SUBPART A: GENERAL PROVISIONS
Section 704.101 Content
The regulations in this Subpart A set forth the specific requirements for the UIC (Underground Injection Control) permit program. These rules are intended to implement the UIC permit requirement of Section 12(g) of the Environmental Protection Act (Act) [415 ILCS 5/12(g)]. These rules are intended to be identical in substance to United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) rules found in 40 CFR 144. The regulations in this Subpart A are supplemental to the requirements in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, which contains requirements for both the RCRA and UIC permit programs. Operating requirements for injection wells are included in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.1 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.102 Scope of the Permit or Rule Requirement
Although six classes of wells are set forth in Section 704.106, the UIC (Underground Injection Control) permit program described in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 704, 705, and 730 regulates underground injection for only five classes of wells (see definition of “well injection,” 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110). Class II wells (Section 704.106(b)) are not subject to the requirements found in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702, 704, 705, and 730. The UIC permit program for Class II wells is regulated by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines and Minerals, Oil and Gas Division, pursuant to the Illinois Oil and Gas Act [225 ILCS 725] (see 62 Ill. Adm. Code 240). The owner or operator of a Class I, Class III, Class IV, or Class V injection well must be authorized either by permit or by rule. In carrying out the mandate of the SDWA, this Part provides that no injection may be authorized by permit or by rule if it results in movement of fluid containing any contaminant into underground sources of drinking water (USDWs) (Section 704.122), if the presence of that contaminant may cause a violation of any primary drinking water regulation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611, or if the presence of that contaminant may adversely affect the health of persons (Section 704.122). Section 704.124 prohibits the construction, operation, or maintenance of a Class IV injection well. A Class V injection well is regulated under Subpart I of this Part. If remedial action appears necessary for a Class V injection well, an individual permit may be required (Subpart C of this Part) or the Agency must require remedial action or closure by order (see Section 704.122(c)).
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.1(g) preamble (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.103 Identification of Aquifers
During UIC program development, the Agency may identify aquifers and portions of aquifers that are actual or potential sources of drinking water. This identification will provide an aid to the Agency in carrying out its duty to protect all USDWs. An aquifer is a USDW if it fits the definition in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110, even if it has not been identified by the Agency.
BOARD NOTE: See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.106. Derived from 40 CFR 144.1(g) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.104 Exempted Aquifers
The Board may designate “exempted aquifers” using criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730. Such an aquifer is one that would otherwise qualify as a USDW to be protected, but which has no real potential to be used as a source of drinking water. Therefore they are not USDWs. No aquifer is an exempted aquifer until it has been affirmatively designated under the procedures set forth in Section 704.123. An aquifer that does not fit the definition of a USDW is not an exempted aquifer. It is simply not subject to the special protection afforded a USDW. During initial Class VI injection well program development, the areal extent of an existing Class II enhanced oil recovery or enhanced gas recovery aquifer exemption for Class VI injection wells must not be expanded. All Class II to Class VI injection well aquifer exemption expansions previously issued must be incorporated into the Class VI injection well program descriptions required by USEPA pursuant to 40 CFR 145.23(f)(9).
BOARD NOTE: See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.105. Derived from 40 CFR 144.1(g) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.105 Specific Inclusions and Exclusions
a) The following wells are included among those types of injection activities that are covered by the UIC regulations. (This list is not intended to be exclusive but is for clarification only.)
1) Any injection well located on a drilling platform inside territorial waters of the State of Illinois;
2) Any dug hole or well that is deeper than its largest surface dimension, where the principal function of the hole is emplacement of fluids;
3) Any well used by generators of hazardous waste, or by owners or operators of hazardous waste management facilities, to dispose of fluids containing hazardous waste. This includes the disposal of hazardous waste into what would otherwise be a septic system or cesspool, regardless of its capacity;
4) Any septic tank, cesspool, or other well used by a multiple dwelling, community, or regional system for the injection of wastes.
b) The following are not covered by this Part:
1) An injection well located on a drilling platform or other site that is beyond the territorial waters of the State of Illinois;
2) An individual or single family residential waste disposal system, such as a domestic cesspool or septic system;
3) A nonresidential cesspool, septic system, or similar waste disposal system if such system is used solely for the disposal of sanitary waste, and has the capacity to serve fewer than 20 persons a day;
4) An injection well used for injection of hydrocarbons that are of pipeline quality and are gases at standard temperature and pressure for the purpose of storage;
5) Any dug hole, drilled hole, or bored shaft that is not used for the subsurface emplacement of fluids;
6) A Class II injection well.
c) The prohibition applicable to a Class IV injection well under Section 704.124 does not apply to injection of hazardous wastes into an aquifer or portion of an aquifer that has been exempted pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.1(g)(1) through (g)(3) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.106 Classification of Injection Wells
Injection wells are classified as follows:
a) Class I injection wells. Any of the following is a Class I injection well:
1) A well used by a generator of hazardous waste or the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management facility to inject hazardous waste beneath the lowermost formation containing a USDW within 402 meters (one-quarter mile) of the well bore.
2) Any other industrial and municipal disposal well that injects fluids beneath the lowermost formation containing a USDW within 402 meters (one-quarter mile) of the well bore.
3) A radioactive waste disposal well that injects fluids below the lowermost formation containing a USDW within 402 meters (one-quarter mile) of the well bore.
b) Class II injection wells. Any well that injects any of the following fluids is a Class II injection well:
1) Fluids that are brought to the surface in connection with natural gas storage operations, or conventional oil or natural gas production, and which may be commingled with waste waters from gas plants that are an integral part of production operations, unless those waters are classified as a hazardous waste at the time of injection;
2) Fluids injected for enhanced recovery of oil or natural gas; and
3) Fluids injected for storage of hydrocarbons that are liquid at standard temperature and pressure.
c) Class III injection wells. Any well that injects fluids for the extraction of minerals, including the following:
1) The mining of sulfur by the Frasch process;
2) The in-situ production of uranium or other metals. This category includes only in-situ production from ore bodies that have not been conventionally mined. Solution mining of conventional mines, such as stopes leaching, is included as a Class V injection well; and
3) Solution mining of salts or potash.
d) Class IV injection wells. Any of the following is a Class IV injection well:
1) A well used by a generator of hazardous waste or of radioactive waste, by the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management facility or by the owner or operator of a radioactive waste disposal site to dispose of hazardous wastes or radioactive wastes into a formation that contains a USDW within 402 meters (one-quarter mile) of the well.
