability coverage to be provided” means the amount of coverage for sudden and nonsudden accidental occurrences required to be provided by the owner or operator by this Section, less the amount of financial assurance for liability coverage that is being provided by other financial assurance mechanisms being used to demonstrate financial assurance by the owner or operator.
4) The wording of the trust fund must be as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.248 Incapacity of Owners or Operators, Guarantors, or Financial Institutions
a) An owner or operator must notify the Agency by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under 11 USC (Bankruptcy) naming the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 days after commencement of the proceeding. A guarantor of a corporate guarantee as specified in Sections 725.243(e) and 725.245(e) must make such a notification if the guarantor is named as a debtor, as required under the terms of the corporate guarantee (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.251).
b) An owner or operator that fulfills the requirements of Sections 725.243, 725.245 or 725.247 by obtaining a trust fund, surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy will be deemed to be without the required financial assurance or liability coverage in the event of bankruptcy of the trustee or issuing institution, or a suspension or revocation of the authority of the trustee institution to act as trustee or of the institution issuing the surety bond, letter of credit, or insurance policy to issue such instruments. The owner or operator must establish other financial assurance or liability coverage within 60 days after such an event.
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.251 Promulgation of Forms (Repealed)
SUBPART I: USE AND MANAGEMENT OF CONTAINERS
Section 725.270 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart I apply to owners and operators of all hazardous waste facilities that store containers of hazardous waste, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.271 Condition of Containers
If a container holding hazardous waste is not in good condition or if it begins to leak, the owner or operator must transfer the hazardous waste from this container to a container that is in good condition or manage the waste in some other way that it complies with the requirements of this Part.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.272 Compatibility of Waste with Containers
The owner or operator must use a container made of or lined with materials that will not react with and are otherwise compatible with the hazardous waste to be stored, so that the ability of the container to contain the waste is not impaired.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.273 Management of Containers
a) A container holding hazardous waste must always be closed during storage, except when it is necessary to add or remove waste.
b) A container holding hazardous waste must not be opened, handled, or stored in a manner that may rupture the container or cause it to leak.
BOARD NOTE: Re-use of containers in transportation is governed by USDOT regulations, including those set forth in 49 CFR 173.28 (Reuse, Reconditioning, and Remanufacture of Packagings), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.274 Inspections
At least weekly, the owner or operator must inspect areas where containers are stored. The owner or operator must look for leaking containers and for deterioration of containers caused by corrosion or other factors. See Section 725.171 for remedial action required if deterioration or leaks are detected.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.276 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
Containers holding ignitable or reactive waste must be located at least 15 meters (50 feet) from the facility’s property line.
BOARD NOTE: See Section 725.117(a) for additional requirements.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.277 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
a) Incompatible wastes or incompatible wastes and materials (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for examples) must not be placed in the same container, unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
b) Hazardous waste must not be placed in an unwashed container that previously held an incompatible waste or material (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265, for examples), unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
c) A storage container holding a hazardous waste that is incompatible with any waste or other materials stored nearby in other containers, piles, open tanks, or surface impoundments must be separated from the other materials or protected from them by means of a dike, berm, wall, or other device.
BOARD NOTE: The purpose of this is to prevent fires, explosions, gaseous emissions, leaching, or other discharge or hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that could result from the mixing of incompatible wastes or materials if containers break or leak.
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.278 Air Emission Standards
The owner or operator must manage all hazardous waste placed in a container in accordance with the requirements of Subparts AA, BB, and CC of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART J: TANK SYSTEMS
Section 725.290 Applicability
The regulations of this Subpart J apply to owners and operators of facilities that use tank systems for storing or treating hazardous waste, except as otherwise provided in subsection (a), (b), or (c) or in Section 725.101.
a) Tank systems that are used to store or treat hazardous waste that contains no free liquids and that are situated inside a building with an impermeable floor are exempted from the requirements in Section 725.293. To demonstrate the absence or presence of free liquids in the stored or treated waste, the following test must be used: USEPA Method 9095B (Paint Filter Liquids Test), as described in “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods”, USEPA publication number EPA-530/SW-846, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
b) Tank systems, including sumps, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110, that serve as part of a secondary containment system to collect or contain releases of hazardous wastes are exempted from the requirements in Section 725.293(a).
c) Tanks, sumps, and other collection devices used in conjunction with drip pads, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110 and regulated under Subpart W, must meet the requirements of this Subpart J.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.291 Assessment of Existing Tank System Integrity
a) For each existing tank system that does not have secondary containment meeting the requirements of Section 725.293, the owner or operator must determine either that the tank system is not leaking or that it is unfit for use. Except as provided in subsection (c), the owner or operator must obtain and keep on file at the facility a written assessment reviewed and certified by a qualified Professional Engineer, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126(d), that attests to the tank system’s integrity.
b) This assessment must determine whether the tank system is adequately designed and has sufficient structural strength and compatibility with the wastes to be stored or treated to ensure that it will not collapse, rupture, or fail. At a minimum, this assessment must consider the following:
1) Design standards, if available, according to which the tank and ancillary equipment were constructed;
2) Hazardous characteristics of the wastes that have been or will be handled;
3) Existing corrosion protection measures;
4) Documented age of the tank system, if available, (otherwise, an estimate of the age); and
5) Results of a leak test, internal inspection, or other tank integrity examination, such that the following conditions are met:
A) For non-enterable underground tanks, this assessment must consist of a leak test that is capable of taking into account the effects of temperature variations, tank end deflection, vapor pocket, and high water table effects.
B) For other than non-enterable underground tanks and for ancillary equipment, this assessment must be either a leak test, as described above, or an internal inspection or other tank integrity examination certified by a qualified Professional Engineer, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126(d), that addresses cracks, leaks, corrosion, and erosion.
BOARD NOTE: The practices described in the American Petroleum Institute (API) Publication, “Guide for Inspection of Refinery Equipment”, Chapter XIII, “Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Storage Tanks”, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used, where applicable, as guidelines in conducting the integrity examination of an other than non-enterable underground tank system.
c) Tank systems that store or treat materials that become hazardous wastes must conduct this assessment within 12 months after the date that the waste becomes a hazardous waste.
d) If, as a result of the assessment conducted in accordance with subsection (a), a tank system is found to be leaking or unfit for use, the owner or operator must comply with the requirements of Sections 725.296.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.292 Design and Installation of New Tank Systems or Components
a) An owner or operator of a new tank system or component must ensure that the foundation, structural support, seams, connections, and pressure controls (if applicable) are adequately designed and that the tank system has sufficient structural strength, compatibility with the wastes to be stored or treated, and corrosion protection so that it will not collapse, rupture, or fail. The owner or operator must obtain a written assessment reviewed and certified by a qualified Professional Engineer, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126(d), attesting that the system has sufficient structural integrity and is acceptable for the storing and treating of hazardous waste. This assessment must include the following information:
1) Design standards according to which the tanks and ancillary equipment is or will be constructed.
2) Hazardous characteristics of the wastes to be handled.
3) For new tank systems or components in which the external shell of a metal tank or any external metal component of the tank system is or will be in contact with the soil or with water, a determination by a corrosion expert of the following:
A) Factors affecting the potential for corrosion, including but not limited to the following:
i) Soil moisture content;
ii) Soil pH;
iii) Soil sulfides level;
iv) Soil resistivity;
v) Structure to soil potential;
vi) Influence of nearby underground metal structures (e.g., piping);
vii) Stray electric current;
viii) Existing corrosion-protection measures (e.g., coating, cathodic protection, etc.); and
B) The type and degree of external corrosion protection that are needed to ensure the integrity of the tank system during the use of the tank system or component, consisting of one or more of the following:
i) Corrosion-resistant materials of construction such as special alloys, or fiberglass-reinforced plastic;
ii) Corrosion-resistant coating (such as epoxy, fiberglass, etc.) with cathodic protection (e.g., impressed current or sacrificial anodes); and
iii) Electrical isolation devices such as insulating joints and flanges, etc.
BOARD NOTE: The practices described in the National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE) Standard, “Control of External Corrosion on Metallic Buried, Partially Buried, or Submerged Liquid Storage Systems”, NACE Recommended Practice RP0285, and “Cathodic Protection of Underground Petroleum Storage Tanks and Piping Systems”, API Recommended Practice 1632, each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used, where applicable, as guidelines in providing corrosion protection for tank systems.
4) For underground tank system components that are likely to be affected by vehicular traffic, a determination of design or operational measures that will protect the tank system against potential damage; and
5) Design considerations to ensure the following:
A) Tank foundations will maintain the load of a full tank;
B) Tank systems will be anchored to prevent flotation or dislodgement where the tank system is placed in a saturated zone, or is located within a seismic fault zone; and
C) Tank systems will withstand the effects of frost heave.
b) The owner and operator of a new tank system must ensure that proper handling procedures are adhered to in order to prevent damage to the system during installation. Prior to covering, enclosing or placing a new tank system or component in use, an independent, qualified installation inspector or a qualified Professional Engineer, either of whom is trained and experienced in the proper installation of tank systems or components, must inspect the system or component for the presence of any of the following items:
1) Weld breaks;
2) Punctures;
3) Scrapes of protective coatings;
4) Cracks;
5) Corrosion; and
6) Other structural damage or inadequate construction or installation. All discrepancies must be remedied before the tank system is covered, enclosed, or placed in use.
c) New tank systems or components and piping that are placed underground and which are backfilled must be provided with a backfill material that is a noncorrosive, porous, and homogeneous substance which is carefully installed so that the backfill is placed completely around the tank and compacted to ensure that the tank and piping are fully and uniformly supported.
d) All new tanks and ancillary equipment must be tested for tightness prior to being covered, enclosed or placed in use. If a tank system is found not to be tight, all repairs necessary to remedy the leaks in the system must be performed prior to the tank system being covered, enclosed, or placed in use.
e) Ancillary equipment must be supported and protected against physical damage and excessive stress due to settlement, vibration, expansion, or contraction.
BOARD NOTE: The piping system installation procedures described in “Installation of Underground Petroleum Storage Systems”, API Recommended Practice 1615, or “Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping”, ASME/ANSI Standard B31.3-1987, as supplemented by B31.3a-1988 and B31.3b-1988, each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used where applicable, as guidelines for proper installation of piping systems.
f) The owner and operator must provide the type and degree of corrosion protection necessary, based on the information provided under subsection (a)(3), to ensure the integrity of the tank system during use of the tanks system. An independent corrosion expert must supervise the installation of a corrosion protection system that is field fabricated to ensure proper installation.
g) The owner and operator must obtain and keep on file at the facility written statements by those persons required to certify the design of the tank system and supervise the installation of the tank system in accordance with the requirements of subsections (b) through (f) to attest that the tank system was properly designed and installed and that repairs, pursuant to subsections (b) and (d) were performed. These written statements must also include the certification statement, as required in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126(d).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.293 Containment and Detection of Releases
a) In order to prevent the release of hazardous waste or hazardous constituents to the environment, secondary containment that meets the requirements of this Section must be provided (except as provided in subsections (f) and (g)).
1) For a new or existing tank system or component, prior to its being put into service.
2) For a tank system that stores or treats materials that become hazardous wastes, within two years after the hazardous waste listing, or when the tank system has reached 15 years of age, whichever comes later.
b) Secondary containment systems must be as follows:
1) Designed, installed, and operated to prevent any migration of wastes or accumulated liquid out of the system to the soil, groundwater, or surface water at any time during the use of the tank system; and
2) Capable of detecting and collecting releases and accumulated liquids until the collected material is removed.
c) To meet the requirements of subsection (b), secondary containment systems must be at a minimum as follows:
1) Constructed of or lined with materials that are compatible with the wastes to be placed in the tank system and of sufficient strength and thickness to prevent failure due to pressure gradients (including static head and external hydrological forces), physical contact with the waste to which they are exposed, climatic conditions, the stress of installation, and the stress of daily operation (including stresses from nearby vehicular traffic);
2) Placed on a foundation or base capable of providing support to the secondary containment system and resistance to pressure gradients above and below the system and capable of preventing failure due to settlement, compression, or uplift;
3) Provided with a leak detection system that is designed and operated so that it will detect the failure of either the primary and secondary containment structure or any release of hazardous waste or accumulated liquid in the secondary containment system within 24 hours, or as otherwise provided in the RCRA permit if the operator has demonstrated to the Agency, by way of permit application, that the existing detection technology or site conditions will not allow detection of a release within 24 hours;
4) Sloped or otherwise designed or operated to drain and remove liquids resulting from leaks, spills, or precipitation. Spilled or leaked waste and accumulated precipitation must be removed from the secondary containment system within 24 hours, or as otherwise provided in the RCRA permit if the operator has demonstrated to the Agency, by way of permit application, that removal of the released waste or accumulated precipitation cannot be accomplished within 24 hours.
BOARD NOTE: If the collected material is a hazardous waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721, it is subject to management as a hazardous waste in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722 through 728. If the collected material is discharged through a point source to waters of the State, it is subject to the NPDES permit requirement of Section 12(f) of the Environmental Protection Act and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 309. If discharged to a Publicly Owned Treatment Works (POTW), it is subject to the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 307 and 310. If the collected material is released to the environment, it may be subject to the reporting requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 750.410 and federal 40 CFR 302.6.
d) Secondary containment for tanks must include one or more of the following devices:
1) A liner (external to the tank);
2) A vault;
3) A double-walled tank; or
4) An equivalent device as approved by the Board in an adjusted standards proceeding.
e) In addition to the requirements of subsections (b), (c), and (d), secondary containment systems must satisfy the following requirements:
1) External liner systems must be as follows:
A) Designed or operated to contain 100 percent of the capacity of the largest tank within the liner system’s boundary;
B) Designed or operated to prevent run-on or infiltration of precipitation into the secondary containment system, unless the collection system has sufficient excess capacity to contain run-on or infiltration. Such additional capacity must be sufficient to contain precipitation from a 25-year, 24-hour rainfall event;
C) Free of cracks or gaps; and
D) Designed and installed to completely surround the tank and to cover all surrounding earth likely to come into contact with the waste if released from the tanks (i.e., capable of preventing lateral as well as vertical migration of the waste).
2) Vault systems must be as follows:
A) Designed or operated to contain 100 percent of the capacity of the largest tank within the vault system’s boundary;
B) Designed or operated to prevent run-on or infiltration of precipitation into the secondary containment system, unless the collection system has sufficient excess capacity to contain run-on or infiltration. Such additional capacity must be sufficient to contain precipitation from a 25-year, 24-hour rainfall event;
C) Constructed with chemical-resistant water stops in place at all joints (if any);
D) Provided with an impermeable interior coating or lining that is compatible with the stored waste and that will prevent migration of waste into the concrete;
E) Provided with a means to protect against the formation of and ignition of vapors within the vault, if the waste being stored or treated:
i) Meets the definition of ignitable waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121; or
ii) Meets the definition of reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.123 and may form an ignitable or explosive vapor; and
F) Provided with an exterior moisture barrier or be otherwise designed or operated to prevent migration of moisture into the vault if the vault is subject to hydraulic pressure.
3) Double-walled tanks must be as follows:
A) Designed as an integral structure (i.e., an inner tank within an outer shell) so that any release from the inner tank is contained by the outer shell;
B) Protected, if constructed of metal, from both corrosion of the primary tank interior and the external surface of the outer shell; and
C) Provided with a built-in continuous leak detection system capable of detecting a release within 24 hours or as otherwise provided in the RCRA permit if the operator has demonstrated to the Agency, by way of permit application, that the existing leak detection technology or site conditions will not allow detection of a release within 24 hours.
BOARD NOTE: The provisions outlined in the Steel Tank Institute (STI) document “Standard for Dual Wall Underground Steel Storage Tanks”, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used as guidelines for aspects of the design of underground steel double-walled tanks.
f) Ancillary equipment must be provided with full secondary containment (e.g., trench, jacketing, double-walled piping, etc.) that meets the requirements of subsections (c) and (h), except for the following:
1) Aboveground piping (exclusive of flanges, joints, valves, and connections) that are visually inspected for leaks on a daily basis;
2) Welded flanges, welded joints, and welded connections that are visually inspected for leaks on a daily basis;
3) Sealless or magnetic coupling pumps and sealless valves that are visually inspected for leaks on a daily basis; and
4) Pressurized aboveground piping systems with automatic shut-off devices (e.g., excess flow check valves, flow metering shutdown devices, loss of pressure actuated shut-off devices, etc.) that are visually inspected for leaks on a daily basis.
g) Pursuant to Section 28.1 of the Environmental Protection Act, and in accordance with Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104, an adjusted standard will be granted by the Board regarding alternative design and operating practices only if the Board finds either that the alternative design and operating practices, together with location characteristics, will prevent the migration of any hazardous waste or hazardous constituents into the groundwater or surface water at least as effectively as secondary containment during the active life of the tank system, or that in the event of a release that does migrate to groundwater or surface water, no substantial present or potential hazard will be posed to human health or the environment. New underground tank systems may not receive an adjusted standard from the secondary containment requirements of this Section through a justification in accordance with subsection (g)(2).
1) When determining whether to grant alternative design and operating practices based on a demonstration of equivalent protection of groundwater and surface water, the Board will consider whether the petitioner has justified an adjusted standard based on the following factors:
A) The nature and quantity of the waste;
B) The proposed alternate design and operation;
C) The hydrogeologic setting of the facility, including the thickness of soils between the tank system and groundwater; and
D) All other factors that would influence the quality and mobility of the hazardous constituents and the potential for them to migrate to groundwater or surface water.
2) In deciding whether to grant alternative design and operating practices based on a demonstration of no substantial present or potential hazard, the Board will consider whether the petitioner has justified an adjusted standard based on the following factors:
A) The potential adverse effects on groundwater, surface water, and land quality taking the following into account:
i) The physical and chemical characteristics of the waste in the tank system, including its potential for migration;
ii) The hydrogeological characteristics of the facility and surrounding land;
iii) The potential for health risks caused by human exposure to waste constituents;
iv) The potential for damage to wildlife; crops, vegetation, and physical structures caused by exposure to waste constituents; and
v) The persistence and permanence of the potential adverse effects;
B) The potential adverse effects of a release on groundwater quality, taking the following into account:
i) The quantity and quality of groundwater and the direction of groundwater flow;
ii) The proximity and withdrawal rates of water in the area;
iii) The current and future uses of groundwater in the area; and
iv) The existing quality of groundwater, including other sources of contamination and their cumulative impact on the groundwater quality;
C) The potential adverse effects of a release on surface water quality, taking the following into account:
i) The quantity and quality of groundwater and the direction of groundwater flow;
ii) The patterns of rainfall in the region;
iii) The proximity of the tank system to surface waters;
iv) The current and future uses of surface waters in the area and water quality standards established for those surface waters; and
v) The existing quality of surface water, including other sources of contamination and the cumulative impact on surface water quality; and
D) The potential adverse effects of a release on the land surrounding the tank system, taking the following into account:
i) The patterns of rainfall in the region; and
ii) The current and future uses of the surrounding land.
3) The owner or operator of a tank system, for which alternative design and operating practices had been granted in accordance with the requirements of subsection (g)(1), at which a release of hazardous waste has occurred from the primary tank system but has not migrated beyond the zone of engineering control (as established in the alternative design and operating practices), must fulfill the following requirements:
A) It must comply with the requirements of Section 725.296, except Section 725.296(d); and
B) It must decontaminate or remove contaminated soil to the extent necessary to assure the following:
i) It must enable the tank system, for which alternative design and operating practices were granted, to resume operation with the capability for the detection of and response to releases at least equivalent to the capability it had prior to the release; and
ii) It must prevent the migration of hazardous waste or hazardous constituents to groundwater or surface water.
C) If contaminated soil cannot be removed or decontaminated in accordance with subsection (g)(3)(B), it must comply with the requirements of Section 725.297(b).
4) The owner or operator of a tank system, for which alternative design and operating practices had been granted in accordance with the requirements of subsection (g)(1), at which a release of hazardous waste has occurred from the primary tank system and has migrated beyond the zone of engineering control (as established in the alternative design and operating practices, must fulfill the following requirements:
A) It must comply with the requirements of Section 725.296(a), (b), (c), and (d); and
B) It must prevent the migration of hazardous waste or hazardous constituents to groundwater or surface water, if possible, and decontaminate or remove contaminated soil. If contaminated soil cannot be decontaminated or removed, or if groundwater has been contaminated, the owner or operator must comply with the requirements of Section 725.297(b);
C) If repairing, replacing, or reinstalling the tank system, it must provide secondary containment in accordance with the requirements of subsections (a) through (f), or make the alternative design and operating practices demonstration to the Board again with respect to secondary containment and meet the requirements for new tank systems in Section 725.292 if the tank system is replaced. The owner or operator must comply with these requirements even if contaminated soil is decontaminated or removed, and groundwater or surface water has not been contaminated.
h) In order to make an alternative design and operating practices demonstration, the owner or operator must follow the following procedures, in addition to those specified in Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104:
1) The owner or operator must file a petition for approval of alternative design and operating practices according to the following schedule:
A) For existing tank systems, at least 24 months prior to the date that secondary containment must be provided in accordance with subsection (a); and
B) For new tank systems, at least 30 days prior to entering into a contract for installation of the tank system.
2) As part of the petition, the owner or operator must also submit the following to the Board:
A) A description of the steps necessary to conduct the demonstration and a timetable for completing each of the steps. The demonstration must address each of the factors listed in subsection (g)(1) or (g)(2); and
B) The portion of the Part B permit application specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.202.
3) The owner or operator must complete its showing within 180 days after filing its petition for approval of alternative design and operating practices.
4) The Agency must issue or modify the RCRA permit so as to require the permittee to construct and operate the tank system in the manner that was provided in any Board order approving alternative design and operating practices.
i) All tank systems, until such time as secondary containment meeting the requirements of this Section is provided, must comply with the following:
1) For non-enterable underground tanks, a leak test that meets the requirements of Section 725.291(b)(5) must be conducted at least annually.
2) For other than non-enterable underground tanks and for all ancillary equipment, the owner or operator must either conduct a leak test, as described in subsection (i)(1), or an internal inspection or other tank integrity examination, by a qualified Professional Engineer, that addresses cracks, leaks, and corrosion or erosion at least annually. The owner or operator must remove the stored waste from the tank, if necessary, to allow the condition of all internal tank surfaces to be assessed.
BOARD NOTE: The practices described in API Publication “Guide for Inspection of Refinery Equipment”, Chapter XIII, “Atmospheric and Low Pressure Storage Tanks”, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used, when applicable, as guidelines for assessing the overall condition of the tank system.
3) The owner or operator must maintain on file at the facility a record of the results of the assessments conducted in accordance with subsections (i)(1) through (i)(3).
4) If a tank system or component is found to be leaking or unfit for use as a result of the leak test or assessment in subsections (i)(1) through (i)(3), the owner or operator must comply with the requirements of Section 725.296.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.294 General Operating Requirements
a) Hazardous wastes or treatment reagents must not be placed in a tank system if they could cause the tank, its ancillary equipment or the secondary containment system to rupture, leak, corrode, or otherwise fail.
b) The owner or operator must use appropriate controls and practices to prevent spills and overflows from tank or secondary containment systems. These include the following, at a minimum:
1) Spill prevention controls (e.g., check valves, dry disconnect couplings, etc.);
2) Overfill prevention controls (e.g., level sensing devices, high level alarms, automatic feed cutoff, or bypass to a standby tank); and
3) Maintenance of sufficient freeboard in uncovered tanks to prevent overtopping by wave or wind action or by precipitation.
c) The owner or operator must comply with the requirements of Section 725.296 if a leak or spill occurs in the tank system.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.295 Inspections
a) The owner or operator must inspect the following, where present, at least once each operating day, data gathered from monitoring and leak detection equipment (e.g., pressure or temperature gauges, monitoring wells, etc.) to ensure that the tank system is being operated according to its design.
b) Except as noted under subsection (c), the owner or operator must inspect the following at least once each operating day:
1) Overfill/spill control equipment (e.g., waste-feed cutoff systems, bypass systems, and drainage systems) to ensure that it is in good working order;
2) Above ground portions of the tank system, if any, to detect corrosion or releases of waste; and
3) The construction materials and the area immediately surrounding the externally accessible portion of the tank system, including the secondary containment system (e.g., dikes) to detect erosion or signs of releases of hazardous waste (e.g., wet spots, dead vegetation, etc.).
BOARD NOTE: Section 725.115(c) requires the owner or operator to remedy any deterioration or malfunction the owner or operator finds. Section 725.296 requires the owner or operator to notify the Agency within 24 hours of confirming a release. Also, federal 40 CFR 302 may require the owner or operator to notify the National Response Center of a release.
c) The owner or operator of a tank system that either uses leak detection equipment to alert facility personnel to leaks or implements established workplace practices to ensure leaks are promptly identified must inspect at least weekly those areas described in subsections (b)(1) through (b)(3). Use of the alternate inspection schedule must be documented in the facility’s operating record. This documentation must include a description of the established workplace practices at the facility.
d) This subsection (d) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.195(d), which USEPA has removed and marked “reserved”. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal requirements.
e) Ancillary equipment that is not provided with secondary containment, as described in Section 725.293(f)(1) through (f)(4), must be inspected at least once each operating day.
f) The owner or operator must inspect cathodic protection systems, if present, according to, at a minimum, the following schedule to ensure that they are functioning properly:
1) The proper operation of the cathodic protection system must be confirmed within six months after initial installation, and annually thereafter; and
2) All sources of impressed current must be inspected or tested, as appropriate, at least every other month.
BOARD NOTE: The practices described in “Control of External Corrosion on Metallic Buried, Partially Buried, or Submerged Liquid Storage Systems”, NACE Recommended Practice RP0285-85, or “Cathodic Protection of Underground Petroleum Storage Tanks and Piping Systems”, API Recommended Practice 1632, each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), may be used, where applicable, as guidelines in maintaining and inspecting cathodic protection systems.
g) The owner or operator must document in the operating record of the facility an inspection of those items in subsections (a) and (b).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.296 Response to Leaks or Spills and Disposition of Tank Systems
A tank system or secondary containment system from which there has been a leak or spill, or which is unfit for use, must be removed from service immediately. The owner or operator must satisfy the following requirements:
a) Cease Using; Prevent Flow or Addition of Wastes. The owner or operator must immediately stop the flow of hazardous waste into the tank system or secondary containment system and inspect the system to determine the cause of the release.
b) Removal of Waste from Tank System or Secondary Containment System
1) If the release was from the tank system, the owner or operator must, within 24 hours after detection of the leak, remove as much of the waste as is necessary to prevent further release of hazardous waste to the environment and to allow inspection and repair of the tank system to be performed.
2) If the release was to a secondary containment system, all released materials must be removed within 24 hours to prevent harm to human health and the environment.
c) Containment of Visible Releases to the Environment. The owner or operator must immediately conduct a visual inspection of the release and, based upon that inspection, do the following:
1) Prevent further migration of the leak or spill to soils or surface water; and
2) Remove and properly dispose of any visible contamination of the soil or surface water.
d) Notifications; Reports
1) Any release to the environment, except as provided in subsection (d)(2), must be reported to the Agency within 24 hours after detection.
2) A leak or spill of hazardous waste is exempted from the requirements of this subsection (d) if the following occur:
A) The spill is less than or equal to a quantity of one pound (0.45 kg); and
B) The spill is immediately contained and cleaned-up.
3) Within 30 days after detection of a release to the environment, a report containing the following information must be submitted to the Agency:
A) Likely route of migration of the release;
B) Characteristics of the surrounding soil (soil composition, geology, hydrogeology, climate, etc.);
C) Results of any monitoring or sampling conducted in connection with the release (if available). If sampling or monitoring data relating to the release are not available within 30 days, these data must be submitted to the Agency as soon as they become available;
D) Proximity to downgradient drinking water, surface water, and population areas; and
E) Description of response actions taken or planned.
e) Provision of Secondary Containment, Repair, or Closure
1) Unless the owner or operator satisfies the requirements of subsections (e)(2) through (e)(4), the tank system must be closed in accordance with Section 725.297.
2) If the cause of the release was a spill that has not damaged the integrity of the system, the owner or operator may return the system to service as soon as the released waste is removed and repairs, if necessary, are made.
3) If the cause of the release was a leak from the primary tank system into the secondary containment system, the system must be repaired prior to returning the tank system to service.
4) If the source of the release was a leak to the environment from a component of a tank system without secondary containment, the owner or operator must provide the component of the system from which the leak occurred with secondary containment that satisfies the requirements of Section 725.293 before it is returned to service, unless the source of the leak is an aboveground portion of a tank system. If the source is an aboveground component that can be inspected visually, the component must be repaired and may be returned to service without secondary containment as long as the requirements of subsection (f) are satisfied. If a component is replaced to comply with the requirements of this subsection (e)(4), that component must satisfy the requirements for new tank systems or components in Sections 725.292 and 725.293. Additionally, if a leak has occurred in any portion of a tank system component that is not readily accessible for visual inspection (e.g., the bottom of an inground or on-ground tank), the entire component must be provided with secondary containment in accordance with Section 725.293 prior to being returned to use.
f) Certification of Major Repairs. If the owner or operator has repaired a tank system in accordance with subsection (e), and the repair has been extensive (e.g., installation of an internal liner, repair of a ruptured primary containment or secondary containment vessel, etc.), the tank system must not be returned to service unless the owner or operator has obtained a certification by a qualified Professional Engineer, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126(d), that the repaired system is capable of handling hazardous wastes without release for the intended life of the system. This certification must be placed in the operating record and maintained until closure of the facility.
BOARD NOTE: See Section 725.115(c) for the requirements necessary to remedy a failure. Also, federal 40 CFR 302.6 requires the owner or operator to notify the National Response Center of a release of any “reportable quantity”.
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
Section 725.297 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At closure of a tank system, the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components (liners, etc.), contaminated soils and structures and equipment contaminated with waste, and manage them as hazardous waste, unless 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(d) applies. The closure plan, closure activities, cost estimates for closure, and financial responsibility for tank systems must meet all of the requirements specified in Subparts G and H.
b) If the owner or operator demonstrates that not all contaminated soils can be practicably removed or decontaminated as required in subsection (a), then the owner or operator must close the tank system and perform post-closure care in accordance with the closure and post-closure care requirements that apply to landfills (Section 725.410). In addition, for the purposes of closure, post-closure and financial responsibility, such a tank system is then considered to be a landfill, and the owner or operator must meet all of the requirements of landfills specified in Subparts G and H.
c) If an owner or operator has a tank system that does not have secondary containment that meets the requirements of Section 725.293(b) through (f), and which is not exempt from the secondary containment requirements in accordance with Section 725.293(g), then the following requirements apply:
1) The closure plan for the tank system must include both a plan for complying with subsection (a), and a contingent plan for complying with subsection (b);
2) A contingent post-closure plan for complying with subsection (b) must be prepared and submitted as part of the permit application;
3) The cost estimates calculated for closure and post-closure care must reflect the costs of complying with the contingent closure plan and the contingent post-closure plan, if these costs are greater than the costs of complying with the closure plan prepared for the expected closure under subsection (a);
4) Financial assurance must be based on the cost estimates in subsection (c)(3); and
5) For the purposes of the contingent closure and post-closure plans, such a tank system is considered to be a landfill, and the contingent plans must meet all of the closure, post-closure care, and financial responsibility requirements for landfills under Subparts G and H.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.298 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
a) Ignitable or reactive waste must not be placed in a tank system, unless either of the following conditions is fulfilled:
1) The waste is treated, rendered or mixed before or immediately after placement in the tank system so that the following two conditions are fulfilled:
A) The resulting waste, mixture, or dissolved material no longer meets the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123; and
B) Section 725.117(b) is complied with;
2) The waste is stored or treated in such a way that it is protected from any material or conditions that may cause the waste to ignite or react; or
3) The tank system is used solely for emergencies.
b) The owner or operator of a facility where ignitable or reactive waste is stored or tested in tanks must comply with the requirements for the maintenance of protective distances between the waste management area and any public ways, streets, alleys, or an adjoining property line that can be built upon as required in Tables 2-1 through 2-6 of “Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code”, NFPA 30, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.299 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
a) Incompatible wastes or incompatible wastes and materials must not be placed in the same tank system, unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
b) Hazardous waste must not be placed in a tank system that has not been decontaminated and which previously held an incompatible waste or material unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.300 Waste Analysis and Trial Tests
In addition to performing the waste analysis required by Section 725.113, whenever a tank system is to be used to chemically treat or to store a hazardous waste that is substantially different from waste previously treated or stored in that tank system, or to treat chemically a hazardous waste with a substantially different process than any previously used in that tank system, the owner or operator must do the following:
a) It must conduct waste analyses and trial treatment or storage tests (e.g., bench-scale or pilot-plant scale tests); or
b) It must obtain written, documented information on similar waste under similar operating conditions to show that the proposed treatment or storage will meet the requirements of Section 725.294(a).
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.301 Generators of 100 to 1,000 Kilograms of Hazardous Waste Per Month (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.302 Air Emission Standards
The owner or operator must manage all hazardous waste placed in a tank in accordance with the requirements of Subparts AA, BB, and CC.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART K: SURFACE IMPOUNDMENTS
Section 725.320 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart K apply to owners and operators of facilities that use surface impoundments to treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.321 Design and Operating Requirements
a) The owner or operator of each new surface impoundment unit, each lateral expansion of a surface impoundment unit, and each replacement of an existing surface impoundment unit must install two or more liners and a leachate collection and removal system between such liners, and operate the leachate collection and removal system, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(c), unless exempted under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(d), (e), or (f).
b) The owner or operator of each unit referred to in subsection (a) must notify the Agency at least sixty days prior to receiving waste. The owner or operator of each facility submitting notice must file a Part B application within six months of the receipt of such notice.
c) The owner or operator of any replacement surface impoundment unit is exempt from subsection (a) if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The existing unit was constructed in compliance with the design standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(c), (d), and (e); and
BOARD NOTE: The cited subsections implemented the design standards of sections 3004(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5) of RCRA (42 USC 6924(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5)).
2) There is no reason to believe that the liner is not functioning as designed.
d) The Agency must not require a double liner as set forth in subsection (a) for any monofill, if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The monofill contains only hazardous wastes from foundry furnace emission controls or metal casting molding sand, and such wastes do not contain constituents that render the wastes hazardous for reasons other than the toxicity characteristic in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.124, with USEPA hazardous waste numbers D004 through D017; and
2) No Migration Demonstration
A) Design and Location Requirements
i) The monofill has at least one liner for which there is no evidence that such liner is leaking. For the purposes of this subsection (d)(2)(A)(i) the term “liner” means a liner designed, constructed, installed, and operated to prevent hazardous waste from passing into the liner at any time during the active life of the facility, or a liner designed, constructed, installed, and operated to prevent hazardous waste from migrating beyond the liner to adjacent subsurface soil, groundwater, or surface water at any time during the active life of the facility. In the case of any surface impoundment that has been exempted from the requirements of subsection (a), of a liner designed, constructed, installed, and operated to prevent hazardous waste from passing beyond the liner, at the closure of such impoundment the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, all contaminated liner material and contaminated soil to the extent practicable. If all contaminated soil is not removed or decontaminated, the owner or operator of such impoundment must comply with appropriate post-closure requirements, including but not limited to groundwater monitoring and corrective action;
ii) The monofill is located more than one-quarter mile from an underground source of drinking water (as that term is defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110); and
iii) The monofill is in compliance with generally applicable groundwater monitoring requirements for facilities with RCRA permits; or
B) The owner or operator demonstrates to the Board that the monofill is located, designed, and operated so as to assure that there will be no migration of any hazardous constituent into groundwater or surface water at any future time.
e) In the case of any unit in which the liner and leachate collection system have been installed pursuant to the requirements of subsection (a), and in good faith compliance with subsection (a) and with guidance documents governing liners and leachate collection systems under subsection (a), the Agency must not require a liner or leachate collection system that is different from that which was so installed pursuant to subsection (a) when issuing the first permit to such facility, except that the Agency is not precluded from requiring installation of a new liner when the Agency finds that any liner installed pursuant to the requirements of subsection (a) is leaking.
f) A surface impoundment must maintain enough freeboard to prevent any overtopping of the dike by overfilling, wave action, or a storm. Except as provided in subsection (g), there must be at least 60 centimeters (two feet) of freeboard.
g) A freeboard level less than 60 centimeters (two feet) may be maintained if the owner or operator obtains certification by a qualified engineer that alternate design features or operating plans will, to the best of the engineer’s knowledge and opinion, prevent overtopping of the dike. The certification, along with a written identification of alternate design features or operating plans preventing overtopping, must be maintained at the facility.
BOARD NOTE: Any point source discharge from a surface impoundment to waters of the State is subject to the requirements of Section 12 of the Environmental Protection Act. Spills may be subject to Section 311 of the Clean Water Act (33 USC 1321).
h) Surface impoundments that are newly subject to this Part due to the promulgation of additional listings or characteristics for the identification of hazardous waste must be in compliance with subsections (a), (c), or (d) not later than 48 months after the promulgation of the additional listing or characteristic. This compliance period must not be cut short as the result of the promulgation of land disposal prohibitions under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728 or the granting of an extension to the effective date of a prohibition pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.105, within this 48 month period.
i) Refusal to grant an exemption or waiver, or grant with conditions, may be appealed to the Board.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.322 Action Leakage Rate
a) The owner or operator of surface impoundment units subject to Section 725.321(a) must submit a proposed action leakage rate to the Agency when submitting the notice required under Section 725.321(b). Within 60 days of receipt of the notification, the Agency must do either of the following: establish an action leakage rate, either as proposed by the owner or operator or modified using the criteria in this Section, or extend the review period for up to 30 days. If no action is taken by the Agency before the original 60 or extended 90 day review periods, the action leakage rate will be approved as proposed by the owner or operator.
b) The Agency must approve an action leakage rate for surface impoundment units subject to Section 725.321(a). The action leakage rate is the maximum design flow rate that the leak detection system (LDS) can remove without the fluid head on the bottom liner exceeding one foot. The action leakage rate must include an adequate safety margin to allow for uncertainties in the design (e.g., slope, hydraulic conductivity, thickness of drainage material, etc.), construction, operation, and location of the LDS; waste and leachate characteristics; the likelihood and amounts of other sources of liquids in the LDS; and proposed response actions (e.g., the action leakage rate must consider decreases in the flow capacity of the system over time resulting from siltation and clogging, rib layover, and creep of synthetic components of the system; overburden pressures; etc.).
c) To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the owner or operator must convert the weekly or monthly flow rate from the monitoring data obtained under Section 725.326(b) to an average daily flow rate (gallons per acre per day) for each sump. The average daily flow rate for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period and, if the unit is closed in accordance with Section 725.328(a)(2), monthly during the post-closure care period, unless the Agency approves a different frequency pursuant to Section 725.326(b).