2) A well used by a generator of hazardous waste or of radioactive waste, by the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management facility, or by the owner or operator of a radioactive waste disposal site to dispose of hazardous waste or radioactive waste above a formation that contains a USDW within 402 meters (one-quarter mile) of the well.
3) A well used by a generator of hazardous waste or the owner or operator of a hazardous waste management facility to dispose of hazardous waste that cannot be classified under any of subsections (a)(1), (d)(1), or (d)(2) of this Section (e.g., a well that is used to dispose of hazardous waste into or above a formation that contains an aquifer that has been exempted pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104).
e) Class V injection wells. Any injection well that is not classified as a Class I, II, III, IV, or VI injection well. Section 704.281 describes specific types of Class V injection wells.
f) Class VI injection wells.
1) An injection well that is not experimental in nature which is used for geologic sequestration of carbon dioxide beneath the lowermost formation containing a USDW;
2) An injection well that is used for geologic sequestration of carbon dioxide which has been granted a permit that includes alternative injection well depth requirements pursuant to Section 730.195; or
3) An injection well that is used for geologic sequestration of carbon dioxide which has received an expansion to the areal extent of an existing Class II enhanced oil recovery or enhanced gas recovery aquifer exemption pursuant to Section 704.123(d) and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.6 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.107 Definitions
The definitions of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 apply to this Part. Specific types of Class V injection wells are described in Section 704.281.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.3 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.108 Electronic Reporting
The filing of any document pursuant to any provision of this Part as an electronic document is subject to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.104.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 3 and 145.11(a)(33), as added at 70 Fed. Reg. 59848 (Oct. 13, 2005).
(Source: Added at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
SUBPART B: PROHIBITIONS
Section 704.121 Prohibition Against Unauthorized Injection
Any underground injection, except into a well authorized by permit or rule issued pursuant to this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705 is prohibited. The construction of any well required to have a permit under this Part is prohibited until the permit has been issued.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.11 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.122 Prohibition Against Movement of Fluid into USDW
a) No owner or operator may construct, operate, maintain, convert, plug, abandon, or conduct any other injection activity in a manner that allows the movement of fluid containing any contaminant into a USDW, if the presence of that contaminant could cause a violation of any national primary drinking water regulation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611 (derived from 40 CFR 141) or could otherwise adversely affect the health of persons. The applicant for a permit has the burden of showing that the requirement of this subsection (a) is met.
b) For a Class I, III, or VI injection well, if any water quality monitoring of a USDW indicates the movement of any contaminant into the USDW, except as authorized under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730, the Agency must prescribe such additional requirements for construction, corrective action, operation, monitoring or reporting (including closure of the injection well) as are necessary to prevent such movement. In the case of a well authorized by permit, these additional requirements must be imposed by modifying the permit in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.183 through 702.185, or appropriate enforcement action may be taken if the permit has been violated, and the permit may be subject to revocation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.186 if cause exists. In the case of wells authorized by rule, see Section 704.141 through 704.146.
c) For a Class V injection well, if at any time the Agency learns that a Class V injection well could cause a violation of any national primary drinking water regulation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611 (derived from 40 CFR 141), it must undertake one of the following actions:
1) It must require the injector to obtain an individual permit;
2) It must issue a permit that requires the injector to take such actions (including, where necessary, closure of the injection well) as may be necessary to prevent the violation; or
3) It may initiate enforcement action.
d) Whenever the Agency learns that a Class V injection well may be otherwise adversely affecting the health of persons, it may prescribe such actions as may be necessary to prevent the adverse effect, including any action authorized under subsection (c) of this Section.
e) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Section, the Agency may take emergency action upon receipt of information that a contaminant that is present in or is likely to enter a public water system or a USDW may present an imminent and substantial endangerment to the health of persons. The Agency may declare an emergency and affix a seal pursuant to Section 34 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/34].
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.12 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.123 Identification of USDWs and Exempted Aquifers
a) The Agency may identify (by narrative description, illustrations, maps, or other means) and must protect as a USDW, any aquifer or part of an aquifer that meets the definition of a USDW set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110, except as one of the exceptions of subsections (a)(1) and (a)(2) of this Section applies Other than Agency-approved aquifer exemption expansions that meet the criteria set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104, a new aquifer exemption must not be issued for a Class VI injection well. Even if an aquifer has not been specifically identified by the Agency, it is a USDW if it meets the definition in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.110. Identification of USDWs must be made according to criteria adopted by the Agency pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.106.
1) The Agency may not identify an aquifer or part of an aquifer as a USDW to the extent that there is an applicable aquifer exemption under subsection (b) of this Section.
2) The Agency may not identify an aquifer or part of an aquifer as a USDW to the extent that the aquifer or part of an aquifer is an expansion to the areal extent of an existing Class II enhanced oil recovery or is subject to an enhanced gas recovery aquifer exemption for the exclusive purpose of Class VI injection for geologic sequestration under subsection (d) of this Section.
b) Identification of an exempted aquifer.
1) The Agency may identify (by narrative description, illustrations, maps, or other means) and describe in geographic or geometric terms (such as vertical and lateral limits and gradient) that are clear and definite, any aquifer or part of an aquifer that the Agency desires the Board to designate as an exempted aquifer using the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104, as described in this subsection (b).
2) No designation of an exempted aquifer may be final until approved by USEPA as part of the State program.
3) Subsequent to program approval, the Board may identify additional exempted aquifers.
4) Identification of exempted aquifers must be by rulemaking pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 102 and 702.105 and Sections 27 and 28 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/27 and 28], considering the criteria set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104.
c) For a Class III injection well, an applicant for a permit that necessitates an aquifer exemption under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104(b)(1) must furnish the data necessary to demonstrate that the aquifer is expected to be mineral or hydrocarbon producing. Information contained in the mining plan for the proposed project, such as a map and general description of the mining zone, general information on the mineralogy and geochemistry of the mining zone, analysis of the amenability of the mining zone to the proposed mining method, and a timetable of planned development of the mining zone must be considered by the Board in addition to the information required by Section 704.161(c). Approval of the exempted aquifer must be by rulemaking pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 102 and 702.105 and Sections 27 and 28 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/27 and 28]. Rules will not become final until approved by USEPA as a program revision.
d) Expansion to the Areal Extent of Existing Class II Aquifer Exemptions for Class VI Wells. The owner or operator of a Class II enhanced oil recovery or enhanced gas recovery well may request that the Agency approve an expansion to the areal extent of an aquifer exemption already in place for a Class II enhanced oil recovery or enhanced gas recovery well for the exclusive purpose of Class VI injection for geologic sequestration. A request for areal expansion must be treated as a revision to the applicable federal UIC program under 40 CFR 147 or as a substantial program revision to an approved state UIC program under 40 CFR 145.32 and will not be final until approved by USEPA.
1) The request for an expansion of the areal extent of an existing aquifer exemption for the exclusive purpose of Class VI injection for geologic sequestration must define (by narrative description, illustrations, maps, or other means) and describe in geographic or geometric terms (such as vertical and lateral limits and gradient) that are clear and definite, all aquifers or parts of aquifers that are requested to be designated as exempted using the criteria in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104.
2) In making a determination to expand the areal extent of an aquifer exemption of a Class II enhanced oil recovery or enhanced gas recovery well for the purpose of Class VI injection, the Agency must determine that the request meets the criteria for exemptions in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104. In evaluating a request, the Agency must consider:
A) Any current and potential future use of the USDWs to be exempted as drinking water resources;
B) The predicted extent of the injected carbon dioxide plume, and any mobilized fluids that may result in degradation of water quality, over the lifetime of the geologic sequestration project, as informed by computational modeling performed pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.184(c)(1), in order to ensure that the proposed injection operation will not at any time endanger USDWs including non-exempted portions of the injection formation;
C) Whether the areal extent of the expanded aquifer exemption is of sufficient size to account for any possible revisions to the computational model during reevaluation of the area of review, pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.184(e); and
D) Any information submitted to support a request by the owner or operator for a permit that includes alternative injection well depth requirements pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.195, if appropriate.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.7 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.124 Prohibition Against Class IV Injection Wells
a) The following are prohibited, except as provided in subsection (c) of this Section:
1) The construction of any Class IV injection well.
2) The operation or maintenance of any Class IV injection well.
3) Any increase in the amount of hazardous waste or change in the type of hazardous waste injected into a Class IV injection well.
b) A Class IV injection well must comply with the requirements of Section 704.203 and the Class IV injection well closure requirements of Section 704.145.
c) A well used to inject contaminated groundwater that has been treated and is being reinjected into the same formation from which it was originally drawn is not prohibited by this Section if such injection is approved by the Agency pursuant to provisions in the Act for preventive or corrective action, by the USEPA pursuant to provisions for cleanup of releases under the Comprehensive Environmental Response Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA) (42 USC 9601 et seq.), by USEPA pursuant to requirements and provisions under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) (42 USC 6901 et seq.), or by the Agency pursuant to Section 39 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/39].
d) Clarification. This Section does not prohibit any of the following injection wells:
1) A well used to inject hazardous waste into an aquifer or a portion of an aquifer that has been exempted pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104 if the exempted aquifer into which waste is injected underlies the lowermost formation containing a USDW. Such a well is a Class I injection well, as specified in Section 704.106(a)(1), and the owner or operator must comply with the requirements applicable to a Class I injection well.
2) A well used to inject hazardous waste where no USDW exists within one quarter mile of the well bore in any underground formation, provided that the Agency determines that such injection is into a formation sufficiently isolated to ensure that injected fluids do not migrate from the injection zone. Such a well is a Class I injection well, as specified in Section 704.106(a)(1), and the owner or operator must comply with the requirements applicable to a Class I injection well.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.13 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.125 Prohibition Against Non-Experimental Class V Injection Wells for Geologic Sequestration
The construction, operation, or maintenance of any non-experimental Class V geologic sequestration well is prohibited.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.15 (2011).
(Source: Added at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.128 Requirements for Class VI Injection Wells
The owner or operator of a Class VI injection well must obtain a permit. A Class VI well cannot be authorized by rule to inject carbon dioxide.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.18 (2011).
(Source: Added at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.129 Transitioning from a Class II Injection Well to a Class VI Injection Well
a) The owner or operator of a Class II injection well that is injecting carbon dioxide into an oil and gas reservoir for the primary purpose of long-term storage must apply for and obtain a Class VI injection well geologic sequestration permit when there is an increased risk to a USDW compared to usual Class II injection well operations. In determining if there is an increased risk to a USDW, the owner or operator must consider the factors specified for Agency consideration in subsection (b) of this Section.
b) The Agency must determine when there is an increased risk to a USDW from injecting carbon dioxide into an oil and gas reservoir for the primary purpose of long-term storage compared to usual Class II injection well operations and that a Class VI injection well permit is required. In order to make this determination, the Agency must consider the following factors:
1) Any increase in reservoir pressure within the injection zones;
2) Any increase in carbon dioxide injection rates;
3) Any decrease in reservoir production rates;
4) The distance between the injection zones and USDWs;
5) The suitability of the Class II injection well area of review delineation;
6) The quality of abandoned well plugs within the area of review;
7) The owner’s or operator’s plan for recovery of carbon dioxide after the cessation of injection;
8) The source and properties of injected carbon dioxide; and
9) Any additional site-specific factors that the Agency determines are necessary to determine whether the injection poses greater risk than usual Class II operations.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.19 (2011).
(Source: Added at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
SUBPART C: AUTHORIZATION OF UNDERGROUND INJECTION BY RULE
Section 704.141 Existing Class I and III Injection Wells
a) Injection into an existing Class I or Class III injection well is authorized by rule if the owner or operator fulfills either of the conditions of subsection (a)(1) or (a)(2) of this Section, subject to subject (a)(3) of this Section:
1) It injected into the existing well within one year after March 3, 1984, or
2) It inventories the well pursuant to Section 704.148.