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.323 Containment System
An earthen dike must have a protective cover, such as grass, shale, or rock to minimize wind and water erosion and to preserve its structural integrity.
(Source: Renumbered from Section 725.324 and amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.324 Response Actions
a) The owner or operator of surface impoundment units subject to Section 725.321(a) must develop and keep on site a response action plan. The response action plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. At a minimum, the response action plan must describe the actions specified in subsection (b).
b) If the flow rate into the LDS exceeds the action leakage rate for any sump, the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Notify the Agency in writing of the exceedance within seven days after the determination;
2) Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Agency within 14 days of the determination, as to the amount of liquids; likely sources of liquids; possible location, size, and cause of any leaks; and short-term actions taken and planned;
3) Determine to the extent practicable the location, size, and cause of any leak;
4) Determine whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed; whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls; and whether or not the unit should be closed;
5) Determine any other short-term and longer-term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
6) Within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, submit to the Agency the results of the determinations specified in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the results of actions taken, and actions planned. Monthly thereafter, as long as the flow rate in the LDS exceeds the action leakage rate, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency a report summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
c) To make the leak or remediation determinations in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the owner or operator must do either of the following:
1) Perform the following assessments:
A) Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
B) Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, or other analyses of the liquids in the LDS to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
C) Assess the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment; or
2) Document why such assessments are not needed.
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.325 Waste Analysis and Trial Tests
In addition to the waste analyses required by Section 725.113, whenever a surface impoundment is to be used for either of the purposes in subsections (a) and (b), the owner or operator must, before treating the different waste or using the different process, perform either of the required actions listed in subsection (c):
a) Chemically treat a hazardous waste that is substantially different from waste previously treated in that impoundment; or
b) Chemically treat hazardous waste with a substantially different process than and previously used in that impoundment.
c) Required Actions
1) The owner or operator must conduct waste analyses and trial treatment tests (e.g., bench scale or pilot plant scale tests); or
2) The owner or operator must obtain written, documented information on similar treatment of similar waste under similar operating conditions, to show that this treatment will comply with Section 725.117(b).
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.113, the waste analyses plan must include analyses needed to comply with Sections 725.329 and 725.330. As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results from each waste analysis and trial test, or the documented information in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.326 Monitoring and Inspections
a) The owner or operator must inspect the following:
1) The freeboard level at least once each operating day to ensure compliance with Section 725.322; and
2) The surface impoundment, including dikes and vegetation surrounding the dike, at least once a week to detect any leaks, deterioration, or failures in the impoundment.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.115(c), the owner or operator must remedy any deterioration or malfunction the owner or operator finds.
b) LDS
1) An owner or operator required to have a LDS under Section 725.321(a) must record the amount of liquids removed from each LDS sump at least once each week during the active life and closure period.
2) After the final cover is installed, the amount of liquids removed from each LDS sump must be recorded at least monthly. If the liquid level in the sump stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive months, the amount of liquids in the sumps must be recorded at least quarterly. If the liquid level in the sump stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive quarters, the amount of liquids in the sumps must be recorded at least semi-annually. If at any time during the post-closure care period the pump operating level is exceeded at units on quarterly or semi-annual recording schedules, the owner or operator must return to monthly recording of amounts of liquids removed from each sump until the liquid level again stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive months.
3) “Pump operating level” is a liquid level proposed by the owner or operator and approved by the Agency based on pump activation level, sump dimensions, and level that avoids backup into the drainage layer and minimizes head in the sump. The timing for submission and approval of the proposed “pump operating level” will be in accordance with Section 725.322(a).
c) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.328 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At closure, the owner or operator must do either of the following:
1) Remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components (liners, etc.), contaminated subsoils, and structures and equipment contaminated with waste or leachate and manage them as hazardous waste, unless 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(d) applies; or
2) Close the impoundment and provide post-closure care for a landfill under Subpart G and Section 725.410, including the following:
A) Eliminate free liquids by removing liquid wastes or solidifying the remaining wastes and waste residues;
B) Stabilize remaining wastes to a bearing capacity sufficient to support final cover; and
C) Cover the surface impoundment with a final cover designed and constructed to do the following:
i) Provide long-term minimization of the migration of liquids through the closed impoundment;
ii) Function with minimum maintenance;
iii) Promote drainage and minimize erosion or abrasion of the cover;
iv) Accommodate settling and subsidence so that the cover’s integrity is maintained; and
v) Have a permeability less than or equal to the permeability of any bottom liner system or natural subsoils present.
b) In addition to the requirements of Subpart G of this Part and Section 725.410, during the post-closure care period the owner or operator of a surface impoundment in which wastes, waste residues or contaminated materials remain after closure in accordance with subsection (a)(2) must:
1) Maintain the integrity and effectiveness of the final cover, including making repairs to the cover as necessary to correct the effects of settling, subsidence, erosion, or other events;
2) Maintain and monitor the LDS in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.321(c)(2)(D) and (c)(3) and 725.326(b) and comply with all other applicable LDS requirements of this Part;
3) Maintain and monitor the groundwater monitoring system and comply with all other applicable requirements of Subpart F of this Part; and
4) Prevent run-on and run-off from eroding or damaging the final cover.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.329 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
Ignitable or reactive waste must not be placed in a surface impoundment, unless the waste and impoundment satisfy all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, and one of the following conditions is fulfilled:
a) The waste is treated, rendered, or mixed before or immediately after placement in the impoundment so that the following conditions are true:
1) The resulting waste, mixture, or dissolution of material no longer meets the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123; and
2) Section 725.117(b) is complied with; or
b) Management conditions.
1) The waste is managed in such a way that it is protected from any material or conditions that may cause it to ignite or react; and
2) The owner or operator obtains a certification from a qualified chemist or engineer that, to the best of the chemist’s or engineer’s knowledge and opinion, the design features or operating plans of the facility will prevent ignition or reaction; and
3) The certification and the basis for it are maintained at the facility; or
c) The surface impoundment is used solely for emergencies.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.330 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
Incompatible wastes, or incompatible waste and materials (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for examples) must not be placed in the same surface impoundment, unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.331 Air Emission Standards
The owner or operator must manage all hazardous waste placed in a surface impoundment in accordance with the requirements of Subparts BB and CC of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART L: WASTE PILES
Section 725.350 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart L apply to owners and operators of facilities that treat or store hazardous waste in piles, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise. Alternatively, a pile of hazardous waste may be managed as a landfill under Subpart N.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.351 Protection from Wind
The owner or operator of a pile containing hazardous waste that could be subject to dispersal by wind must cover or otherwise manage the pile so that wind dispersal is controlled.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.352 Waste Analysis
a) In addition to the waste analyses required by Section 725.113, the owner or operator must analyze a representative sample of waste from each incoming movement before adding the waste to any existing pile unless either of the following conditions is fulfilled:
1) The only wastes the facility receives that are amenable to piling are compatible with each other, or
2) The waste received is compatible with the waste in the pile to which it is to be added.
b) The analysis conducted must be capable of differentiating between the types of hazardous waste the owner or operator places in piles, so that mixing of incompatible waste does not inadvertently occur. The analysis must include a visual comparison of color and texture.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.113, the waste analysis plan must include analyses needed to comply with Sections 725.356 and 725.357. As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results of this analysis in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.353 Containment
If leachate or run-off from a pile is a hazardous waste, then control of the leachate or run-off must be accomplished by either of the following means:
a) Control by Pile Design, Construction, and Operation
1) The pile must be placed on an impermeable base that is compatible with the waste under the conditions of treatment or storage;
2) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate and maintain a run-on control system capable of preventing flow onto the active portion of the pile during peak discharge from at least a 25-year storm;
3) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate and maintain a run-off management system to collect and control at least the water volume resulting from a 24-hour, 25-year storm; and
4) Collection and holding facilities (e.g., tanks or basins) associated with run-on and run-off control systems must be emptied or otherwise managed expeditiously to maintain design capacity of the system; or
b) Alternative Control
1) The pile must be protected from precipitation and run-on by some other means; and
2) No liquids or wastes containing free liquids may be placed in the pile.
BOARD NOTE: If collected leachate or run-off is discharged through a point source to waters of the United States, it is subject to the requirements of Section 12 of the Act.
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 6049, May 2, 2019)
Section 725.354 Design and Operating Requirements
The owner or operator of each new waste pile on which construction commences after January 29, 1992, each lateral expansion of a waste pile unit on which construction commences after July 29, 1992, and each such replacement of an existing waste pile unit that is to commence reuse after July 29, 1992, must install two or more liners and a leachate collection and removal system above and between such liners and operate the leachate collection and removal systems, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.351(c), unless exempted under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.351(d), (e) or (f); and must comply with the procedures of Section 725.321(b). “Construction commences” is as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110 under “existing facility”. The owner or operator of each unit referred to in this Section must notify the Agency at least sixty days prior to receiving waste. The owner or operator of each facility submitting notice must file a Part B application within six months after the receipt of such notice.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.355 Action Leakage Rates
a) The owner or operator of waste pile units subject to Section 725.354 must submit a proposed action leakage rate to the Agency when submitting the notice required under Section 725.354. Within 60 days after receipt of the notification, the Agency must either establish an action leakage rate, either as proposed by the owner or operator or modified using the criteria in this Section, or it must extend the review period for up to 30 days. If no action is taken by the Agency before the original 60 or extended 90 day review period, the action leakage rate must be approved as proposed by the owner or operator.
b) The Agency must approve an action leakage rate for waste pile units subject to Section 725.354. The action leakage rate is the maximum design flow rate that the LDS can remove without the fluid head on the bottom liner exceeding one foot. The action leakage rate must include an adequate safety margin to allow for uncertainties in the design (e.g., slope, hydraulic conductivity, thickness of drainage material, etc.), construction, operation, and location of the LDS; waste and leachate characteristics; the likelihood and amounts of other sources of liquids in the LDS; and proposed response actions (e.g., the action leakage rate must consider decreases in the flow capacity of the system over time resulting from siltation and clogging, rib layover, and creep of synthetic components of the system; overburden pressures; etc.).
c) To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the owner or operator must convert the weekly flow rate from the monitoring data obtained under Section 725.360, to an average daily flow rate (gallons per acre per day) for each sump. The average daily flow rate for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period.
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.356 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
Ignitable or reactive waste must not be placed in a pile, unless the waste and pile meet all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, and either of the following is true:
a) Both of the following are true of addition of the waste to an existing pile:
1) The addition results in the waste or mixture no longer meeting the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123; and
2) The addition complies with Section 725.117(b); or
b) The waste is managed in such a way that it is protected from any material or conditions that may cause it to ignite or react.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.357 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
a) Incompatible wastes, or incompatible wastes and materials (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for examples) must not be placed in the same pile, unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
b) A pile of hazardous waste that is incompatible with any waste or other material stored nearby in other containers, piles, open tanks, or surface impoundments must be separated from the other materials or protected from them by means of a dike, berm, wall, or other device.
BOARD NOTE: The purpose of this is to prevent fires, explosions, gaseous emissions, leaching, or other discharge of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents that could result from the contact or mixing of incompatible wastes or materials.
c) Hazardous waste must not be piled on the same area where incompatible wastes or materials were previously piled, unless that area has been decontaminated sufficiently to ensure compliance with Section 725.117(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.358 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At closure, the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components (liners, etc.), contaminated subsoils, and structures and equipment contaminated with waste and leachate and manage them as hazardous waste, unless 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(d) applies; or
b) If, after removing or decontaminating all residues and making all reasonable efforts to effect removal or decontamination of contaminated components, subsoils, structures, and equipment, as required in subsection (a), the owner or operator finds that not all contaminated subsoils can be practicably removed or decontaminated, it must close the facility and perform post-closure care in accordance with the closure and post-closure requirements that apply to landfills (Section 725.410).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.359 Response Actions
a) The owner or operator of waste pile units subject to Section 725.354 must submit a response action plan to the Agency when submitting the proposed action leakage rate under Section 725.355. The response action plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. At a minimum, the response action plan must describe the actions specified in subsection (b).
b) If the flow rate into the leak determination system exceeds the action leakage rate for any sump, the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Notify the Agency in writing of the exceedance within seven days after the determination;
2) Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Agency within 14 days after the determination as to the amount of liquids; likely sources of liquids; possible location, size, and cause of any leaks; and short-term actions taken and planned;
3) Determine to the extent practicable the location, size, and cause of any leak;
4) Determine whether waste receipts should cease or be curtailed; whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls; and whether or not the unit should be closed;
5) Determine any other short-term and longer-term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
6) Within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, submit to the Agency the results of the determinations specified in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the results of actions taken, and actions planned. Monthly thereafter, as long as the flow rate in the LDS exceeds the action leakage rate, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency a report summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
c) To make the leak or remediation determinations in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the owner or operator must do either of the following:
1) Perform the following assessments:
A) Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
B) Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent, or other analyses of the liquids in the LDS to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
C) Assess the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment; or
2) Document why such assessments are not needed.
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.360 Monitoring and Inspections
An owner or operator required to have a LDS under Section 725.354 must record the amount of liquids removed from each LDS sump at least once each week during the active life and closure period.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART M: LAND TREATMENT
Section 725.370 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart M apply to owners and operators of hazardous waste land treatment facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.372 General Operating Requirements
a) Hazardous waste must not be placed in or on a land treatment facility, unless the waste can be made less hazardous or non-hazardous by degradation, transformation, or immobilization processes occurring in or on the soil.
b) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-on control system capable of preventing flow onto the active portions of the unit during peak discharge from at least a 25-year storm.
c) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-off management system capable of collecting and controlling a water volume at least equivalent to a 24-hour, 25-year storm.
d) Collection and holding facilities (e.g., tanks or basins) associated with run-on and run-off control systems must be emptied or otherwise managed expeditiously after storms to maintain design capacity of the system.
e) If the treatment zone contains particulate matter that may be subject to wind dispersal the owner or operator must manage the unit to control wind dispersal.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.373 Waste Analysis
In addition to the waste analyses required by Section 725.113, before placing a hazardous waste in or on a land treatment facility, the owner or operator must do each of the following:
a) Determine the concentrations in the waste of any substances that equal or exceed the maximum concentrations contained in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.124 that cause a waste to exhibit the toxicity characteristic;
b) For any waste listed in Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721, determine the concentrations of any substances that caused the waste to be listed as a hazardous waste; and
c) If food chain crops are grown, determine the concentrations in the waste of each of the following constituents: arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury, unless the owner or operator has written, documented data that show that the constituent is not present.
BOARD NOTE: 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721 specifies the substances for which a waste is listed as a hazardous waste. As required by Section 725.113 the waste analysis plan must include analyses needed to comply with Sections 725.381 and 725.382. As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results from each waste analysis, or the documented information, in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 44 Ill. Reg. 15374, effective September 3, 2020)
Section 725.376 Food Chain Crops
a) This subsection (a) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.276(a), which required notification of activity before a date long past. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal rules.
BOARD NOTE: Growing food chain crops at a facility that has never before been used for this purpose is a significant change in process under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.155. The owner or operator of such a land treatment facility that proposes to grow food chain crops after May 17, 1982 must have submitted a new or revised Part A permit application.
b) Limitation Relating to Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, and Other Constituents
1) Food chain crops must not be grown on the treated area of a hazardous waste land treatment facility, unless the owner or operator can demonstrate, based on field testing, that either of the following is true of any arsenic, lead, mercury, or other constituents identified under Section 725.373(b):
A) They will not be transferred to the food portion of the crop by plant uptake or direct contact and will not otherwise be ingested by food chain animals (e.g., by grazing); or
B) They will not occur in greater concentrations in the crops grown on the land treatment facility than in the same crops grown on untreated soils under similar conditions in the same region.
2) The information necessary to make the demonstration required by subsection (b)(1) must be kept at the facility and must, at a minimum, fulfill the following conditions:
A) It must be based on tests for the specific waste and application rates being used at the facility; and
B) It must include descriptions of crop and soil characteristics, sample selection, criteria, sample size determination, analytical methods, and statistical procedures.
c) Limitation Relating to Cadmium. Food chain crops must not be grown on a land treatment facility receiving waste that contains cadmium unless all requirements of subsections (c)(1)(A) through (c)(1)(C) or all requirements of subsection (c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(D) are met.
1) Cadmium Limitation for Crops for Human Consumption. Application of waste must comply with all of the following conditions:
A) The pH of the waste and soil mixture is 6.5 or greater at the time of each waste application, except for waste containing cadmium at concentrations of 2 mg/kg (dry weight) or less;
B) The annual application of cadmium from waste does not exceed 0.5 kg/ha (0.45 lb/acre) on land used for production of tobacco, leafy vegetables, or root crops grown for human consumption. For other food chain crops the annual cadmium application rate does not exceed 0.5 kg/ha (0.45 lb/acre).
C) The cumulative application of cadmium from waste does not exceed the levels in either subsection (c)(1)(C)(i) or (c)(1)(C)(ii).
i) Maximum Cumulative Application of Cadmium
Maximum Cumulative Application of Cadmium
(kilograms per hectare)
For Background Soil pH Less Than 6.5
Soil Cation Exchange Capacity (milliequivalents per 100 grams)
Less than 5 5
5 to 15 5Greater than 15 5
FOR BACKGROUND SOIL pH GREATER THAN 6.5
Soil Cation Exchange Capacity (milliequivalents per 100 grams)
Less than 5 5
5 to 15 10Greater than 15 20
ii) For soils with a background pH of less than 6.5, the cumulative cadmium application rate does not exceed the levels below (provided, that the pH of the waste and soil mixture is adjusted to and maintained at 6.5 or greater whenever food chain crops are grown):
Maximum Cumulative Application of Cadmium
(kilograms per hectare)
For Background Soil pH Less Than 6.5 with pH Adjustment
Soil Cation Exchange Capacity (milliequivalents per 100 grams)
Less than 5 5
5 to 15 10Greater than 15 20
2) Cadmium Limitation for Crops for Animal Feed. Application of waste must comply with all of the following conditions:
A) The only food chain crop produced is animal feed;
B) The pH of the waste and soil mixture is 6.5 or greater at the time of waste application or at the time the crop is planted, whichever occurs later and this pH level is maintained whenever food chain crops are grown;
C) There is a facility operating plan that demonstrates how the animal feed will be distributed to preclude ingestion by humans. The facility operating plan describes the measures to be taken to safeguard against possible health hazards from cadmium entering the food chain that may result from alternative land uses; and
D) Future property owners are notified by a stipulation in the land record or property deed that states that the property has received waste at high cadmium application rates and that food chain crops must not be grown except in compliance with subsection (c)(2).
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.173, if an owner or operator grows food chain crops on his land treatment facility, he must place the information developed in this Section in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.378 Unsaturated Zone (Zone of Aeration) Monitoring
a) The owner or operator must have in writing, and must implement, an unsaturated zone monitoring plan that is designed to accomplish the following:
1) It must detect the vertical migration of hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents under the active portion of the land treatment facility, and
2) It must provide information on the background concentrations of the hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents in similar but untreated soil nearby. This background monitoring must be conducted before or in conjunction with the monitoring required under subsection (a)(1).
b) The unsaturated zone monitoring plan must include, at a minimum, both of the following:
1) Soil monitoring using soil cores, and
2) Soil-pore water monitoring using devices, such as lysimeters.
c) To comply with subsection (a)(1), the owner or operator must demonstrate in his unsaturated zone monitoring plan that ensures the following:
1) The depth at which soil and soil-pore water samples are to be taken is below the depth to which the waste is incorporated into the soil;
2) The number of soil and soil-pore water samples to be taken is based on the variability of the following:
A) The hazardous waste constituents (as identified in Section 725.373(a) and(b)) in the waste and in the soil, and
B) The soil types; and
3) The frequency and timing of soil and soil-pore water sampling is based on the frequency, time, and rate of waste application, proximity to ground water, and soil permeability.
d) The owner or operator must keep at the facility its unsaturated zone monitoring plan and the rationale used in developing this plan.
e) The owner or operator must analyze the soil and soil-pore water samples for the hazardous waste constituents that were found in the waste during the waste analysis under Section 725.373(a) and (b).
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place all data and information developed under this Section in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.379 Recordkeeping
The owner or operator must include hazardous waste application dates and rates in the operating record required under Section 725.173. Section 725.380 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) In the closure plan under Section 725.212 and the post-closure plan under Section 725.218 the owner or operator must address the following objectives and indicate how they will be achieved:
1) Control of the migration of hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents from the treated area into the groundwater;
2) Control of the release of contaminated runoff from the facility into surface water;
3) Control of the release of airborne particulate contaminants caused by wind erosion; and
4) Compliance with Section 725.376 concerning the growth of food-chain crops.
b) The owner or operator must consider at least the following factors in addressing the closure and post-closure care objectives of subsection (a):
1) The type and amount of hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents applied to the land treatment facility;
2) The mobility and the expected rate of migration of the hazardous waste and hazardous waste constituents;
3) The site location, topography, and surrounding land use with respect to the potential effects of pollutant migration (e.g., proximity to groundwater, surface water, and drinking water sources);
4) Climate, including amount, frequency, and pH of precipitation;
5) Geological and soil profiles and surface and subsurface hydrology of the site and soil characteristics, including cation exchange capacity, total organic carbon, and pH;
6) Unsaturated zone monitoring information obtained under Section 725.378; and
7) The type, concentration, and depth of migration of hazardous waste constituents in the soil, as compared to their background concentrations.
c) The owner or operator must consider at least the following methods in addressing the closure and post-closure care objectives of subsection (a):
1) Removal of contaminated soils;
2) Placement of a final cover, considering the following:
A) Functions of the cover (e.g., infiltration control, erosion and runoff control, and wind erosion control); and
B) Characteristics of the cover, including material, final surface contours, thickness, porosity and permeability, slope, length of run of slope, and type of vegetation on the cover; and
3) Monitoring of groundwater.
d) In addition to the requirements of Subpart G of this Part during the closure period the owner or operator of a land treatment facility must do the following:
1) It must continue unsaturated zone monitoring in a manner and frequency specified in the closure plan, except that soil pore liquid monitoring may be terminated 90 days after the last application of waste to the treatment zone;
2) It must maintain the run-on control system required under Section 725.372(b);
3) It must maintain the run-off management system required under Section 725.372(c); and
4) It must control wind dispersal of particulate matter that may be subject to wind dispersal.
e) For the purpose of complying with Section 725.215, when closure is completed the owner or operator may submit to the Agency certification both by the owner or operator and by an independent, qualified soil scientist, in lieu of a qualified Professional Engineer, that the facility has been closed in accordance with the specifications in the approved closure plan.
f) In addition to the requirements of Section 725.217, during the post-closure care period the owner or operator of a land treatment unit must fulfill the following requirements:
1) It must continue soil-core monitoring by collecting and analyzing samples in a manner and frequency specified in the post-closure plan;
2) It must restrict access to the unit as appropriate for its post-closure use;
3) It must assure that growth of food chain crops complies with Section 725.376; and
4) It must control wind dispersal of hazardous waste.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.381 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
The owner or operator must not apply ignitable or reactive waste to the treatment zone unless the waste and treatment zone meet all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, and:
a) The waste is immediately incorporated into the soil so that the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The resulting waste, mixture, or dissolution of material no longer meets the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123; and
2) Section 724.117(b) is complied with; or
b) The waste is managed in such a way that it is protected from any material or conditions that may cause it to ignite or react.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.382 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
Incompatible wastes or incompatible wastes and materials (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for examples) must not be placed in the same land treatment area unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
SUBPART N: LANDFILLS
Section 725.400 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart N apply to owners and operators of facilities that dispose of hazardous waste in landfills, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise. A waste pile used as a disposal facility is a landfill and is governed by this Subpart N.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.401 Design Requirements
a) The owner or operator of each new landfill unit, each lateral expansion of a landfill unit, and each replacement of an existing landfill unit must install two or more liners and a leachate collection and removal system above and between such liners, and operate the leachate collection and removal system, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.401(c), unless exempted by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.401(d), (e) or (f).
b) The owner or operator of each unit referred to in subsection (a) must notify the Agency at least 60 days prior to receiving waste. The owner or operator of each facility submitting notice must file a Part B application within six months of the receipt of such notice.
c) The owner or operator of any replacement landfill unit is exempt from subsection (a) if both of the following are true:
1) The existing unit was constructed in compliance with the design standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.401(c), (d), and (e); and
BOARD NOTE: The cited subsections implemented the design standards of sections 3004(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5) of RCRA (42 USC 6924(o)(1)(A)(i) and (o)(5)).
2) There is no reason to believe that the liner is not functioning as designed.
d) The Agency must not require a double liner as set forth in subsection (a) for any monofill, if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The monofill contains only hazardous wastes from foundry furnace emission controls or metal casting molding sand, and such wastes do not contain constituents that render the wastes hazardous for reasons other the toxicity characteristic in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.124, with USEPA hazardous waste numbers D004 through D017; and
2) Alternative Demonstration
A) Liner and Location Requirements
i) The monofill has at least one liner for which there is no evidence that such liner is leaking;
ii) The monofill is located more than one-quarter mile from an underground source of drinking water (as that term is defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110); and
iii) The monofill is in compliance with generally applicable groundwater monitoring requirements for facilities with RCRA permits; or
B) The owner or operator demonstrates to the Board that the monofill is located, designed, and operated so as to assure that there will be no migration of any hazardous constituent into groundwater or surface water at any future time.
e) In the case of any unit in which the liner and leachate collection system have been installed pursuant to the requirements of subsection (a), and in good faith compliance with subsection (a) and with guidance documents governing liners and leachate collection systems under subsection (a), the Agency must not require a liner or leachate collection system that is different from that which was so installed pursuant to subsection (a) when issuing the first permit to such facility, except that the Agency is not precluded from requiring installation of a new liner when the Agency finds that any liner installed pursuant to the requirements of subsection (a) is leaking.
f) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-on control system capable of preventing flow onto the active portion of the landfill during peak discharge from at least a 25-year storm.
g) The owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-off management system to collect and control at least the water volume resulting from a 24 hour, 25-year storm.
h) Collection and holding facilities (e.g., tanks or basins) associated with run-on and run-off control systems must be emptied or otherwise managed expeditiously after storms to maintain design capacity of the system.
i) The owner or operator of a landfill containing hazardous waste that is subject to dispersal by wind must cover or otherwise manage the landfill so that wind dispersal of the hazardous waste is controlled.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.113, the waste analysis plan must include analyses needed to comply with Sections 725.412, 725.413, and 725.414. As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results of these analyses in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.402 Action Leakage Rate
a) The owner or operator of landfill units subject to Section 725.401(a) must submit a proposed action leakage rate to the Agency when submitting the notice required under Section 725.401(b). Within 60 days after receipt of the notification, the Agency must establish an action leakage rate, either as proposed by the owner or operator or modified using the criteria in this Section, or extend the review period for up to 30 days. If no action is taken by the Agency before the original 60 or extended 90 day review periods, the action leakage rate will be approved as proposed by the owner or operator.
b) The Agency must approve an action leakage rate for landfill units subject to Section 725.401(a). The action leakage rate is the maximum design flow rate that the LDS can remove without the fluid head on the bottom liner exceeding one foot. The action leakage rate must include an adequate safety margin to allow for uncertainties in the design (e.g., slope, hydraulic conductivity, thickness of drainage material, etc.); construction, operation, and location of the LDS; waste and leachate characteristics, likelihood and amounts of other sources of liquids in the LDS; and proposed response actions (e.g., the action leakage rate must consider decreases in the flow capacity of the system over time resulting from siltation and clogging, rib layover, and creep of synthetic components of the system; overburden pressures; etc.).
c) To determine if the action leakage rate has been exceeded, the owner or operator must convert the weekly or monthly flow rate from the monitoring data obtained under Section 725.404 to an average daily flow rate (gallons per acre per day) for each sump. The average daily flow rate for each sump must be calculated weekly during the active life and closure period, and monthly during the post-closure care period unless the Agency approves a different period under Section 725.404(b).
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.403 Response Actions
a) The owner or operator of landfill units subject to Section 725.401(a) must develop and keep on site until closure of the facility a response action plan. The response action plan must set forth the actions to be taken if the action leakage rate has been exceeded. At a minimum, the response action plan must describe the actions specified in subsection (b).
b) If the flow rate into the LDS exceeds the action leakage rate for any sump, the owner or operator must do each of the following:
1) Notify the Agency in writing of the exceedance within seven days after the determination;
2) Submit a preliminary written assessment to the Agency within 14 days after the determination, as to the amount of liquids; likely sources of liquids; possible location, size, and cause of any leaks; and short-term actions taken and planned;
3) Determine to the extent practicable the location, size, and cause of any leak;
4) Determine whether waste receipt should cease or be curtailed; whether any waste should be removed from the unit for inspection, repairs, or controls; and whether or not the unit should be closed;
5) Determine any other short-term and longer-term actions to be taken to mitigate or stop any leaks; and
6) Within 30 days after the notification that the action leakage rate has been exceeded, submit to the Agency the results of the determinations specified in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the results of actions taken, and actions planned. Monthly thereafter, as long as the flow rate in the LDS exceeds the action leakage rate, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency a report summarizing the results of any remedial actions taken and actions planned.
c) To make the leak or remediation determinations in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(5), the owner or operator must do either of the following:
1) Perform the following assessments:
A) Assess the source of liquids and amounts of liquids by source;
B) Conduct a fingerprint, hazardous constituent or other analyses of the liquids in the LDS to identify the source of liquids and possible location of any leaks, and the hazard and mobility of the liquid; and
C) Assess the seriousness of any leaks in terms of potential for escaping into the environment; or
2) Document why such assessments are not needed.
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.404 Monitoring and Inspections
a) An owner or operator required to have an LDS under Section 725.401(a) must record the amount of liquids removed from each LDS sump at least once each week during the active life and closure period.
b) After the final cover is installed, the amount of liquids removed from each LDS sump must be recorded at least monthly. If the liquid level in the sump stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive months, the amount of liquids in the sumps must be recorded at least quarterly. If the liquid level in the sump stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive quarters, the amount of liquids in the sumps must be recorded at least semi-annually. If at any time during the post-closure care period the pump operating level is exceeded at units on quarterly or semi-annual recording schedules, the owner or operator must return to monthly recording of amounts of liquids removed from each sump until the liquid level again stays below the pump operating level for two consecutive months.
c) “Pump operating level” is a liquid level proposed by the owner or operator and approved by the Agency based on pump activation level, sump dimensions and level that avoids backup into the drainage layer and minimizes head in the sump. The timing for submission and approval of the proposed “pump operating level” will be in accordance with Section 725.402(a).
d) Final Agency determinations pursuant to this Section are deemed to be permit denials for purposes of appeal to the Board pursuant to Section 40 of the Environmental Protection Act.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.409 Surveying and Recordkeeping
The owner or operator of a landfill must maintain the following items in the operating record required in Section 725.173: On a map, the exact location and dimensions, including depth, of each cell with respect to permanently surveyed benchmarks; and b) The contents of each cell and the approximate location of each hazardous waste type within each cell. Section 725.410 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At final closure of the landfill or upon closure of any cell, the owner or operator must cover the landfill or cell with a final cover designed and constructed to accomplish the following:
1) It must provide long-term minimization of migration of liquids through the closed landfill;
2) It must function with minimum maintenance;
3) It must promote drainage and minimize erosion or abrasion of the cover;
4) It must accommodate settling and subsidence so that the cover’s integrity is maintained; and
5) It must have a permeability less than or equal to the permeability of any bottom liner system or natural subsoils present.
b) After final closure, the owner or operator must comply with all post-closure requirements contained in Section 725.217 through 725.220 including maintenance and monitoring throughout the post-closure care period. The owner or operator must do the following:
1) It must maintain the integrity and effectiveness of the final cover, including making repairs to the cover as necessary to correct the effects of settling, subsidence, erosion, or other events;
2) It must maintain and monitor the LDS in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.401(c)(3)(D) and (c)(4) and Section 725.404(b), and comply with all other applicable LDS requirements of this Part;
3) It must maintain and monitor the groundwater monitoring system and comply with all other applicable requirements of Subpart F;
4) It must prevent run-on and run-off from eroding or otherwise damaging the final cover; and
5) It must protect and maintain surveyed benchmarks used in complying with Section 725.409.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.412 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
a) Except as provided in subsection (b) and in Section 725.416, ignitable or reactive waste must not be placed in a landfill, unless the waste and landfill meets all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, and the waste is treated, rendered or mixed before or immediately after placement in a landfill so that both of the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The resulting waste, mixture, or dissolution of material no longer meets the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123; and
2) Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
b) Except for prohibited wastes that remain subject to treatment standards in Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728, ignitable waste in containers may be landfilled without meeting the requirements of subsection (a), provided that the wastes are disposed of in such a way that they are protected from any material or conditions that may cause them to ignite. At a minimum, ignitable wastes must be disposed of in non-leaking containers that are carefully handled and placed so as to avoid heat, sparks, rupture, or any other condition that might cause ignition of the wastes; must be covered daily with soil or other non-combustible material to minimize the potential for ignition of the wastes; and must not be disposed in cells that contain or will contain other wastes that may generate heat sufficient to cause ignition of the waste.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.413 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
Incompatible wastes or incompatible wastes and materials (see appendix V of 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for examples) must not be placed in the same landfill cell, unless Section 725.117(b) is complied with.
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.414 Special Requirements for Liquid Wastes
a) The placement of bulk or non-containerized liquid hazardous waste or hazardous waste containing free liquids (whether or not sorbents have been added) in any landfill is prohibited.
b) Containers holding free liquids must not be placed in a landfill unless one of the following conditions is fulfilled:
1) One of the following occurs with regard to all free-standing liquid:
A) It has been removed by decanting or other methods;
B) It has been mixed with sorbent or solidified so that free-standing liquid is no longer observed; or
C) It has been otherwise eliminated;
2) The container is very small, such as an ampule;
3) The container is designed to hold free liquids for use other than storage, such as a battery or capacitor; or
4) The container is a lab pack, as defined in Section 724.416, and is disposed of in accordance with Section 724.416.
c) To demonstrate the absence or presence of free liquids in either a containerized or a bulk waste, the following test must be used: Method 9095B (Paint Filter Liquids Test), as described in “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods”, USEPA publication number EPA-530/SW-846, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
d) This subsection (d) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.314(d), which recites a past effective date. This statement maintains structural parity with the federal regulations.
e) Sorbents used to treat free liquids to be disposed of in landfills must be nonbiodegradable. Nonbiodegradable sorbents are one of the following: materials listed or described in subsection (e)(1); materials that pass one of the tests in subsection (e)(2); or materials that are determined by the Board to be nonbiodegradable through the adjusted standard procedure of Section 28.1 of the Act and Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104.
1) Nonbiodegradable sorbents are the following:
A) Inorganic minerals, other inorganic materials, and elemental carbon (e.g., aluminosilicates, clays, smectites, Fuller’s earth, bentonite, calcium bentonite, montmorillonite, calcined montmorillonite, kaolinite, micas (illite), vermiculites, zeolites, calcium carbonate (organic free limestone), oxides/hydroxides, alumina, lime, silica (sand), diatomaceous earth, perlite (volcanic glass), expanded volcanic rock, volcanic ash, cement kiln dust, fly ash, rice hull ash, activated charcoal/activated carbon, etc.); or
B) High molecular weight synthetic polymers (e.g., polyethylene, high density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene, polystyrene, polyurethane, polyacrylate, polynorborene, polyisobutylene, ground synthetic rubber, cross-linked allylstyrene, and tertiary butyl copolymers). This does not include polymers derived from biological material or polymers specifically designed to be degradable; or
C) Mixtures of these nonbiodegradable materials.
2) Tests for Nonbiodegradable Sorbents
A) The sorbent material is determined to be nonbiodegradable under ASTM Method G21-70 (1984a) (Standard Practice for Determining Resistance of Synthetic Polymer Materials to Fungi), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a);
B) The sorbent material is determined to be nonbiodegradable under ASTM Method G22-76 (1984b) (Standard Practice for Determining Resistance of Plastics to Bacteria), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a); or
C) The sorbent material is determined to be non-biodegradable under OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, Method 301B (CO2 Evolution (Modified Sturm Test)), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
f) The placement of any liquid that is not a hazardous waste in a landfill is prohibited. (See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 729.311.)
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.415 Special Requirements for Containers
Unless they are very small, such as an ampule, containers must be in either of the following conditions:
a) They must be at least 90 percent full when placed in the landfill; or
b) They must be crushed, shredded, or similarly reduced in volume to the maximum practical extent before burial in the landfill.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.416 Disposal of Small Containers of Hazardous Waste in Overpacked Drums (Lab Packs)
Small containers of hazardous waste in overpacked drums (lab packs) may be placed in a landfill if the following requirements are met:
a) Hazardous waste must be packaged in non-leaking inside containers. The inside containers must be of a design and constructed of a material that will not react dangerously with, be decomposed by, or be ignited by the waste held therein. Inside containers must be tightly and securely sealed. The inside containers must be of the size and type specified in the USDOT hazardous materials regulations (49 CFR 173 (Shippers—General Requirements for Shipments and Packages), 178 (Specifications for Packagings), and 179 (Specifications for Tank Cars), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b)), if those regulations specify a particular inside container for the waste.
b) The inside containers must be overpacked in an open head USDOT-specification metal shipping container (49 CFR 178 (Specifications for Packagings) and 179 (Specifications for Tank Cars), of no more than 416 ℓ (110 gallon) capacity and surrounded by, at a minimum, a sufficient quantity of sorbent material, determined to be nonbiodegradable in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 725.414(e) to completely sorb all of the liquid contents of the inside containers. The metal outer container must be full after packing with inside containers and sorbent material.
c) The sorbent material used must not be capable of reacting dangerously with, being decomposed by, or being ignited by the contents of the inside containers, in accordance with Section 725.117(b).
d) Incompatible wastes, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110, must not be placed in the same outside container.
e) Reactive waste, other than cyanide- or sulfide-bearing waste, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.123(a)(5), must be treated or rendered non-reactive prior to packaging in accordance with subsections (a) through (d). Cyanide- or sulfide-bearing reactive waste may be packaged in accordance with subsections (a) through (d) without first being treated or rendered non-reactive.
f) Such disposal is in compliance with the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728. Persons that incinerate lab packs according to the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.142(c)(1) may use fiber drums in place of metal outer containers. Such fiber drums must meet the USDOT specifications in 49 CFR 173.12 (Exceptions for Shipments of Waste Materials), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), and be overpacked according to subsection (b).
g) Pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 729.312, the use of labpacks for disposal of liquid wastes or wastes containing free liquids allowed under this Section is restricted to labwaste and non-periodic waste, as those terms are defined in that Part.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART O: INCINERATORS
Section 725.440 Applicability
a) The regulations in this Subpart O apply to owners or operators of hazardous waste incinerators (as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110), except as 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.101 provides otherwise.
b) Integration of the MACT Standards
1) Except as provided by subsections (b)(2) and (b)(3), the standards of this Part no longer apply when an owner or operator demonstrates compliance with the maximum achievable control technology (MACT) requirements of subpart EEE of 40 CFR 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants from Hazardous Waste Combustors), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), by conducting a comprehensive performance test and submitting to the Agency a Notification of Compliance, under 40 CFR 63.1207(j) and 63.1210(d), documenting compliance with the requirements of subpart EEE of 40 CFR 63.