3) The owner or operator of a well that is authorized by rule pursuant to this Section must rework, operate, maintain, convert, plug, abandon, or inject into the well in compliance with applicable regulations.
b) Class III injection wells in existing fields or projects. Notwithstanding the prohibition in Section 704.121, this Section authorizes Class III injection wells or projects in existing fields or projects to continue normal operations until permitted, including construction, operation, and plugging and abandonment of wells as part of the operation provided the owner or operator maintains compliance with all applicable requirements.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.21(a) and (d) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.142 Prohibitions Against Injection into Wells Authorized by Rule
An owner or operator of a well authorized by rule pursuant to this Subpart C is prohibited from injecting into the well on the occurrence of any of the following:
a) Upon the effective date of an applicable permit denial;
b) Upon a failure to submit a permit application in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.147 or 704.161;
c) Upon a failure to submit inventory information in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.148;
d) Upon a failure to comply with a request for information in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.149;
e) Upon a failure to provide alternative financial assurance pursuant to Section 704.150(d)(6);
f) 48 hours after receipt of a determination by the Agency pursuant to Section 704.150(f)(3) that the well lacks mechanical integrity, unless the Agency orders immediate cessation pursuant to Section 34 of the Act or as ordered by a court pursuant to Section 43 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/43];
g) Upon receipt of notification from the Agency that the transferee has not demonstrated financial assurance pursuant to Section 704.150(d);
h) For Class I and Class III injection wells: after March 3, 1989, unless a timely and complete permit application for a permit was pending the Agency’s decision; or
i) This subsection (i) corresponds with 40 CFR 144.21(c)(9), a provision related to Class II injection wells, which are regulated by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines and Minerals, and not by the Board. This statement maintains structural consistency with USEPA rules.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.21(c) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.143 Expiration of Authorization
The authorization provided in Section 704.141 expires upon the earliest of the following events:
a) Upon the effective date of a permit issued pursuant to any of Sections 704.147, 704.161, 704.162, or 704.163;
b) After plugging or abandonment in accordance with an approved plugging and abandonment plan pursuant to Section 704.150(c) and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110, and upon submission of a plugging and abandonment report pursuant to Section 704.150(k); or
c) Upon conversion in compliance with Section 704.150(j).
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.21(b) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.144 Requirements
Any person authorized by rule under Section 704.141 must comply with the applicable requirements of Section 704.148 and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.21(e) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.145 Existing Class IV Injection Wells
a) Injection into a Class IV injection well, as defined in Section 704.106(d)(1), is not authorized. The owner or operator of any such well must comply with Sections 704.124 and 704.203.
b) Closure.
1) Prior to abandoning any Class IV injection well, the owner or operator must plug or otherwise close the well in a manner acceptable to the Agency.
2) By September 27, 1986, the owner and operator of any Class IV injection well was to have submitted to the Agency a plan for plugging or otherwise closing and abandoning the well.
3) The owner or operator of a Class IV injection well must notify the Agency of intent to abandon the well at least 30 days prior to abandonment.
c) Notwithstanding subsections (a) and (b) of this Section, an injection well that is used to inject contaminated groundwater that has been treated and which is being injected into the same formation from which it was drawn is authorized by rule for the life of the well if such subsurface emplacement of fluids is approved by USEPA pursuant to provisions for cleanup of releases under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA) (42 USC 9601 et seq.), by USEPA pursuant to requirements and provisions under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) (42 USC 6901 et seq.), or by the the Agency pursuant to Section 39 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/39].
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.23 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.146 Class V Injection Wells
a) A Class V injection well is authorized by rule, subject to the conditions set forth in Section 704.284.
b) Duration of well authorization by rule. Well authorization under this Section expires upon the effective date of a permit issued pursuant to any of Sections 704.147, 704.161, 704.162, or 704.163.
c) Prohibition of injection. An owner or operator of a well that is authorized by rule pursuant to this Section is prohibited from injecting into the well on the occurrence of any of the following:
1) Upon the effective date of an applicable permit denial;
2) Upon a failure to submit a permit application in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.147 or 704.161;
3) Upon a failure to submit inventory information in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.148; or
4) Upon a failure to comply with a request for information in a timely manner pursuant to Section 704.149.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.24 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.147 Requiring a Permit
a) The Agency may require the owner or operator of any Class I, Class III, or Class V injection well that is authorized by rule under this Subpart C to apply for and obtain an individual or area UIC permit. Cases where individual or area UIC permits may be required include the following:
1) The injection well is not in compliance with any requirement of this Subpart C;
BOARD NOTE: Any underground injection that violates any rule under this Subpart C is subject to appropriate enforcement action.
2) The injection well is not or no longer is within the category of wells and types of well operations authorized in the rule;
3) The protection of USDWs requires that the injection operation be regulated by requirements, such as for corrective action, monitoring and reporting, or operation, that are not contained in this Subpart C; or
4) When the injection well is a Class I or Class III injection well, in accordance with a schedule established by the Agency pursuant to Section 704.161(b).
b) The Agency may require the owner or operator of any well that is authorized by rule under this Subpart C to apply for an individual or area UIC permit under this subsection (b) only if the owner or operator has been notified in writing that a permit application is required. The owner or operator of a well that is authorized by rule is prohibited from injecting into the well on the occurrence of either of the circumstances of subsection (b)(1) or (b)(2) of this Section, subject to subsection (b)(3) of this Section.
1) Upon the effective date of a permit denial; or
2) Upon the failure of the owner or operator to submit an application in a timely manner as specified in the notice.
3) The notice must include all of the following:
A) A brief statement of the reasons for this decision;
B) An application form;
C) A statement setting a time for the owner or operator to file the application; and
D) A statement of the consequences of denial or issuance of the permit, or failure to submit an application, as described in this subsection (b).
c) An owner or operator of a well that is authorized by rule may request to be excluded from the coverage of the rule by applying for an individual or area UIC permit. The owner or operator must submit to the Agency an application under Section 704.161 with reasons supporting the request. The Agency may grant any such request.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.25 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.148 Inventory Requirements
The owner or operator of an injection well that is authorized by rule under this Subpart C must submit inventory information to the Agency. Such an owner or operator is prohibited from injecting into the well upon failure to submit inventory information for the well to the Agency within the time frame specified in subsection (d) of this Section.
a) Contents. As part of the inventory, the owner or operator must submit at least the following information:
1) The facility name and location;
2) The name and address of legal contact;
3) The ownership of facility;
4) The nature and type of injection wells; and
5) The operating status of injection wells.
BOARD NOTE: This information is requested on national form “Inventory of Injection Wells,” USEPA Form 7520-16, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a).
b) Additional contents. The owner or operator of a well listed in subsection (b)(1) of this Section must provide the information listed in subsection (b)(2) of this Section.
1) This Section applies to the following wells:
A) Corresponding 40 CFR 144.26(b)(1)(i) pertains to Class II injection wells, which are regulated by the Department of Natural Resources pursuant to the Illinois Oil and Gas Act [225 ILCS 725] (see 62 Ill. Adm. Code 240). This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal provisions;
B) Class IV injection wells;
C) The following types of Class V injection wells:
i) A sand or other backfill well, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.105(e)(8);
ii) A radioactive waste disposal well that is not a Class I injection well, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.105(e)(11);
iii) A geothermal energy recovery well, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.105(e)(12);
iv) A brine return flow well, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.105(e)(14);
v) A well used in an experimental technology, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.105(e)(15);
vi) A municipal or industrial disposal well other than a Class I injection well; and
vii) Any other Class V injection well, at the discretion of the Agency.
2) The owner or operator of a well listed in subsection (b)(1) of this Section must provide a listing of all wells owned or operated setting forth the following information for each well. (A single description of wells at a single facility with substantially the same characteristics is acceptable.)
A) Corresponding 40 CFR 144.26(b)(2)(i) pertains to Class II wells, which are regulated by the Department of Natural Resources pursuant to the Illinois Oil and Gas Act [225 ILCS 725] (see 62 Ill. Adm. Code 240). This statement maintains structural consistency with the corresponding federal provisions;
B) The location of each well or project given by Township, Range, Section, and Quarter-Section;
C) The date of completion of each well;
D) Identification and depth of the formations into which each well is injecting;
E) The total depth of each well;
F) The casing and cementing record, tubing size, and depth of packer;
G) The nature of the injected fluids;
H) The average and maximum injection pressure at the wellhead;
I) The average and maximum injection rate; and
J) The date of the last mechanical integrity tests, if any.
c) This subsection (c) corresponds with 40 CFR 144.26(c), a provision relating to USEPA notification to facilities upon authorization of the state’s program. This statement maintains structural consistency with USEPA rules.
d) Deadlines. The owner or operator of an injection well must submit inventory information no later than March 3, 1985. The Agency need not require inventory information from any facility with RCRA interim status under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.
e) Deadlines for a Class V injection well.
1) The owner or operator of a Class V injection well in which injection took place before March 3, 1985, and who failed to submit inventory information for the well within the time specified in subsection (d) of this Section may resume injection 90 days after submittal of the inventory information to the Agency, unless the owner or operator receives notice from the Agency that injection may not resume or that it may resume sooner.
2) The owner or operator of a Class V injection well in which injection started later than March 3, 1985, must submit inventory information prior to May 2, 1995.
3) The owner or operator of a Class V injection well in which injection started after May 2, 1994 must submit inventory information prior to starting injection.
4) The owner or operator of a Class V injection well prohibited from injecting for failure to submit inventory information for the well within the time specified in subsection (e)(2) or (e)(3) of this Section may resume injection 90 days after submittal of the inventory information to the Agency, unless the owner or operator receives notice from the Agency that injection may not resume, or that it may resume sooner.
BOARD NOTE: A well that was in existence as of March 3, 1984, was required to submit inventory information by March 3, 1985. Since all wells other than a Class V injection well is now either prohibited or required to file a permit application, the inventory requirement will apply only to a new Class V injection well.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.26 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.149 Requiring other Information
a) In addition to the inventory requirements of Section 704.148, the Agency may require the owner or operator of any well authorized by rule under this Subpart C to submit information as deemed necessary by the Agency to determine whether a well may be endangering a USDW in violation of Section 704.122.
b) Such information requirements may include, but are not limited to the following:
1) Performance of groundwater monitoring and the periodic submission of reports of such monitoring;
2) An analysis of injected fluids, including periodic submission of such analyses; and
3) A description of the geologic strata through and into which injection is taking place.
c) Any request for information under this Section must be made in writing, and include a brief statement of the reasons for requiring the information. An owner or operator must submit the information within the time periods provided in the notice. d) An owner or operator of an injection well authorized by rule under this Subpart C is prohibited from injecting into the well upon failure of the owner or operator to comply with a request for information within the time period specified by the Agency pursuant to subsection (c) of this Section. An owner or operator of a well prohibited from injection under this Section may not resume injection, except under a permit issued pursuant to any of Sections 704.147, 704.161, 704.162, or 704.163. BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.27 (2005). Section 704.150 Requirements for Class I and III Injection Wells Authorized by Rule
The following requirements apply to the owner or operator of a Class I or Class III well authorized by rule under this Subpart C, as provided by Section 704.144.
a) The owner or operator must comply with all applicable requirements of this Subpart C and with Sections 704.121, 704.122, 704.124, 704.201, 704.202, and 704.203. Any noncompliance with these requirements constitutes a violation of the Act and SDWA and is grounds for enforcement action, except that the owner or operator need not comply with these requirements to the extent and for the duration such noncompliance is authorized by an emergency permit under Section 704.163.
b) Twenty-four hour reporting. The owner or operator must report any noncompliance that may endanger health or the environment, including either of the events described in subsection (b)(1) or (b)(2) of this Section, subject to the conditions of subsection (b)(3) of this Section:
1) Any monitoring or other information that indicates that any contaminant may cause an endangerment to a USDW; or
2) Any noncompliance or malfunction of the injection system that may cause fluid migration into or between USDWs.
3) Any information must be provided orally within 24 hours from the time the owner or operator becomes aware of the circumstances. A written submission must also be provided within five days of the time the owner or operator becomes aware of the circumstances. The written submission must contain a description of the noncompliance and its cause; the period of noncompliance, including exact dates and times, and if the noncompliance has not been corrected, the anticipated time it is expected to continue; and steps taken or planned to reduce, eliminate, and prevent recurrence of the noncompliance.
c) Plugging and abandonment plan.
1) The owner or operator must prepare, maintain, and comply with a plan for plugging and abandonment of the wells or project that meets the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110. For purposes of this subsection (c), temporary intermittent cessation of injection operations is not abandonment.
2) Submission of plan.
A) The owner or operator must submit the plan on any forms prescribed by the Agency.
B) The owner or operator must submit any proposed significant revision to the method of plugging reflected in the plan no later than the notice of plugging required by subsection (i) of this Section (i.e., 45 days prior to plugging, unless shorter notice is approved).
C) The plan must include the following information:
i) The nature and quantity and material to be used in plugging;
ii) The location and extent (by depth) of the plugs;
iii) Any proposed test or measurement to be made;
iv) The amount, size, and location (by depth) of casing to be left in the well;
v) The method and location where casing is to be parted; and
vi) The estimated cost of plugging the well.
D) After a cessation of operations of two years, the owner or operator must plug and abandon the well in accordance with the plan, unless the owner or operator performs both of the following actions:
i) It provides written notice to the Agency; and
ii) It describes actions or procedures, satisfactory to the Agency that the owner or operator will take to ensure that the well will not endanger a USDW during the period of temporary abandonment. These actions and procedures must include compliance with the technical requirements applicable to active injection wells, unless the operator obtains regulatory relief in the form of a variance or adjusted standard from the technical requirements pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104 and Title IX of the Act [415 ILCS 5/Title IX].