2) The MACT standards of subpart EEE of 40 CFR 63 do not replace the closure requirements of Section 724.451 or the applicable requirements of Subparts A through H, BB, and CC.
3) Section 725.445, generally prohibiting burning of hazardous waste during startup and shutdown, remains in effect if the owner or operator elects to comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.320(b)(1)(A) to minimize emissions of toxic compounds from startup and shutdown.
BOARD NOTE: Operating conditions used to determine effective treatment of hazardous waste remain effective after the owner or operator demonstrates compliance with the standards of subpart EEE of 40 CFR 63. Sections 9.1 and 39.5 of the Environmental Protection Act make the federal MACT standards directly applicable to entities in Illinois and authorize the Agency to issue permits based on the federal standards.
c) An owner or operator of an incinerator that burns hazardous waste is exempt from all of the requirements of this Subpart O, except Section 725.451 (Closure), provided that the owner or operator has documented, in writing, that the waste would not reasonably be expected to contain any of the hazardous constituents listed in Appendix H to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721 and such documentation is retained at the facility, if the waste to be burned is one of the following:
1) It is listed as a hazardous waste in Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721, solely because it is ignitable (Hazard Code I), corrosive (Hazard Code C), or both;
2) It is listed as a hazardous waste in Subpart D of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721, solely because it is reactive (Hazard Code R) for characteristics other than those listed in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.123(a)(4) and (a)(5), and will not be burned when other hazardous wastes are present in the combustion zone;
3) It is a hazardous waste solely because it possesses the characteristic of ignitability, corrosivity, or both, as determined by the tests for characteristics of hazardous wastes under Subpart C of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721; or
4) It is a hazardous waste solely because it possesses the reactivity characteristics described by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.123 (a)(1), (a)(2), (a)(3), (a)(6), (a)(7), or (a)(8) and will not be burned when other hazardous wastes are present in the combustion zone.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.441 Waste Analysis
In addition to the waste analyses required by Section 725.113, the owner or operator must sufficiently analyze any waste that he has not previously burned in his incinerator to enable him to establish steady state (normal) operating conditions (including waste and auxiliary fuel feed and air flow) and to determine the type of pollutants that might be emitted. At a minimum, the analysis must determine the following:
a) Heating value of the waste;
b) Halogen content and sulfur content in the waste; and
c) Concentrations in the waste of lead and mercury, unless the owner or operator has written, documented data that show that the element is not present.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results from each waste analysis or the documented information in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.445 General Operating Requirements
During startup and shutdown of an incinerator, the owner or operator must not feed hazardous waste unless the incinerator is at steady state (normal) conditions of operation, including steady state operating temperature and airflow.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.447 Monitoring and Inspections
The owner or operator must conduct, as a minimum, the following monitoring and inspections when incinerating hazardous waste:
a) Existing instruments that relate to combustion and emission control must be monitored at least every 15 minutes. Appropriate corrections to maintain steady state combustion conditions must be made immediately either automatically or by the operator. Instruments that relate to combustion and emission control would normally include those measuring waste feed, auxiliary fuel feed, air flow, incinerator temperature, scrubber flow, scrubber pH, and relevant level controls.
b) The complete incinerator and associated equipment (pumps, valves, conveyors, pipes, etc.) must be inspected at least daily for leaks, spills, and fugitive emissions and all emergency shutdown controls and system alarms must be checked to assure proper operation.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.451 Closure
At closure, the owner or operator must remove all hazardous waste and hazardous waste residues (including but not limited to ash, scrubber waters, and scrubber sludges) from the incinerator.
BOARD NOTE: At closure, as throughout the operating period, unless the owner or operator can demonstrate, in accordance with Section 721.103(d), that the residue removed from his incinerator is not a hazardous waste, the owner or operator becomes a generator of hazardous waste and must manage it in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722 through 728.
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 1031, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 725.452 Interim Status Incinerators Burning Particular Hazardous Wastes
a) An owner or operator of an incinerator subject to this Subpart O may burn hazardous wastes numbers F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, or F027 if it receives a certification from the Agency that they can meet the performance standards to Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 when it burns these wastes.
b) The following standards and procedures will be used in determining whether to certify an incinerator:
1) The owner or operator must submit an application to the Agency containing applicable information in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.125, 703.222, 703.223, 703.224, and 703.225 demonstrating that the incinerator can meet the performance standards in Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 when they burn these wastes.
2) The Agency must issue a tentative decision as to whether the incinerator can meet the performance standards in Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724. Notification of this tentative decision will be provided by newspaper advertisement and radio broadcast in the county where the incinerator is located. The Agency must accept comment on the tentative decision for 60 days. The Agency also may hold a public hearing upon request or at its discretion.
3) After the close of the public comment period, the Agency must issue a decision whether or not to certify the incinerator.
4) Any person that participated may appeal the Agency’s decision to the Board, pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705.212.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART P: THERMAL TREATMENT
Section 725.470 Other Thermal Treatment
The regulations in this Subpart P apply to owners and operators of facilities that thermally treat hazardous waste in devices other than enclosed devices using controlled flame combustion except, as Section 725.101 provides otherwise. Thermal treatment in enclosed devices using controlled flame combustion is subject to the requirements of Subpart O if the unit is an incinerator, and Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726, if the unit is a boiler or industrial furnace, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.110.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.473 General Operating Requirements
Before adding hazardous waste, the owner or operator must bring his thermal treatment process to steady state (normal) conditions of operation,including steady state operating temperature-using auxiliary fuel or other means, unless the process is a non-continuous (batch) thermal treatment process that requires a complete thermal cycle to treat a discrete quantity of hazardous waste.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.475 Waste Analysis
In addition to the waste analyses required by Section 725.113, the owner or operator must sufficiently analyze any waste that he has not previously treated in his thermal process to enable him to establish steady state (normal) or other appropriate (for a noncontinuous process) operating conditions (including waste and auxiliary fuel feed) and to determine the type of pollutants that might be emitted. At minimum, the analysis must determine the following:
a) Heating value of the waste;
b) Halogen content and sulfur content in the waste; and
c) Concentrations in the waste of lead and mercury, unless the owner or operator has written, documented data that show that the element is not present.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results from each waste analysis or the documented information in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.477 Monitoring and Inspections
The owner or operator must conduct, as a minimum, the following monitoring and inspections when thermally treating hazardous waste:
a) Existing instruments that relate to temperature and emission control (if an emission control device is present) must be monitored at least every 15 minutes. Appropriate corrections to maintain steady state or other appropriate thermal treatment conditions must be made immediately either automatically or by the operator. Instruments that relate to temperature and emission control would normally include those measuring waste feed, auxiliary fuel feed, treatment process temperature, and relevant process flow and level controls.
b) The stack plume (emissions), where present, must be observed visually at least hourly for normal appearance (color and opacity). The operator must immediately make any indicated operating corrections necessary to return any visible emissions to their normal appearance.
c) The complete thermal treatment process and associated equipment (pumps, valves, conveyors, pipes, etc.) must be inspected at least daily for leaks, spills, and fugitive emissions, and all emergency shutdown controls and system alarms must be checked to assure proper operation.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.481 Closure
At closure, the owner or operator must remove all hazardous waste and hazardous waste residues (including, but not limited to, ash) from the thermal treatment process or equipment.
BOARD NOTE: At closure, as throughout the operating period, unless the owner or operator can demonstrate, in accordance with Section 721.103(c) or (d) that any solid waste removed from his thermal treatment process or equipment is not a hazardous waste, the owner or operator becomes a generator of hazardous waste and must manage it in accordance with all applicable requirements of Parts 722, 723, and 725.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.482 Open Burning; Waste Explosives
Open burning of hazardous waste is prohibited except for the open burning and detonation of waste explosives. Waste explosives include waste that has the potential to detonate and bulk military propellants that cannot safely be disposed of through other modes of treatment. Detonation is an explosion in which chemical transformation passes through the material faster than the speed of sound (0.33 kilometers/second at sea level). Owners or operators choosing to open burn or detonate waste explosives must do so in accordance with the following table and in a manner that does not threaten human health or the environment.
or Propellants
Burning or Detonation To
the Property of Others
0 to 100 204 meters (670 feet) 101 to 1,000 380 meters (1,250 feet) 1,001 to 10,000 530 meters (1,730 feet) 10,001 to 30,000 690 meters (2,260 feet) (Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.483 Interim Status Thermal Treatment Devices Burning Particular Hazardous Wastes
a) An owner or operator of a thermal treatment device subject to this Subpart P may burn hazardous waste numbers F020, F021, F022, F023, F026, or F027 if it receives a certification from the Agency that it can meet the performance standards of Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 when it burns these wastes.
b) The following standards and procedures must be used in determining whether to certify a thermal treatment unit:
1) The owner or operator must submit an application to the Agency containing the applicable information in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.125, 703.222, 703.223, 703.224, and 703.225 demonstrating that the thermal treatment unit can meet the performance standard in Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 when it burns these wastes.
2) The Agency must issue a tentative decision as to whether the thermal treatment unit can meet the performance standards in Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724. Notification of this tentative decision must be provided by newspaper advertisement and radio broadcast in the county where the thermal treatment device is located. The Agency must accept comment on the tentative decision for 60 days. The Agency also may hold a public hearing upon request or at its discretion.
3) After the close of the public comment period, the Agency must issue a decision whether or not to certify the thermal treatment unit.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART Q: CHEMICAL, PHYSICAL, AND BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT
Section 725.500 Applicability
The regulations in this Subpart Q apply to owners and operators of facilities that treat hazardous waste by chemical, physical, or biological methods in other than tanks, surface impoundments, and land treatment facilities, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise. Chemical, physical, and biological treatment of hazardous waste in tanks, surface impoundments and land treatment facilities must be conducted in accordance with Subparts J, K, and M, respectively.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.501 General Operating Requirements
a) Chemical, physical, or biological treatment of hazardous waste must comply with Section 725.117(b).
b) Hazardous waste or treatment reagents must not be placed in the treatment process or equipment if they could cause the treatment process or equipment to rupture, leak, corrode, or otherwise fail before the end of its intended life.
c) Where hazardous waste is continuously fed into a treatment process or equipment, the process or equipment must be equipped with a means to stop this inflow (e.g., a waste feed cutoff system or bypass system to a standby containment device).
BOARD NOTE: These systems are intended to be used in the event of a malfunction in the treatment process or equipment.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.502 Waste Analysis and Trial Tests
a) In addition to the waste analysis required by Section 725.113(b) applies whenever either of the following conditions exist:
1) A hazardous waste that is substantially different from waste previously treated in a treatment process or equipment at the facility is to be treated in that process or equipment; or
2) A substantially different process from any previously used at the facility is to be used to chemically treat hazardous waste.
b) To show that this proposed treatment will meet all applicable requirements of Section 725.501(a) and (b), the owner or operator must, before treating the different waste or using the different process or equipment:
1) Conduct waste analyses and trial treatment tests (e.g., bench scale or pilot plant scale tests); or
2) Obtain written, documented information on similar treatment of similar waste under similar operating conditions.
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.113, the waste analysis plan must include analyses needed to comply with Sections 725.505 and 725.506. As required by Section 725.173, the owner or operator must place the results from each waste analysis and trial test, or the documented information, in the operating record of the facility.
(Source: Amended at 40 Ill. Reg. 11830, effective August 9, 2016)
Section 725.503 Inspections
The owner operator of a treatment facility must inspect the following, where present:
a) Discharge control and safety equipment (e.g., waste feed cutoff systems, bypass systems, drainage systems, and pressure relief systems) at least once each operating day to ensure that it is in good working order;
b) Data gathered from monitoring equipment (e.g., pressure and temperature gauges) at least once each operating day to ensure that the treatment process or equipment is being operated according to its design;
c) The construction materials of the treatment process or equipment at least weekly to detect corrosion or leaking of fixtures or seams; and
d) The construction materials of, and the area immediately surrounding, discharge confinement structures (e.g., dikes) at least weekly to detect erosion or obvious signs of leakage (e.g., wet spots or dead vegetation).
BOARD NOTE: As required by Section 725.115(c), the owner or operator must remedy any deterioration or malfunction it finds.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.504 Closure
At closure, all hazardous waste and hazardous waste residues must be removed from treatment processes or equipment, discharge control equipment, and discharge confinement structures.
BOARD NOTE: At closure, as throughout the operating period, unless the owner or operator can demonstrate, in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(c) or (d), that any solid waste removed from his treatment process or equipment is not a hazardous waste, the owner or operator becomes a generator of hazardous waste and must manage it in accordance with all applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722, 723, and 725.
(Source: Amended at 19 Ill. Reg. 9566, effective June 27, 1995)
Section 725.505 Special Requirements for Ignitable or Reactive Wastes
Ignitable or reactive waste must not be placed in a treatment process or equipment unless either of the following conditions exists:
a) The waste is treated, rendered, or mixed before or immediately after placement in the treatment process or equipment so that both of the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The resulting waste, mixture, or dissolution of material no longer meets the definition of ignitable or reactive waste under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.121 or 721.123, and
2) Section 725.117(b) is complied with; or
b) The waste is treated in such a way that it is protected from any material or conditions that may cause the waste to ignite or react.
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.506 Special Requirements for Incompatible Wastes
a) An owner or operator must not place incompatible wastes or incompatible wastes and materials (see Appendix E to this Part for examples) in the same treatment process or equipment unless it complies with Section 725.117(b).
b) An owner or operator must not place hazardous waste in unwashed treatment equipment that previously held an incompatible waste or material, unless it complies with Section 725.117(b).
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART R: UNDERGROUND INJECTION
Section 725.530 Applicability
Except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise, the following apply:
a) The owner or operator of a facility that disposes of hazardous waste by underground injection is excluded from the requirements of Subparts G and H.
b) The requirements of this Subpart R apply to owners and operators of wells that are used to dispose of hazardous waste which are classified as Class I under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.106(a) and which are classified as Class IV under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.106(d).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART W: DRIP PADS
Section 725.540 Applicability
a) The requirements of this Subpart W apply to owners and operators of facilities that use new or existing drip pads to convey treated wood drippage, precipitation or surface water run-on to an associated collection system.
1) An “existing drip pad” is one that fulfills the following conditions:
A) It was constructed before December 6, 1990; or
B) It was one for which the owner or operator had a design and had entered into binding financial or other agreements for construction prior to December 6, 1990.
2) All other drip pads are “new drip pads”.
3) The requirements of Section 725.543(b)(3) to install a leak collection system applies only to those drip pads that are constructed after December 24, 1992, except for those constructed after December 24, 1992 for which the owner or operator has a design and has entered into binding financial or other agreements for construction prior to December 24, 1992.
b) The owner or operator of any drip pad that is inside or under a structure that provides protection from precipitation so that neither run-off nor run-on is generated is not subject to regulation under Section 724.672(e) or (f).
c) The requirements of this subsection are not applicable to the management of infrequent and incidental drippage in storage yards provided that the owner or operator maintains and complies with a written contingency plan that describes how the owner or operator will respond immediately to the discharge of infrequent and incidental drippage. At a minimum, the contingency plan must describe how the owner or operator will do the following:
1) Clean up the drippage;
2) Document the clean-up of the drippage;
3) Retain documentation regarding the clean-up for three years; and
4) Manage the contaminated media in a manner consistent with State and federal regulations.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.541 Assessment of Existing Drip Pad Integrity
a) For each existing drip pad, the owner or operator must evaluate the drip pad and determine that it meets all of the requirements of this Subpart W, except the requirements for liners and leak detection systems of Section 725.543(b). The owner or operator must obtain and keep on file at the facility a written assessment of the drip pad, reviewed and certified by a qualified Professional Engineer that attests to the results of the evaluation. The assessment must be reviewed, updated, and re-certified annually until all upgrades, repairs, or modifications necessary to achieve compliance with all the standards of Section 725.543 are complete. The evaluation must document the extent to which the drip pad meets each of the design and operating standards of Section 725.543, except the standards for liners and leak detection systems specified in Section 725.543(b).
b) The owner or operator must develop a written plan for upgrading, repairing and modifying the drip pad to meet the requirements of Section 725.543(b) and submit the plan to the Agency no later than two years before the date that all repairs, upgrades, and modifications will be complete. This written plan must describe all changes to be made to the drip pad in sufficient detail to document compliance with all the requirements of Section 725.543. The plan must be reviewed and certified by a qualified Professional Engineer.
c) Upon completion of all repairs and modifications, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency, the as-built drawings for the drip pad, together with a certification by a qualified Professional Engineer attesting that the drip pad conforms to the drawings.
d) If the drip pad is found to be leaking or unfit for use, the owner or operator must comply with the provisions of Section 725.543(m) or close the drip pad in accordance with Section 725.545.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.542 Design and Installation of New Drip Pads
Owners and operators of new drip pads must ensure that the pads are designed, installed and operated in accordance with one of the following:
a) All of the requirements of Sections 725.543 (except 725.543(a)(4)), 725.544, and 725.545; or
b) All of the requirements of Section 725.543 (except 725.543(b)), 725.544, and 725.545.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.543 Design and Operating Requirements
a) Drip pads must fulfill the following requirements:
1) It must not be constructed of earthen materials, wood, or asphalt, unless the asphalt is structurally supported;
2) It must be sloped to free-drain to the associated collection system treated wood drippage, rain, other waters, or solutions of drippage and water or other wastes;
3) It must have a curb or berm around the perimeter;
4) In addition, the drip pad must fulfill the following requirements:
A) It must have a hydraulic conductivity of less than or equal to 1 ´ 10-7 centimeters per second, e.g., existing concrete drip pads must be sealed, coated, or covered with a surface material with a hydraulic conductivity of less than or equal to 1 ´ 10-7 centimeters per second such that the entire surface where drippage occurs or may run across is capable of containing such drippage and mixtures of drippage and precipitation, materials, or other wastes while being routed to an associated collection system. This surface material must be maintained free of cracks and gaps that could adversely affect its hydraulic conductivity, and the material must be chemically compatible with the preservatives that contact the drip pad. The requirements of this provision apply only to the existing drip pads and those drip pads for which the owner or operator elects to comply with Section 725.542(b) instead of Section 725.542(a).
B) The owner or operator must obtain and keep on file at the facility a written assessment of the drip pad, reviewed and certified by a qualified Professional Engineer that attests to the results of the evaluation. The assessment must be reviewed, updated, and recertified annually. The evaluation must document the extent to which the drip pad meets the design and operating standards of this Section, except for in subsection (b).
5) It must be of sufficient structural strength and thickness to prevent failure due to physical contact, climatic conditions, the stress of installation, and the stress of daily operations, e.g., variable and moving loads such as vehicle traffic, movement of wood, etc.
BOARD NOTE: In judging the structural integrity requirement of this subsection (a), the Agency should generally consider applicable standards established by professional organizations generally recognized by the industry, including ACI 318-83 (Building Code Requirements for Reinforced Concrete) or ASTM C 94-90 (Standard Specification for Ready-Mixed Concrete), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
b) If an owner or operator elects to comply with Section 725.542(a) instead of Section 725.542(b), the drip pad must have the following features:
1) A synthetic liner installed below the drip pad that is designed, constructed, and installed to prevent leakage from the drip pad into the adjacent subsurface soil or groundwater or surface water at any time during the active life (including the closure period) of the drip pad. The liner must be constructed of materials that will prevent waste from being absorbed into the liner and to prevent releases into the adjacent subsurface soil or groundwater or surface water during the active life of the facility. The liner must be constructed as follows:
A) It must be constructed of materials that have appropriate chemical properties and sufficient strength and thickness to prevent failure due to pressure gradients (including static head and external hydrogeologic forces), physical contact with the waste or drip pad leakage to which they are exposed, climatic conditions, the stress of installation, and the stress of daily operation (including stresses from vehicular traffic on the drip pad);
B) It must be placed upon a foundation or base capable of providing support to the liner and resistance to pressure gradients above and below the liner to prevent failure of the liner due to settlement, compression, or uplift; and
C) It must be installed to cover all surrounding earth that could come in contact with the waste or leakage; and
2) A leakage detection system immediately above the liner that is designed, constructed, maintained, and operated to detect leakage from the drip pad. The leakage detection system must be constructed as follows:
A) It must be constructed of materials that fulfill the following requirements:
i) They are chemically resistant to the waste managed in the drip pad and the leakage that might be generated; and
ii) They are of sufficient strength and thickness to prevent collapse under the pressures exerted by overlaying materials and by any equipment used at the drip pad; and
B) It must be designed and operated to function without clogging through the scheduled closure of the drip pad; and
C) It must be designed so that it will detect the failure of the drip pad or the presence of a release of hazardous waste or accumulated liquid at the earliest practicable time.
3) A leakage collection system immediately above the liner that is designed, constructed, maintained, and operated to collect leakage from the drip pad such that it can be removed from below the drip pad. The date, time, and quantity of any leakage collected in this system and removed must be documented in the operating log.
c) Drip pads must be maintained such that they remain free of cracks, gaps, corrosion, or other deterioration that could cause hazardous waste to be released from the drip pad.
BOARD NOTE: See subsection (m) for remedial action required if deterioration or leakage is detected.
d) The drip pad and associated collection system must be designed and operated to convey, drain and collect liquid resulting from drippage or precipitation in order to prevent run-off.
e) Unless the drip pad is protected by a structure, as described in Section 725.540(b), the owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-on control system capable of preventing flow onto the drip pad during peak discharge from at least a 24-hour, 25-year storm, unless the system has sufficient excess capacity to contain any run-on that might enter the system.
f) Unless the drip pad is protected by a structure or cover, as described in Section 725.540(b), the owner or operator must design, construct, operate, and maintain a run-off management system to collect and control at least the water volume resulting from a 24-hour, 25-year storm.
g) The drip pad must be evaluated to determine that it meets the requirements of subsections (a) through (f). The owner or operator must obtain a statement from a qualified, Professional Engineer certifying that the drip pad design meets the requirements of this Section.
h) Drippage and accumulated precipitation must be removed from the associated collection system as necessary to prevent overflow onto the drip pad.
i) The drip pad surface must be cleaned thoroughly at least once every seven days using an appropriate and effective cleaning technique, including but not limited to, rinsing, washing with detergents or other appropriate solvents, or steam cleaning, with residues being properly managed, such that accumulated residues of hazardous waste or other materials are removed as to allow weekly inspections of the entire drip pad surface without interference or hindrance from accumulated residues of hazardous waste or other materials on the drip pad. The owner or operator must document, in the facility’s operating log, the date and time of each cleaning and the cleaning procedure.
j) Drip pads must be operated and maintained in a manner to minimize tracking of hazardous waste or hazardous waste constituents off the drip pad as a result of activities by personnel or equipment.
k) After being removed from the treatment vessel, treated wood from pressure and non-pressure processes must be held on the drip pad until drippage has ceased. The owner or operator must maintain records sufficient to document that all treated wood is held on the pad, in accordance with this Section, following treatment.
l) Collection and holding units associated with run-on and run-off control systems must be emptied or otherwise managed as soon as possible after storms to maintain design capacity of the system.
m) Throughout the active life of the drip pad, if the owner or operator detects a condition that may have caused or has caused a release of hazardous waste, the condition must be repaired within a reasonably prompt period of time following discovery, in accordance with the following procedures:
1) Upon detection of a condition that may have caused or has caused a release of hazardous waste (e.g., upon detection of leakage in the leak detection system), the owner or operator must perform the following acts:
A) It must enter a record of the discovery in the facility operating log;
B) It must immediately remove from service the portion of the drip pad affected by the condition;
C) It must determine what steps must be taken to repair the drip pad, clean up any leakage from below the drip pad, and establish a schedule for accomplishing the clean up and repairs;
D) Within 24 hours after discovery of the condition, the owner or operator must notify the Agency of the condition and, within 10 working days, provide written notice to the Agency with a description of the steps that will be taken to repair the drip pad and clean up any leakage, and the schedule for accomplishing this work.
2) The Agency must: review the information submitted; make a determination regarding whether the pad must be removed from service completely or partially until repairs and clean up are complete; and notify the owner or operator of the determination and the underlying rationale in writing.
3) Upon completing all repairs and clean up, the owner or operator must notify the Agency in writing and provide a certification, signed by an independent, qualified, registered professional engineer, that the repairs and clean up have been completed according to the written plan submitted in accordance with subsection (m)(1)(D).
n) The owner or operator must maintain, as part of the facility operating log, documentation of past operating and waste handling practices. This must include identification of preservative formulations used in the past, a description of drippage management practices and a description of treated wood storage and handling practices.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.544 Inspections
a) During construction or installation, liners and cover systems (e.g., membranes, sheets, or coatings) must be inspected for uniformity, damage, and imperfections (e.g., holes, cracks, thin spots, or foreign materials). Immediately after construction or installation, liners must be inspected and certified as meeting the requirements of Section 725.543 by a qualified Professional Engineer. This certification must be maintained at the facility as part of the facility operating record. After installation, liners and covers must be inspected to ensure tight seams and joints and the absence of tears, punctures, or blisters.
b) While a drip pad is in operation, it must be inspected weekly and after storms to detect evidence of any of the following:
1) Deterioration, malfunctions, or improper operation of run-on and run-off control systems;
2) The presence of leakage in and proper functioning of leak detection system.
3) Deterioration or cracking of the drip pad surface.
BOARD NOTE: See Section 725.543(m) for remedial action required if deterioration or leakage is detected.
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.545 Closure
a) At closure, the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components (pad, liners, etc.), contaminated subsoils, and structures and equipment contaminated with waste and leakage and manage them as hazardous waste.
b) If, after removing or decontaminating all residues and making all reasonable efforts to effect removal or decontamination of contaminated components, subsoils, structures, and equipment as required in subsection (a) of this Section, the owner or operator finds that not all contaminated subsoils can be practically removed or decontaminated. The operator must close the unit and perform post-closure care in accordance with closure and post-closure care requirements that apply to landfills (Section 725.410). For permitted units, the requirement to have a permit continues throughout the post-closure period.
c) Existing drip pads without liners.
1) The owner or operator of an existing drip pad that does not comply with the liner requirements of Section 725.543(b)(1) must do the following:
A) It must include in the closure plan for the drip pad under Section 725.212 both a plan for complying with subsection (a) of this Section and a contingent plan for complying with subsection (b) of this Section in case not all contaminated subsoils can be practicably removed at closure; and
B) It must prepare a contingent post-closure plan under Section 725.218 for complying with subsection (b) of this Section in case not all contaminated subsoils can be practicably removed at closure.
2) The cost estimates calculated under Sections 725.212 and 725.244 for closure and post closure care of a drip pad subject to this subsection must include the cost of complying with the contingent closure plan and the contingent post closure plan, but are not required to include the cost of expected closure under subsection (a) of this Section.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
SUBPART AA: AIR EMISSION STANDARDS FOR PROCESS VENTS
Section 725.930 Applicability
a) This Subpart AA applies to owners and operators of facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous wastes (except as provided in Section 725.101).
b) Except for Section 725.934(d) and (e), this Subpart AA applies to process vents associated with distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operations that manage hazardous wastes with organic concentrations of at least 10 ppmw (parts per million by weight), if these operations are conducted in one of the following:
1) A unit that is subject to the permitting requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705;
2) A unit (including a hazardous waste recycling unit) that is not exempt from permitting under the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.117 (i.e., a hazardous waste recycling unit that is not a 90-day tank or container) and that is located on a hazardous waste management facility otherwise subject to the permitting requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705; or
3) A unit that is exempt from permitting under the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.117 (i.e., a “90-day” tank or container) and which is not a recycling unit under the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.106.
BOARD NOTE: The requirements of Sections 725.932 through 725.936 apply to process vents on hazardous waste recycling units previously exempt under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.106(c)(1). Other exemptions under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.104 and 725.101(c) are not affected by these requirements.
c) Agency decisions pursuant to this Part must be made in writing, are in the nature of permit decisions pursuant to Section 39 of the Environmental Protection Act and may be appealed to the Board pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 105.
d) The requirements of this Subpart AA do not apply to the process vents at a facility where the facility owner or operator certifies that all of the process vents that would otherwise be subject to this Subpart AA are equipped with and operating air emission controls in accordance with the process vent requirements of an applicable federal Clean Air Act regulation codified under 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63. The documentation of compliance under regulations at 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63 must be kept with, or made readily available with, the facility operating record.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.931 Definitions
As used in this Subpart AA, all terms not defined in this Subpart AA have the meaning given them in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.931, section 1004 of RCRA, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728, and 738.
“BTU” means British thermal unit.
“ft” means foot.
“h” means hour.
“kg” means kilogram.
“kPa” means kilopascals.
“lb” means pound.
“m” means meter.
“Mg” means Megagrams, or metric tonnes.
“MJ” means Megajoules, or ten to the sixth Joules.
“MW” means Megawatts.
“ppmv” means parts per million by volume.
“ppmw” meant parts per million by weight.
“s” means second.
“scm” means standard cubic meter.
“scft” meant standard cubic foot.
“yr” means year.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.932 Standards: Process Vents
a) The owner or operator of a facility with process vents associated with distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operations managing hazardous wastes with organic concentrations of at least 10 ppmw must do either of the following:
1) Reduce total organic emissions from all affected process vents at the facility below 1.4 kg/h (3 lb/h) and 2.8 Mg/yr (3.1 tons/yr); or
2) Reduce, by use of a control device, total organic emissions from all affected process vents at the facility by 95 weight percent.
b) If the owner or operator installs a closed-vent system and control device to comply with the provisions of subsection (a), the closed-vent system and control device must meet the requirements of Section 725.933.
c) Determinations of vent emissions and emission reductions or total organic compound concentrations achieved by add-on control devices must be based on either engineering calculations or performance tests. If performance tests are used to determine vent emissions, emission reductions, or total organic compound concentrations achieved by add-on control devices, the performance tests must conform with the requirements of Section 725.934(c).
d) When an owner or operator and the Agency do not agree on determinations of vent emissions or emission reductions or total organic compound concentrations achieved by add-on control devices based on engineering calculations, the test methods in Section 725.934(c) must be used to resolve the disagreement.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.933 Standards: Closed-Vent Systems and Control Devices
a) Compliance Required
1) Owners or operators of closed-vent systems and control devices used to comply with provisions of this Part must comply with the provisions of this Section.
2) Implementation Schedule
A) The owner or operator of an existing facility that cannot install a closed-vent system and control device to comply with the provisions of this Subpart AA on the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA must prepare an implementation schedule that includes dates by which the closed-vent system and control device will be installed and in operation. The controls must be installed as soon as possible, but the implementation schedule may allow up to 30 months after the effective date that the facility becomes subject to this Subpart AA for installation and startup.
B) Any unit that is subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA when operation begins, must comply with the rules immediately (i.e., must have control devices installed and operating on startup of the affected unit); the 30-month implementation schedule does not apply.
C) The owner or operator of any facility in existence on the effective date of a statutory or regulatory amendment that renders the facility subject to this Subpart AA must comply with all requirements of this Subpart AA as soon as practicable but no later than 30 months after the effective date of the amendment. When control equipment required by this Subpart AA cannot be installed and begin operation by the effective date of the amendment, the facility owner or operator must prepare an implementation schedule that includes the following information: specific calendar dates for award of contracts or issuance of purchase orders for the control equipment, initiation of on-site installation of the control equipment, completion of the control equipment installation, and performance of any testing to demonstrate that the installed equipment meets the applicable standards of this Subpart AA. The owner or operator must enter the implementation schedule in the operating record or in a permanent, readily available file located at the facility.
D) An owner or operator of a facility or unit that becomes newly subject to the requirements of this Subpart AA due to an action other than those described in subsection (a)(2)(iii) must comply with all applicable requirements immediately (i.e., the facility or unit must have control devices installed and operating on the date the facility or unit becomes subject to this Subpart AA; the 30-month implementation schedule does not apply).
b) A control device involving vapor recovery (e.g., a condenser or adsorber) must be designed and operated to recover the organic vapors vented to it with an efficiency of 95 weight percent or greater unless the total organic emission limits of Section 725.932(a)(1) for all affected process vents is attained at an efficiency less than 95 weight percent.
c) An enclosed combustion device (e.g., a vapor incinerator, boiler, or process heater) must be designed and operated to reduce the organic emissions vented to it by 95 weight percent or greater; to achieve a total organic compound concentration of 20 ppmv, expressed as the sum of the actual compounds, not carbon equivalents, on a dry basis corrected to three percent oxygen; or to provide a minimum residence time of 0.50 seconds at a minimum temperature of 760 °C. If a boiler or process heater is used as the control device, then the vent stream must be introduced into the flame combustion zone of the boiler or process heater.
d) Flares
1) A flare must be designed for and operated with no visible emissions as determined by the methods specified in subsection (e)(1) except for periods not to exceed a total of five minutes during any two consecutive hours.
2) A flare must be operated with a flame present at all times, as determined by the methods specified in subsection (f)(2)(C).
3) A flare must be used only if the net heating value of the gas being combusted is 11.2 MJ/scm (300 Btu/scf) or greater if the flare is steam-assisted or air-assisted, or if the net heating value of the gas being combusted is 7.45 MJ/scm (200 Btu/scf) or greater if the flare is nonassisted. The net heating value of the gas being combusted must be determined by the methods specified in subsection (e)(2).
4) Exit Velocity
A) A steam-assisted or nonassisted flare must be designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the methods specified in subsection (e)(3), less than 18.3 m/s (60 ft/s), except as provided in subsections (d)(4)(B) and (d)(4)(C).
B) A steam-assisted or nonassisted flare designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the methods specified in subsection (e)(3), equal to or greater than 18.3 m/s (60 ft/s) but less than 122 m/s (400 ft/s) is allowed if the net heating value of the gas being combusted is greater than 37.3 MJ/scm (1,000 Btu/scf).
C) A steam-assisted or nonassisted flare designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the methods specified in subsection (e)(3), less than the velocity, V as determined by the method specified in subsection (e)(4) and less than 122 m/s (400 ft/s) is allowed.
5) An air-assisted flare must be designed and operated with an exit velocity less than the velocity, V, as determined by the method specified in subsection (e)(5).
6) A flare used to comply with this Section must be steam-assisted, air-assisted, or nonassisted.
e) Compliance Determination and Equations
1) Reference Method 22 (Visual Determination of Fugitive Emissions from Material Sources and Smoke Emissions from Flares) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), must be used to determine the compliance of a flare with the visible emission provisions of this Subpart AA. The observation period is two hours and must be used according to Reference Method 22.
2) The net heating value of the gas being combusted in a flare must be calculated using the following equation:
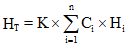
Where:
HT = the net heating value of the sample in MJ/scm; where the net enthalpy per mole of offgas is based on combustion at 25 °C and 760 mm Hg, but the standard temperature for determining the volume corresponding to 1 mole is 20 °C
K = 1.74 ´ 107 (1/ppm)(g mol/scm)(MJ/kcal) where the standard temperature for (g mol/scm) is 20 °C
SXi = the sum of the values of X for each component i, from i=1 to n
Ci = the concentration of sample component i in ppm on a wet basis, as measured for organics by Reference Method 18 (Measurement of Gaseous Organic Compound Emissions by Gas Chromatography) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), and for carbon monoxide, by ASTM D 1946-90 (Standard Practice for Analysis of Reformed Gas by Gas Chromatography), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111Hi = the net heat of combustion of sample component i, kcal/gmol at 25 °C and 760 mm Hg. The heats of combustion must be determined using ASTM D 2382-88 (Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter (High Precision Method)), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), if published values are not available or cannot be calculated
3) The actual exit velocity of a flare must be determined by dividing the volumetric flow rate (in units of standard temperature and pressure), as determined by Reference Methods 2 (Determination of Stack Gas Velocity and Volumetric Flow Rate (Type S Pitot Tube)), 2A (Direct Measurement of Gas Volume through Pipes and Small Ducts), 2C (Determination of Gas Velocity and Volumetric Flow Rate in Small Stacks or Ducts (Standard Pitot Tube)), or 2D (Measurement of Gas Volume Flow Rates in Small Pipes and Ducts) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), as appropriate, by the unobstructed (free) cross-sectional area of the flare tip.
4) The maximum allowed velocity in m/s, V for a flare complying with subsection (d)(4)(C) must be determined by the following equation:
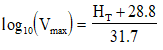
Where:
log10 = logarithm to the base 10
HT = the net heating value as determined in subsection (e)(2)
5) The maximum allowed velocity in m/s, V, for an air-assisted flare must be determined by the following equation:
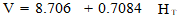
Where:
HT = the net heating value as determined in subsection (e)(2)
f) The owner or operator must monitor and inspect each control device required to comply with this Section to ensure proper operation and maintenance of the control device by implementing the following requirements:
1) Install, calibrate, maintain, and operate according to the manufacturer’s specifications a flow indicator that provides a record of vent stream flow from each affected process vent to the control device at least once every hour. The flow indicator sensor must be installed in the vent stream at the nearest feasible point to the control device inlet but before being combined with other vent streams.
2) Install, calibrate, maintain, and operate according to the manufacturer’s specifications a device to continuously monitor control device operation, as specified below:
A) For a thermal vapor incinerator, a temperature monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder. The device must have accuracy of ±1 percent of the temperature being monitored in °C or ±0.5 °C, whichever is greater. The temperature sensor must be installed at a location in the combustion chamber downstream of the combustion zone.
B) For a catalytic vapor incinerator, a temperature monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder. The device must be capable of monitoring temperature at two locations and have an accuracy of ±1 percent of the temperature being monitored in °C or ±0.5 °C, whichever is greater. One temperature sensor must be installed in the vent stream at the nearest feasible point to the catalyst bed inlet and a second temperature sensor must be installed in the vent stream at the nearest feasible point to the catalyst bed outlet.
C) For a flare, a heat sensing monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder that indicates the continuous ignition of the pilot flame.
D) For a boiler or process heater having a design heat input capacity less than 44 MW, a temperature monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder. The device must have an accuracy of ±1 percent of the temperature being monitored in °C or ±0.5 °C, whichever is greater. The temperature sensor must be installed at a location in the furnace downstream of the combustion zone.
E) For a boiler or process heater having a design heat input capacity greater than or equal to 44 MW, a monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder to measure parameters that indicate good combustion operating practices are being used.