E) The owner or operator of any well that has been temporarily abandoned (ceased operations for more than two years and which has met the requirements of subsections (c)(2)(D)(i) and (c)(2)(D)(ii)) of this Section must notify the Agency in writing prior to resuming operation of the well.
d) Financial responsibility.
1) The owner or operator or transferor of a Class I or Class III injection well is required to demonstrate and maintain financial responsibility and resources to close, plug, and abandon the underground injection operation in a manner acceptable to the Agency until one of the following has occurred:
A) The well has been plugged and abandoned in accordance with an approved plugging and abandonment plan pursuant to subsection (c) of this Section and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110 and submission of a plugging and abandonment report has been made pursuant to subsection (k) of this Section;
B) The well has been converted in compliance with subsection (j) of this Section; or
C) The transferor has received notice from the Agency that the transferee has demonstrated financial responsibility for the well. The owner or operator must show evidence of such financial responsibility to the Agency by the submission of a surety bond or other adequate assurance, such as a financial statement.
2) The owner or operator was to have submitted such evidence no later than March 3, 1985. Where the ownership or operational control of the well was transferred later than March 3, 1985, the transferee must submit such evidence no later than the date specified in the notice required pursuant to subsection (l)(2) of this Section.
3) The Agency may require the owner or operator to submit a revised demonstration of financial responsibility if the Agency has reason to believe that the original demonstration is no longer adequate to cover the cost of closing, plugging, and abandoning the well.
4) The owner or operator of a well injecting hazardous waste must comply with the financial responsibility requirements of Subpart G of this Part.
5) An owner or operator must notify the Agency by certified mail of the commencement of any voluntary or involuntary proceeding under Title 11 (Bankruptcy) of the United States Code that names the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 business days after the commencement of the proceeding. Any party acting as guarantor for the owner or operator for the purpose of financial responsibility must so notify the Agency if the guarantor is named as debtor in any such proceeding.
6) In the event of commencement of a proceeding specified in subsection (d)(5) of this Section, an owner or operator that has furnished a financial statement for the purpose of demonstrating financial responsibility pursuant to this Section will be deemed to be in violation of this subsection (d) until an alternative financial assurance demonstration acceptable to the Agency is provided either by the owner or operator or by its trustee in bankruptcy, receiver, or other authorized party. All parties must be prohibited from injecting into the well until such alternative financial assurance is provided.
e) This subsection (e) corresponds with 40 CFR 144.28(e), which pertains exclusively to enhanced recovery and hydrocarbon storage wells (Class II wells). Those wells are regulated by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines and Minerals, rather than by the Board and the Agency. This statement maintains structural consistency with USEPA rules.
f) Operating requirements.
1) No person must cause or allow injection between the outermost casing protecting USDWs and the well bore.
2) Maintenance of mechanical integrity.
A) The owner or operator of a Class I or Class III injection well authorized by rule under this Subpart C must establish and maintain mechanical integrity, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.106, until either of the following has occurred:
i) The well is properly plugged and abandoned in accordance with an approved plugging and abandonment plan pursuant to subsection (c) of this Section and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110 and a plugging and abandonment report is submitted pursuant to subsection (k); or
ii) The well is converted in compliance with subsection (j) of this Section.
B) The Agency may require by permit condition that the owner or operator comply with a schedule describing when mechanical integrity demonstrations must be made.
3) Cessation upon Lack of Mechanical Integrity.
A) When the Agency determines that a Class I (non-hazardous) or Class III injection well lacks mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108, the Agency must give written notice of its determination to the owner or operator.
B) Unless the Agency requires immediate cessation, the owner or operator must cease injection into the well within 48 hours of receipt of the Agency’s determination.
C) The Agency may allow plugging of the well in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110, or require the owner or operator to perform such additional construction, operation, monitoring, reporting, and corrective action as is necessary to prevent the movement of fluid into or between USDWs caused by the lack of mechanical integrity.
D) The owner or operator may resume injection upon receipt of written notification from the Agency that the owner or operator has demonstrated mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108.
4) The Agency may allow the owner or operator of a well that lacks mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108(a)(1) to continue or resume injection if the owner or operator has made a satisfactory demonstration that there is no movement of fluid into or between USDWs.
5) For a Class I injection well, unless an alternative to a packer has been approved under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.112(c), the owner or operator must fill the annulus between the tubing and the long string of casings with a fluid approved by the Agency and maintain a pressure, also approved by the Agency, on the annulus. The owner or operator of a Class I well completed with tubing and packer must fill the annulus between tubing and casing with a non-corrosive fluid and maintain a positive pressure on the annulus. For any other Class I injection well, the owner or operator must insure that the alternative completion method will reliably provide a comparable level of protection of USDWs.
6) Injection pressure for Class I and III injection wells.
A) Except during stimulation, the owner or operator must not exceed an injection pressure at the wellhead that must be calculated so as to assure that the pressure during injection does not initiate new fractures or propagate existing fractures in the injection zone; and
B) The owner or operator must not inject at a pressure that will initiate fractures in the confining zone or cause the movement of injection or formation fluids into a USDW.
g) Monitoring Requirements. The owner or operator must perform the monitoring as described in this subsection (g). Monitoring of the nature of the injected fluids must comply with applicable analytical methods cited in tables IA (List of Approved Biological Methods), IB (List of Approved Inorganic Test Procedures), IC (List of Approved Test Procedures for Non-Pesticide Organic Compounds), ID (List of Approved Test Procedures for Pesticides), IE (List of Approved Radiologic Test Procedures), and IF (List of Approved Methods for Pharmaceutical Pollutants) of 40 CFR 136.3 (Identification of Test Procedures) or in appendix III of 40 CFR 261 (Chemical Analysis Test Methods), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), or with other methods that have been approved by the Agency.
1) The owner or operator of a Class I injection well must undertake the following actions:
A) It must analyze the nature of the injected fluids with sufficient frequency to yield data representative of their characteristics;
B) It must install and use continuous recording devices to monitor injection pressure, flow rate and volume, and the pressure on the annulus between the tubing and the long string of casing; and
C) It must install and use monitoring wells within the area of review, if required by the Agency, to monitor any migration of fluids into and pressure in the USDWs. The type, number, and location of the wells; the parameters to be measured; and the frequency of monitoring must be approved by the Agency.
2) This subsection (g)(2) corresponds with 40 CFR 144.28(g)(2), a provision related to Class II injection wells, which are regulated by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines and Minerals, and not by the Board. This statement maintains structural consistency with USEPA rules.
3) The owner or operator of a Class III injection well must undertake the following actions:
A) It must provide to the Agency a qualitative analysis and ranges in concentrations of all constituents of injected fluids at least once within the first year of authorization and thereafter whenever the injection fluid is modified to the extent that the initial data are incorrect or incomplete.
i) The owner or operator may request confidentiality pursuant to Sections 7 and 7.1 of the Act and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 130.
ii) If the information is proprietary the owner or operator may in lieu of the ranges in concentrations choose to submit maximum concentrations that must not be exceeded.
iii) In such a case the owner or operator must retain records of the undisclosed concentration and provide them upon request to the Agency as part of any enforcement investigation;
B) It must monitor injection pressure and either flow rate or volume semi-monthly, or meter and record daily injected and produced fluid volumes as appropriate;
C) It must monitor the fluid level in the injection zone semi-monthly, where appropriate; and
D) All Class III injection wells may be monitored on a field or project basis rather than an individual well basis by manifold monitoring. Manifold monitoring may be used in cases of facilities consisting of more than one injection well, operating with a common manifold. Separate monitoring systems for each well are not required provided the owner or operator demonstrates to the Agency that manifold monitoring is comparable to individual well monitoring.
h) Reporting requirements. The owner or operator must submit reports to the Agency as follows:
1) For a Class I injection well, quarterly reports on all of the following:
A) The physical, chemical, and other relevant characteristics of the injection fluids;
B) Monthly average, maximum and minimum values for injection pressure, flow rate and volume, and annular pressure;
C) The results from groundwater monitoring wells prescribed in subsection (f)(1)(C) of this Section;
D) The results of any test of the injection well conducted by the owner or operator during the reported quarter if required by the Agency; and
E) Any well work over performed during the reported quarter.
2) This subsection (h)(2) corresponds with 40 CFR 144.28(h)(2), a provision related to Class II injection wells, which are regulated by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines and Minerals, and not by the Board. This statement maintains structural consistency with USEPA rules.
3) For a Class III injection well, all of the following:
A) Quarterly reporting on all monitoring, as required in subsections (f)(2)(A), (f)(2)(B), and (f)(2)(C) of this Section;
B) Quarterly reporting of the results of any periodic tests required by the Agency that are performed during the reported quarter; and
C) Monitoring may be reported on a project or field basis rather than an individual well basis where manifold monitoring is used.
i) Retention of records. The owner or operator must retain records of all monitoring information, including the following:
1) Calibration and maintenance records and all original strip chart recordings for continuous monitoring instrumentation, and copies of all reports required by this section, for a period of at least three years from the date of the sample, measurement or report. This period may be extended by request of the Agency at any time; and
2) The nature and composition of all injected fluids until three years after the completion of any plugging and abandonment procedures specified under Section 704.188. The owner or operator must retain the records after the three year retention period unless it delivers the records to the Agency or obtains written approval from the Agency to discard the records.
j) Notice of abandonment. The owner or operator must notify the Agency at least 45 days before conversion or abandonment of the well.
k) Plugging and abandonment report. Within 60 days after plugging a well or at the time of the next quarterly report (whichever is less) the owner or operator must submit a report to the Agency. If the quarterly report is due less than 15 days before completion of plugging, then the report must be submitted within 60 days. The report must be certified as accurate by the person who performed the plugging operation. Such report must consist of either:
1) A statement that the well was plugged in accordance with the plan previously submitted to the Agency; or
2) Where actual plugging differed from the plan previously submitted, an updated version of the plan, on any form supplied by the Agency, specifying the different procedures used.
l) Change of ownership.
1) The owner or operator must notify the Agency of a transfer of ownership or operational control of the well at least 30 days in advance of the proposed transfer.
2) The notice must include a written agreement between the transferor and the transferee containing a specific date when the financial responsibility demonstration of subsection (d) of this Section will be met by the transferee.
3) The transferee is authorized to inject unless it receives notification from the Agency that the transferee has not demonstrated financial responsibility pursuant to subsection (d) of this Section.
m) Requirements for a Class I hazardous waste injection well. The owner or operator of any Class I injection well injecting hazardous waste must comply with Section 704.203. In addition the owner or operator must properly dispose of, or decontaminate by removing all hazardous waste residues, all injection well equipment.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.28 (2012).
(Source: Amended at 37 Ill. Reg. 17708, effective October 24, 2013)
Section 704.151 RCRA Interim Status for Class I Injection Wells
The minimum standards that define acceptable injection of hazardous waste during the period of interim status under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703 are set out in the applicable provisions of this Part, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 725.530 and 730. The issuance of a UIC permit does not automatically terminate interim status. A Class I injection well’s interim status does, however, automatically terminate upon issuance of a RCRA permit to that well, or upon the well’s receiving a RCRA permit by rule under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 703.141. Thus, until a Class I injection well injecting hazardous waste receives a RCRA permit or RCRA permit by rule, the well’s interim status requirements are the applicable requirements imposed pursuant to this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 725 and 730, including any requirements imposed in the UIC permit.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.1(h) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
SUBPART D: APPLICATION FOR PERMIT
Section 704.161 Application for Permit; Authorization by Permit
a) Permit application. Unless an underground injection well is authorized by rule under Subpart C of this Part, all injection activities, including construction of an injection well, are prohibited until the owner or operator is authorized by permit. An owner or operator of a well currently authorized by rule must apply for a permit under this Section unless the well authorization was for the life of the well or project. Authorization by rule for a well or project for which a permit application has been submitted terminates for the well or project upon the effective date of the permit. Procedures for application, issuance, and administration of emergency permits are found exclusively in Section 704.163. A RCRA permit applying the standards of Subpart C of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724 will constitute a UIC permit for hazardous waste injection wells for which the technical standards in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730 are not generally appropriate.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (a) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.31(a) (2005).
b) Time to apply. Any person who performs or proposes an underground injection for which a permit was or will be required must submit an application to the Agency as follows:
1) For existing wells, the application was to have been filed before the applicable of the following deadlines:
A) Within 180 days after the Agency notifies such person that an application is required;
B) If the waste being injected into the well is a hazardous waste accompanied by a manifest or delivery document, before August 1, 1984; or
C) Except as otherwise provided in subsections (b)(1)(A) and (b)(1)(B) of this Section, before March 3, 1986.