F) For a condenser, either of the following:
i) A monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder to measure the concentration level of the organic compounds in the exhaust vent stream from the condenser; or
ii) A temperature monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder. The device must be capable of monitoring temperature with an accuracy of ±1 percent of the temperature being monitored in °C or ±0.5 °C, whichever is greater. The temperature sensor must be installed at a location in the exhaust vent stream from the condenser exit (i.e., product side).
G) For a carbon adsorption system, such as a fixed-bed carbon adsorber that regenerates the carbon bed directly in the control device, either of the following:
i) A monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder to measure the concentration level of the organic compounds in the exhaust vent stream from the carbon bed; or
ii) A monitoring device equipped with a continuous recorder to measure a parameter that indicates the carbon bed is regenerated on a regular, predetermined time cycle.
3) Inspect the readings from each monitoring device required by subsections (f)(1) and (f)(2) at least once each operating day to check control device operation and, if necessary, immediately implement the corrective measures necessary to ensure the control device operates in compliance with the requirements of this Section.
g) An owner or operator using a carbon adsorption system such as a fixed-bed carbon adsorber that regenerates the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device must replace the existing carbon in the control device with fresh carbon at a regular, predetermined time interval that is no longer than the carbon service life established as a requirement of Section 725.935(b)(4)(C)(vi).
h) An owner or operator using a carbon adsorption system, such as a carbon canister, that does not regenerate the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device must replace the existing carbon in the control device with fresh carbon on a regular basis by using one of the following procedures:
1) Monitor the concentration level of the organic compounds in the exhaust vent stream from the carbon adsorption system on a regular schedule, and replace the existing carbon with fresh carbon immediately when carbon breakthrough is indicated. The monitoring frequency must be daily or at an interval no greater than 20 percent of the time required to consume the total carbon working capacity established as a requirement of Section 725.935(b)(4)(C)(vii), whichever is longer.
2) Replace the existing carbon with fresh carbon at a regular, predetermined time interval that is less than the design carbon replacement interval established as a requirement of Section 725.935(b)(4)(C)(vii).
i) An owner or operator of an affected facility seeking to comply with the provisions of this Part by using a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser, or carbon adsorption system is required to develop documentation including sufficient information to describe the control device operation and identify the process parameter or parameters that indicate proper operation and maintenance of the control device.
j) A closed-vent system must meet either of the following design requirements:
1) A closed-vent system must be designed to operate with no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppmv above background, as determined by the methods specified at Section 725.934(b), and by visual inspections; or
2) A closed-vent system must be designed to operate at a pressure below atmospheric pressure. The system must be equipped with at least one pressure gauge or other pressure measurement device that can be read from a readily accessible location to verify that negative pressure is being maintained in the closed-vent system when the control device is operating.
k) The owner or operator must monitor and inspect each closed-vent system required to comply with this Section to ensure proper operation and maintenance of the closed-vent system by implementing the following requirements:
1) Each closed-vent system that is used to comply with subsection (j)(1) must be inspected and monitored in accordance with the following requirements:
A) An initial leak detection monitoring of the closed-vent system must be conducted by the owner or operator on or before the date that the system becomes subject to this Section. The owner or operator must monitor the closed-vent system components and connections using the procedures specified in Section 725.934(b) to demonstrate that the closed-vent system operates with no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppmv above background.
B) After initial leak detection monitoring required in subsection (k)(1)(A), the owner or operator must inspect and monitor the closed-vent system as follows:
i) Closed-vent system joints, seams, or other connections that are permanently or semi-permanently sealed (e.g., a welded joint between two sections of hard piping or a bolted and gasketed ducting flange) must be visually inspected at least once per year to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. The owner or operator must monitor a component or connection using the procedures specified in Section 725.934(b) to demonstrate that it operates with no detectable emissions following any time the component is repaired or replaced (e.g., a section of damaged hard piping is replaced with new hard piping) or the connection is unsealed (e.g., a flange is unbolted).
ii) Closed-vent system components or connections other than those specified in subsection (k)(1)(B)(i) must be monitored annually and at other times as requested by the Agency, except as provided for in subsection (n), using the procedures specified in Section 725.934(b) to demonstrate that the components or connections operate with no detectable emissions.
C) In the event that a defect or leak is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect or leak in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k)(3).
D) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection and monitoring in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.935.
2) Each closed-vent system that is used to comply with subsection (j)(2) must be inspected and monitored in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The closed-vent system must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to, visible cracks, holes, or gaps in ductwork or piping or loose connections.
B) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the closed-vent system on or before the date that the system becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year.
C) In the event that a defect or leak is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k)(3).
D) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection and monitoring in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.935.
3) The owner or operator must repair all detected defects as follows:
A) Detectable emissions, as indicated by visual inspection or by an instrument reading greater than 500 ppmv above background, must be controlled as soon as practicable, but not later than 15 calendar days after the emission is detected, except as provided for in subsection (k)(3)(C).
B) A first attempt at repair must be made no later than five calendar days after the emission is detected.
C) Delay of repair of a closed-vent system for which leaks have been detected is allowed if the repair is technically infeasible without a process unit shutdown, or if the owner or operator determines that emissions resulting from immediate repair would be greater than the fugitive emissions likely to result from delay of repair. Repair of such equipment must be completed by the end of the next process unit shutdown.
D) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the defect repair in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.935.
l) A closed-vent system or control device used to comply with provisions of this Subpart AA must be operated at all times when emissions may be vented to it.
m) The owner or operator using a carbon adsorption system to control air pollutant emissions must document that all carbon removed that is a hazardous waste and that is removed from the control device is managed in one of the following manners, regardless of the volatile organic concentration of the carbon:
1) It is regenerated or reactivated in a thermal treatment unit that meets one of the following:
A) The owner or operator of the unit has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 that implements the requirements of Subpart X of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724; or
B) The unit is equipped with and operating air emission controls in accordance with the applicable requirements of Subparts AA and CC or 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724; or
C) The unit is equipped with and operating air emission controls in accordance with a federal national emission standard for hazardous air pollutants under 40 CFR 61 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants) or 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants for Source Categories), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
2) It is incinerated in a hazardous waste incinerator for which the owner or operator has done either of the following:
A) The owner or operator has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 that implements the requirements of Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724; or
B) The owner or operator has designed and operates the incinerator in accordance with the interim status requirements of Subpart O.
3) It is burned in a boiler or industrial furnace for which the owner or operator has done either of the following:
A) The owner or operator has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 that implements the requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726; or
B) The owner or operator has designed and operates the boiler or industrial furnace in accordance with the interim status requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726.
n) Any components of a closed-vent system that are designated, as described in Section 725.935(c)(9), as unsafe to monitor are exempt from the requirements of subsection (k)(1)(B)(ii) if both of the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The owner or operator of the closed-vent system has determined that the components of the closed-vent system are unsafe to monitor because monitoring personnel would be exposed to an immediate danger as a consequence of complying with subsection (k)(1)(B)(ii); and
2) The owner or operator of the closed-vent system adheres to a written plan that requires monitoring the closed-vent system components using the procedure specified in subsection (k)(1)(B)(ii) as frequently as practicable during safe-to-monitor times.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.934 Test Methods and Procedures
a) Each owner or operator subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA must comply with the test methods and procedures requirements provided in this Section.
b) When a closed-vent system is tested for compliance with no detectable emissions, as required in Section 725.933(k), the test must comply with the following requirements:
1) Monitoring must comply with Reference Method 21 (Determination of Volatile Organic Compound Leaks) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
2) The detection instrument must meet the performance criteria of Reference Method 21.
3) The instrument must be calibrated before use on each day of its use by the procedures specified in Reference Method 21.
4) Calibration gases must be:
A) Zero air (less than 10 ppm of hydrocarbon in air).
B) A mixture of methane or n-hexane and air at a concentration of approximately, but less than, 10,000 ppm methane or n-hexane.
5) The background level must be determined as set forth in Reference Method 21.
6) The instrument probe must be traversed around all potential leak interfaces as close to the interface as possible, as described in Reference Method 21.
7) The arithmetic difference between the maximum concentration indicated by the instrument and the background level is compared with 500 ppm for determining compliance.
c) Performance tests to determine compliance with Section 725.932(a) and with the total organic compound concentration limit of Section 725.933(c) must comply with the following:
1) Performance tests to determine total organic compound concentrations and mass flow rates entering and exiting control devices must be conducted and data reduced in accordance with the following reference methods and calculation procedures:
A) Reference Method 2 (Determination of Stack Gas Velocity and Volumetric Flow Rate (Type S Pitot Tube)) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for velocity and volumetric flow rate.
B) Reference Method 18 (Measurement of Gaseous Organic Compound Emissions by Gas Chromatography) or 25A (Determination of Total Gaseous Organic Concentration Using a Flame Ionization Analyzer) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for organic content. If Reference Method 25A is used, the organic hazardous air pollutant (HAP) used as the calibration gas must be the single HAP that represents the largest percent by volume of the emissions. The use of Reference Method 25A is acceptable if the response from the high-level calibration gas is at least 20 times the standard deviation of the response from the zero calibration gas when the instrument is zeroed on the most sensitive scale.
C) Each performance test must consist of three separate runs, each run conducted for at least 1 hour under the conditions that exist when the hazardous waste management unit is operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur. For the purpose of determining total organic compound concentrations and mass flow rates, the average of results of all runs applies. The average must be computed on a time-weighted basis.
D) Total organic mass flow rates must be determined by the following equation:
i) For a source utilizing Reference Method 18:
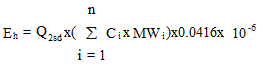
Where:
Eh = The total organic mass flow rate, kg/h
Q2sd = The volumetric flow rate of gases entering or exiting control device, dscm/h, as determined by Reference Method 2
n = The number of organic compounds in the vent gas
Ci = The organic concentration in ppm, dry basis, of compound i in the vent gas, as determined by Reference Method 18
MWi = The molecular weight of organic compound i in the vent gas, kg/kg-mol
0.0416 = The conversion factor for molar volume, kg-mol/m3, at 293 K and 760 mm Hg10-6 = The conversion factor from ppm
ii) For a source utilizing Reference Method 25A:
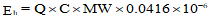
Where:
Eh = The total organic mass flow rate, kg/h
Q = The volumetric flow rate of gases entering or exiting control device, dscm/h, as determined by Reference Method 2
C = The organic concentration in ppm, dry basis, of compound i in the vent gas, as determined by Reference Method 25A
MW = The molecular weight of propane, 44 kg/kg-mol
0.0416 = The conversion factor for molar volume, kg-mol/m3, at 293 K and 760 mm Hg10-6 = The conversion factor from ppm
E) The annual total organic emission rate must be determined by the following equation:
A = F ´ H
Where:
A = total organic emission rate, kg/y
F = the total organic mass flow rate, kg/h, as calculated in subsection (c)(1)(D)H = the total annual hours of operation for the affected unit, h/y
F) Total organic emissions from all affected process vents at the facility must be determined by summing the hourly total organic mass emissions rates (F, as determined in subsection (c)(1)(D)) and by summing the annual total organic mass emission rates (A, as determined in subsection (c)(1)(E)) for all affected process vents at the facility.
2) The owner or operator must record such process information as is necessary to determine the conditions of the performance tests. Operations during periods of startup, shutdown, and malfunction do not constitute representative conditions for the purpose of a performance test.
3) The owner or operator of an affected facility must provide, or cause to be provided, performance testing facilities as follows:
A) Sampling ports adequate for the test methods specified in subsection (c)(1).
B) Safe sampling platforms.
C) Safe access to sampling platforms.
D) Utilities for sampling and testing equipment.
4) For the purpose of making compliance determinations, the time-weighted average of the results of the three runs must apply. In the event that a sample is accidentally lost or conditions occur in which one of the three runs must be discontinued because of forced shutdown, failure of an irreplaceable portion of the sample train, extreme meteorological conditions, or other circumstances beyond the owner or operator’s control, compliance may, upon the Agency’s approval, be determined using the average of the results of the two other runs.
d) To show that a process vent associated with a hazardous waste distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operation is not subject to the requirements of this Subpart AA, the owner or operator must make an initial determination that the time-weighted, annual average total organic concentration of the waste managed by the waste management unit is less than 10 ppmw using one of the following two methods:
1) Direct measurement of the organic concentration of the waste using the following procedures:
A) The owner or operator must take a minimum of four grab samples of waste for each wastestream managed in the affected unit under process conditions expected to cause the maximum waste organic concentration.
B) For waste generated onsite, the grab samples must be collected at a point before the waste is exposed to the atmosphere, such as in an enclosed pipe or other closed system that is used to transfer the waste after generation to the first affected distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operation. For waste generated offsite, the grab samples must be collected at the inlet to the first waste management unit that receives the waste provided the waste has been transferred to the facility in a closed system such as a tank truck and the waste is not diluted or mixed with other waste.
C) Each sample must be analyzed and the total organic concentration of the sample must be computed using Method 9060A (Total Organic Carbon) of “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods”, USEPA publication number EPA-530/SW-846, incorporated by reference under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), or analyzed for its individual constituents.
D) The arithmetic mean of the results of the analyses of the four samples apply for each wastestream managed in the unit in determining the time-weighted, annual average total organic concentration of the waste. The time-weighted average is to be calculated using the annual quantity of each waste stream processed and the mean organic concentration of each wastestream managed in the unit.
2) Using knowledge of the waste to determine that its total organic concentration is less than 10 ppmw. Documentation of the waste determination is required. Examples of documentation that must be used to support a determination under this subsection (d)(2) include the following:
A) Production process information documenting that no organic compounds are used;
B) Information that the waste is generated by a process that is identical to a process at the same or another facility that has previously been demonstrated by direct measurement to generate a wastestream having a total organic content less than 10 ppmw; or
C) Prior speciation analysis results on the same wastestream where it is documented that no process changes have occurred since that analysis that could affect the waste total organic concentration.
e) The determination that distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operations that manage hazardous wastes with time-weighted, annual average total organic concentrations less than 10 ppmw must be made as follows:
1) By the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA or by the date when the waste is first managed in a waste management unit, whichever is later;
2) For continuously generated waste, annually; and
3) Whenever there is a change in the waste being managed or a change in the process that generates or treats the waste.
f) When an owner or operator and the Agency do not agree on whether a distillation, fractionation, thin-film evaporation, solvent extraction, or air or steam stripping operation manages a hazardous waste with organic concentrations of at least 10 ppmw based on knowledge of the waste, the dispute may be resolved using direct measurement, as specified in subsection (d)(1).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.935 Recordkeeping Requirements
a) Compliance Required
1) Each owner or operator subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA must comply with the recordkeeping requirements of this Section.
2) An owner or operator of more than one hazardous waste management unit subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA may comply with the recordkeeping requirements for these hazardous waste management units in one recordkeeping system if the system identifies each record by each hazardous waste management unit.
b) Owners and operators must record the following information in the facility operating record:
1) For facilities that comply with the provisions of Section 725.933(a)(2), an implementation schedule that includes dates by which the closed-vent system and control device will be installed and in operation. The schedule must also include a rationale of why the installation cannot be completed at an earlier date. The implementation schedule must be in the facility operating record by the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of this Subpart AA.
2) Up-to-date documentation of compliance with the process vent standards in Section 725.932, including the following:
A) Information and data identifying all affected process vents, annual throughput and operating hours of each affected unit, estimated emission rates for each affected vent and for the overall facility (i.e., the total emissions for all affected vents at the facility), and the approximate location within the facility of each affected unit (e.g., identify the hazardous waste management units on a facility plot plan).
B) Information and data supporting determination of vent emissions and emission reductions achieved by add-on control devices based on engineering calculations or source tests. For the purpose of determining compliance, determinations of vent emissions and emission reductions must be made using operating parameter values (e.g., temperatures, flow rates, or vent stream organic compounds and concentrations) that represent the conditions that result in maximum organic emissions, such as when the waste management unit is operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur. If the owner or operator takes any action (e.g., managing a waste of different composition or increasing operating hours of affected waste management units) that would result in an increase in total organic emissions from affected process vents at the facility, then a new determination is required.
3) Where an owner or operator chooses to use test date to determine the organic removal efficiency or total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device, a performance test plan. The test plan must include the following:
A) A description of how it is determined that the planned test is going to be conducted when the hazardous waste management unit is operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur. This must include the estimated or design flow rate and organic content of each vent stream and define the acceptable operating ranges of key process and control device parameters during the test program.
B) A detailed engineering description of the closed-vent system and control device including the following:
i) Manufacturer’s name and model number of control device;
ii) Type of control device;
iii) Dimensions of the control device;
iv) Capacity; and
v) Construction materials.
C) A detailed description of sampling and monitoring procedures, including sampling and monitoring locations in the system, the equipment to be used, sampling and monitoring frequency, and planned analytical procedures for sample analysis.
4) Documentation of compliance with Section 725.933 must include the following information:
A) A list of all information references and sources used in preparing the documentation;
B) Records, including the dates of each compliance test required by Section 725.933(j);
C) If engineering calculations are used, a design analysis, specifications, drawings, schematics, and piping and instrumentation diagrams based on the appropriate sections of “APTI Course 415: Control of Gaseous Emissions”, USEPA publication number EPA-450/2-81-005, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), or other engineering texts, approved by the Agency, that present basic control device design information. Documentation provided by the control device manufacturer or vendor that describes the control device design in accordance with subsections (b)(4)(C)(i) through (b)(4)(C)(vii) may be used to comply with this requirement. The design analysis must address the vent stream characteristics and control device operation parameters as specified below.
i) For a thermal vapor incinerator, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, and flow rate. The design analysis must also establish the design minimum and average temperature in the combustion zone and the combustion zone residence time.
ii) For a catalytic vapor incinerator, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, and flow rate. The design analysis must also establish the design minimum and average temperatures across the catalyst bed inlet and outlet.
iii) For a boiler or process heater, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, and flow rate. The design analysis must also establish the design minimum and average flame zone temperatures, combustion zone residence time and description of method and location where the vent stream is introduced into the combustion zone.
iv) For a flare, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, and flow rate. The design analysis must also consider the requirements specified in Section 725.933(d).
v) For a condenser, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, flow rate, relative humidity, and temperature. The design analysis must also establish the design outlet organic compound concentration level, design average temperature of the condenser exhaust vent stream and design average temperatures of the coolant fluid at the condenser inlet and outlet.
vi) For a carbon adsorption system, such as a fixed-bed adsorber that regenerates the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, flow rate, relative humidity and temperature. The design analysis must also establish the design exhaust vent stream organic compound concentration level, number and capacity of carbon beds, type and working capacity of activated carbon used for carbon beds, design total steam flow over the period of each complete carbon bed regeneration cycle, duration of the carbon bed steaming and cooling/drying cycles, design carbon bed temperature after regeneration, design carbon bed regeneration time and design service life of carbon.
vii) For a carbon adsorption system, such as a carbon canister that does not regenerate the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device, the design analysis must consider the vent stream composition, constituent concentrations, flow rate, relative humidity and temperature. The design analysis must also establish the design outlet organic concentration level, capacity of carbon bed, type and working capacity of activated carbon used for carbon bed and design carbon replacement interval based on the total carbon working capacity of the control device and source operating schedule;
D) A statement signed and dated by the owner or operator certifying that the operating parameters used in the design analysis reasonably represent the conditions that exist when the hazardous waste management unit is or would be operating at the highest load or capacity level reasonably expected to occur;
E) A statement signed and dated by the owner or operator certifying that the control device is designed to operate at an efficiency of 95 percent or greater unless the total organic concentration limit of Section 725.932(a) is achieved at an efficiency less than 95 weight percent or the total organic emission limits of Section 725.932(a) for affected process vents at the facility are attained by a control device involving vapor recovery at an efficiency less than 95 weight percent. A statement provided by the control device manufacturer or vendor certifying that the control equipment meets the design specifications may be used to comply with this requirement; and
F) If performance tests are used to demonstrate compliance, all test results.
c) Design documentation and monitoring operating and inspection information for each closed-vent system and control device required to comply with the provisions of this Part must be recorded and kept up-to-date in the facility operating record. The information must include the following:
1) Description and date of each modification that is made to the closed-vent system or control device design;
2) Identification of operating parameter, description of monitoring device, and diagram of monitoring sensor location or locations used to comply with Section 725.933(f)(1) and (f)(2);
3) Monitoring, operating and inspection information required by Section 725.933(f) through (k);
4) Date, time, and duration of each period that occurs while the control device is operating when any monitored parameter exceeds the value established in the control device design analysis, as specified below:
A) For a thermal vapor incinerator designed to operate with a minimum residence time of 0.50 second at a minimum temperature of 760 °C, any period when the combustion temperature is below 760 °C.
B) For a thermal vapor incinerator designed to operate with an organic emission reduction efficiency of 95 percent or greater, any period when the combustion zone temperature is more than 28 °C below the design average combustion zone temperature established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(i).
C) For a catalytic vapor incinerator, any period when either of the following occurs:
i) Temperature of the vent stream at the catalyst bed inlet is more than 28 °C below the average temperature of the inlet vent stream established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(ii); or
ii) Temperature difference across the catalyst bed is less than 80 percent of the design average temperature difference established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(ii).
D) For a boiler or process heater, any period when either of the following occurs:
i) Flame zone temperature is more than 28 °C below the design average flame zone temperature established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(iii); or
ii) Position changes where the vent stream is introduced to the combustion zone from the location established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(iii).
E) For a flare, period when the pilot flame is not ignited.
F) For a condenser that complies with Section 725.933(f)(2)(F)(i), any period when the organic compound concentration level or readings of organic compounds in the exhaust vent stream from the condenser are more than 20 percent greater than the design outlet organic compound concentration level established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(v).
G) For a condenser that complies with Section 725.933(f)(2)(F)(ii), any period when either of the following occurs:
i) Temperature of the exhaust vent stream from the condenser is more than 6 °C above the design average exhaust vent stream temperature established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(v); or
ii) Temperature of the coolant fluid exiting the condenser is more than 6 °C above the design average coolant fluid temperature at the condenser outlet established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(v).
H) For a carbon adsorption system, such as a fixed-bed carbon adsorber that regenerates the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device and which complies with Section 725.933(f)(2)(G)(i), any period when the organic compound concentration level or readings of organic compounds in the exhaust vent stream from the carbon bed are more than 20 percent greater than the design exhaust vent stream organic compound concentration level established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(vi).
I) For a carbon adsorption system, such as a fixed-bed carbon adsorber that regenerates the carbon bed directly onsite in the control device and which complies with Section 725.933(f)(2)(G)(ii), any period when the vent stream continues to flow through the control device beyond the predetermined carbon bed regeneration time established as a requirement of subsection (b)(4)(C)(vi);
5) Explanation for each period recorded under subsection (c)(4) of the cause for control device operating parameter exceeding the design value and the measures implemented to correct the control device operation;
6) For carbon adsorption systems operated subject to requirements specified in Section 725.933(g) or (h)(2), any date when existing carbon in the control device is replaced with fresh carbon;
7) For carbon adsorption systems operated subject to requirements specified in Section 725.933(h)(1), a log that records:
A) Date and time when control device is monitored for carbon breakthrough and the monitoring device reading.
B) Date when existing carbon in the control device is replaced with fresh carbon;
8) Date of each control device startup and shutdown;
9) An owner or operator designating any components of a closed-vent system as unsafe to monitor pursuant to Section 725.933(n) must record in a log that is kept in the facility operating record the identification of closed-vent system components that are designated as unsafe to monitor in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(n), an explanation for each closed-vent system component stating why the closed-vent system component is unsafe to monitor, and the plan for monitoring each closed-vent system component; and
10) When each leak is detected, as specified in Section 725.933(k), the following information must be recorded:
A) The instrument identification number, the closed-vent system component identification number, and the operator name, initials, or identification number;
B) The date the leak was detected and the date of first attempt to repair the leak;
C) The date of successful repair of the leak;
D) Maximum instrument reading measured by Reference Method 21 (Determination of Volatile Organic Compound Leaks) of appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), after it is successfully repaired or determined to be nonrepairable; and
E) “Repair delayed” and the reason for the delay if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days after discovery of the leak.
i) The owner or operator may develop a written procedure that identifies the conditions that justify a delay of repair. In such cases, reasons for delay of repair may be documented by citing the relevant sections of the written procedure.
ii) If delay of repair was caused by depletion of stocked parts, there must be documentation that the spare parts were sufficiently stocked on-site before depletion and the reason for depletion.
d) Records of the monitoring, operating and inspection information required by subsections (c)(3) through (c)(10) must be maintained by the owner or operator for at least three years following the date of each occurrence, measurement, corrective action, or record.
e) For a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser or carbon adsorption system, monitoring and inspection information indicating proper operation and maintenance of the control device must be recorded in the facility operating record.
f) Up-to-date information and data used to determine whether or not a process vent is subject to the requirements in Section 725.932, including supporting documentation as required by Section 725.934(d)(2), when application of the knowledge of the nature of the hazardous waste stream or the process by which it was produced is used, must be recorded in a log that is kept in the facility operating record.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART BB: AIR EMISSION STANDARDS FOR EQUIPMENT LEAKS
Section 725.950 Applicability
a) The regulations in this Subpart BB apply to owners and operators of facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous wastes (except as provided in Section 725.101).
b) Except as provided in Section 725.964(k), this Subpart BB applies to equipment that contains or contacts hazardous wastes with organic concentrations of at least 10 percent by weight that are managed in one of the following:
1) A unit that is subject to the RCRA permitting requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705;
2) A unit (including a hazardous waste recycling unit) that is not exempt from permitting under the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.117 (i.e., a hazardous waste recycling unit that is not a “90-day” tank or container) and that is located at a hazardous waste management facility otherwise subject to the permitting requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705; or
3) A unit that is exempt from permitting under the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 722.117 (i.e., a “90-day” tank or container) and which is not a recycling unit under the provisions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.106.
c) Each piece of equipment to which this Subpart BB applies must be marked in such a manner that it can be distinguished readily from other pieces of equipment.
d) Equipment that is in vacuum service is excluded from the requirements of Sections 725.952 to 725.960, if it is identified as required in Section 725.964(g)(5).
e) Equipment that contains or contacts hazardous waste with an organic concentration of at least 10 percent by weight for less than 300 hours per calendar year is excluded from the requirements of Sections 725.952 through 725.960 if it is identified as required in Section 725.964(g)(6).
f) This subsection (f) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.1050(f), which relates exclusively to a facility outside Illinois. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal regulations.
g) Purged coatings and solvents from surface coating operations subject to the federal national emission standards for hazardous air pollutants (NESHAPs) for the surface coating of automobiles and light-duty trucks at subpart IIII of 40 CFR 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants: Surface Coating of Automobiles and Light-Duty Trucks) are not subject to the requirements of this Subpart BB.
BOARD NOTE: The requirements of Sections 725.952 through 725.964 apply to equipment associated with hazardous waste recycling units previously exempt under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.106(c)(1). Other exemptions under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.104 and 725.101(e) are not affected by these requirements.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.951 Definitions
As used in this Subpart BB, all terms have the meaning given them in Section 725.931, section 1004 of RCRA, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728, and 738.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.952 Standards: Pumps in Light Liquid Service
a) Monitoring.
1) Each pump in light liquid service must be monitored monthly to detect leaks by the methods specified in Section 725.963(b), except as provided in subsections (d), (e), and (f).
2) Each pump in light liquid service must be checked by visual inspection each calendar week for indications of liquids dripping from the pump seal.
b) Leaks.
1) If an instrument reading of 10,000 ppm or greater is measured, a leak is detected.
2) If there are indications of liquids dripping from the pump seal, a leak is detected.
c) Repairs.
1) When a leak is detected, it must be repaired as soon as practicable, but not later than 15 calendar days after it is detected, except as provided in Section 725.959.
2) A first attempt at repair (e.g., tightening the packing gland) must be made no later than 5 calendar days after each leak is detected.
d) Each pump equipped with a dual mechanical seal system that includes a barrier fluid system is exempt from the requirements of subsection (a), provided the following requirements are met:
1) Each dual mechanical seal system must be as follows:
A) Operated with the barrier fluid at a pressure that is at all times greater than the pump stuffing box pressures;
B) Equipped with a barrier fluid degassing reservoir that is connected by a closed-vent system to a control device that complies with the requirements of Section 725.960; or
C) Equipped with a system that purges the barrier fluid into a hazardous wastestream with no detectable emissions to the atmosphere;
2) The barrier fluid system must not be a hazardous waste with organic concentrations 10 percent or greater by weight;
3) Each barrier fluid system must be equipped with a sensor that will detect failure of the seal system, the barrier fluid system, or both;
4) Each pump must be checked by visual inspection, each calendar week, for indications of liquids dripping from the pump seals;
5) Alarms.
A) Each sensor described in subsection (d)(3), must be checked daily or be equipped with an audible alarm that must be checked monthly to ensure that it is functioning properly.
B) The owner or operator must determine, based on design considerations and operating experience, a criterion that indicates failure of the seal system, the barrier fluid system, or both; and
6) Leaks.
A) If there are indications of liquids dripping from the pump seal or the sensor indicates failure of the seal system, the barrier fluid system, or both, based on the criterion determined in subsection (d)(5)(B), a leak is detected.
B) When a leak is detected, it must be repaired as soon as practicable, but not later than 15 calendar days after it is detected, except as provided in Section 725.959.
C) A first attempt at repair (e.g., relapping the seal) must be made no later than five calendar days after each leak is detected.
e) Any pump that is designated, as described in Section 725.964(g)(2), for no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, is exempt from the requirements of subsections (a), (c), and (d), if the pump meets the following requirements:
1) Must have no externally actuated shaft penetrating the pump housing;
2) Must operate with no detectable emissions as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background as measured by the methods specified in Section 725.963(c); and
3) Must be tested for compliance with subsection (e)(2), initially upon designation, annually and at other times as specified by the Agency.
f) If any pump is equipped with a closed-vent system capable of capturing and transporting any leakage from the seal or seals to a control device that complies with the requirements of Section 725.960, it is exempt from the requirements of subsections (a) through (e).
(Source: Amended at 40 Ill. Reg. 11830, effective August 9, 2016)
Section 725.953 Standards: Compressors
a) Each compressor must be equipped with a seal system that includes a barrier fluid system and that prevents leakage of total organic emissions to the atmosphere, except as provided in subsections (h) and (i).
b) The following must be true of each compressor seal system, as required in subsection (a):
1) Operated with the barrier fluid at a pressure that is at all times greater than the compressor stuffing box pressure;
2) Equipped with a barrier fluid system that is connected by a closed-vent system to a control device that complies with the requirements of Section 725.960; or
3) Equipped with a system that purges the barrier fluid into a hazardous wastestream with no detectable emissions to atmosphere.
c) The barrier fluid must not be a hazardous waste with organic concentrations 10 percent or greater by weight.
d) Each barrier fluid system, as described in subsections (a) through (c), must be equipped with a sensor that will detect failure of the seal system, barrier fluid system, or both.
e) Inspections
1) Each sensor, as required in subsection (d), must be checked daily or must be equipped with an audible alarm that must be checked monthly to ensure that it is functioning properly, unless the compressor is located within the boundary of an unmanned plant site, in which case the sensor must be checked daily.
2) The owner or operator must determine, based on design considerations and operating experience, a criterion that indicates failure of the seal system, the barrier fluid system, or both.
f) If the sensor indicates failure of the seal system, the barrier fluid system, or both based on the criterion determined under subsection (e)(2), a leak is detected.
g) Repairs
1) When a leak is detected, it must be repaired as soon as practicable, but not later than 15 calendar days after it is detected, except as provided in Section 725.959.
2) A first attempt at repair (e.g., tightening the packing gland) must be made no later than five calendar days after each leak is detected.
h) A compressor is exempt from the requirements of subsections (a) and (b) if it is equipped with a closed-vent system capable of capturing and transporting any leakage from the seal to a control device that complies with the requirements of Section 725.960, except as provided in subsection (i).
i) Any compressor that is designated, as described in Section 725.964(g)(2), for no detectable emission as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, is exempt from the requirements of subsections (a) through (h) if the following is true of the compressor:
1) It is determined to be operating with no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, as measured by the method specified in Section 725.963(c).
2) It is tested for compliance with subsection (i)(1) initially upon designation, annually and other times as specified by the Agency pursuant to Section 725.950(e).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.954 Standards: Pressure Relief Devices in Gas/Vapor Service
a) Except during pressure releases, each pressure relief device in gas/vapor service must be operated with no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background as measured by the method specified in Section 725.963(c).
b) Actions Following Pressure Release
1) After each pressure release, the pressure relief device must be returned to a condition of no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, as soon as practicable, but no later than 5 calendar days after each pressure release, except as provided in Section 725.959.
2) No later than five calendar days after the pressure release, the pressure relief device must be monitored to confirm the condition of no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, as measured by the method specified in Section 725.963(c).
c) Any pressure relief device that is equipped with a closed-vent system capable of capturing and transporting leakage from the pressure relief device to a control device as described in Section 725.960 is exempt from the requirements of subsections (a) and (b).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.955 Standards: Sampling Connecting Systems
a) Each sampling connection system must be equipped with a closed-purge, closed-loop, or closed-vent system. This system must collect the sample purge for return to the process or for routing to the appropriate treatment system. Gases displaced during filling of the sample container are not required to be collected or captured.
b) Each closed-purge, closed-loop, or closed-vent system as required in subsection (a) must meet one of the following requirements:
1) Return the purged process fluid directly to the process line;
2) Collect and recycle the purged process fluid; or
3) Be designed and operated to capture and transport all the purged process fluid to a waste management unit that complies with the applicable requirements of Sections 725.985 through 725.987 or a control device that complies with the requirements of Section 725.960.
c) In-situ sampling systems and sampling systems without purges are exempt from the requirements of subsections (a) and (b).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.956 Standards: Open-Ended Valves or Lines
a) Equipment
1) Each open-ended valve or line must be equipped with a cap, blind flange, plug, or a second valve.
2) The cap, blind flange, plug, or second valve must seal the open end at all times except during operations requiring hazardous wastestream flow through the open-ended valve or line.
b) Each open-ended valve or line equipped with a second valve must be operated in a manner such that the valve on the hazardous wastestream end is closed before the second valve is closed.
c) When a double block and bleed system is being used, the bleed valve or line may remain open during operations that require venting the line between the block valves but must comply with subsection (a) at all other times.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.957 Standards: Valves in Gas/Vapor or Light Liquid Service
a) Each valve in gas/vapor or light liquid service must be monitored monthly to detect leaks by the methods specified in Section 725.963(b) and must comply with subsections (b) through (e), except as provided in subsections (f), (g), and (h) and in Sections 725.961 and 725.962.
b) If an instrument reading of 10,000 ppm or greater is measured, a leak is detected.
c) Monitoring Frequency
1) Any valve for which a leak is not detected for two successive months must be monitored the first month of every succeeding quarter, beginning with the next quarter, until a leak is detected.
2) If a leak is detected, the valve must be monitored monthly until a leak is not detected for two successive months,
d) Leak Repair
1) When a leak is detected, it must be repaired as soon as practicable, but no later than 15 calendar days after the leak is detected, except as provided in Section 725.959.
2) A first attempt at repair must be made no later than five calendar days after each leak is detected.
e) First attempts at repair include, but are not limited to the following best practices where practicable:
1) Tightening of bonnet bolts;
2) Replacement of bonnet bolts;
3) Tightening of packing gland nuts; or
4) Injection of lubricant into lubricated packing.
f) Any valve that is designated, as described in Section 725.964(g)(2), for no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, is exempt from the requirements of subsection (a) if the valve fulfills the following requirements:
1) It has no external actuating mechanism in contact with the hazardous wastestream;
2) It is operated with emissions less than 500 ppm above background as determined by the method specified in Section 725.963(c); and
3) It is tested for compliance with subsection (f)(2) initially upon designation, annually, and at other times as specified by the Agency pursuant to Section 725.950(e).
g) Any valve that is designated, as described in Section 725.964(h)(1), as an unsafe-to-monitor valve is exempt from the requirements of subsection (a), if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The owner or operator of the valve determines that the valve is unsafe to monitor because monitoring personnel would be exposed to an immediate danger as a consequence of complying with subsection (a); and
2) The owner or operator of the valve adheres to a written plan that requires monitoring of the valve as frequently as practicable during safe-to-monitor times.
h) Any valve that is designated, as described in Section 725.964(h)(2), as a difficult-to-monitor valve is exempt from the requirements of subsection (a), if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The owner or operator of the valve determines that the valve cannot be monitored without elevating the monitoring personnel more than two meters above a support surface;
2) The hazardous waste management unit within which the valve is located was in operation before June 21, 1990; and
3) The owner or operator of the valve follows a written plan that requires monitoring of the valve at least once per calendar year.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.958 Standards: Pumps, Valves, Pressure Relief Devices, Flanges, and Other Connectors
a) Pumps and valves in heavy liquid service, pressure relief devices in light liquid or heavy liquid service and flanges and other connectors must be monitored within five days by the method specified in Section 725.963(b), if evidence of a potential leak is found by visual, audible, olfactory, or any other detection method.
b) If an instrument reading of 10,000 ppm or greater is measured, a leak is detected.
c) Repairs
1) When a leak is detected, it must be repaired as soon as practicable, but not later than 15 calendar days after it is detected, except as provided in Section 725.959.
2) The first attempt at repair must be made no later than five calendar days after each leak is detected.
d) First attempts at repair include, but are not limited to, the best practices described under Section 725.957(e).
e) Any connector that is inaccessible or is ceramic or ceramic-lined (e.g., porcelain, glass, or glass-lined) is exempt from the monitoring requirements of subsection (a) and from the recordkeeping requirements of Section 725.964.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.959 Standards: Delay of Repair
a) Delay of repair of equipment for which leaks have been detected is allowed if the repair is technically infeasible without a hazardous waste management unit shutdown. In such a case, repair of this equipment must occur before the end of the next hazardous waste management unit shutdown.
b) Delay of repair of equipment for which leaks have been detected is allowed for equipment that is isolated from the hazardous waste management unit and that does not continue to contain or contact hazardous waste with organic concentrations at least 10 percent by weight.
c) Delay of repair for valves is allowed if the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The owner or operator determines that emissions of purged material resulting from immediate repair are greater than the emissions likely to result from delay of repair; and
2) When repair procedures are effected, the purged material is collected and destroyed or recovered in a control device complying with Section 725.960.
d) Delay of repair for pumps is allowed if the following conditions are met:
1) Repair requires the use of a dual mechanical seal system that includes a barrier fluid system; and
2) Repair is completed as soon as practicable, but not later than six months after the leak was detected.
e) Delay of repair beyond a hazardous waste management unit shutdown is allowed for a valve if valve assembly replacement is necessary during the hazardous waste management unit shutdown, valve assembly supplies have been depleted, and valve assembly supplies had been sufficiently stocked before the supplies were depleted. Delay of repair beyond the next hazardous waste management unit shutdown is not allowed unless the next hazardous waste management unit shutdown occurs sooner than six months after the first hazardous waste management unit shutdown.
(Source: Amended at 29 Ill. Reg. 6389, effective April 22, 2005)
Section 725.960 Standards: Closed-Vent Systems and Control Devices
a) An owner or operator of a closed-vent system or control device subject to this Subpart BB must comply with the provisions of Section 725.933.
b) Implementation Schedule
1) The owner or operator of an existing facility that cannot install a closed-vent system and control device to comply with the provisions of this Subpart BB on the effective date that the facility becomes subject to the provisions of this Subpart BB must prepare an implementation schedule that includes dates by which the closed-vent system and control device will be installed and in operation. The controls must be installed as soon as possible, but the implementation schedule may allow up to 30 months after the effective date that the facility becomes subject to this Subpart BB for installation and startup.
2) Any unit that is subject to the provisions of this Subpart BB when operation begins, must comply with the rules immediately (i.e., the unit must have control devices installed and operating on startup of the affected unit); the 30-month implementation schedule does not apply.
3) The owner or operator of any facility in existence on the effective date of a statutory or regulatory amendment that renders the facility subject to this Subpart BB must comply with all requirements of this Subpart BB as soon as practicable but no later than 30 months after the effective date of the amendment. When control equipment required by this Subpart BB cannot be installed and begin operation by the effective date of the amendment, the facility owner or operator must prepare an implementation schedule that includes the following information: Specific calendar dates for award of contracts or issuance of purchase orders for the control equipment, initiation of on-site installation of the control equipment, completion of the control equipment installation, and performance of any testing to demonstrate that the installed equipment meets the applicable standards of this Subpart BB. The owner or operator must enter the implementation schedule in the operating record or in a permanent, readily available file located at the facility.
4) An owner or operator of a facility or unit that becomes newly subject to the requirements of this Subpart BB due to an action other than those described in subsection (b)(3) must comply with all applicable requirements immediately (i.e., the facility or unit must have control devices installed and operating on the date the facility or unit becomes subject to this Subpart BB; the 30-month implementation schedule does not apply).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.961 Percent Leakage Alternative for Valves
a) An owner or operator subject to the requirements of Section 725.957 may elect to have all valves within a hazardous waste management unit comply with an alternative standard that allows no greater than two percent of the valves to leak.
b) The following requirements must be met if an owner or operator decides to comply with the alternative standard of allowing two percent of valves to leak:
1) A performance test as specified in subsection (c) must be conducted initially upon designation, annually and other times as specified by the Agency pursuant to Section 725.950(e); and
2) If a valve leak is detected it must be repaired in accordance with Section 725.957(d) and (e).
c) Performance tests must be conducted in the following manner:
1) All valves subject to the requirements in Section 725.957 within the hazardous waste management unit must be monitored within 1 week by the methods specified in Section 725.963(b);
2) If an instrument reading of 10,000 ppm or greater is measured, a leak is detected; and
3) The leak percentage must be determined by dividing the number of valves subject to the requirements in Section 725.957 for which leaks are detected by the total number of valves subject to the requirements in Section 725.957 within the hazardous waste management unit.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.962 Skip Period Alternative for Valves
a) An owner or operator subject to the requirements of Section 725.957 may elect for all valves within a hazardous waste management unit to comply with one of the alternative work practices specified in subsections (b)(2) and (b)(3).
b) Reduced Monitoring
1) An owner or operator must comply with the requirements for valves, as described in Section 725.957, except as described in subsections (b)(2) and (b)(3).
2) After two consecutive quarterly leak detection periods with the percentage of valves leaking equal to or less than two percent, an owner or operator may begin to skip one of the quarterly leak detection periods (i.e., the owner or operator may monitor for leaks once every six months) for the valves subject to the requirements in Section 725.957.
3) After five consecutive quarterly leak detection periods with the percentage of valves leaking equal to or less than two percent, an owner or operator may begin to skip three of the quarterly leak detection periods (i.e., the owner or operator may monitor for leaks once every year) for the valves subject to the requirements in Section 725.957.
4) If the percentage of valves leaking is greater than two percent, the owner or operator must monitor monthly in compliance with the requirements in Section 725.957, but may again elect to use this Section after meeting the requirements of Section 725.957(c)(1).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.963 Test Methods and Procedures
a) Each owner or operator subject to the provisions of this Subpart BB must comply with the test methods and procedures requirements provided in this Section.
b) Leak detection monitoring, as required in Sections 725.952 through 725.962, must comply with the following requirements:
1) Monitoring must comply with Reference Method 21 (Determination of Volatile Organic Compound Leaks) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b);
2) The detection instrument must meet the performance criteria of Reference Method 21;
3) The instrument must be calibrated before use on each day of its use by the procedures specified in Reference Method 21;
4) Calibration gases must be as follows:
A) Zero air (less than 10 ppm of hydrocarbon in air);
B) A mixture of methane or n-hexane and air at a concentration of approximately, but less than, 10,000 ppm methane or n-hexane; and
5) The instrument probe must be traversed around all potential leak interfaces as close to the interface as possible as described in Reference Method 21.
c) When equipment is tested for compliance with no detectable emissions, as required in Sections 725.952(e), 725.953(i), 725.954, and 725.957(f), the test must comply with the following requirements:
1) The requirements of subsections (b)(1) through (b)(4) apply;
2) The background level must be determined as set forth in Reference Method 21;
3) The instrument probe must be traversed around all potential leak interfaces as close to the interface as possible as described in Reference Method 21; and
4) This arithmetic difference between the maximum concentration indicated by the instrument and the background level is compared with 500 ppm for determining compliance.
d) In accordance with the waste analysis plan required by Section 725.113(b), an owner or operator of a facility must determine, for each piece of equipment, whether the equipment contains or contacts a hazardous waste with organic concentration that equals or exceeds 10 percent by weight using the following:
1) Methods described in ASTM Methods D 2267-88 (Standard Test Method for Aromatics in Light Naphthas and Aviation Gasolines by Gas Chromatography), E 168-88 (Standard Practices for General Techniques of Infrared Quantitative Analysis), E 169-87 (Standard Practices for General Techniques of Ultraviolet-Visible Quantitative Analysis), or E 260-85 (Standard Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a);
2) Method 9060A (Total Organic Carbon) of “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods”, USEPA publication number EPA-530/SW-846, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a), or analyzed for its individual organic constituents; or
3) Application of the knowledge of the nature of the hazardous wastestream or the process by which it was produced. Documentation of a waste determination by knowledge is required. Examples of documentation that must be used to support a determination under this provision include production process information documenting that no organic compounds are used, information that the waste is generated by a process that is identical to a process at the same or another facility that has previously been demonstrated by direct measurement to have a total organic content less than 10 percent, or prior speciation analysis results on the same wastestream where it is also documented that no process changes have occurred since that analysis that could affect the waste total organic concentration.
e) If an owner or operator determines that a piece of equipment contains or contacts a hazardous waste with organic concentrations at least 10 percent by weight, the determination can be revised only after following the procedures in subsection (d)(1) or (d)(2).
f) When an owner or operator and the Agency do not agree on whether a piece of equipment contains or contacts a hazardous waste with organic concentrations at least 10 percent by weight, the procedures in subsection (d)(1) or (d)(2) must be used to resolve the dispute.
g) Samples used in determining the percent organic content must be representative of the highest total organic content hazardous waste that is expected to be contained in or contact the equipment.
h) To determine if pumps or valves are in light liquid service, the vapor pressures of constituents must either be obtained from standard reference texts or be determined by ASTM D 2879-92 (Standard Test Method for Vapor Pressure-Temperature Relationship and Initial Decomposition Temperature of Liquids by Isoteniscope), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
i) Performance tests to determine if a control device achieves 95 weight percent organic emission reduction must comply with the procedures of Section 725.934(c)(1) through (c)(4).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.964 Recordkeeping Requirements
a) Lumping Units
1) Each owner or operator subject to the provisions of this Subpart BB must comply with the recordkeeping requirements of this Section.
2) An owner or operator of more than one hazardous waste management unit subject to the provisions of this Subpart BB may comply with the recordkeeping requirements for these hazardous waste management units in one recordkeeping system if the system identifies each record by each hazardous waste management unit.
b) Owners and operators must record the following information in the facility operating record:
1) For each piece of equipment to which this Subpart BB applies, the following:
A) Equipment identification number and hazardous waste management unit identification;
B) Approximate locations within the facility (e.g., identify the hazardous waste management unit on a facility plot plan);
C) Type of equipment (e.g., a pump or pipeline valve);
D) Percent-by-weight total organics in the hazardous wastestream at the equipment;
E) Hazardous waste state at the equipment (e.g., gas/vapor or liquid); and
F) Method of compliance with the standard (e.g., “monthly leak detection and repair” or “equipped with dual mechanical seals”);
2) For facilities that comply with the provisions of Section 725.933(a)(2), an implementation schedule, as specified in that Section;
3) Where an owner or operator chooses to use test data to demonstrate the organic removal efficiency or total organic compound concentration achieved by the control device, a performance test plan, as specified in Section 725.935(b)(3); and
4) Documentation of compliance with Section 725.960, including the detailed design documentation or performance test results specified in Section 725.935(b)(4).
c) When each leak is detected, as specified in Section 725.952, 725.953, 725.957, or 725.958, the following requirements apply:
1) A weatherproof and readily visible identification, marked with the equipment identification number, the date evidence of a potential leak was found in accordance with Section 725.958(a), and the date the leak was detected, must be attached to the leaking equipment;
2) The identification on equipment except on a valve, may be removed after it has been repaired; and
3) The identification on a valve may be removed after it has been monitored for two successive months as specified in Section 725.957(c) and no leak has been detected during those two months.
d) When each leak is detected, as specified in Sections 725.952, 725.953, 725.957, or 725.958, the following information must be recorded in an inspection log and must be kept in the facility operating record:
1) The instrument and operator identification numbers and the equipment identification number;
2) The date evidence of a potential leak was found in accordance with Section 725.958(a);
3) The date the leak was detected and the dates of each attempt to repair the leak;
4) Repair methods applied in each attempt to repair the leak;
5) “Above 10,000”, if the maximum instrument reading measured by the methods specified in Section 725.963(b) after each repair attempt is equal to or greater than 10,000 ppm;
6) “Repair delayed” and the reason for the delay if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days after discovery of the leak;
7) Documentation supporting the delay of repair of a valve in compliance with Section 725.959(c);
8) The signature of the owner or operator (or designate) whose decision it was that repair could not be effected without a hazardous waste management unit shutdown;
9) The expected date of successful repair of the leak if a leak is not repaired within 15 calendar days; and
10) The date of successful repair of the leak.
e) Design documentation and monitoring, operating, and inspection information for each closed-vent system and control device required to comply with the provisions of Section 725.960 must be recorded and kept up-to-date in the facility operating record as specified in Section 725.935(c)(1) and (c)(2), and monitoring, operating and inspection information in Section 725.935(c)(3) through (c)(8).
f) For a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, catalytic vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser, or carbon adsorption system, monitoring and inspection information indicating proper operation and maintenance of the control device must be recorded in the facility operating record.
g) The following information pertaining to all equipment subject to the requirements in Sections 725.952 through 725.960 must be recorded in a log that is kept in the facility operating record:
1) A list of identification numbers for equipment (except welded fittings) subject to the requirements of this Subpart BB.
2) List of Equipment
A) A list of identification numbers for equipment that the owner or operator elects to designate for no detectable emissions, as indicated by an instrument reading of less than 500 ppm above background, under the provisions of Sections 725.952(e), 725.953(i), and 725.957(f).
B) The designation of this equipment as subject to the requirements of Section 725.952(e), 725.953(i), or 725.957(f) must be signed by the owner or operator.
3) A list of equipment identification numbers for pressure relief devices required to comply with Section 725.954(a).
4) Compliance Tests
A) The dates of each compliance test required in Sections 725.952(e), 725.953(i), 725.954, and 725.957(f).
B) The background level measured during each compliance test.
C) The maximum instrument reading measured at the equipment during each compliance test.
5) A list of identification numbers for equipment in vacuum service.
6) Identification, either by list or location (area or group) of equipment that contains or contacts hazardous waste with an organic concentration of at least 10 percent by weight for less than 300 hours per year.
h) The following information pertaining to all valves subject to the requirements of Section 725.957(g) and (h) must be recorded in a log that is kept in the facility operating record:
1) A list of identification numbers for valves that are designated as unsafe to monitor, an explanation for each valve stating why the valve is unsafe to monitor, and the plan for monitoring each valve; and
2) A list of identification numbers for valves that are designated as difficult to monitor, an explanation for each valve stating why the valve is difficult to monitor, and the planned schedule for monitoring each valve.
i) The following information must be recorded in the facility operating record for valves complying with Section 725.962:
1) A schedule of monitoring; and
2) The percent of valves found leaking during each monitoring period.
j) The following information must be recorded in a log that is kept in the facility operating record:
1) Criteria required in Sections 725.952(d)(5)(B) and 725.953(e)(2) and an explanation of the criteria; and
2) Any changes to these criteria and the reasons for the changes.
k) The following information must be recorded in a log that is kept in the facility operating record for use in determining exemptions, as provided in Section 725.950 and other specific Subparts:
1) An analysis determining the design capacity of the hazardous waste management unit;
2) A statement listing the hazardous waste influent to and effluent from each hazardous waste management unit subject to the requirements in Sections 725.952 through 725.960 and an analysis determining whether these hazardous wastes are heavy liquids; and
3) An up-to-date analysis and the supporting information and data used to determine whether or not equipment is subject to the requirements in Sections 725.952 through 725.960. The record must include supporting documentation, as required by Section 725.963(d)(3), when application of the knowledge of the nature of the hazardous wastestream or the process by which it was produced is used. If the owner or operator takes any action (e.g., changing the process that produced the waste) that could result in an increase in the total organic content of the waste contained in or contacted by equipment determined not to be subject to the requirements in Sections 725.952 through 725.960, then a new determination is required.
l) Records of the equipment leak information required by subsection (d) and the operating information required by subsection (e) need be kept only three years.
m) The owner or operator of any facility with equipment that is subject to this Subpart and to federal regulations at 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63 may elect to determine compliance with this Subpart BB by documentation of compliance either pursuant to Section 725.964 or by documentation of compliance with the regulations at 40 CFR 60 (Standards of Performance for New Stationary Sources), 61 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants), or 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants for Source Categories), pursuant to the relevant provisions of 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63, each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The documentation of compliance under the regulation at 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63 must be kept with or made readily available with the facility operating record.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART CC: AIR EMISSION STANDARDS FOR TANKS, SURFACE IMPOUNDMENTS, AND CONTAINERS
Section 725.980 Applicability
a) The requirements of this Subpart CC apply to owners and operators of all facilities that treat, store, or dispose of hazardous waste in tanks, surface impoundments, or containers that are subject to Subpart I, J, or K, except as Section 725.101 and subsection (b) provide otherwise.
b) The requirements of this Subpart CC do not apply to the following waste management units at the facility:
1) A waste management unit that holds hazardous waste placed in the unit before December 6, 1996, and in which no hazardous waste was added to the unit on or after December 6, 1996;
2) A container that has a design capacity less than or equal to 0.1 m3 (3.5 ft3 or 26.4 gal);
3) A tank in which an owner or operator has stopped adding hazardous waste and the owner or operator has begun implementing or completed closure pursuant to an approved closure plan;
4) A surface impoundment in which an owner or operator has stopped adding hazardous waste (except to implement an approved closure plan) and the owner or operator has begun implementing or completed closure pursuant to an approved closure plan;
5) A waste management unit that is used solely for on-site treatment or storage of hazardous waste that is placed in the unit as a result of implementing remedial activities required pursuant to the Act or Board regulations or pursuant to the corrective action authorities of RCRA sections 3004(u), 3004(v), or 3008(h); CERCLA authorities; or similar federal or State authorities;
6) A waste management unit that is used solely for the management of radioactive mixed waste in accordance with all applicable regulations pursuant to the authority of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954 (42 USC 2011 et seq.) and the Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982 (42 USC 10101 et seq.);
7) A hazardous waste management unit that the owner or operator certifies is equipped with and operating air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of an applicable federal Clean Air Act regulation codified pursuant to 40 CFR 60 (Standards of Performance for New Stationary Sources), 61 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants), or 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants for Source Categories). For the purpose of complying with this subsection (b)(7), a tank for which the air emission control includes an enclosure, as opposed to a cover, must be in compliance with the enclosure and control device requirements of Section 725.985(i), except as provided in Section 725.983(c)(5); and
8) A tank that has a process vent, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 725.931.
c) This subsection (c) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.1080(c), which requires incorporation of requirements of Subpart CC of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 into a permit issued prior to a date long past and compliance with this Subpart CC until the permit issues. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal rules.
d) The requirements of this Subpart CC, except for the recordkeeping requirements specified in Section 725.990(i), are stayed for a tank or container used for the management of hazardous waste generated by organic peroxide manufacturing and its associated laboratory operations, when the owner or operator of the unit meets all of the following conditions:
1) The owner or operator identifies that the tank or container receives hazardous waste generated by an organic peroxide manufacturing process producing more than one functional family of organic peroxides or multiple organic peroxides within one functional family, that one or more of these organic peroxides could potentially undergo self-accelerating thermal decomposition at or below ambient temperatures, and that organic peroxides are the predominant products manufactured by the process. For the purposes of this subsection, “organic peroxide” means an organic compound that contains the bivalent OO structure and which may be considered to be a structural derivative of hydrogen peroxide where one or both of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an organic radical;
2) The owner or operator prepares documentation, in accordance with Section 725.990(i), explaining why an undue safety hazard would be created if air emission controls specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988 are installed and operated on the tanks and containers used at the facility to manage the hazardous waste generated by the organic peroxide manufacturing process or processes meeting the conditions of subsection (d)(1); and
3) The owner or operator notifies the Agency in writing that hazardous waste generated by an organic peroxide manufacturing process or processes meeting the conditions of subsection (d)(1) are managed at the facility in tanks or containers meeting the conditions of subsection (d)(2). The notification must state the name and address of the facility and be signed and dated by an authorized representative of the facility owner or operator.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.981 Definitions
As used in this Subpart CC, all terms not defined in this Section will have the meanings given to them in section 1004 of RCRA, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111, and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720 through 728.
“Average volatile organic concentration” or “average VO concentration” means the mass-weighted average volatile organic concentration of a hazardous waste, as determined in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.984.
“Closure device” means a cap, hatch, lid, plug, seal, valve, or other type of fitting that blocks an opening in a cover so that when the device is secured in the closed position it prevents or reduces air pollutant emissions to the atmosphere. Closure devices include devices that are detachable from the cover (e.g., a sampling port cap), manually operated (e.g., a hinged access lid or hatch), or automatically operated (e.g., a spring-loaded pressure relief valve).
“Continuous seal” means a seal that forms a continuous closure that completely covers the space between the edge of the floating roof and the wall of a tank. A continuous seal may be a vapor-mounted seal, liquid-mounted seal, or metallic shoe seal. A continuous seal may be constructed of fastened segments so as to form a continuous seal.
“Cover” means a device that provides a continuous barrier over the hazardous waste managed in a unit to prevent or reduce air emissions to the atmosphere. A cover may have openings (such as access hatches, sampling ports, and gauge wells) that are necessary for operation, inspection, maintenance, or repair of the unit on which the cover is used. A cover may be a separate piece of equipment that can be detached and removed from the unit or a cover may be formed by structural features permanently integrated into the design of the unit.
“Enclosure” means a structure that surrounds a tank or container, captures organic vapors emitted from the tank or container, and vents the captured vapors through a closed-vent system to a control device.
“External floating roof” means a pontoon-type or double-deck type cover that rests on the surface of a hazardous waste being managed in a tank with no fixed roof.
“Fixed roof” means a cover that is mounted on a unit in a stationary position and does not move with fluctuations in the level of the material managed in the unit.
“Floating membrane cover” means a cover consisting of a synthetic flexible membrane material that rests upon and is supported by the hazardous waste being managed in a surface impoundment.
“Floating roof” means a cover consisting of a double-deck, pontoon single-deck, or internal floating cover that rests upon and is supported by the material being contained, and is equipped with a continuous seal.
“Hard-piping” means pipe or tubing that is manufactured and properly installed in accordance with relevant standards and good engineering practices.
“In light material service” means that the container is used to manage a material for which both of the following conditions apply: the vapor pressure of one or more of the organic constituents in the material is greater than 0.3 kilopascals (kPa) at 20 °C (1.2 inches H2O at 68 °F); and the total concentration of the pure organic constituents having a vapor pressure greater than 0.3 kPa at 20 °C (1.2 inches H2O at 68 °F) is equal to or greater than 20 percent by weight.
“Internal floating roof” means a cover that rests or floats on the material surface (but not necessarily in complete contact with it) inside a tank that has a fixed roof.
“Liquid-mounted seal” means a foam or liquid-filled primary seal mounted in contact with the hazardous waste between the tank wall and the floating roof, continuously around the circumference of the tank.
“Malfunction” means any sudden, infrequent, and not reasonably preventable failure of air pollution control equipment, process equipment, or a process to operate in a normal or usual manner. A failure that is caused in part by poor maintenance or careless operation is not a malfunction.
“Maximum organic vapor pressure” means the sum of the individual organic constituent partial pressures exerted by the material contained in a tank at the maximum vapor pressure-causing conditions (i.e., temperature, agitation, pH effects of combining wastes, etc.) reasonably expected to occur in the tank. For the purpose of this Subpart CC, maximum organic vapor pressure is determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(c).
“Metallic shoe seal” means a continuous seal that is constructed of metal sheets that are held vertically against the wall of the tank by springs, weighted levers, or other mechanisms and that is connected to the floating roof by braces or other means. A flexible coated fabric (envelope) spans the annular space between the metal sheet and the floating roof.
“No detectable organic emissions” means no escape of organics to the atmosphere, as determined using the procedure specified in Section 725.984(d).
“Point of waste origination” means as follows:
When the facility owner or operator is the generator of the hazardous waste, the “point of waste origination” means the point where a solid waste produced by a system, process, or waste management unit is determined to be a hazardous waste, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.
BOARD NOTE: In this case, this term is being used in a manner similar to the use of the term “point of generation” in air standards established for waste management operations under authority of the federal Clean Air Act in 40 CFR 60 (Standards of Performance for New Stationary Sources), 61 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants), and 63 (National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants for Source Categories).
When the facility owner and operator are not the generator of the hazardous waste, “point of waste origination” means the point where the owner or operator accepts delivery or takes possession of the hazardous waste.
“Point of waste treatment” means the point where a hazardous waste to be treated in accordance with Section 725.983(c)(2) exits the treatment process. Any waste determination must be made before the waste is conveyed, handled, or otherwise managed in a manner that allows the waste to volatilize to the atmosphere.
“Safety device” means a closure device, such as a pressure relief valve, frangible disc, fusible plug, or any other type of device that functions exclusively to prevent physical damage or permanent deformation to a unit or its air emission control equipment by venting gases or vapors directly to the atmosphere during unsafe conditions resulting from an unplanned, accidental, or emergency event. For the purpose of this Subpart CC, a safety device is not used for routine venting of gases or vapors from the vapor headspace underneath a cover such as during filling of the unit or to adjust the pressure in this vapor headspace in response to normal daily diurnal ambient temperature fluctuations. A safety device is designed to remain in a closed position during normal operations and open only when the internal pressure, or another relevant parameter, exceeds the device threshold setting applicable to the air emission control equipment as determined by the owner or operator based on manufacturer recommendations, applicable regulations, fire protection and prevention codes, standard engineering codes and practices, or other requirements for the safe handling of flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive, or hazardous materials.
“Single-seal system” means a floating roof having one continuous seal. This seal may be vapor-mounted, liquid-mounted, or a metallic shoe seal.
“Vapor-mounted seal” means a continuous seal that is mounted so that there is a vapor space between the hazardous waste in the unit and the bottom of the seal.
“Volatile organic concentration” or “VO concentration” means the fraction by weight of organic compounds contained in a hazardous waste expressed in terms of parts per million (ppmw), as determined by direct measurement or by knowledge of the waste, in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.984. For the purpose of determining the VO concentration of a hazardous waste, organic compounds with a Henry’s law constant value of at least 0.1 mole-fraction-in-the-gas-phase/mole-fraction-in-the-liquid-phase (0.1 Y/X) (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 10-6 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C (77 °F) must be included. Appendix F presents a list of compounds known to have a Henry’s law constant value less than the cutoff level.
“Waste determination” means performing all applicable procedures in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.984 to determine whether a hazardous waste meets standards specified in this Subpart CC. Examples of a waste determination include performing the procedures in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.984 to determine the average VO concentration of a hazardous waste at the point of waste origination, determining the average VO concentration of a hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment and comparing the results to the exit concentration limit specified for the process used to treat the hazardous waste, the organic reduction efficiency and the organic biodegradation efficiency for a biological process used to treat a hazardous waste and comparing the results to the applicable standards, or determining the maximum volatile organic vapor pressure for a hazardous waste in a tank and comparing the results to the applicable standards.
“Waste stabilization process” means any physical or chemical process used to either reduce the mobility of hazardous constituents in a hazardous waste or eliminate free liquids as determined by Test Method 9095B (Paint Filter Liquids Test) in “Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods”, USEPA publication number EPA-530/SW-846, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a). A waste stabilization process includes mixing the hazardous waste with binders or other materials and curing the resulting hazardous waste and binder mixture. Other synonymous terms used to refer to this process are “waste fixation” or “waste solidification”. This does not include the addition of absorbent materials to the surface of a waste to absorb free liquid without mixing, agitation, or subsequent curing.
(Source: Amended at 44 Ill. Reg. 15374, effective September 3, 2020)
Section 725.982 Schedule for Implementation of Air Emission Standards
a) This subsection (a) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.1082(a), which required compliance before dates long past. This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal rules.
b) An owner or operator of a facility or unit in existence on the effective date of statutory or regulatory amendments under the Act that render the facility subject to Subpart I, J, or K must meet the following requirements:
1) The owner or operator must install and begin operation of all control equipment required to comply with this Subpart CC and complete modifications of production or treatment processes to satisfy exemption criteria of Section 725.983(c) by the effective date of the amendment, except as provided in subsection (b)(2).
2) When control equipment or waste management units required to comply with this Subpart CC cannot be installed and begin operation or when modifications of production or treatment processes to satisfy the exemption criteria of Section 725.983(c) cannot be completed by the effective date of the amendment, the owner or operator must undertake the following actions:
A) Install and begin operation of the control equipment or waste management unit and complete modification of production or treatment processes as soon as possible, but no later than 30 months after the effective date of the amendment; and
B) Maintenance of Implementation Schedule
i) For facilities subject to the recordkeeping requirements of Section 725.173, enter and maintain the implementation schedule specified in subsection (a)(2)(B) in the operating record no later than the effective date of the amendment, or
ii) For facilities not subject to Section 725.173, the owner or operator must enter and maintain the implementation schedule specified in subsection (a)(2)(B) in a permanent, readily available file located at the facility site no later than the effective date of the amendment.
c) The owner or operator of a facility or unit that becomes newly subject to the requirements of this Subpart CC due to an action other than those described in subsection (b) must comply with all applicable requirements immediately (i.e., the owner or operator must have control devices installed and operating on the date the facility or unit becomes subject to the requirements of this Subpart CC; the 30-month implementation schedule does not apply to the owner or operator of such a facility).
d) This subsection (d) corresponds with 40 CFR 265.1082(d), which allowed extension of a long-past compliance date. This statement maintains structural consistency with the federal rule.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.983 Standards: General
a) This Section applies to the management of hazardous waste in tanks, surface impoundments, and containers subject to this Subpart CC.
b) The owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from each hazardous waste management unit in accordance with the standards specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988, as applicable to the hazardous waste management unit, except as provided for in subsection (c).
c) A tank, surface impoundment, or container is exempted from standards specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988, provided that all hazardous waste placed in the waste management unit is one of the following:
1) A tank, surface impoundment, or container for which all hazardous waste entering the unit has an average VO concentration at the point of waste origination of less than 500 parts per million by weight (ppmw). The average VO concentration must be determined by the procedures specified in Section 725.984(a). The owner or operator must review and update, as necessary, this determination at least once every 12 months following the date of the initial determination for the hazardous waste streams entering the unit;
2) A tank, surface impoundment, or container for which the organic content of all the hazardous waste entering the waste management unit has been reduced by an organic destruction or removal process that achieves any one of the following conditions:
A) The process removes or destroys the organics contained in the hazardous waste to such a level that the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment is less than the exit concentration limit (Ct) established for the process. The average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment and the exit concentration limit for the process must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b);
B) The process removes or destroys the organics contained in the hazardous waste to such a level that the organic reduction efficiency (R) for the process is equal to or greater than 95 percent, and the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment is less than 100 ppmw. The organic reduction efficiency for the process and the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b);
C) The process removes or destroys the organics contained in the hazardous waste to such a level that the actual organic mass removal rate (MR) for the process is equal to or greater than the required organic mass removal rate (RMR) established for the process. The required organic mass removal rate and the actual organic mass removal rate for the process must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b);
D) The process is a biological process that destroys or degrades the organics contained in the hazardous waste so that either of the following conditions is met:
i) The organic reduction efficiency (R) for the process is equal to or greater than 95 percent, and the organic biodegradation efficiency (Rbio) for the process is equal to or greater than 95 percent. The organic reduction efficiency and the organic biodegradation efficiency for the process must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b); and
ii) The total actual organic mass biodegradation rate (MRbio) for all hazardous waste treated by the process is equal to or greater than the required organic mass removal rate (RMR). The required organic mass removal rate and the actual organic mass biodegradation rate for the process must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b);
E) The process is one that removes or destroys the organics contained in the hazardous waste and meets all of the following conditions:
i) From the point of waste origination through the point where the hazardous waste enters the treatment process, the hazardous waste is continuously managed in waste management units that use air emission controls in accordance with the standards specified in Section 725.985 through Section 725.988, as applicable to the waste management unit;
ii) From the point of waste origination through the point where the hazardous waste enters the treatment process, any transfer of the hazardous waste is accomplished through continuous hard-piping or other closed system transfer that does not allow exposure of the waste to the atmosphere;
BOARD NOTE: The USEPA considers a drain system that meets the requirements of federal subpart RR of 40 CFR 63 (National Emission Standards for Individual Drain Systems) to be a closed system.
iii) The average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment is less than the lowest average VO concentration at the point of waste origination determined for each of the individual hazardous waste streams entering the process or 500 ppmw, whichever value is lower. The average VO concentration of each individual hazardous waste stream at the point of waste origination must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(a). The average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(b);
F) A process that removes or destroys the organics contained in the hazardous waste to a level such that the organic reduction efficiency (R) for the process is equal to or greater than 95 percent and the owner or operator certifies that the average VO concentration at the point of waste origination for each of the individual waste streams entering the process is less than 10,000 ppmw. The organic reduction efficiency for the process and the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste origination must be determined using the procedures specified in Sections 725.984(b) and 725.984(a), respectively;
G) A hazardous waste incinerator for which either of the following conditions is true:
i) The owner or operator has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 that implements the requirements of Subpart O of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724; or
ii) The owner or operator has designed and operates the incinerator in accordance with the interim status requirements of Subpart O;
H) A boiler or industrial furnace for which either of the following conditions is true:
i) The owner or operator has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 that implements the requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726; or
ii) The owner or operator has designed and operates the industrial furnace or incinerator in accordance with the interim status requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726; and
I) For the purpose of determining the performance of an organic destruction or removal process in accordance with the conditions in each of subsections (c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(F), the owner or operator must account for VO concentrations determined to be below the limit of detection of the analytical method by using the following VO concentration:
i) If Reference Method 25D (Determination of the Volatile Organic Concentration of Waste Samples) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), is used for the analysis, one-half the blank value determined in the method at Section 4.4 of Reference Method 25D or a value of 25 ppmw, whichever is less; and
ii) If any other analytical method is used, one-half the sum of the limits of detection established for each organic constituent in the waste that has a Henry’s law constant value at least 0.1 mole-fraction-in-the-gas-phase/mole-fraction-in-the-liquid-phase (0.1 Y/X) (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 106 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C;
3) A tank or surface impoundment used for biological treatment of hazardous waste in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(2)(D);
4) A tank, surface impoundment, or container for which all hazardous waste placed in the unit fulfills either of the following two conditions:
A) It meets the numerical concentration limits for organic hazardous constituents, applicable to the hazardous waste, as specified in Table T to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728; or
B) The organic hazardous constituents in the waste have been treated by the treatment technology established by USEPA for the waste, as set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.142(a), or treated by an equivalent method of treatment approved by the Agency pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.142(b); or
5) A tank used for bulk feed of hazardous waste to a waste incinerator, and all of the following conditions are met:
A) The tank is located inside an enclosure vented to a control device that is designed and operated in accordance with all applicable requirements specified under federal subpart FF of 40 CFR 61 (National Emission Standards for Benzene Waste Operations), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), for a facility at which the total annual benzene quantity from the facility waste is equal to or greater than 10 megagrams (11 tons) per year;
B) The enclosure and control device serving the tank were installed and began operation prior to November 25, 1996; and
C) The enclosure is designed and operated in accordance with the criteria for a permanent total enclosure as specified in “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” under appendix B to 40 CFR 52.741 (VOM Measurement Techniques for Capture Efficiency), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The enclosure may have permanent or temporary openings to allow worker access; passage of material into or out of the enclosure by conveyor, vehicles, or other mechanical or electrical equipment; or to direct air flow into the enclosure. The owner or operator must perform the verification procedure for the enclosure as specified in Section 5.0 of “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” annually.
d) The Agency may at any time perform or request that the owner or operator perform a waste determination for a hazardous waste managed in a tank, surface impoundment, or container that is exempted from using air emission controls under the provisions of this Section as follows:
1) The waste determination for average VO concentration of a hazardous waste at the point of waste origination must be performed using direct measurement in accordance with the applicable requirements of Section 725.984(a). The waste determination for a hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment must be performed in accordance with the applicable requirements of Section 725.984(b);
2) In performing a waste determination pursuant to subsection (d)(1), the sample preparation and analysis must be conducted as follows:
A) In accordance with the method used by the owner or operator to perform the waste analysis, except in the case specified in subsection (d)(2)(B); and
B) If the Agency determines that the method used by the owner or operator was not appropriate for the hazardous waste managed in the tank, surface impoundment, or container, then the Agency may choose an appropriate method;
3) Where the owner or operator is requested to perform the waste determination, the Agency may elect to have an authorized representative observe the collection of the hazardous waste samples used for the analysis;
4) Where the results of the waste determination performed or requested by the Agency do not agree with the results of a waste determination performed by the owner or operator using knowledge of the waste, then the results of the waste determination performed in accordance with the requirements of subsection (d)(1) must be used to establish compliance with the requirements of this Subpart CC; and
5) Where the owner or operator has used an averaging period greater than one hour for determining the average VO concentration of a hazardous waste at the point of waste origination, the Agency may elect to establish compliance with this Subpart CC by performing or requesting that the owner or operator perform a waste determination using direct measurement, based on waste samples collected within a 1-hour period, as follows:
A) The average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste origination must be determined by direct measurement in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.984(a);
B) Results of the waste determination performed or requested by the Agency showing that the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste origination is equal to or greater than 500 ppmw must constitute noncompliance with this Subpart CC, except in a case as provided for in subsection (d)(5)(C); and
C) Where the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste origination previously has been determined by the owner or operator using an averaging period greater than one hour to be less than 500 ppmw but because of normal operating process variations the VO concentration of the hazardous waste determined by direct measurement for any given 1-hour period may be equal to or greater than 500 ppmw, information that was used by the owner or operator to determine the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste (e.g., test results, measurements, calculations, and other documentation) and recorded in the facility records in accordance with the requirements of Sections 725.984(a) and 725.990 must be considered by the Agency together with the results of the waste determination performed or requested by the Agency in establishing compliance with this Subpart CC.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.984 Waste Determination Procedures
a) Determination of Volatile Organic (VO) Concentration at the Point of Waste Origination
1) An owner or operator must determine the average VO concentration at the point of waste origination for each hazardous waste placed in a waste management unit exempted under the provisions of Section 725.983(c)(1) from using air emission controls in accordance with standards specified in Section 725.985 through Section 725.988, as applicable to the waste management unit.
A) An owner or operator must make an initial determination of the average VO concentration of the waste stream before the first time any portion of the material in the hazardous waste stream is placed in a waste management unit exempted under the provisions of Section 725.983(c)(1) from using air emission controls. Thereafter, an owner or operator must make an initial determination of the average VO concentration of the waste stream for each averaging period that a hazardous waste is managed in the unit.
B) An owner or operator must perform a new waste determination whenever changes to the source generating the waste stream are reasonably likely to cause the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste to increase to a level that is equal to or greater than the VO concentration limits specified in Section 725.983(c)(1).
2) For a waste determination that is required by subsection (a)(1), the average VO concentration of a hazardous waste at the point of waste origination must be determined using either direct measurement, as specified in subsection (a)(3), or by knowledge of the waste, as specified in subsection (a)(4).
3) Direct Measurement
A) Identification. The owner or operator must identify and record the point of waste origination for the hazardous waste.
B) Sampling. Samples of the hazardous waste stream must be collected at the point of waste origination in such a manner that volatilization of organics contained in the waste and in the subsequent sample is minimized and an adequately representative sample is collected and maintained for analysis by the selected method.
i) The averaging period to be used for determining the average VO concentration for the hazardous waste stream on a mass-weighted average basis must be designated and recorded. The averaging period can represent any time interval that the owner or operator determines is appropriate for the hazardous waste stream but must not exceed one year.
ii) A sufficient number of samples, but no fewer than four samples, must be collected for a hazardous waste determination. All of the samples for a given waste determination must be collected within a one-hour period. The average of the four or more sample results constitutes a waste determination for the waste stream. One or more waste determinations may be required to represent the complete range of waste compositions and quantities that occur during the entire averaging period due to normal variations in the operating conditions for the source or process generating the hazardous waste stream. Examples of such normal variations are seasonal variations in waste quantity or fluctuations in ambient temperature.
iii) All samples must be collected and handled in accordance with written procedures prepared by the owner or operator and documented in a site sampling plan. This plan must describe the procedure by which representative samples of the hazardous waste stream are collected so that a minimum loss of organics occurs throughout the sample collection and handling process, and by which sample integrity is maintained. A copy of the written sampling plan must be maintained on-site in the facility operating records. An example of an acceptable sampling plan includes a plan incorporating sample collection and handling procedures in Reference Method 25D (Determination of the Volatile Organic Concentration of Waste Samples) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
iv) Sufficient information, as specified in the “site sampling plan” required under subsection (a)(3)(B)(iii), must be prepared and recorded to document the waste quantity represented by the samples and, as applicable, the operating conditions for the source or process generating the hazardous waste represented by the samples.
C) Analysis. Each collected sample must be prepared and analyzed in accordance with Reference Method 25D in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 for the total concentration of volatile organic constituents or using one or more methods when the individual organic compound concentrations are identified and summed and the summed waste concentration accounts for and reflects all organic compounds in the waste with Henry’s law constant values at least 0.1 mole-fraction-in-the-gas-phase/mole-fraction-in-the-liquid-phase (0.1 Y/X) (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 10-6 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C (77 °F). At the owner’s or operator’s discretion, the owner or operator may adjust test data measured by any appropriate method to discount any contribution to the total volatile organic concentration that is a result of including a compound with a Henry’s law constant value of less than 0.1 Y/X at 25 °C. If the owner or operator elects to adjust test data, the adjustment must be made to all individual chemical constituents with a Henry’s law constant value greater than or equal to 0.1 Y/X at 25 °C contained in the waste. To adjust these data, the measured concentration of each individual chemical constituent contained in the waste is multiplied by the constituent-specific adjustment factor (fm25D) approved in writing by the Agency. Other test methods may be used if they meet the requirements in subsection (a)(3)(C)(i) or (a)(3)(C)(ii) and provided the requirement is met to reflect all organic compounds in the waste with Henry’s law constant values greater than or equal to 0.1 Y/X (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 106 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C.
i) Any USEPA standard method that has been validated in accordance with appendix D to 40 CFR 63 (Alternative Validation Procedure for EPA Waste and Wastewater Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); or
ii) Any other analysis method that has been validated in accordance with the procedures specified in Section 5.1 or 5.3, and the corresponding calculations in Section 6.1 or 6.3, of Method 301 (Field Validation of Pollutant Measurement Methods from Various Waste Media) in appendix A to 40 CFR 63 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The data are acceptable if they meet the criteria specified in Section 6.1.5 or 6.3.3 of Method 301. If correction is required under Section 6.3.3 of Method 301, the data are acceptable if the correction factor is within the range 0.7 to 1.30. Other sections of Method 301 are not required.
D) Calculations
i) The average VO concentration (
) on a mass-weighted basis must be calculated by using the results for all waste determinations conducted in accordance with subsections (a)(3)(B) and (a)(3)(C) and the following equation:
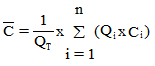
Where:
= Average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste origination on a mass-weighted basis, in ppmw
i = Individual waste determination “i” of the hazardous waste
n = Total number of waste determinations of the hazardous waste conducted for the averaging period (not to exceed one year)
Qi = Mass quantity of the hazardous waste stream represented by Ci, in kg/hr
QT = Total mass quantity of the hazardous waste during the averaging period, in kg/hrCi = Measured VO concentration of waste determination “i”, as determined in accordance with subsection (a)(3)(C) (i.e., the average of the four or more samples specified in subsection (a)(3)(B)(ii)), in ppmw
ii) For the purpose of determining Ci, for individual waste samples analyzed in accordance with subsection (a)(3)(C), the owner or operator must account for VO concentrations determined to be below the limit of detection of the analytical method by using the VO concentration determined according to subsection (a)(3)(G).
E) Provided that the test method is appropriate for the waste as required under subsection (a)(3)(C), the Agency must determine compliance based on the test method used by the owner or operator as recorded under Section 725.990(f)(1).
F) The quality assurance program elements required under subsections (a)(3)(C)(vi) and (a)(3)(C)(vii) are as follows:
i) Documentation of site-specific procedures to minimize the loss of compounds due to volatilization, biodegradation, reaction, or sorption during the sample collection, storage, preparation, introduction, and analysis steps.
ii) Measurement of the overall accuracy and precision of the specific procedures.
BOARD NOTE: Subsections (a)(3)(F)(i) and (a)(3)(F)(ii) are derived from 40 CFR 265.984(a)(3)(iii)(F)(1), (a)(3)(iii)(F)(2), (a)(3)(iii)(G)(1), and (a)(3)(iii)(G)(2), which the Board has codified here to comport with Illinois Administrative Code format requirements.
G) VO concentrations below the limit of detection must be considered to be as follows:
i) If Reference Method 25D is used for the analysis, the VO concentration must be considered to be one-half the blank value determined in the method at Section 4.4 of Reference Method 25D.
ii) If any other analytical method is used, the VO concentration must be considered to be one-half the sum of the limits of detection established for each organic constituent in the waste that has a Henry’s law constant value at least 0.1 mole-fraction-in-the-gas-phase/mole-fraction-in-the-liquid-phase (0.1 Y/X) (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 10-6 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C (77 °F).
BOARD NOTE: Subsections (a)(3)(G)(i) and (a)(3)(G)(ii) are derived from 40 CFR 265.984(a)(3)(iv)(A)(1) and (a)(3)(iv)(A)(2), which the Board has codified here to comport with Illinois Administrative Code format requirements.
4) Use of Owner or Operator Knowledge
A) Documentation must be prepared that presents the information used as the basis for the owner’s or operator’s knowledge of the hazardous waste stream’s average VO concentration. Examples of information that may be used as the basis for knowledge include the following: material balances for the source or process generating the hazardous waste stream; constituent-specific chemical test data for the hazardous waste stream from previous testing that are still applicable to the current waste stream; previous test data for other locations managing the same type of waste stream; or other knowledge based on information included in manifests, shipping papers, or waste certification notices.
B) If test data are used as the basis for knowledge, then the owner or operator must document the test method, sampling protocol, and the means by which sampling variability and analytical variability are accounted for in the determination of the average VO concentration. For example, an owner or operator may use organic concentration test data for the hazardous waste stream that are validated in accordance with Method 301 as the basis for knowledge of the waste.
C) An owner or operator using chemical constituent-specific concentration test data as the basis for knowledge of the hazardous waste may adjust the test data to the corresponding average VO concentration value that would have been obtained had the waste samples been analyzed using Reference Method 25D. To adjust these data, the measured concentration for each individual chemical constituent contained in the waste is multiplied by the appropriate constituent-specific adjustment factor (fm25D).
D) In the event that the Agency and the owner or operator disagree on a determination of the average VO concentration for a hazardous waste stream using knowledge, then the results from a determination of average VO concentration using direct measurement, as specified in subsection (a)(3), must be used to establish compliance with the applicable requirements of this Subpart CC. The Agency may perform or request that the owner or operator perform this determination using direct measurement. The owner or operator may choose one or more appropriate methods to analyze each collected sample in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)(3)(C).
b) Determination of VO Concentration at the Point of Waste Treatment
1) An owner or operator must perform the applicable waste determination for each treated hazardous waste placed in a waste management unit exempted under the provisions of Section 725.983(c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(F) from using air emission controls in accordance with the standards specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988, as applicable to the waste management unit.
A) An owner or operator must make an initial determination of the average VO concentration of the waste stream before the first time any portion of the material in the treated waste stream is placed in the waste management unit exempt under Section 725.983(c)(2), (c)(3), or (c)(4) from using air emission controls. Thereafter, an owner or operator must update the information used for the waste determination at least once every 12 months following the date of the initial waste determination.
B) An owner or operator must perform a new waste determination whenever changes to the process generating or treating the waste stream are reasonably likely to cause the average VO concentration of the hazardous waste to increase to such a level that the applicable treatment conditions specified in Section 725.983 (c)(2), (c)(3), or (c)(4) are not achieved.
2) The owner or operator must designate and record the specific provision in Section 725.983(c)(2) under which the waste determination is being performed. The waste determination for the treated hazardous waste must be performed using the applicable procedures specified in subsections (b)(3) through (b)(9).
3) Procedure for Determination of VO Concentration
A) Identification. The owner or operator must identify and record the point of waste treatment for the hazardous waste.
B) Sampling. Samples of the hazardous waste stream must be collected at the point of waste treatment in such a manner that volatilization of organics contained in the waste and in the subsequent sample is minimized and an adequately representative sample is collected and maintained for analysis by the selected method.
i) The averaging period to be used for determining the average VO concentration for the hazardous waste stream on a mass-weighted average basis must be designated and recorded. The averaging period can represent any time interval that the owner or operator determines is appropriate for the hazardous waste stream but must not exceed one year.
ii) A sufficient number of samples, but no fewer than four samples, must be collected and analyzed for a hazardous waste determination. All of the samples for a given waste determination must be collected within a one-hour period. The average of the four or more sample results constitutes a waste determination for the hazardous waste stream. One or more waste determinations may be required to represent the complete range of waste compositions and quantities that occur during the entire averaging period due to normal variations in the operating conditions for the process generating or treating the hazardous waste stream. Examples of such normal variations are seasonal variations in waste quantity or fluctuations in ambient temperature.
iii) All samples must be collected and handled in accordance with written procedures prepared by the owner or operator and documented in a site sampling plan. This plan must describe the procedure by which representative samples of the hazardous waste stream are collected so that a minimum loss of organics occurs throughout the sample collection and handling process, and by which sample integrity is maintained. A copy of the written sampling plan must be maintained on-site in the facility operating records. An example of an acceptable sample collection and handling procedures for a total organic constituent concentration may be found in Reference Method 25D.
iv) Sufficient information, as specified in the “site sampling plan” required under subsection (a)(3)(B)(iii), must be prepared and recorded to document the waste quantity represented by the samples and, as applicable, the operating conditions for the process treating the hazardous waste represented by the samples.
C) Analysis. Each collected sample must be prepared and analyzed in accordance with Reference Method 25D for the total concentration of volatile organic constituents or using one or more methods when the individual organic compound concentrations are identified and summed, and the summed waste concentration accounts for and reflects all organic compounds in the waste with Henry’s law constant values at least 0.1 mole-fraction-in-the-gas-phase/mole-fraction-in-the-liquid-phase (0.1 Y/X) (which can also be expressed as 1.8 × 106 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C (77 °F). When the owner or operator is making a waste determination for a treated hazardous waste that is to be compared to an average VO concentration at the point of waste origination or the point of waste entry to the treatment system, to determine if the conditions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.982(c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(F) or Section 725.983(c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(F) are met, then the waste samples must be prepared and analyzed using the same method or methods as were used in making the initial waste determinations at the point of waste origination or at the point of entry to the treatment system. At the owner’s or operator’s discretion, the owner or operator may adjust test data obtained by any appropriate method to discount any contribution to the total volatile organic concentration that is a result of including a compound with a Henry’s law constant value less than 0.1 Y/X at 25 °C. If the owner or operator elects to adjust test data, the adjustment must be made to all individual chemical constituents with a Henry’s law constant value greater than or equal to 0.1 Y/X at 25 °C contained in the waste. To adjust these data, the measured concentration of each individual chemical constituent contained in the waste is multiplied by the constituent-specific adjustment factor (fm25D) approved in writing by the Agency. Other test methods may be used if they meet the requirements in subsection (a)(3)(C)(i) or (a)(3)(C)(ii) and provided the requirement is met to reflect all organic compounds in the waste with Henry’s law constant values greater than or equal to 0.1 Y/X (which can also be expressed as 1.8 ´ 106 atmospheres/gram-mole/m3) at 25 °C.
i) Any USEPA standard method that has been validated in accordance with appendix D to 40 CFR 63, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); or
ii) Any other analysis method that has been validated in accordance with the procedures specified in Section 5.1 or 5.3, and the corresponding calculations in Section 6.1 or 6.3, of Method 301 in appendix A to 40 CFR 63, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The data are acceptable if they meet the criteria specified in Section 6.1.5 or 6.3.3 of Method 301. If correction is required under Section 6.3.3 of Method 301, the data are acceptable if the correction factor is within the range 0.7 to 1.30. Other sections of Method 301 are not required.
D) Calculations. The average VO concentration (
) on a mass-weighted basis must be calculated by using the results for all samples analyzed in accordance with subsection (b)(3)(C) and the following equation:
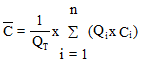
Where:
= Average VO concentration of the hazardous waste at the point of waste treatment on a mass-weighted basis, in ppmw
i = Individual determination “i” of the hazardous waste
n = Total number of waste determinations of the hazardous waste collected for the averaging period (not to exceed one year)
Qi = Mass quantity of the hazardous waste stream represented by Ci, in kg/hr
QT = Total mass quantity of hazardous waste during the averaging period, in kg/hrCi = Measured VO concentration of waste determinations “i”, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(3)(C) (i.e., the average of the four or more samples specified in subsection (b)(3)(B)(ii)), in ppmw
E) Provided that the test method is appropriate for the waste as required under subsection (b)(3)(C), compliance must be determined based on the test method used by the owner or operator as recorded under Section 725.990(f)(1).
4) Procedure for Determination of Exit Concentration Limit (Ct)
A) The point of waste origination for each hazardous waste treated by the process at the same time must be identified.
B) If a single hazardous waste stream is identified in subsection (b)(4)(A), then the exit concentration limit (Ct) must be 500 ppmw.
C) If more than one hazardous waste stream is identified in subsection (b)(4)(A), then the average VO concentration of each hazardous waste stream at the point of waste origination must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a). The exit concentration limit (Ct) must be calculated by using the results determined for each individual hazardous waste stream and the following equation:
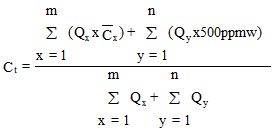
Where:
Ct = Exit concentration limit for treated hazardous waste, in ppmw
x = Individual hazardous waste stream “x” that has an average VO concentration less than 500 ppmw at the point of waste origination, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)
y = Individual hazardous waste stream “y” that has an average VO concentration equal to or greater than 500 ppmw at the point of waste origination, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)
m = Total number of “x” hazardous waste streams treated by process
n = Total number of “y” hazardous waste streams treated by process
Qx = Annual mass quantity of hazardous waste stream “x”, in kg/yr
Qy = Annual mass quantity of hazardous waste stream “y”, in kg/yr
= Average VO concentration of hazardous waste stream “x” at the point of waste origination, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a), in ppmw
5) Procedure for Determination of Organic Reduction Efficiency (R)
A) The organic reduction efficiency (R) for a treatment process must be determined based on results for a minimum of three consecutive runs.
B) All hazardous waste streams entering the process and all hazardous waste streams exiting the treatment process must be identified. The owner or operator must prepare a sampling plan for measuring these streams that accurately reflects the retention time of the hazardous waste in the process.
C) For each run, information must be determined for each hazardous waste stream identified in subsection (b)(5)(B), using the following procedures:
i) The mass quantity of each hazardous waste stream entering the process (Qb) and the mass quantity of each hazardous waste stream exiting the process (Qa) must be determined; and
ii) The average VO concentration at the point of waste origination of each hazardous waste stream entering the process (Cb) during the run must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)(3). The average VO concentration at the point of waste treatment of each hazardous waste stream exiting the process (Ca) during the run must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(3).
D) The waste volatile organic mass flow entering the process (Eb) and the waste volatile organic mass flow exiting the process (Ea) must be calculated by using the results determined in accordance with subsection (b)(5)(C) and the following equations:
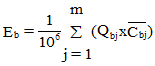
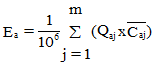
Where:
Ea = Waste volatile organic mass flow exiting the process, in kg/hr
Eb = Waste volatile organic mass flow entering the process, in kg/hr
m = Total number of runs (at least 3);
j = Individual run “j”
Qbj = Mass quantity of hazardous waste entering the process during run “j”, in kg/hr
Qaj = Average mass quantity of waste exiting the process during run “j”, in kg/hr= Average VO concentration of hazardous waste exiting the process during run “j”, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(3), in ppmw
= Average VO concentration of hazardous waste entering the process during run “j”, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)(3), in ppmw
E) The organic reduction efficiency of the process must be calculated by using the results determined in accordance with subsection (b)(5)(D) and the following equation:
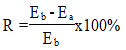
Where:
R = Organic reduction efficiency, in percent
Eb = Waste volatile organic mass flow entering the process, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D), in kg/hrEa = Waste volatile organic mass flow exiting the process, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D), in kg/hr
6) Procedure for Determination of Organic Biodegradation Efficiency (Rbio)
A) The fraction of organics biodegraded (Fbio) must be determined using the procedure specified in appendix C to 40 CFR 63 (Determination of the Fraction Biodegraded (Fbio) in a Biological Treatment Unit), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
B) The organic biodegradation efficiency (Rbio) must be calculated by using the following equation:
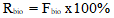
Where:
Rbio = Organic biodegradation efficiency, in percent
Fbio = Fraction of organic biodegraded, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(6)(A)
7) Procedure for Determination of Required Organic Mass Removal Rate (RMR)
A) All of the hazardous waste streams entering the treatment process must be identified.
B) The average VO concentration of the hazardous waste stream at the point of waste origination must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a).
C) For each individual hazardous waste stream that has an average volatile organic concentration equal to or greater than 500 ppmw at the point of waste origination, the average volumetric flow rate of hazardous waste and the density of the hazardous waste stream at the point of waste origination must be determined.
D) The required organic mass removal rate (RMR) for the hazardous waste must be calculated by using the average VO concentration, average volumetric flow rate, and density determined for each individual hazardous waste stream, and the following equation:
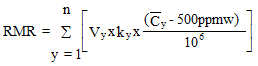
Where:
RMR = Required organic mass removal rate, in kg/hr;
y = Individual hazardous waste stream “y” that has an average volatile organic (VO) concentration equal to or greater than 500 ppmw at the point of waste origination, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a)
n = Total number of “y” hazardous waste streams treated by process
Vy = Average volumetric flow rate of hazardous waste stream “y” at the point of waste origination, in m3/hr
ky = Density of hazardous waste stream “y”, in kg/m3
= Average VO concentration of hazardous waste stream “y” at the point of waste origination, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (a), in ppmw
8) Procedure for Determination of Actual Organic Mass Removal Rate (MR)
A) The actual organic mass removal rate (MR) must be determined based on results for a minimum of three consecutive runs. The sampling time for each run must be one hour.
B) The waste volatile organic mass flow entering the process (Eb) and the waste volatile organic mass flow exiting the process (Ea) must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D).
C) The actual organic mass removal rate (MR) must be calculated by using the mass flow rate determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(8)(B) and the following equation:
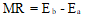
Where:
MR = Actual organic mass removal rate, in kg/hr
Eb = Waste volatile organic mass flow entering the process, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D), in kg/hrEa = Waste volatile organic mass flow exiting the process, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D), in kg/hr
9) Procedure for Determination of Actual Organic Mass Biodegradation Rate (MRbio)
A) The actual organic mass biodegradation rate (MRbio) must be determined based on results for a minimum of three consecutive runs. The sampling time for each run must be one hour.
B) The waste organic mass flow entering the process (Eb) must be determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D).
C) The fraction of organic biodegraded (Fbio) must be determined using the procedure specified in appendix C to 40 CFR 63 (Determination of the Fraction Biodegraded (Fbio) in a Biological Treatment Unit), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
D) The actual organic mass biodegradation rate (MRbio) must be calculated by using the mass flow rates and fraction of organic biodegraded, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsections (b)(9)(B) and (b)(9)(C), respectively, and the following equation:
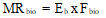
Where:
MRbio = Actual organic mass biodegradation rate, in kg/hr
Eb = Waste organic mass flow entering the process, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(5)(D), in kg/hrFbio = Fraction of organic biodegraded, as determined in accordance with the requirements of subsection (b)(9)(C)
c) Procedure for Determination of VO in a Tank
1) An owner or operator must determine the maximum organic vapor pressure for each hazardous waste placed in a tank using Tank Level 1 controls in accordance with standards specified in Section 725.985(c).
2) An owner or operator must use either direct measurement, as specified in subsection (c)(3), or knowledge of the waste, as specified by subsection (c)(4), to determine the maximum organic vapor pressure that is representative of the hazardous waste composition stored or treated in the tank.
3) Direct Measurement to Determine VO
A) Sampling. A sufficient number of samples must be collected to be representative of the waste contained in the tank. All samples must be conducted and handled in accordance with written procedures prepared by the owner or operator and documented in a site sampling plan. This plan must describe the procedure by which representative samples of the hazardous waste are collected so that a minimum loss of organics occurs throughout the sample collection and handling process and by which sample integrity is maintained. A copy of the written sampling plan must be maintained on-site in the facility operating records. An example of acceptable sample collection and handling procedures may be found in Reference Method 25D.
B) Analysis. Any appropriate one of the following methods may be used to analyze the samples and compute the maximum organic vapor pressure of the hazardous waste:
i) Reference Method 25E (Determination of Vapor Phase Organic Concentration in Waste Samples) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b);
ii) Methods described in API publication 2517 (Evaporative Loss from External Floating-Roof Tanks), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a);
iii) Methods obtained from standard reference texts;
iv) ASTM Method D 2879-92 (Standard Test Method for Vapor Pressure-Temperature Relationship and Initial Decomposition Temperature of Liquids by Isoteniscope), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a); or
v) Any other method approved by the Agency.
4) Use of Knowledge to Determine the Maximum Organic Vapor Pressure of the Hazardous Waste. Documentation must be prepared and recorded that presents the information used as the basis for the owner’s or operator’s knowledge that the maximum organic vapor pressure of the hazardous waste is less than the maximum vapor pressure limit listed in Section 725.985(b)(1)(A) for the applicable tank design capacity category. An example of information that may be used is documentation that the hazardous waste is generated by a process for which at other locations it previously has been determined by direct measurement that the waste maximum organic vapor pressure is less than the maximum vapor pressure limit for the appropriate tank design capacity category.
d) The procedure for determining no detectable organic emissions for the purpose of complying with this Subpart CC is as follows:
1) The test must be conducted in accordance with the procedures specified in Reference Method 21 (Determination of Volatile Organic Compound Leaks) of appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). Each potential leak interface (i.e., a location where organic vapor leakage could occur) on the cover and associated closure devices must be checked. Potential leak interfaces that are associated with covers and closure devices include, but are not limited to, any of the following: the interface of the cover and its foundation mounting, the periphery of any opening on the cover and its associated closure device, and the sealing seat interface on a spring-loaded pressure relief valve.
2) The test must be performed when the unit contains a hazardous waste having an organic concentration representative of the range of concentrations for the hazardous waste expected to be managed in the unit. During the test, the cover and closure devices must be secured in the closed position.
3) The detection instrument must meet the performance criteria of Reference Method 21, except the instrument response factor criteria in Section 3.1.2(a) of Reference Method 21 must be for the average composition of the organic constituents in the hazardous waste placed in the waste management unit, not for each individual organic constituent.
4) The detection instrument must be calibrated before use on each day of its use by the procedures specified in Reference Method 21.
5) Calibration gases must be as follows:
A) Zero air (less than 10 ppmv hydrocarbon in air), and
B) A mixture of methane or n-hexane in air at a concentration of approximately, but less than, 10,000 ppmv methane or n-hexane.
6) The background level must be determined according to the procedures in Reference Method 21.
7) Each potential leak interface must be checked by traversing the instrument probe around the potential leak interface as close to the interface as possible, as described in Reference Method 21. If the configuration of the cover or closure device prevents a complete traverse of the interface, all accessible portions of the interface must be sampled. If the configuration of the closure device prevents any sampling at the interface and the device is equipped with an enclosed extension or horn (e.g., some pressure relief devices), the instrument probe inlet must be placed at approximately the center of the exhaust area to the atmosphere.
8) The arithmetic difference between the maximum organic concentration indicated by the instrument and the background level must be compared with the value of 500 ppmv except when monitoring a seal around a rotating shaft that passes through a cover opening, in which case the comparison must be as specified in subsection (d)(9). If the difference is less than 500 ppmv, then the potential leak interface is determined to operate with no detectable organic emissions.
9) For the seals around a rotating shaft that passes through a cover opening, the arithmetic difference between the maximum organic concentration indicated by the instrument and the background level must be compared with the value of 10,000 ppmw. If the difference is less than 10,000 ppmw, then the potential leak interface is determined to operate with no detectable organic emissions.
(Source: Amended at 44 Ill. Reg. 15374, effective September 3, 2020)
Section 725.985 Standards: Tanks
a) The provisions of this Section apply to the control of air pollutant emissions from tanks for which Section 725.983(b) references the use of this Section for such air emission control.
b) The owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from each tank subject to this Section in accordance with the following requirements, as applicable:
1) For a tank that manages hazardous waste that meets all of the conditions specified in subsections (b)(1)(A) through (b)(1)(C), the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the tank in accordance with the Tank Level 1 controls specified in subsection (c) or the Tank Level 2 controls specified in subsection (d).
A) The hazardous waste in the tank has a maximum organic vapor pressure that is less than the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank’s design capacity category, as follows:
i) For a tank design capacity equal to or greater than 151 m3 (5333 ft3 or 39,887 gal), the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank is 5.2 kPa (0.75 psia or 39 mm Hg);
ii) For a tank design capacity equal to or greater than 75 m3 (2649 ft3 or 19,810 gal) but less than 151 m3 (5333 ft3 or 39,887 gal), the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank is 27.6 kPa (4.0 psia or 207 mm Hg); or
iii) For a tank design capacity less than 75 m3 (2649 ft3 or 19,810 gal), the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank is 76.6 kPa (11.1 psia or 574 mm Hg).
B) The hazardous waste in the tank is not heated by the owner or operator to a temperature that is greater than the temperature at which the maximum organic vapor pressure of the hazardous waste is determined for the purpose of complying with subsection (b)(1)(A).
C) The hazardous waste in the tank is not treated by the owner or operator using a waste stabilization process, as defined in Section 725.981.
2) For a tank that manages hazardous waste that does not meet all of the conditions specified in subsections (b)(1)(A) through (b)(1)(C), the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the tank by using Tank Level 2 controls in accordance with the requirements of subsection (d). Examples of tanks required to use Tank Level 2 controls include the following: a tank used for a waste stabilization process and a tank for which the hazardous waste in the tank has a maximum organic vapor pressure that is equal to or greater than the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank’s design capacity category, as specified in subsection (b)(1)(A).
c) An owner or operator controlling air pollutant emissions from a tank using Tank Level 1 controls must meet the requirements specified in subsections (c)(1) through (c)(4):
1) The owner or operator must determine the maximum organic vapor pressure for a hazardous waste to be managed in the tank using Tank Level 1 controls before the first time the hazardous waste is placed in the tank. The maximum organic vapor pressure must be determined using the procedures specified in Section 725.984(c). Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform a new determination whenever changes to the hazardous waste managed in the tank could potentially cause the maximum organic vapor pressure to increase to a level that is equal to or greater than the maximum organic vapor pressure limit for the tank design capacity category specified in subsection (b)(1)(A), as applicable to the tank.
2) The tank must be equipped with a fixed roof designed to meet the following specifications:
A) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be designed to form a continuous barrier over the entire surface area of the hazardous waste in the tank. The fixed roof may be a separate cover installed on the tank (e.g., a removable cover mounted on an open-top tank) or may be an integral part of the tank structural design (e.g., a horizontal cylindrical tank equipped with a hatch).
B) The fixed roof must be installed in such a manner that there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces between roof section joints or between the interface of the roof edge and the tank wall.
C) Either of the following must be true of each opening in the fixed roof and of any manifold system associated with the fixed roof must be either:
i) The opening or manifold system is equipped with a closure device designed to operate so that when the closure device is secured in the closed position there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces in the closure device or between the perimeter of the opening and the closure device; or
ii) The opening or manifold system is connected by a closed-vent system that is vented to a control device. The control device must remove or destroy organics in the vent stream, and it must be operating whenever hazardous waste is managed in the tank, except as provided for in subsection (c)(2)(E).
D) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be made of suitable materials that will minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere, to the extent practical, and which will maintain the integrity of the fixed roof and closure devices throughout their intended service life. Factors to be considered when selecting the materials for and designing the fixed roof and closure devices must include the following: organic vapor permeability; the effects of any contact with the hazardous waste or its vapors managed in the tank; the effects of outdoor exposure to wind, moisture, and sunlight; and the operating practices used for the tank on which the fixed roof is installed.
E) The control device operated pursuant to subsection (c)(2)(C) needs not remove or destroy organics in the vent stream under the following conditions:
i) During periods when it is necessary to provide access to the tank for performing the activities of subsection (c)(2)(E)(ii), venting of the vapor headspace underneath the fixed roof to the control device is not required, opening of closure devices is allowed, and removal of the fixed roof is allowed. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable, and resume operation of the control device; and
ii) During periods of routine inspection, maintenance, or other activities needed for normal operations, and for the removal of accumulated sludge or other residues from the bottom of the tank.
BOARD NOTE: Subsections (c)(2)(E)(i) and (c)(2)(E)(ii) are derived from 40 CFR 265.985(c)(2)(iii)(B)(1) and (c)(2)(iii)(B)(2), which the Board has codified here to comport with Illinois Administrative Code format requirements.
3) Whenever a hazardous waste is in the tank, the fixed roof must be installed with each closure device secured in the closed position, except as follows:
A) Opening of closure devices or removal of the fixed roof is allowed at the following times:
i) To provide access to the tank for performing routine inspection, maintenance, or other activities needed for normal operations. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to sample the liquid in the tank, or when a worker needs to open a hatch to maintain or repair equipment. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable, to the tank.
ii) To remove accumulated sludge or other residues from the bottom of tank.
B) Opening of a spring-loaded pressure-vacuum relief valve, conservation vent, or similar type of pressure relief device that vents to the atmosphere is allowed during normal operations for the purpose of maintaining the tank internal pressure in accordance with the tank design specifications. The device must be designed to operate with no detectable organic emissions when the device is secured in the closed position. The settings at which the device opens must be established so that the device remains in the closed position whenever the tank internal pressure is within the internal pressure operating range determined by the owner or operator based on the tank manufacturer recommendations; applicable regulations; fire protection and prevention codes; standard engineering codes and practices; or other requirements for the safe handling of flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive, or hazardous materials. Examples of normal operating conditions that may require these devices to open are during those times when the tank internal pressure exceeds the internal pressure operating range for the tank as a result of loading operations or diurnal ambient temperature fluctuations.
C) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
4) The owner or operator must inspect the air emission control equipment in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to, visible cracks, holes, or gaps in the roof sections or between the roof and the tank wall; broken, cracked, or otherwise damaged seals or gaskets on closure devices; and broken or missing hatches, access covers, caps, or other closure devices.
B) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the fixed roof and its closure devices on or before the date that the tank becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year, except under the special conditions provided for in subsection (l).
C) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k).
D) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(b).
d) An owner or operator controlling air pollutant emissions from a tank using Tank Level 2 controls must use one of the following tanks:
1) A fixed-roof tank equipped with an internal floating roof in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (e);
2) A tank equipped with an external floating roof in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (f);
3) A tank vented through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (g);
4) A pressure tank designed and operated in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (h); or
5) A tank located inside an enclosure that is vented through a closed-vent system to an enclosed combustion control device in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (i).
e) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions from a tank using a fixed roof with an internal floating roof must meet the requirements specified in subsections (e)(1) through (e)(3).
1) The tank must be equipped with a fixed roof and an internal floating roof in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The internal floating roof must be designed to float on the liquid surface except when the floating roof must be supported by the leg supports.
B) The internal floating roof must be equipped with a continuous seal between the wall of the tank and the floating roof edge that meets either of the following requirements:
i) A single continuous seal that is either a liquid-mounted seal or a metallic shoe seal, as defined in Section 725.981; or
ii) Two continuous seals mounted one above the other. The lower seal may be a vapor-mounted seal.
C) The internal floating roof must meet the following specifications:
i) Each opening in a noncontact internal floating roof except for automatic bleeder vents (vacuum breaker vents) and the rim space vents is to provide a projection below the liquid surface;
ii) Each opening in the internal floating roof must be equipped with a gasketed cover or a gasketed lid except for leg sleeves, automatic bleeder vents, rim space vents, column wells, ladder wells, sample wells, and stub drains;
iii) Each penetration of the internal floating roof for the purpose of sampling must have a slit fabric cover that covers at least 90 percent of the opening;
iv) Each automatic bleeder vent and rim space vent must be gasketed;
v) Each penetration of the internal floating roof that allows for passage of a ladder must have a gasketed sliding cover; and
vi) Each penetration of the internal floating roof that allows for passage of a column supporting the fixed roof must have a flexible fabric sleeve seal or a gasketed sliding cover.
2) The owner or operator must operate the tank in accordance with the following requirements:
A) When the floating roof is resting on the leg supports, the process of filling, emptying, or refilling must be continuous and must be completed as soon as practical;
B) Automatic bleeder vents are to be set closed at all times when the roof is floating, except when the roof is being floated off or is being landed on the leg supports; and
C) Prior to filling the tank, each cover, access hatch, gauge float well or lid on any opening in the internal floating roof must be bolted or fastened closed (i.e., no visible gaps). Rim space vents are to be set to open only when the internal floating roof is not floating or when the pressure beneath the rim exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended setting.
3) The owner or operator must inspect the internal floating roof in accordance with the procedures specified as follows:
A) The floating roof and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to, the following: when the internal floating roof is not floating on the surface of the liquid inside the tank; when liquid has accumulated on top of the internal floating roof; when any portion of the roof seals have detached from the roof rim; when holes, tears, or other openings are visible in the seal fabric; when the gaskets no longer close off the hazardous waste surface from the atmosphere; or when the slotted membrane has more than 10 percent open area;
B) The owner or operator must inspect the internal floating roof components as follows, except as provided in subsection (e)(3)(C):
i) Visually inspect the internal floating roof components through openings on the fixed roof (e.g., manholes and roof hatches) at least once every 12 months after initial fill, and
ii) Visually inspect the internal floating roof, primary seal, secondary seal (if one is in service), gaskets, slotted membranes, and sleeve seals (if any) each time the tank is emptied and degassed and at least once every 10 years;
C) As an alternative to performing the inspections specified in subsection (e)(3)(B) for an internal floating roof equipped with two continuous seals mounted one above the other, the owner or operator may visually inspect the internal floating roof, primary and secondary seals, gaskets, slotted membranes, and sleeve seals (if any) each time the tank is emptied and degassed and at least every five years;
D) Prior to each inspection required by subsection (e)(3)(B) or (e)(3)(C), the owner or operator must notify the Agency in advance of each inspection to provide the Agency with the opportunity to have an observer present during the inspection. The owner or operator must notify the Agency of the date and location of the inspection as follows:
i) Prior to each visual inspection of an internal floating roof in a tank that has been emptied and degassed, written notification must be prepared and sent by the owner or operator so that it is received by the Agency at least 30 calendar days before refilling the tank, except when an inspection is not planned, as provided for in subsection (e)(3)(D)(ii); and
ii) When a visual inspection is not planned and the owner or operator could not have known about the inspection 30 calendar days before refilling the tank, the owner or operator must notify the Agency as soon as possible, but no later than seven calendar days before refilling of the tank. This notification may be made by telephone and immediately followed by a written explanation for why the inspection is unplanned. Alternatively, written notification, including the explanation for the unplanned inspection, may be sent so that it is received by the Regional Administrator at least seven calendar days before refilling the tank;
E) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k); and
F) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(b).
4) Safety devices, as defined in Section 725.981, may be installed and operated as necessary on any tank complying with the requirements of this subsection (e).
f) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions from a tank using an external floating roof must meet the requirements specified in subsections (f)(1) through (f)(3).
1) The owner or operator must design the external floating roof in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The external floating roof must be designed to float on the liquid surface except when the floating roof must be supported by the leg supports;
B) The floating roof must be equipped with two continuous seals, one above the other, between the wall of the tank and the roof edge. The lower seal is referred to as the primary seal, and the upper seal is referred to as the secondary seal.
i) The primary seal must be a liquid-mounted seal or a metallic shoe seal, as defined in Section 725.981. The total area of the gaps between the tank wall and the primary seal must not exceed 212 square centimeters (cm2) per meter (10.0 in2 per foot) of tank diameter, and the width of any portion of these gaps must not exceed 3.8 centimeters (cm) (1.5 inches). If a metallic shoe seal is used for the primary seal, the metallic shoe seal must be designed so that one end extends into the liquid in the tank and the other end extends a vertical distance of at least 61 centimeters (24 inches) above the liquid surface.
ii) The secondary seal must be mounted above the primary seal and cover the annular space between the floating roof and the wall of the tank. The total area of the gaps between the tank wall and the secondary seal must not exceed 21.2 cm2 per meter (1.0 in2 per foot) of tank diameter, and the width of any portion of these gaps must not exceed 1.3 cm (0.5 inch); and
C) The external floating roof must meet the following specifications:
i) Except for automatic bleeder vents (vacuum breaker vents) and rim space vents, each opening in a noncontact external floating roof must provide a projection below the liquid surface;
ii) Except for automatic bleeder vents, rim space vents, roof drains, and leg sleeves, each opening in the roof must be equipped with a gasketed cover, seal, or lid;
iii) Each access hatch and each gauge float well must be equipped with a cover designed to be bolted or fastened when the cover is secured in the closed position;
iv) Each automatic bleeder vent and each rim space vent must be equipped with a gasket;
v) Each roof drain that empties into the liquid managed in the tank must be equipped with a slotted membrane fabric cover that covers at least 90 percent of the area of the opening;
vi) Each unslotted and slotted guide pole well must be equipped with a gasketed sliding cover or a flexible fabric sleeve seal;
vii) Each unslotted guide pole must be equipped with a gasketed cap on the end of the pole;
viii) Each slotted guide pole must be equipped with a gasketed float or other device that closes off the liquid surface from the atmosphere; and
ix) Each gauge hatch and each sample well must be equipped with a gasketed cover.
2) The owner or operator must operate the tank in accordance with the following requirements:
A) When the floating roof is resting on the leg supports, the process of filling, emptying, or refilling must be continuous and must be completed as soon as practical;
B) Except for automatic bleeder vents, rim space vents, roof drains, and leg sleeves, each opening in the roof must be secured and maintained in a closed position at all times except when the closure device must be open for access;
C) Covers on each access hatch and each gauge float well must be bolted or fastened when secured in the closed position;
D) Automatic bleeder vents must be set closed at all times when the roof is floating, except when the roof is being floated off or is being landed on the leg supports;
E) Rim space vents must be set to open only at those times that the roof is being floated off the roof leg supports or when the pressure beneath the rim seal exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended setting;
F) The cap on the end of each unslotted guide pole must be secured in the closed position at all times except when measuring the level or collecting samples of the liquid in the tank;
G) The cover on each gauge hatch or sample well must be secured in the closed position at all times except when the hatch or well must be opened for access; and
H) Both the primary seal and the secondary seal must completely cover the annular space between the external floating roof and the wall of the tank in a continuous fashion except during inspections.
3) The owner or operator must inspect the external floating roof in accordance with the procedures specified as follows:
A) The owner or operator must measure the external floating roof seal gaps in accordance with the following requirements:
i) The owner or operator must perform measurements of gaps between the tank wall and the primary seal within 60 calendar days after initial operation of the tank following installation of the floating roof and, thereafter, at least once every five years;
ii) The owner or operator must perform measurements of gaps between the tank wall and the secondary seal within 60 calendar days after initial operation of the tank following installation of the floating roof and, thereafter, at least once every year;
iii) If a tank ceases to hold hazardous waste for a period of one year or more, subsequent introduction of hazardous waste into the tank must be considered an initial operation for the purposes of subsections (f)(3)(A)(i) and (f)(3)(A)(ii);
iv) The owner or operator must determine the total surface area of gaps in the primary seal and in the secondary seal individually using the procedure set forth in subsection (f)(3)(D);
v) In the event that the seal gap measurements do not conform to the specifications in subsection (f)(1)(B), the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k); and
vi) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(b);
B) The owner or operator must visually inspect the external floating roof in accordance with the following requirements:
i) The floating roof and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to any of the following: holes, tears, or other openings in the rim seal or seal fabric of the floating roof; a rim seal detached from the floating roof; all or a portion of the floating roof deck being submerged below the surface of the liquid in the tank; broken, cracked, or otherwise damaged seals or gaskets on closure devices; and broken or missing hatches, access covers, caps, or other closure devices;
ii) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the external floating roof and its closure devices on or before the date that the tank becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year except for the special conditions provided for in subsection (l);
iii) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k); and
iv) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(b);
C) Prior to each inspection required by subsection (f)(3)(A) or (f)(3)(B), the owner or operator must notify the Agency in advance of each inspection to provide the Agency with the opportunity to have an observer present during the inspection. The owner or operator must notify the Agency of the date and location of the inspection as follows:
i) Prior to each inspection to measure external floating roof seal gaps as required under subsection (f)(3)(A), written notification must be prepared and sent by the owner or operator so that it is received by the Agency at least 30 calendar days before the date the measurements are scheduled to be performed;
ii) Prior to each visual inspection of an external floating roof in a tank that has been emptied and degassed, written notification must be prepared and sent by the owner or operator so that it is received by the Agency at least 30 calendar days before refilling the tank except when an inspection is not planned, as provided for in subsection (f)(3)(C)(iii); and
iii) When a visual inspection is not planned and the owner or operator could not have known about the inspection 30 calendar days before refilling the tank, the owner or operator must notify the Agency as soon as possible, but no later than seven calendar days before refilling of the tank. This notification may be made by telephone and immediately followed by a written explanation for why the inspection is unplanned. Alternatively, written notification, including the explanation for the unplanned inspection, may be sent so that it is received by the Regional Administrator at least seven calendar days before refilling the tank;
D) Procedure for determining gaps in the primary seal and in the secondary seal for the purposes of subsection (f)(3)(A)(iv):
i) The seal gap measurements must be performed at one or more floating roof levels when the roof is floating off the roof supports;
ii) Seal gaps, if any, must be measured around the entire perimeter of the floating roof in each place where a 0.32-cm (¼-inch) diameter uniform probe passes freely (without forcing or binding against the seal) between the seal and the wall of the tank and measure the circumferential distance of each such location;
iii) For a seal gap measured under this subsection (f)(3), the gap surface area must be determined by using probes of various widths to measure accurately the actual distance from the tank wall to the seal and multiplying each such width by its respective circumferential distance; and
iv) The total gap area must be calculated by adding the gap surface areas determined for each identified gap location for the primary seal and the secondary seal individually, and then dividing the sum for each seal type by the nominal diameter of the tank. These total gap areas for the primary seal and secondary seal are then compared to the respective standards for the seal type, as specified in subsection (f)(1)(B); and
BOARD NOTE: Subsections (f)(3)(D)(i) through (f)(3)(D)(iv) are derived from 40 CFR 265.1085(f)(3)(i)(D)(1) through (f)(3)(i)(D)(4), which the Board has codified here to comport with Illinois Administrative Code format requirements.
4) Safety devices, as defined in Section 725.981, may be installed and operated as necessary on any tank complying with the requirements of this subsection (f).
g) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions from a tank by venting the tank to a control device must meet the requirements specified in subsections (g)(1) through (g)(3).
1) The tank must be covered by a fixed roof and vented directly through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be designed to form a continuous barrier over the entire surface area of the liquid in the tank;
B) Each opening in the fixed roof not vented to the control device must be equipped with a closure device. If the pressure in the vapor headspace underneath the fixed roof is less than atmospheric pressure when the control device is operating, the closure devices must be designed to operate so that when the closure device is secured in the closed position there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces in the closure device or between the perimeter of the cover opening and the closure device. If the pressure in the vapor headspace underneath the fixed roof is equal to or greater than atmospheric pressure when the control device is operating, the closure device must be designed to operate with no detectable organic emissions;
C) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be made of suitable materials that will minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere, to the extent practical, and will maintain the integrity of the fixed roof and closure devices throughout their intended service life. Factors to be considered when selecting the materials for and designing the fixed roof and closure devices must include the following: organic vapor permeability; the effects of any contact with the liquid and its vapor managed in the tank; the effects of outdoor exposure to wind, moisture, and sunlight; and the operating practices used for the tank on which the fixed roof is installed; and
D) The closed-vent system and control device must be designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.988.
2) Whenever a hazardous waste is in the tank, the fixed roof must be installed with each closure device secured in the closed position and the vapor headspace underneath the fixed roof vented to the control device except as follows:
A) Venting to the control device is not required, and opening of closure devices or removal of the fixed roof is allowed at the following times:
i) To provide access to the tank for performing routine inspection, maintenance, or other activities needed for normal operations. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to sample liquid in the tank, or when a worker needs to open a hatch to maintain or repair equipment. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable, to the tank; and
ii) To remove accumulated sludge or other residues from the bottom of a tank; and
B) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
3) The owner or operator must inspect and monitor the air emission control equipment in accordance with the following procedures:
A) The fixed roof and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to any of the following: visible cracks, holes, or gaps in the roof sections or between the roof and the tank wall; broken, cracked, or otherwise damaged seals or gaskets on closure devices; and broken or missing hatches, access covers, caps, or other closure devices;
B) The closed-vent system and control device must be inspected and monitored by the owner or operator in accordance with the procedures specified in Section 725.988;
C) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the air emission control equipment on or before the date that the tank becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year except for the special conditions provided for in subsection (l);
D) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (k); and
E) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(b).
h) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions by using a pressure tank must meet the following requirements:
1) The tank must be designed not to vent to the atmosphere as a result of compression of the vapor headspace in the tank during filling of the tank to its design capacity;
2) All tank openings must be equipped with closure devices designed to operate with no detectable organic emissions as determined using the procedure specified in Section 725.984(d); and
3) Whenever a hazardous waste is in the tank, the tank must be operated as a closed-vent system that does not vent to the atmosphere, except under either of the following two conditions:
A) The tank does not need to be operated as a closed-vent system at those times when the opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is required to avoid an unsafe condition; and
B) The tank does not need to be operated as a closed-vent system at those times when the purging of inerts from the tank is required and the purge stream is routed to a closed-vent system and control device designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.988.
i) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions by using an enclosure vented through a closed-vent system to an enclosed combustion control device must meet the requirements specified in subsections (i)(1) through (i)(4).
1) The tank must be located inside an enclosure. The enclosure must be designed and operated in accordance with the criteria for a permanent total enclosure, as specified in “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” under appendix B to 40 CFR 52.741 (VOM Measurement Techniques for Capture Efficiency), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The enclosure may have permanent or temporary openings to allow worker access; passage of material into or out of the enclosure by conveyor, vehicles, or other mechanical means; entry of permanent mechanical or electrical equipment; or direct airflow into the enclosure. The owner or operator must perform the verification procedure for the enclosure as specified in Section 5.0 of “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” initially when the enclosure is first installed and, thereafter, annually;
2) The enclosure must be vented through a closed-vent system to an enclosed combustion control device that is designed and operated in accordance with the standards for either a vapor incinerator, boiler, or process heater specified in Section 725.988;
3) Safety devices, as defined in Section 725.981, may be installed and operated as necessary on any enclosure, closed-vent system, or control device used to comply with the requirements of subsections (i)(1) and (i)(2); and
4) The owner or operator must inspect and monitor the closed-vent system and control device, as specified in Section 725.988.
j) The owner or operator must transfer hazardous waste to a tank subject to this Section in accordance with the following requirements:
1) Transfer of hazardous waste, except as provided in subsection (j)(2), to the tank from another tank subject to this Section or from a surface impoundment subject to Section 725.986 must be conducted using continuous hard-piping or another closed system that does not allow exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere. For the purpose of complying with this provision, an individual drain system is considered to be a closed system when it meets the requirements of subpart RR of 40 CFR 63 (National Emission Standards for Individual Drain Systems), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); and
2) The requirements of subsection (j)(1) do not apply when transferring a hazardous waste to the tank under any of the following conditions:
A) The hazardous waste meets the average VO concentration conditions specified in Section 725.983(c)(1) at the point of waste origination;
B) The hazardous waste has been treated by an organic destruction or removal process to meet the requirements in Section 725.983(c)(2); and
C) The hazardous waste meets the requirements of Section 725.983(c)(4).
k) The owner or operator must repair each defect detected during an inspection performed in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(4), (e)(3), (f)(3), or (g)(3) as follows:
1) The owner or operator must make first efforts at repair of the defect no later than five calendar days after detection, and repair must be completed as soon as possible but no later than 45 calendar days after detection except as provided in subsection (k)(2); and
2) Repair of a defect may be delayed beyond 45 calendar days if the owner or operator determines that repair of the defect requires emptying or temporary removal from service of the tank and no alternative tank capacity is available at the site to accept the hazardous waste normally managed in the tank. In this case, the owner or operator must repair the defect the next time the process or unit that is generating the hazardous waste managed in the tank stops operation. Repair of the defect must be completed before the process or unit resumes operation.
l) Following the initial inspection and monitoring of the cover as required by the applicable provisions of this Subpart CC, subsequent inspection and monitoring may be performed at intervals longer than one year under the following special conditions:
1) Where inspecting or monitoring the cover would expose a worker to dangerous, hazardous, or other unsafe conditions, then the owner or operator may designate a cover as an “unsafe to inspect and monitor cover” and comply with all of the following requirements:
A) Prepare a written explanation for the cover stating the reasons why the cover is unsafe to visually inspect or to monitor, if required; and
B) Develop and implement a written plan and schedule to inspect and monitor the cover, using the procedures specified in the applicable Section of this Subpart CC, as frequently as practicable during those times when a worker can safely access the cover; and
2) If a tank is buried partially or entirely underground, an owner or operator is required to inspect and monitor, as required by the applicable provisions of this Section, only those portions of the tank cover and those connections to the tank (e.g., fill ports, access hatches, gauge wells, etc.) that are located on or above the ground surface.
(Source: Amended at 40 Ill. Reg. 11830, effective August 9, 2016)
Section 725.986 Standards: Surface Impoundments
a) The provisions of this Section apply to the control of air pollutant emissions from surface impoundments for which Section 725.983(b) of this Subpart CC references the use of this Section for such air emission control.
b) The owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the surface impoundment by installing and operating either of the following:
1) A floating membrane cover in accordance with the provisions specified in subsection (c); or
2) A cover that is vented through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the requirements specified in subsection (d).
c) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions from a surface impoundment using a floating membrane cover must meet the requirements specified in subsections (c)(1) through (c)(3).
1) The surface impoundment must be equipped with a floating membrane cover designed to meet the following specifications:
A) The floating membrane cover must be designed to float on the liquid surface during normal operations and form a continuous barrier over the entire surface area of the liquid;
B) The cover must be fabricated from a synthetic membrane material that is either of the following:
i) High density polyethylene (HDPE) with a thickness no less than 2.5 millimeters (mm) (0.10 inch); or
ii) A material or a composite of different materials determined to have both organic permeability properties that are equivalent to those of the material listed in subsection (c)(1)(B)(i) and chemical and physical properties that maintain the material integrity for the intended service life of the material;
C) The cover must be installed in a manner such that there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces between cover section seams or between the interface of the cover edge and its foundation mountings;
D) Except as provided for in subsection (c)(1)(E), each opening in the floating membrane cover must be equipped with a closure device so designed as to operate that when the closure device is secured in the closed position there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces in the closure device or between the perimeter of the cover opening and the closure device;
E) The floating membrane cover may be equipped with one or more emergency cover drains for removal of stormwater. Each emergency cover drain must be equipped with a slotted membrane fabric cover that covers at least 90 percent of the area of the opening or a flexible fabric sleeve seal; and
F) The closure devices must be made of suitable materials that will minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere, to the extent practical, and will maintain the integrity of the closure devices throughout their intended service life. Factors to be considered when selecting the materials of construction and designing the cover and closure devices must include the following: the organic vapor permeability; the effects of any contact with the liquid and its vapor managed in the surface impoundment; the effects of outdoor exposure to wind, moisture, and sunlight; and the operating practices used for the surface impoundment on which the floating membrane cover is installed.
2) Whenever a hazardous waste is in the surface impoundment, the floating membrane cover must float on the liquid and each closure device must be secured in the closed position, except as follows:
A) Opening of closure devices or removal of the cover is allowed at the following times:
i) To provide access to the surface impoundment for performing routine inspection, maintenance, or other activities needed for normal operations. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to sample the liquid in the surface impoundment, or when a worker needs to open a hatch to maintain or repair equipment. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly replace the cover and secure the closure device in the closed position, as applicable; or
ii) To remove accumulated sludge or other residues from the bottom of surface impoundment; and
B) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
3) The owner or operator must inspect the floating membrane cover in accordance with the following procedures:
A) The floating membrane cover and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to, visible cracks, holes, or gaps in the cover section seams or between the interface of the cover edge and its foundation mountings; broken, cracked, or otherwise damaged seals or gaskets on closure devices; and broken or missing hatches, access covers, caps, or other closure devices;
B) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the floating membrane cover and its closure devices on or before the date that the surface impoundment becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year except for the special conditions provided for in subsection (g);
C) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (f); and
D) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(c).
d) The owner or operator that controls air pollutant emissions from a surface impoundment using a cover vented to a control device must meet the requirements specified in subsections (d)(1) through (d)(3).
1) The surface impoundment must be covered by a cover and vented directly through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the following requirements:
A) The cover and its closure devices must be designed to form a continuous barrier over the entire surface area of the liquid in the surface impoundment;
B) Each opening in the cover not vented to the control device must be equipped with a closure device. If the pressure in the vapor headspace underneath the cover is less than atmospheric pressure when the control device is operating, the closure devices must be designed to operate such that when the closure device is secured in the closed position there are no visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces in the closure device or between the perimeter of the cover opening and the closure device. If the pressure in the vapor headspace underneath the cover is equal to or greater than atmospheric pressure when the control device is operating, the closure device must be designed to operate with no detectable organic emissions using the procedure specified in Section 725.984(d);
C) The cover and its closure devices must be made of suitable materials that will minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere to the extent practical and which will maintain the integrity of the cover and closure devices throughout their intended service life. Factors to be considered when selecting the materials of construction and designing the cover and closure devices must include the following: the organic vapor permeability; the effects of any contact with the liquid or its vapors managed in the surface impoundment; the effects of outdoor exposure to wind, moisture, and sunlight; and the operating practices used for the surface impoundment on which the cover is installed; and
D) The closed-vent system and control device must be designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.988.
2) Whenever a hazardous waste is in the surface impoundment, the cover must be installed with each closure device secured in the closed position and the vapor headspace underneath the cover vented to the control device, except as follows:
A) Venting to the control device is not required, and opening of closure devices or removal of the cover is allowed at the following times:
i) To provide access to the surface impoundment for performing routine inspection, maintenance, or other activities needed for normal operations. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to sample liquid in the surface impoundment, or when a worker needs to open a hatch to maintain or repair equipment. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable, to the surface impoundment; or
ii) To remove accumulated sludge or other residues from the bottom of the surface impoundment; and
B) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
3) The owner or operator must inspect and monitor the air emission control equipment in accordance with the following procedures:
A) The surface impoundment cover and its closure devices must be visually inspected by the owner or operator to check for defects that could result in air pollutant emissions. Defects include, but are not limited to, visible cracks, holes, or gaps in the cover section seams or between the interface of the cover edge and its foundation mountings; broken, cracked, or otherwise damaged seals or gaskets on closure devices; and broken or missing hatches, access covers, caps, or other closure devices;
B) The closed-vent system and control device must be inspected and monitored by the owner or operator in accordance with the procedures specified in Section 725.988;
C) The owner or operator must perform an initial inspection of the air emission control equipment on or before the date that the surface impoundment becomes subject to this Section. Thereafter, the owner or operator must perform the inspections at least once every year except for the special conditions provided for in subsection (g);
D) In the event that a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (f); and
E) The owner or operator must maintain a record of the inspection in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.990(c).
e) The owner or operator must transfer hazardous waste to a surface impoundment subject to this Section in accordance with the following requirements:
1) Transfer of hazardous waste, except as provided in subsection (e)(2), to the surface impoundment from another surface impoundment subject to this Section or from a tank subject to Section 725.985 must be conducted using continuous hard-piping or another closed system that does not allow exposure of the waste to the atmosphere. For the purpose of complying with this provision, an individual drain system is considered to be a closed system when it meets the requirements of subpart RR of 40 CFR 63 (National Emission Standards for Individual Drain Systems), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); and
2) The requirements of subsection (e)(1) do not apply when transferring a hazardous waste to the surface impoundment under any of the following conditions:
A) The hazardous waste meets the average VO concentration conditions specified in Section 725.983(c)(1) at the point of waste origination;
B) The hazardous waste has been treated by an organic destruction or removal process to meet the requirements in Section 725.983(c)(2); or
C) The hazardous waste meets the requirements of Section 725.983(c)(4).
f) The owner or operator must repair each defect detected during an inspection performed in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(3) or (d)(3) as follows:
1) The owner or operator must make first efforts at repair of the defect no later than five calendar days after detection, and repair must be completed as soon as possible but no later than 45 calendar days after detection except as provided in subsection (f)(2); and
2) Repair of a defect may be delayed beyond 45 calendar days if the owner or operator determines that repair of the defect requires emptying or temporary removal from service of the surface impoundment and no alternative capacity is available at the site to accept the hazardous waste normally managed in the surface impoundment. In this case, the owner or operator must repair the defect the next time the process or unit that is generating the hazardous waste managed in the tank stops operation. Repair of the defect must be completed before the process or unit resumes operation.
g) Following the initial inspection and monitoring of the cover, as required by the applicable provisions of this Subpart CC, subsequent inspection and monitoring may be performed at intervals longer than one year in the case when inspecting or monitoring the cover would expose a worker to dangerous, hazardous, or other unsafe conditions. In this case, the owner or operator may designate the cover as an “unsafe to inspect and monitor cover” and comply with all of the following requirements:
1) Prepare a written explanation for the cover stating the reasons why the cover is unsafe to visually inspect or to monitor, if required; and
2) Develop and implement a written plan and schedule to inspect and monitor the cover using the procedures specified in the applicable Section of this Subpart CC as frequently as practicable during those times when a worker can safely access the cover.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.987 Standards: Containers
a) The provisions of this Section apply to the control of air pollutant emissions from containers for which Section 725.983(b) references the use of this Section for air emission control.
b) General Requirements
1) The owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from each container subject to this Section in accordance with the following requirements, as applicable to the container, except when the following special provisions for waste stabilization processes specified in subsection (b)(2) apply to the container:
A) For a container having a design capacity greater than 0.1 m3 (26 gal) and less than or equal to 0.46 m3 (120 gal), the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the container in accordance with the Container Level 1 standards specified in subsection (c);
B) For a container having a design capacity greater than 0.46 m3 (120 gal) that is not in light material service, the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the container in accordance with the Container Level 1 standards specified in subsection (c); and
C) For a container having a design capacity greater than 0.46 m3 (120 gal) that is in light material service, the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the container in accordance with the Container Level 2 standards specified in subsection (d).
2) When a container having a design capacity greater than 0.1 m3 (26 gal) is used for treatment of a hazardous waste by a waste stabilization process, the owner or operator must control air pollutant emissions from the container in accordance with the Container Level 3 standards specified in subsection (e) at those times during the waste stabilization process when the hazardous waste in the container is exposed to the atmosphere.
c) Container Level 1 Standards
1) A container using Container Level 1 controls is one of the following:
A) A container that meets the applicable USDOT regulations on packaging hazardous materials for transportation, as specified in subsection (f);
B) A container equipped with a cover and closure devices that form a continuous barrier over the container openings so that when the cover and closure devices are secured in the closed position there are no visible holes, gaps, or other open spaces into the interior of the container. The cover may be a separate cover installed on the container (e.g., a lid on a drum or a suitably secured tarp on a roll-off box) or may be an integral part of the container structural design (e.g., a “portable tank” or bulk cargo container equipped with a screw-type cap); and
C) An open-top container in which an organic-vapor suppressing barrier is placed on or over the hazardous waste in the container so that no hazardous waste is exposed to the atmosphere. One example of such a barrier is application of a suitable organic-vapor suppressing foam.
2) A container used to meet the requirements of subsection (c)(1)(B) or (c)(1)(C) must be equipped with covers and closure devices, as applicable to the container, that are composed of suitable materials to minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere and to maintain the equipment integrity for as long as it is in service. Factors to be considered in selecting the materials of construction and designing the cover and closure devices must include the following: the organic vapor permeability; the effects of contact with the hazardous waste or its vapor managed in the container; the effects of outdoor exposure of the closure device or cover material to wind, moisture, and sunlight; and the operating practices for which the container is intended to be used.
3) Whenever a hazardous waste is in a container using Container Level 1 controls, the owner or operator must install all covers and closure devices for the container, as applicable to the container, and secure and maintain each closure device in the closed position except as follows:
A) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed for the purpose of adding hazardous waste or other material to the container, as follows:
i) If the container is filled to the intended final level in one continuous operation, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install the covers, as applicable to the container, upon conclusion of the filling operation; and
ii) If discrete quantities or batches of material intermittently are added to the container over a period of time, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install covers, as applicable to the container, upon either the container being filled to the intended final level; the completion of a batch loading after which no additional material will be added to the container within 15 minutes; the person performing the loading operation leaving the immediate vicinity of the container; or the shutdown of the process generating the material being added to the container, whichever condition occurs first;
B) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed for the purpose of removing hazardous waste from the container as follows:
i) For the purpose of meeting the requirements of this Section, an empty container, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b), may be open to the atmosphere at any time (i.e., covers and closure devices are not required to be secured in the closed position on an empty container); and
ii) If discrete quantities or batches of material are removed from the container but the container does not meet the conditions to be an empty container, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b), the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install covers, as applicable to the container, upon the completion of a batch removal after which no additional material will be removed from the container within 15 minutes or the person performing the unloading operation leaves the immediate vicinity of the container, whichever condition occurs first;
C) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed when access inside the container is needed to perform routine activities other than transfer of hazardous waste. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to measure the depth of or sample the material in the container, or when a worker needs to open a manhole hatch to access equipment inside the container. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable to the container;
D) Opening of a spring-loaded, pressure-vacuum relief valve, conservation vent, or similar type of pressure relief device that vents to the atmosphere is allowed during normal operations for the purpose of maintaining the container internal pressure in accordance with the design specifications of the container. The device must be designed to operate with no detectable organic emissions when the device is secured in the closed position. The settings at which the device opens must be established so that the device remains in the closed position whenever the internal pressure of the container is within the internal pressure operating range determined by the owner or operator based on container manufacturer recommendations, applicable regulations, fire protection and prevention codes, standard engineering codes and practices, or other requirements for the safe handling of flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive, or hazardous materials. Examples of normal operating conditions that may require these devices to open are during those times when the internal pressure of the container exceeds the internal pressure operating range for the container as a result of loading operations or diurnal ambient temperature fluctuations; and
E) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
4) The owner or operator of containers using Container Level 1 controls must inspect the containers and their covers and closure devices as follows:
A) If a hazardous waste already is in the container at the time the owner or operator first accepts possession of the container at the facility and the container is not emptied within 24 hours after the container is accepted at the facility (i.e., it does not meet the conditions for an empty container as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b)), the owner or operator must visually inspect the container and its cover and closure devices to check for visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces into the interior of the container when the cover and closure devices are secured in the closed position. The container visual inspection must be conducted on or before the date on which the container is accepted at the facility (i.e., the date when the container becomes subject to the Subpart CC container standards). For the purposes of this requirement, the date of acceptance is the date of signature that the facility owner or operator enters on Item 20 of the Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest (USEPA Form 8700-22), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), as required under Section 725.171. If a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(4)(C);
B) If a container used for managing hazardous waste remains at the facility for a period of one year or more, the owner or operator must visually inspect the container and its cover and closure devices initially and thereafter, at least once every 12 months, to check for visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces into the interior of the container when the cover and closure devices are secured in the closed position. If a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(4)(C); and
C) When a defect is detected in the container, cover, or closure devices, the owner or operator must make first efforts at repair of the defect no later than 24 hours after detection, and repair must be completed as soon as possible but no later than five calendar days after detection. If repair of a defect cannot be completed within five calendar days, then the hazardous waste must be removed from the container and the container must not be used to manage hazardous waste until the defect is repaired.
5) The owner or operator must maintain at the facility a copy of the procedure used to determine that containers with capacity of 0.46 m3 (120 gal) or greater which do not meet applicable USDOT regulations, as specified in subsection (f), are not managing hazardous waste in light material service.
d) Container Level 2 Standards
1) A container using Container Level 2 controls is one of the following:
A) A container that meets the applicable USDOT regulations on packaging hazardous materials for transportation as specified in subsection (f);
B) A container that operates with no detectable organic emissions, as defined in Section 725.981, and determined in accordance with the procedure specified in subsection (g); and
C) A container that has been demonstrated within the preceding 12 months to be vapor-tight by using Reference Method 27 (Determination of Vapor Tightness of Gasoline Delivery Tank Using Pressure-Vacuum Test) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), in accordance with the procedure specified in subsection (h).
2) Transfer of hazardous waste into or out of a container using Container Level 2 controls must be conducted in such a manner as to minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere, to the extent practical, considering the physical properties of the hazardous waste and good engineering and safety practices for handling flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive or other hazardous materials. Examples of container loading procedures that the USEPA considers to meet the requirements of this subsection (d)(2) include using any one of the following: a submerged-fill pipe or other submerged-fill method to load liquids into the container; a vapor-balancing system or a vapor-recovery system to collect and control the vapors displaced from the container during filling operations; or a fitted opening in the top of a container through which the hazardous waste is filled and subsequently purging the transfer line before removing it from the container opening.
3) Whenever a hazardous waste is in a container using Container Level 2 controls, the owner or operator must install all covers and closure devices for the container, and secure and maintain each closure device in the closed position, except as follows:
A) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed for the purpose of adding hazardous waste or other material to the container, as follows:
i) If the container is filled to the intended final level in one continuous operation, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install the covers, as applicable to the container, upon conclusion of the filling operation; and
ii) If discrete quantities or batches of material intermittently are added to the container over a period of time, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install covers, as applicable to the container, upon either the container being filled to the intended final level; the completion of a batch loading after which no additional material will be added to the container within 15 minutes; the person performing the loading operation leaving the immediate vicinity of the container; or the shutdown of the process generating the material being added to the container, whichever condition occurs first;
B) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed for the purpose of removing hazardous waste from the container as follows:
i) For the purpose of meeting the requirements of this Section, an empty container as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b) may be open to the atmosphere at any time (i.e., covers and closure devices are not required to be secured in the closed position on an empty container); and
ii) If discrete quantities or batches of material are removed from the container but the container does not meet the conditions to be an empty container as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b), the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure devices in the closed position and install covers, as applicable to the container, upon the completion of a batch removal after which no additional material will be removed from the container within 15 minutes or the person performing the unloading operation leaves the immediate vicinity of the container, whichever condition occurs first;
C) Opening of a closure device or cover is allowed when access inside the container is needed to perform routine activities other than transfer of hazardous waste. Examples of such activities include those times when a worker needs to open a port to measure the depth of or sample the material in the container, or when a worker needs to open a manhole hatch to access equipment inside the container. Following completion of the activity, the owner or operator must promptly secure the closure device in the closed position or reinstall the cover, as applicable to the container;
D) Opening of a spring-loaded, pressure-vacuum relief valve, conservation vent, or similar type of pressure relief device that vents to the atmosphere is allowed during normal operations for the purpose of maintaining the internal pressure of the container in accordance with the container design specifications. The device must be designed to operate with no detectable organic emission when the device is secured in the closed position. The settings at which the device opens must be established so that the device remains in the closed position whenever the internal pressure of the container is within the internal pressure operating range determined by the owner or operator based on container manufacturer recommendations, applicable regulations, fire protection and prevention codes, standard engineering codes and practices, or other requirements for the safe handling of flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive, or hazardous materials. Examples of normal operating conditions that may require these devices to open are during those times when the internal pressure of the container exceeds the internal pressure operating range for the container as a result of loading operations or diurnal ambient temperature fluctuations; and
E) Opening of a safety device, as defined in Section 725.981, is allowed at any time conditions require doing so to avoid an unsafe condition.
4) The owner or operator of containers using Container Level 2 controls must inspect the containers and their covers and closure devices as follows:
A) If a hazardous waste already is in the container at the time the owner or operator first accepts possession of the container at the facility and the container is not emptied within 24 hours after the container is accepted at the facility (i.e., it does not meet the conditions for an empty container as specified in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.107(b)), the owner or operator must visually inspect the container and its cover and closure devices to check for visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces into the interior of the container when the cover and closure devices are secured in the closed position. The container visual inspection must be conducted on or before the date on which the container is accepted at the facility (i.e., the date when the container becomes subject to the Subpart CC container standards). For the purposes of this requirement, the date of acceptance is the date of signature that the facility owner or operator enters on Item 20 of the Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest, in the appendix to 40 CFR 262 (Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest and Instructions (USEPA Forms 8700-22 and 8700-22A and Their Instructions)), as required under Section 725.171. If a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (d)(4)(C);
B) If a container used for managing hazardous waste remains at the facility for a period of one year or more, the owner or operator must visually inspect the container and its cover and closure devices initially and thereafter, at least once every 12 months, to check for visible cracks, holes, gaps, or other open spaces into the interior of the container when the cover and closure devices are secured in the closed position. If a defect is detected, the owner or operator must repair the defect in accordance with the requirements of subsection (d)(4)(C); and
C) When a defect is detected in the container, cover, or closure devices, the owner or operator must make first efforts at repair of the defect no later than 24 hours after detection, and repair must be completed as soon as possible but no later than five calendar days after detection. If repair of a defect cannot be completed within five calendar days, then the hazardous waste must be removed from the container and the container must not be used to manage hazardous waste until the defect is repaired.
e) Container Level 3 Standards
1) A container using Container Level 3 controls is one of the following:
A) A container that is vented directly through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the requirements of subsection (e)(2)(B); or
B) A container that is vented inside an enclosure that is exhausted through a closed-vent system to a control device in accordance with the requirements of subsections (e)(2)(A) and (e)(2)(B).
2) The owner or operator must meet the following requirements, as applicable to the type of air emission control equipment selected by the owner or operator:
A) The container enclosure must be designed and operated in accordance with the criteria for a permanent total enclosure, as specified in “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” under appendix B to 40 CFR 52.741 (VOM Measurement Techniques for Capture Efficiency), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b). The enclosure may have permanent or temporary openings to allow worker access; passage of containers through the enclosure by conveyor or other mechanical means; entry of permanent mechanical or electrical equipment; or direct airflow into the enclosure. The owner or operator must perform the verification procedure for the enclosure, as specified in Section 5.0 of “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure”, initially when the enclosure is first installed and, thereafter, annually; and
B) The closed-vent system and control device must be designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.988.
3) Safety devices, as defined in Section 725.981, may be installed and operated as necessary on any container, enclosure, closed-vent system, or control device used to comply with the requirements of subsection (e)(1).
4) Owners and operators using Container Level 3 controls in accordance with the provisions of this Subpart CC must inspect and monitor the closed-vent systems and control devices, as specified in Section 725.988.
5) Owners and operators that use Container Level 3 controls in accordance with the provisions of this Subpart CC must prepare and maintain the records specified in Section 725.990(d).
6) The transfer of hazardous waste into or out of a container using Container Level 3 controls must be conducted in such a manner as to minimize exposure of the hazardous waste to the atmosphere, to the extent practical considering the physical properties of the hazardous waste and good engineering and safety practices for handling flammable, ignitable, explosive, reactive, or other hazardous materials. Examples of container loading procedures that USEPA considers to meet the requirements of this subsection (e)(6) include using any one of the following: the use of a submerged-fill pipe or other submerged-fill method to load liquids into the container; the use of a vapor-balancing system or a vapor-recovery system to collect and control the vapors displaced from the container during filling operations; or the use of a fitted opening in the top of a container through which the hazardous waste is filled and subsequently purging the transfer line before removing it from the container opening.
f) For the purpose of compliance with subsection (c)(1)(A) or (d)(1)(A), containers must be used that meet the applicable USDOT regulations on packaging hazardous materials for transportation as follows:
1) The container meets the applicable requirements specified by USDOT in 49 CFR 178 (Specifications for Packaging), or 49 CFR 179 (Specifications for Tank Cars), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b);
2) Hazardous waste is managed in the container in accordance with the applicable requirements specified by USDOT in subpart B of 49 CFR 107 (Exemptions), 49 CFR 172 (Hazardous Materials Table, Special Provisions, Hazardous Materials Communications, Emergency Response Information, and Training Requirements), 49 CFR 173 (Shippers—General Requirements for Shipments and Packages), and 49 CFR 180 (Continuing Qualification and Maintenance of Packagings), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b);
3) For the purpose of complying with this Subpart CC, no exceptions to the federal 49 CFR 178 or 179 regulations are allowed, except as provided for in subsection (f)(4); and
4) For a lab pack that is managed in accordance with the USDOT requirements of 49 CFR 178 (Specifications for Packagings) for the purpose of complying with this Subpart CC, an owner or operator may comply with the exceptions for combination packagings specified by USDOT in 49 CFR 173.12(b) (Exceptions for Shipments of Waste Materials), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
g) To determine compliance with the no detectable organic emissions requirements of subsection (d)(1)(B), the procedure specified in Section 725.984(d) must be used.
1) Each potential leak interface (i.e., a location where organic vapor leakage could occur) on the container, its cover, and associated closure devices, as applicable to the container, must be checked. Potential leak interfaces that are associated with containers include but are not limited to: the interface of the cover rim and the container wall; the periphery of any opening on the container or container cover and its associated closure device; and the sealing seat interface on a spring-loaded pressure-relief valve.
2) The test must be performed when the container is filled with a material having a volatile organic concentration representative of the range of volatile organic concentrations for the hazardous wastes expected to be managed in this type of container. During the test, the container cover and closure devices must be secured in the closed position.
h) The procedure for determining a container to be vapor-tight using Reference Method 27 for the purpose of complying with subsection (d)(1)(C) is as follows:
1) The test must be performed in accordance with Reference Method 27;
2) A pressure measurement device must be used that has a precision of ±2.5 mm (0.10 inch) water and that is capable of measuring above the pressure at which the container is to be tested for vapor tightness; and
3) If the test results determined by Reference Method 27 indicate that the container sustains a pressure change less than or equal to 0.75 kPa (0.11 psig) within five minutes after it is pressurized to a minimum of 4.5 kPa (0.65 psig), then the container is determined to be vapor-tight.
(Source: Amended at 43 Ill. Reg. 634, effective December 6, 2018)
Section 725.988 Standards: Closed-Vent Systems and Control Devices
a) This Section applies to each closed-vent system and control device installed and operated by the owner or operator to control air emissions in accordance with standards of this Subpart CC.
b) The closed-vent system must meet the following requirements:
1) The closed-vent system must route the gases, vapors, and fumes emitted from the hazardous waste in the waste management unit to a control device that meets the requirements specified in subsection (c);
2) The closed-vent system must be designed and operated in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.933(j);
3) When the closed-vent system includes bypass devices that could be used to divert the gas or vapor stream to the atmosphere before entering the control device, each bypass device must be equipped with either a flow indicator as specified in subsection (b)(3)(A) or a seal or locking device as specified in subsection (b)(3)(B). For the purpose of complying with this subsection, low leg drains, high point bleeds, analyzer vents, open-ended valves or lines, spring-loaded pressure relief valves, and other fittings used for safety purposes are not considered to be bypass devices.
A) If a flow indicator is used to comply with this subsection (b)(3), the indicator must be installed at the inlet to the bypass line used to divert gases and vapors from the closed-vent system to the atmosphere at a point upstream of the control device inlet. For the purposes of this subsection, a flow indicator means a device that indicates the presence of either gas or vapor flow in the bypass line.
B) If a seal or locking device is used to comply with this subsection (b)(3), the device must be placed on the mechanism by which the bypass device position is controlled (e.g., valve handle or damper lever) when the bypass device is in the closed position such that the bypass device cannot be opened without breaking the seal or removing the lock. Examples of such devices include, but are not limited to, a car-seal or a lock-and-key configuration valve. The owner or operator must visually inspect the seal or closure mechanism at least once every month to verify that the bypass mechanism is maintained in the closed position; and
4) The closed-vent system must be inspected and monitored by the owner or operator in accordance with the procedure specified in Section 725.933(k).
c) The control device must meet the following requirements:
1) The control device must be one of the following devices:
A) A control device designed and operated to reduce the total organic content of the inlet vapor stream vented to the control device by at least 95 percent by weight;
B) An enclosed combustion device designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(c); or
C) A flare designed and operated in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(d);
2) The owner or operator that elects to use a closed-vent system and control device to comply with the requirements of this Section must comply with the requirements specified in subsections (c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(G).
A) Periods of planned routine maintenance of the control device, during which the control device does not meet the specifications of subsection (c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), or (c)(1)(C), as applicable, must not exceed 240 hours per year.
B) The specifications and requirements in subsections (c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), and (c)(1)(C) for control devices do not apply during periods of planned routine maintenance.
C) The specifications and requirements in subsections (c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), and (c)(1)(C) for control devices do not apply during a control device system malfunction.
D) The owner or operator must demonstrate compliance with the requirements of subsection (c)(2)(A) (i.e., planned routine maintenance of a control device, during which the control device does not meet the specifications of subsection (c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), or (c)(1)(C), as applicable, must not exceed 240 hours per year) by recording the information specified in Section 725.990(e)(1)(E).
E) The owner or operator must correct control device system malfunctions as soon as practicable after their occurrence in order to minimize excess emissions of air pollutants.
F) The owner or operator must operate the closed-vent system so that gases, vapors, or fumes are not actively vented to the control device during periods of planned maintenance or control device system malfunction (i.e., periods when the control device is not operating or not operating normally), except in cases when it is necessary to vent the gases, vapors, or fumes to avoid an unsafe condition or to implement malfunction corrective actions or planned maintenance actions;
3) The owner or operator using a carbon adsorption system to comply with subsection (c)(1) must operate and maintain the control device in accordance with the following requirements:
A) Following the initial startup of the control device, all activated carbon in the control device must be replaced with fresh carbon on a regular basis in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(g) or 725.933(h).
B) All carbon that is a hazardous waste and that is removed from the control device must be managed in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(m), regardless of the average volatile organic concentration of the carbon;
4) An owner or operator using a control device other than a thermal vapor incinerator, flare, boiler, process heater, condenser, or carbon adsorption system to comply with subsection (c)(1) must operate and maintain the control device in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.933(i);
5) The owner or operator must demonstrate that a control device achieves the performance requirements of subsection (c)(1) as follows:
A) An owner or operator must demonstrate using either a performance test, as specified in subsection (c)(5)(C), or a design analysis, as specified in subsection (c)(5)(D), the performance of each control device except for the following:
i) A flare;
ii) A boiler or process heater with a design heat input capacity of 44 megawatts or greater;
iii) A boiler or process heater into which the vent stream is introduced with the primary fuel;
iv) A boiler or industrial furnace burning hazardous waste for which the owner or operator has been issued a final permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 703, and 705 and has designed and operates in accordance with the requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726; or
v) A boiler or industrial furnace burning hazardous waste for which the owner or operator has designed and operates in accordance with the interim status requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726;
B) An owner or operator must demonstrate the performance of each flare in accordance with the requirements specified in Section 725.933(e);
C) For a performance test conducted to meet the requirements of subsection (c)(5)(A), the owner or operator must use the test methods and procedures specified in Section 725.934(c)(1) through (c)(4);
D) For a design analysis conducted to meet the requirements of subsection (c)(5)(A), the design analysis must meet the requirements specified in Section 725.935(b)(4)(C); and
E) The owner or operator must demonstrate that a carbon adsorption system achieves the performance requirements of subsection (c)(1) based on the total quantity of organics vented to the atmosphere from all carbon adsorption system equipment that is used for organic adsorption, organic desorption or carbon regeneration, organic recovery, and carbon disposal;
6) If the owner or operator and the Agency do not agree on a demonstration of control device performance using a design analysis, then the disagreement must be resolved using the results of a performance test performed by the owner or operator in accordance with the requirements of subsection (c)(5)(C). The Agency may choose to have an authorized representative observe the performance test; and
7) The closed-vent system and control device must be inspected and monitored by the owner or operator in accordance with the procedures specified in Section 725.933(f)(2) and (k). The readings from each monitoring device required by Section 725.933(f)(2) must be inspected at least once each operating day to check control device operation. Any necessary corrective measures must be immediately implemented to ensure the control device is operated in compliance with the requirements of this Section.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.989 Inspection and Monitoring Requirements
a) The owner or operator must inspect and monitor air emission control equipment used to comply with this Subpart CC in accordance with the requirements specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988.
b) The owner or operator must develop and implement a written plan and schedule to perform the inspections and monitoring required by subsection (a). The owner or operator must incorporate this plan and schedule into the facility inspection plan required under Section 725.115.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.990 Recordkeeping Requirements
a) Each owner or operator of a facility subject to the requirements in this Subpart CC must record and maintain the information specified in subsections (b) through (j), as applicable to the facility. Except for air emission control equipment design documentation and information required by subsections (i) and (j), records required by this Section must be maintained in the operating record for a minimum of three years. Air emission control equipment design documentation must be maintained in the operating record until the air emission control equipment is replaced or is otherwise no longer in service. Information required by subsections (i) and (j) must be maintained in the operating record for as long as the waste management unit is not using air emission controls specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988, in accordance with the conditions specified in Section 725.980(d) or (b)(7), respectively.
b) The owner or operator of a tank using air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.985 must prepare and maintain records for the tank that include the following information:
1) For each tank using air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.985 of this Subpart CC, the owner or operator must record the following information:
A) A tank identification number (or other unique identification description as selected by the owner or operator); and
B) A record for each inspection required by Section 725.985 that includes the following information:
i) Date inspection was conducted; and
ii) For each defect detected during the inspection, the location of the defect, a description of the defect, the date of detection, and corrective action taken to repair the defect. In the event that repair of the defect is delayed in accordance with the provisions of Section 725.985, the owner or operator must also record the reason for the delay and the date that completion of repair of the defect is expected; and
2) In addition to the information required by subsection (b)(1), the owner or operator must record the following information, as applicable to the tank:
A) The owner or operator using a fixed roof to comply with the Tank Level 1 control requirements specified in Section 725.985(c) must prepare and maintain records for each determination for the maximum organic vapor pressure of the hazardous waste in the tank performed in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.985(c). The records must include the date and time the samples were collected, the analysis method used, and the analysis results;
B) The owner or operator using an internal floating roof to comply with the Tank Level 2 control requirements specified in Section 725.985(e) must prepare and maintain documentation describing the floating roof design;
C) Owners and operators using an external floating roof to comply with the Tank Level 2 control requirements specified in Section 725.985(f) must prepare and maintain the following records:
i) Documentation describing the floating roof design and the dimensions of the tank; and
ii) Records for each seal gap inspection required by Section 725.985(f)(3) describing the results of the seal gap measurements. The records must include the date that the measurements were performed, the raw data obtained for the measurements, and the calculations of the total gap surface area. In the event that the seal gap measurements do not conform to the specifications in Section 725.985(f)(1), the records must include a description of the repairs that were made, the date the repairs were made, and the date the tank was emptied, if necessary.
D) Each owner or operator using an enclosure to comply with the Tank Level 2 control requirements specified in Section 725.985(i) must prepare and maintain the following records:
i) Records for the most recent set of calculations and measurements performed by the owner or operator to verify that the enclosure meets the criteria of a permanent total enclosure as specified in “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” under appendix B to 40 CFR 52.741 (VOM Measurement Techniques for Capture Efficiency), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); and
ii) Records required for the closed-vent system and control device in accordance with the requirements of subsection (e).
c) The owner or operator of a surface impoundment using air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.986 must prepare and maintain records for the surface impoundment that include the following information:
1) A surface impoundment identification number (or other unique identification description as selected by the owner or operator);
2) Documentation describing the floating membrane cover or cover design, as applicable to the surface impoundment, that includes information prepared by the owner or operator or provided by the cover manufacturer or vendor describing the cover design, and certification by the owner or operator that the cover meets the specifications listed in Section 725.986(c);
3) A record for each inspection required by Section 725.986 that includes the following information:
A) Date inspection was conducted; and
B) For each defect detected during the inspection the following information: the location of the defect, a description of the defect, the date of detection, and corrective action taken to repair the defect. In the event that repair of the defect is delayed in accordance with the provisions of Section 725.986(f), the owner or operator must also record the reason for the delay and the date that completion of repair of the defect is expected; and
4) For a surface impoundment equipped with a cover and vented through a closed-vent system to a control device, the owner or operator must prepare and maintain the records specified in subsection (e).
d) The owner or operator of containers using Container Level 3 air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.987 must prepare and maintain records that include the following information:
1) Records for the most recent set of calculations and measurements performed by the owner or operator to verify that the enclosure meets the criteria of a permanent total enclosure as specified in “Procedure T—Criteria for and Verification of a Permanent or Temporary Total Enclosure” under appendix B to 40 CFR 52.741 (VOM Measurement Techniques for Capture Efficiency), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b); and
2) Records required for the closed-vent system and control device in accordance with the requirements of subsection (e).
e) The owner or operator using a closed-vent system and control device in accordance with the requirements of Section 725.988 must prepare and maintain records that include the following information:
1) Documentation for the closed-vent system and control device that includes the following:
A) Certification that is signed and dated by the owner or operator stating that the control device is designed to operate at the performance level documented by a design analysis as specified in subsection (e)(1)(B) or by performance tests as specified in subsection (e)(1)(C) when the tank, surface impoundment, or container is or would be operating at capacity or the highest level reasonably expected to occur;
B) If a design analysis is used, then design documentation, as specified in Section 725.935(b)(4). The documentation must include information prepared by the owner or operator or provided by the control device manufacturer or vendor that describes the control device design in accordance with Section 725.935(b)(4)(C) and certification by the owner or operator that the control equipment meets the applicable specifications;
C) If performance tests are used, then a performance test plan as specified in Section 725.935(b)(3) and all test results;
D) Information as required by Section 725.935(c)(1) and (c)(2), as applicable;
E) An owner or operator must record, on a semiannual basis, the following information for those planned routine maintenance operations that would require the control device not to meet the requirements of Section 725.988(c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), or (c)(1)(C), as applicable:
i) A description of the planned routine maintenance that is anticipated to be performed for the control device during the next six-month period. This description must include the type of maintenance necessary, planned frequency of maintenance, and lengths of maintenance periods; and
ii) A description of the planned routine maintenance that was performed for the control device during the previous six-month period. This description must include the type of maintenance performed and the total number of hours during those six months that the control device did not meet the requirements of Section 725.988(c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), or (c)(1)(C), as applicable, due to planned routine maintenance;
F) An owner or operator must record the following information for those unexpected control device system malfunctions that would require the control device not to meet the requirements of Section 725.988(c)(1)(A), (c)(1)(B), or (c)(1)(C), as applicable:
i) The occurrence and duration of each malfunction of the control device system;
ii) The duration of each period during a malfunction when gases, vapors, or fumes are vented from the waste management unit through the closed-vent system to the control device while the control device is not properly functioning; and
iii) Actions taken during periods of malfunction to restore a malfunctioning control device to its normal or usual manner of operation; and
G) Records of the management of carbon removed from a carbon adsorption system conducted in accordance with Section 725.988(c)(3)(B).
f) The owner or operator of a tank, surface impoundment, or container exempted from standards in accordance with the provisions of Section 725.983(c) must prepare and maintain the following records, as applicable:
1) For tanks, surface impoundments, or containers exempted under the hazardous waste organic concentration conditions specified in Section 725.983 (c)(1) or 725.983(c)(2)(A) through (c)(2)(F), the owner or operator must record the information used for each waste determination (e.g., test results, measurements, calculations, and other documentation) in the facility operating log. If analysis results for waste samples are used for the waste determination, then the owner or operator must record the date, time, and location that each waste sample is collected in accordance with the applicable requirements of Section 725.984; and
2) For tanks, surface impoundments, or containers exempted under the provisions of Section 725.983(c)(2)(G) or (c)(2)(H), the owner or operator must record the identification number for the incinerator, boiler, or industrial furnace in which the hazardous waste is treated.
g) An owner or operator designating a cover as “unsafe to inspect and monitor” pursuant to Section 725.985(l) or 725.986(g) must record in a log that is kept in the facility operating record the following information: the identification numbers for waste management units with covers that are designated as “unsafe to inspect and monitor”, the explanation for each cover stating why the cover is unsafe to inspect and monitor, and the plan and schedule for inspecting and monitoring each cover.
h) The owner or operator of a facility that is subject to this Subpart CC and to the control device standards in federal subpart VV of 40 CFR 60 (Standards of Performance for Equipment Leaks of VOC in the Synthetic Organic Chemicals Manufacturing Industry), or subpart V of 40 CFR 61 (National Emission Standard for Equipment Leaks (Fugitive Emission Sources), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 270.111, may elect to demonstrate compliance with the applicable Sections of this Subpart by documentation either pursuant to this Subpart CC, or pursuant to the provisions of subpart VV of 40 CFR 60 or subpart V of 40 CFR 61, to the extent that the documentation required by 40 CFR 60 or 61 duplicates the documentation required by this Section.
i) For each tank or container not using air emission controls specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988 in accordance with the conditions specified in Section 725.980(d), the owner or operator must record and maintain the following information:
1) A list of the individual organic peroxide compounds manufactured at the facility that meet the conditions specified in Section 725.980(d)(1);
2) A description of how the hazardous waste containing the organic peroxide compounds identified pursuant to subsection (i)(1) are managed at the facility in tanks and containers. This description must include the following information:
A) For the tanks used at the facility to manage this hazardous waste, sufficient information must be provided to describe each tank: a facility identification number for the tank, the purpose and placement of this tank in the management train of this hazardous waste, and the procedures used to ultimately dispose of the hazardous waste managed in the tanks; and
B) For containers used at the facility to manage this hazardous waste, sufficient information must be provided to describe the following for each container: a facility identification number for the container or group of containers; the purpose and placement of this container or group of containers in the management train of this hazardous waste; and the procedures used to ultimately dispose of the hazardous waste handled in the containers; and
3) An explanation of why managing the hazardous waste containing the organic peroxide compounds identified pursuant to subsection (i)(1) in the tanks or containers identified pursuant to subsection (i)(2) would create an undue safety hazard if the air emission controls specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988 were installed and operated on these waste management units. This explanation must include the following information:
A) For tanks used at the facility to manage this hazardous waste, sufficient information must be provided to explain: how use of the required air emission controls on the tanks would affect the tank design features and facility operating procedures currently used to prevent an undue safety hazard during the management of this hazardous waste in the tanks; and why installation of safety devices on the required air emission controls, as allowed under this Subpart CC, would not address those situations in which evacuation of tanks equipped with these air emission controls is necessary and consistent with good engineering and safety practices for handling organic peroxides; and
B) For containers used at the facility to manage this hazardous waste, sufficient information must be provided to explain: how use of the required air emission controls on the containers would affect the container design features and handling procedures currently used to prevent an undue safety hazard during management of this hazardous waste in the containers; and why installation of safety devices on the required air emission controls, as allowed under this Subpart CC, would not address those situations in which evacuation of containers equipped with these air emission controls is necessary and consistent with good engineering and safety practices for handling organic peroxides.
j) For each hazardous waste management unit not using air emission controls specified in Sections 725.985 through 725.988 in accordance with the provisions of Section 725.980(b)(7), the owner and operator must record and maintain the following information:
1) The certification that the waste management unit is equipped with and operating air emission controls in accordance with the requirements of an applicable federal Clean Air Act regulation codified under 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63; and
2) An identification of the specific federal requirements codified under 40 CFR 60, 61, or 63 with which the waste management unit is in compliance.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.991 Alternative Tank Emission Control Requirements (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 22 Ill. Reg. 369, effective December 16, 1997)
SUBPART DD: CONTAINMENT BUILDINGS
Section 725.1100 Applicability
The requirements of this Subpart DD apply to owners or operators that store or treat hazardous waste in units designed and operated under Section 725.1101. The owner or operator is not subject to the definition of land disposal in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 728.102 provided that the following is true of the unit:
a) It is a completely enclosed, self-supporting structure that is designed and constructed of manmade materials of sufficient strength and thickness to support themselves, the waste contents, and any personnel and heavy equipment that operate within the unit, and to prevent failure due to any of the following causes:
1) Pressure gradients;
2) Settlement, compression, or uplift;
3) Physical contact with the hazardous wastes to which they are exposed;
4) Climatic conditions; or
5) The stresses of daily operation including the movement of heavy equipment within the unit and contact of such equipment with containment walls;
b) It has a primary barrier that is designed to be sufficiently durable to withstand the movement of personnel, wastes, and handling equipment within the unit;
c) If used to manage liquids, the unit has the following design features:
1) A primary barrier designed and constructed of materials to prevent migration of hazardous constituents into the barrier;
2) A liquid collection system designed and constructed of materials to minimize the accumulation of liquid on the primary barrier; and
3) A secondary containment system designed and constructed of materials to prevent migration of hazardous constituents into the barrier, with a leak detection and liquid collection system capable of detecting, collecting, and removing leaks of hazardous constituents at the earliest possible time, unless the unit has been granted a variance from the secondary containment system requirements under subsection 725.1101(b)(4);
d) It has controls sufficient to prevent fugitive dust emissions to meet the no visible emission standard in subsection 725.1101(c)(1)(D); and
e) It is designed and operated to ensure containment and prevent the tracking of materials from the unit by personnel or equipment.
(Source: Amended at 32 Ill. Reg. 12566, effective July 14, 2008)
Section 725.1101 Design and Operating Standards
a) All containment buildings must comply with the following design and operating standards:
1) The containment building must be completely enclosed with a floor, walls, and a roof to prevent exposure to the elements (e.g., precipitation, wind, run on) and to assure containment of managed wastes;
2) The floor and containment walls of the unit, including the secondary containment system if required under subsection (b), must be designed and constructed of materials of sufficient strength and thickness to support themselves, the waste contents, and any personnel and heavy equipment that operate within the unit, and to prevent failure due to pressure gradients, settlement, compression, or uplift, physical contact with the hazardous wastes to which they are exposed; climatic conditions; and the stresses of daily operation, including the movement of heavy equipment within the unit and contact of such equipment with containment walls. The unit must be designed so that it has sufficient structural strength to prevent collapse or other failure. All surfaces to be in contact with hazardous wastes must be chemically compatible with those wastes. The containment building must meet the structural integrity requirements established by professional organizations generally recognized by the industry such as the American Concrete Institute (ACI) and the American Society of Testing Materials (ASTM). If appropriate to the nature of the waste management operation to take place in the unit, an exception to the structural strength requirement may be made for light-weight doors and windows that meet the following criteria:
A) They provide an effective barrier against fugitive dust emissions under subsection (c)(1)(D); and
B) The unit is designed and operated in a fashion that assures that wastes will not actually come in contact with these openings;
3) Incompatible hazardous wastes or treatment reagents must not be placed in the unit or its secondary containment system if they could cause the unit or secondary containment system to leak, corrode, or otherwise fail; and
4) A containment building must have a primary barrier designed to withstand the movement of personnel, waste, and handling equipment in the unit during the operating life of the unit and appropriate for the physical and chemical characteristics of the waste to be managed.
b) For a containment building used to manage hazardous wastes containing free liquids or treated with free liquids (the presence of which is determined by the paint filter test, a visual examination, or other appropriate means), the owner or operator must include the following design features:
1) A primary barrier designed and constructed of materials to prevent the migration of hazardous constituents into the barrier (e.g., a geomembrane covered by a concrete wear surface).
2) A liquid collection and removal system to minimize the accumulation of liquid on the primary barrier of the containment building, as follows:
A) The primary barrier must be sloped to drain liquids to the associated collection system; and
B) Liquids and waste must be collected and removed to minimize hydraulic head on the containment system at the earliest practicable time.
3) A secondary containment system including a secondary barrier designed and constructed to prevent migration of hazardous constituents into the barrier, and a leak detection system that is capable of detecting failure of the primary barrier and collecting accumulated hazardous wastes and liquids at the earliest practicable time.
A) The requirements of the leak detection component of the secondary containment system are satisfied by installation of a system that is, at a minimum, as follows:
i) It is constructed with a bottom slope of 1 percent or more; and
ii) It is constructed of a granular drainage material with a hydraulic conductivity of 1 ´ 10-2 cm/sec or more and a thickness of 12 inches (30.5 cm) or more, or constructed of synthetic or geonet drainage materials with a transmissivity of 3 ´ 10-5 m2/sec or more.
B) If treatment is to be conducted in the building, an area in which such treatment will be conducted must be designed to prevent the release of liquids, wet materials, or liquid aerosols to other portions of the building.
C) The secondary containment system must be constructed of materials that are chemically resistant to the waste and liquids managed in the containment building and of sufficient strength and thickness to prevent collapse under the pressure exerted by overlaying materials and by any equipment used in the containment building. (Containment buildings can serve as secondary containment systems for tanks placed within the building under certain conditions. A containment building can serve as an external liner system for a tank, provided it meets the requirements of Section 725.293(e)(1). In addition, the containment building must meet the requirements of Section 725.293(b) and (c) to be an acceptable secondary containment system for a tank.)
c) An owner or operator of a containment building must do each of the following:
1) It must use controls and practice to ensure containment of the hazardous waste within the unit, and at a minimum do each of the following:
A) It must maintain the primary barrier to be free of significant cracks, gaps, corrosion, or other deterioration that could cause hazardous waste to be released from the primary barrier;
B) It must maintain the level of the stored or treated hazardous waste within the containment walls of the unit so that the height of any containment wall is not exceeded;
C) It must take measures to prevent the tracking of hazardous waste out of the unit by personnel or by equipment used in handling the waste. An area must be designated to decontaminate equipment and any rinsate must be collected and properly managed; and
D) It must take measures to control fugitive dust emissions such that any openings (doors, windows, vents, cracks, etc.) exhibit no visible emissions (see Reference Method 22 (Visual Determination of Fugitive Emissions from Material Sources and Smoke Emissions from Flares) in appendix A to 40 CFR 60 (Test Methods), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b)). In addition, all associated particulate collection devices (e.g., fabric filter, electrostatic precipitator, etc.) must be operated and maintained with sound air pollution control practices (see 40 CFR 60 for guidance). This state of no visible emissions must be maintained effectively at all times during routine operating and maintenance conditions, including when vehicles and personnel are entering and exiting the unit;
BOARD NOTE: At 40 CFR 264.1101(c)(1)(iv), USEPA cites “40 CFR part 60, subpart 292”. At 57 Fed. Reg. 37217 (Aug. 18, 1992), USEPA repeats this citation in the preamble discussion of adoption of the rules. No such provision exists in the Code of Federal Regulations. While 40 CFR 60.292 of the federal regulations pertains to control of fugitive dust emissions, that provision is limited in its application to glass melting furnaces. The Board has chosen to use the general citation: “40 CFR 60”.
2) It must obtain and keep on site a certification by a qualified Professional Engineer that the containment building design meets the requirements of subsections (a) through (c);
3) Throughout the active life of the containment building, if the owner or operator detects a condition that could lead to or has caused a release of hazardous waste, it must repair the condition promptly, in accordance with the following procedures:
A) Upon detection of a condition that has led to a release of hazardous wastes (e.g., upon detection of leakage from the primary barrier) the owner or operator must do the following:
i) Enter a record of the discovery in the facility operating record;
ii) Immediately remove the portion of the containment building affected by the condition from service;
iii) Determine what steps must be taken to repair the containment building, remove any leakage from the secondary collection system, and establish a schedule for accomplishing the cleanup and repairs; and
iv) Within seven days after the discovery of the condition, notify the Agency in writing of the condition, and within 14 working days, provide a written notice to the Agency with a description of the steps taken to repair the containment building, and the schedule for accomplishing the work;
B) The Agency must review the information submitted, make a determination in accordance with Section 34 of the Act, regarding whether the containment building must be removed from service completely or partially until repairs and cleanup are complete, and notify the owner or operator of the determination and the underlying rationale in writing; and
C) Upon completing all repairs and cleanup the owner and operator must notify the Agency in writing and provide a verification, signed by a qualified, registered professional engineer, that the repairs and cleanup have been completed according to the written plan submitted in accordance with subsection (c)(3)(A)(iv); and
4) At least once every seven days, the owner or operator must inspect and record in the facility’s operating record data gathered from monitoring and leak detection equipment, as well as the containment building and the area immediately surrounding the containment building, to detect signs of releases of hazardous waste.
d) For a containment building that contains areas both with and without secondary containment, the owner or operator must do the following:
1) Design and operate each area in accordance with the requirements enumerated in subsections (a) through (c);
2) Take measures to prevent the release of liquids or wet materials into areas without secondary containment; and
3) Maintain in the facility’s operating log a written description of the operating procedures used to maintain the integrity of areas without secondary containment.
e) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Subpart DD, the Agency must, in writing, allow the use of alternatives to the requirements for secondary containment for a permitted containment building where the Agency has determined that the facility owner or operator has adequately demonstrated that the only free liquids in the unit are limited amounts of dust suppression liquids required to meet occupational health and safety requirements, and where containment of managed wastes and liquids can be assured without a secondary containment system.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.1102 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At closure of a containment building, the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components (liners, etc.), contaminated subsoils, and structures and equipment contaminated with waste and leachate, and manage them as hazardous waste unless 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(e) applies. The closure plan, closure activities, cost estimates for closure, and financial responsibility for containment buildings must meet all of the requirements specified in Subparts G and H.
b) If, after removing or decontaminating all residues and making all reasonable efforts to effect removal or decontamination of contaminated components, subsoils, structures, and equipment as required in subsection (a), the owner or operator finds that not all contaminated subsoils can be practicably removed or decontaminated, he must close the facility and perform post-closure care in accordance with the closure and post-closure requirements that apply to landfills (35 Ill. Adm. Code 725.310). In addition, for the purposes of closure, post-closure, and financial responsibility, such a containment building is then considered to be a landfill, and the owner or operator must meet all the requirements for landfills specified in Subparts G and H.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
SUBPART EE: HAZARDOUS WASTE MUNITIONS AND EXPLOSIVES STORAGE
Section 725.1200 Applicability
The requirements of this Subpart EE apply to owners or operators that store munitions and explosive hazardous wastes, except as Section 725.101 provides otherwise.
BOARD NOTE: Depending on explosive hazards, hazardous waste munitions and explosives may also be managed in other types of storage units, including containment buildings (Subpart DD), tanks (Subpart J), or containers (Subpart I); see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 726.305 for storage of waste military munitions.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.1201 Design and Operating Standards
a) An owner or operator of a hazardous waste munitions and explosives storage unit must design and operate the unit with containment systems, controls, and monitoring that fulfill each of the following requirements:
1) The owner or operator minimizes the potential for detonation or other means of release of hazardous waste, hazardous constituents, hazardous decomposition products, or contaminated run-off to the soil, groundwater, surface water, and atmosphere;
2) The owner or operator provides a primary barrier, which may be a container (including a shell) or tank, designed to contain the hazardous waste;
3) For wastes stored outdoors, the owner or operator provides that the waste and containers will not be in standing precipitation;
4) For liquid wastes, the owner or operator provides a secondary containment system that assures that any released liquids are contained and promptly detected and removed from the waste area or a vapor detection system that assures that any released liquids or vapors are promptly detected and an appropriate response taken (e.g., additional containment, such as overpacking or removal from the waste area); and
5) The owner or operator provides monitoring and inspection procedures that assure the controls and containment systems are working as designed and that releases that may adversely impact human health or the environment are not escaping from the unit.
b) Hazardous waste munitions and explosives stored under this Subpart EE may be stored in one of the following:
1) Earth-Covered Magazines. The owner or operator of an earth-covered magazine must fulfill each of the following requirements:
A) The magazine is constructed of waterproofed, reinforced concrete or structural steel arches, with steel doors that are kept closed when not being accessed;
B) The magazine is so designed and constructed that it fulfills each of the following requirements:
i) The magazine is of sufficient strength and thickness to support the weight of any explosives or munitions stored and any equipment used in the unit;
ii) The magazine provides working space for personnel and equipment in the unit; and
iii) The magazine can withstand movement activities that occur in the unit; and
C) The magazine is located and designed, with walls and earthen covers that direct an explosion in the unit in a safe direction, so as to minimize the propagation of an explosion to adjacent units and to minimize other effects of any explosion.
2) Above-Ground Magazines. Above-ground magazines must be located and designed so as to minimize the propagation of an explosion to adjacent units and to minimize other effects of any explosion.
3) Outdoor or Open Storage Areas. Outdoor or open storage areas must be located and designed so as to minimize the propagation of an explosion to adjacent units and to minimize other effects of any explosion.
c) An owner or operator must store hazardous waste munitions and explosives in accordance with a Standard Operating Procedure that specifies procedures which ensure safety, security, and environmental protection. If these procedures serve the same purpose as the security and inspection requirements of Section 725.114, the preparedness and prevention procedures of Subpart C, and the contingency plan and emergency procedures requirements of Subpart D, then the Standard Operating Procedure may be used to fulfill those requirements.
d) An owner or operator must package hazardous waste munitions and explosives to ensure safety in handling and storage.
e) An owner or operator must inventory hazardous waste munitions and explosives at least annually.
f) An owner or operator must inspect and monitor hazardous waste munitions and explosives and their storage units as necessary to ensure explosives safety and to ensure that there is no migration of contaminants out of the unit.
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.1202 Closure and Post-Closure Care
a) At closure of a magazine or unit that stored hazardous waste under this Subpart EE, the owner or operator must remove or decontaminate all waste residues, contaminated containment system components, contaminated subsoils, and structures and equipment contaminated with waste and manage them as hazardous waste, unless 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103(d) applies. The closure plan, closure activities, cost estimates for closure, and financial responsibility for magazines or units must meet all of the requirements specified in Subparts G and H, except that the owner or operator may defer closure of the unit as long as it remains in service as a munitions or explosives magazine or storage unit.
b) If, after removing or decontaminating all residues and making all reasonable efforts to effect removal or decontamination of contaminated components, subsoils, structures, and equipment as required in subsection (a), the owner or operator finds that not all contaminated subsoils can be practicably removed or decontaminated, the owner or operator must close the facility and perform post-closure care in accordance with the closure and post-closure requirements that apply to landfills (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.410).
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Section 725.Appendix A Recordkeeping Instructions
See appendix I to 40 CFR 265 (Recordkeeping Instructions), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.Appendix B EPA Report Form and Instructions (Repealed)
(Source: Repealed at 9 Ill. Reg. 11869, effective July 24, 1985)
Section 725.Appendix C USEPA Interim Primary Drinking Water Standards
See appendix III to 40 CFR 265 (EPA Interim Primary Drinking Water Standards), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.Appendix D Tests for Significance
See appendix IV to 40 CFR 265 (Tests for Significance), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.Appendix E Examples of Potentially Incompatible Wastes
See appendix V to 40 CFR 265 (Examples of Potentially Incompatible Waste), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b).
(Source: Amended at 30 Ill. Reg. 3460, effective February 23, 2006)
Section 725.APPENDIX F Compounds with Henry’s Law Constant Less Than 0.1 Y/X (at 25 ° C)
(Source: Amended at 42 Ill. Reg. 23725, effective November 19, 2018)
Compound name CAS No. Acetaldol 107-89-1 Acetamide 60-35-5 2-Acetylaminofluorene 53-96-3 3-Acetyl-5-hydroxypiperidine 3-Acetylpiperidine 618-42-8 1-Acetyl-2-thiourea 591-08-2 Acrylamide 79-06-1 Acrylic acid 79-10-7 Adenine 73-24-5 Adipic acid 124-04-9 Adiponitrile 111-69-3 Alachlor 15972-60-8 Aldicarb 116-06-3 Ametryn 834-12-8 4-Aminobiphenyl 92-67-1 4-Aminopyridine 504-24-5 Aniline 62-53-3 o-Anisidine 90-04-0 Anthraquinone 84-65-1 Atrazine 1912-24-9 Benzenearsonic acid 98-05-5 Benzenesulfonic acid 98-11-3 Benzidine 92-87-5 Benzo(a)anthracene 56-55-3 Benzo(k)fluoranthene 207-08-9 Benzoic acid 65-85-0 Benzo(g,h,i)perylene 191-24-2 Benzo(a)pyrene 50-32-8 Benzyl alcohol 100-51-6 g-BHC 58-89-9 Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate 117-81-7 Bromoxynil (3,5-Dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) 1689-84-5 Butyric acid 107-92-6 Caprolactam (hexahydro-2H-azepin-2-one) 105-60-2 Catechol (o-dihydroxybenzene) 120-80-9 Cellulose 9004-34-6 Cell wall Chlorhydrin (3-Chloro-1,2-propanediol) 96-24-2 Chloroacetic acid 79-11-8 2-Chloroacetophenone 93-76-5 p-Chloroaniline 106-47-8 p-Chlorobenzophenone 134-85-0 Chlorobenzilate 510-15-6 p-Chloro-m-cresol (6-chloro-m-cresol) 59-50-7 2-Chloroethane-1,1-diol 15873-56-0 4-Chlorophenol 106-48-9 Chlorophenol polymers (2-chlorophenol & 4-chlorophenol) 95-57-8 & 106-48-9 1-(o-Chlorophenyl)thiourea 5344-82-1 N-Chlorosuccinimide (1-chloropyrrolidine-2,5-dione) 128-09-6 Chrysene 218-01-9 Citric acid 77-92-9 Creosote 8001-58-9 m-Cresol 108-39-4 o-Cresol 95-48-7 p-Cresol 106-44-5 Cresol (mixed isomers) 1319-77-3 4-Cumylphenol 27576-86 Cyanide 57-12-5 Diazinon 333-41-5 Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene 53-70-3 Dibutylphthalate 84-74-2 2,5-Dichloroaniline (N,N’-dichloroaniline) 95-82-9 2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile 1194-65-6 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline 99-30-9 2,5-Dichlorophenol 333-41-5 3,4-Dichlorotetrahydrofuran 3511-19 Dichlorvos (DDVP) 62-73-7 Diethanolamine 111-42-2 N,N-Diethylaniline 91-66-7 Diethylene glycol 111-46-6 Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether (dimethyl Carbitol) 111-96-6 Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether (butyl Carbitol) 112-34-5 Diethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate (Carbitol acetate) 112-15-2 Diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (Carbitol Cellosolve) 111-90-0 Diethylene glycol monomethyl ether (methyl Carbitol) 111-77-3 N,N’-Diethylhydrazine 1615-80-1 Diethyl(4-methylumbelliferyl)thionophosphate 299-45-6 Diethylphosphorothioate 126-75-0 N,N’-Diethylpropionamide 15299-99-7 Dimethoate 60-51-5 2,3-Dimethoxystrychnidin-10-one 357-57-3 4-Dimethylaminoazobenzene 60-11-7 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene 57-97-6 3,3-Dimethylbenzidine 119-93-7 Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride 79-44-7 Dimethyldisulfide 624-92-0 Dimethylformamide 68-12-2 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine 57-14-7 Dimethylphthalate 131-11-3 Dimethylsulfone 67-71-0 Dimethylsulfoxide 67-68-5 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol 534-52-1 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine 122-66-7 Dipropylene glycol (1,1'-oxydi-2-propanol) 110-98-5 Endrin 72-20-8 Epinephrine 51-43-4 mono-Ethanolamine 141-43-5 Ethyl carbamate (urethane) 51-79-6 Ethylene glycol 107-21-1 Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether (butyl Cellosolve) 111-76-2 Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether (Cellosolve) 110-80-5 Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate (Cellosolve acetate) 111-15-9 Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (methyl Cellosolve) 109-86-4 Ethylene glycol monophenyl ether (phenyl Cellosolve) 122-99-6 Ethylene glycol monopropyl ether (propyl Cellosolve) 2807-30-9 Ethylene thiourea (2-imidazolidinethione) 96-45-7 4-Ethylmorpholine 100-74-3 3-Ethylphenol 620-17-7 Fluoroacetic acid, sodium salt 62-74-8 Formaldehyde 50-00-0 Formamide 75-12-7 Formic acid 64-18-6 Fumaric acid 110-17-8 Glutaric acid 110-94-1 Glycerin (Glycerol) 56-81-5 Glycidol 556-52-5 Glycinamide 598-41-4 Glyphosate 1071-83-6 Guthion 86-50-0 Hexamethylene-1,6-diisocyanate (1,6-diisocyanatohexane) 822-06-0 Hexamethyl phosphoramide 680-31-9 Hexanoic acid 142-62-1 Hydrazine 302-01-2 Hydrocyanic acid 74-90-8 Hydroquinone 123-31-9 Hydroxy-2-propionitrile (hydracrylonitrile) 109-78-4 Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene 193-39-5 Lead acetate 301-04-2 Lead subacetate (lead acetate, monobasic) 1335-32-6 Leucine 61-90-5 Malathion 121-75-5 Maleic acid 110-16-7 Maleic anhydride 108-31-6 Mesityl oxide 141-79-7 Methane sulfonic acid 75-75-2 Methomyl 16752-77-5 p-Methoxyphenol 150-76-5 Methylacrylate 96-33-3 2-(Methylamino)acetic acid (sarcosine, N-methylglycine) 107-97-1 Methyl bromochloroacetate 20428-74-4 Methyl-4-(cyanomethyl)benzoate 76469-88-0 4,4'-Methylene-bis-(2-chloroaniline) 101-14-4 4,4'-Methylenediphenyl diisocyanate (diphenyl methane diisocyanate) 101-68-8 4,4'-Methylenedianiline (MDA) 101-77-9 5-Methylfurfural 620-02-0 Methylhydrazine 60-34-4 Methyl methane sulfonate 66-27-3 Methylparathion 298-00-0 Methyl sulfuric acid (sulfuric acid, dimethyl ester) 77-78-1 4-Methylthiophenol 106-45-6 Monomethylformamide (N-methylformamide) 123-39-7 Nabam 142-59-6 a-Naphthol 90-15-3 b-Naphthol 135-19-3 a-Naphthylamine 134-32-7 b-Naphthylamine 91-59-8 Neopentyl glycol 126-30-7 Niacinamide 98-92-0 o-Nitroaniline 88-74-4 Nitroglycerin 55-63-0 2-Nitrophenol 88-75-5 4-Nitrophenol 100-02-7 N-Nitrosodimethylamine 62-75-9 Nitrosoguanidine 674-81-7 N-Nitroso-n-methylurea 684-93-5 N-Nitrosomorpholine (4-nitrosomorpholine) 59-89-2 Oxalic acid 144-62-7 Parathion 56-38-2 Pentaerythritol 115-77-5 Phenacetin 62-44-2 Phenol 108-95-2 Phenylacetic acid 103-82-2 m-Phenylene diamine 108-45-2 o-Phenylene diamine 95-54-5 p-Phenylene diamine 106-50-3 Phenyl mercuric acetate 62-38-4 Phorate 298-02-2 Phthalic anhydride 85-44-9 a-Picoline (2-methyl pyridine) 109-06-8 1,3-Propane sulfone 1120-71-4 b-Propiolactone 57-57-8 Propoxur (Baygon) 2-(1-methylethoxy)phenol N-methylcarbamate 114-26-1 Propylene glycol 57-55-6 Pyrene 129-00-0 Pyridinium bromide 39416-48-3 Quinoline 91-22-5 Quinone (p-benzoquinone) 106-51-4 Resorcinol 108-46-3 Simazine 122-34-9 Sodium acetate 127-09-3 Sodium formate 141-53-7 Strychnine 57-24-9 Succinic acid 110-15-6 Succinimide 123-56-8 Sulfanilic acid 121-47-1 Terephthalic acid 100-21-0 Tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate 3689-24-5 Tetraethylenepentamine 112-57-2 Thiofanox 39196-18-4 Thiosemicarbazide 79-19-6 2,4-Toluenediamine 95-80-7 2,6-Toluenediamine 823-40-5 3,4-Toluenediamine 496-72-0 2,4-Toluene diisocyanate 584-84-9 p-Toluic acid 99-94-5 m-Toluidine 108-44-1 1,1,2-Trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane 76-13-1 Triethanolamine 102-71-6 Triethylene glycol dimethyl ether (2,5,8,11-tetraoxadodecane, 1-methoxy-2-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)ethane) 112-49-2 Tripropylene glycol 24800-44-0 Warfarin 81-81-2 3,4-Xylenol (3,4-dimethylphenol) 95-65-8