2) For new injection wells, except new wells in projects authorized under Section 704.141(b) or covered by an existing area permit under Section 704.162(c), the application must be filed a reasonable time before construction is expected to begin.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (b) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.31(c) (2005).
c) Contents of UIC application. The applicant must demonstrate that the underground injection will not endanger drinking water sources. The form and content of the UIC permit application may be prescribed by the Agency, including the materials required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.123.
d) Information requirements for a Class I hazardous waste injection well.
1) The following information is required for each active Class I hazardous waste injection well at a facility seeking a UIC permit:
A) The dates the well was operated; and
B) Specification of all wastes that have been injected into the well, if available.
2) The owner or operator of any facility containing one or more active hazardous waste injection wells must submit all available information pertaining to any release of hazardous waste or constituents from any active hazardous waste injection well at the facility.
3) The owner or operator of any facility containing one or more active Class I hazardous waste injection wells must conduct such preliminary site investigations as are necessary to determine whether a release is occurring, has occurred, or is likely to have occurred.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (d) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.31(g) (2005).
e) In addition to the materials required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.123, the applicant must provide the following:
1) It must identify and submit on a list with the permit application the names and addresses for all owners of record of land within one-quarter mile (401 meters) of the facility boundary. This requirement may be waived by the Agency where the site is located in a populous area such that the requirement would be impracticable; and
2) It must submit a plugging and abandonment plan that meets the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (e) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.31(e)(9) and (e)(10) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.162 Area Permits
a) The Agency may issue a permit on an area basis, rather than for each injection well individually, provided that the permit is for injection wells for which each of the following is true:
1) The injection wells are described and identified by location in permit applications, if they are existing injection wells, except that the Agency may accept a single description of multiple injection wells with substantially the same characteristics;
2) The injection wells are within the same well field, facility site, reservoir, project, or similar unit in the same state;
3) The injection wells are operated by a single owner or operator;
4) The injection wells are used to inject other than hazardous waste; and
5) The injection wells are other than Class VI injection wells.
b) Area permits must specify both of the following:
1) The area within which underground injections are authorized; and
2) The requirements for construction, monitoring, reporting, operation, and abandonment for all wells authorized by the permit.
c) The area permit may authorize the permittee to construct and operate, convert, or plug and abandon new injection wells within the permit area provided the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The permittee notifies the Agency at such time as the permit requires;
2) The additional well satisfies the criteria in subsection (a) of this Section and meets the requirements specified in the permit under subsection (b) of this Section; and
3) The cumulative effects of drilling and operation of additional injection wells are considered by the Agency during evaluation of the area permit application and are acceptable to the Agency.
d) If the Agency determines that any well constructed pursuant to subsection (c) of this Section does not satisfy the requirements of subsections (c)(1) and (c)(2) of this Section, the Agency may modify the permit under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.183 through 702.185, seek revocation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.186, or take enforcement action. If the Agency determines that cumulative effects are unacceptable, the permit may be modified under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.183 through 702.185.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.33 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.163 Emergency Permits
a) Coverage. Notwithstanding any other provision of this Part or 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 or 705, the Agency may temporarily permit a specific underground injection if an imminent and substantial threat to the health of persons will result unless a temporary emergency permit is granted.
b) Requirements for issuance.
1) Any temporary permit under subsection (a) of this Section must be for no longer term than required to prevent the threat.
2) Notice of any temporary permit under this subsection (b) must be published in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705.163 within 10 days after the issuance of the permit.
3) The temporary permit under this section may be either oral or written. If oral, it must be followed within five calendar days by a written temporary emergency permit.
4) The Agency must condition the temporary permit in any manner it determines is necessary to ensure that the injection will not result in the movement of fluids into a USDW.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.34 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.164 Signatories to Permit Applications
BOARD NOTE: See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.126.
(Source: Amended at 18 Ill. Reg. 18351, effective December 20, 1994)
SUBPART E: PERMIT CONDITIONS
Section 704.181 Additional Conditions
The following conditions apply to all UIC permits, in addition to those set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.140 through 702.152, and these conditions must be incorporated into all permits either expressly or by reference. If incorporated by reference, a specific citation to these regulations must be given in the permit.
a) In addition to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.141 (duty to comply): the permittee needs not comply with the provisions of this permit to the extent and for the duration such noncompliance is authorized in a temporary emergency permit under Section 704.163.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (a) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(a) (2011).
b) In addition to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.150(b) (monitoring and records): the permittee must retain records concerning the nature and composition of all injected fluids until three years after the completion of any plugging and abandonment procedures specified under Section 704.188 or under Subpart G of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730, as appropriate. The owner or operator must continue to retain the records after the three-year retention period, unless the owner or operator delivers the records to the Agency or obtains written approval from the Agency to discard the records.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (b) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(j)(2)(ii) (2011).
c) In addition to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.152(a) (notice of planned changes), the following limitation applies: except for all new wells authorized by an area permit under Section 704.162(c), a new injection well may not commence injection until construction is complete, and both of the following must occur:
1) The permittee must have submitted notice of completion of construction to the Agency; and
2) Inspection review must have occurred, as follows:
A) The Agency has inspected or otherwise reviewed the new injection well and finds it is in compliance with the conditions of the permit; or
B) The permittee has not received notice from the Agency of its intent to inspect or otherwise review the new injection well within 13 days of the date of the notice in subsection (c)(1) of this Section, in which case prior inspection or review is waived, and the permittee may commence injection. The Agency must include in its notice a reasonable time period in which it will inspect the well.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (c) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(m) (2011).
d) Reporting noncompliance.
1) Twenty-four hour reporting. The permittee must report any noncompliance that may endanger health or the environment, including the following:
A) Any monitoring or other information that indicates that any contaminant may cause an endangerment to a USDW; and
B) Any noncompliance with a permit condition or malfunction of the injection system that may cause fluid migration into or between USDWs.
2) Any information must be provided orally within 24 hours from the time the permittee becomes aware of the circumstances. A written submission must also be provided within five days after the time the permittee becomes aware of the circumstances. The written submission must contain a description of the noncompliance and its cause; the period of noncompliance, including exact dates, times, and, if the noncompliance has not been corrected, the anticipated time is expected to continue; and steps taken or planned to reduce, eliminate, and prevent reoccurrence of the noncompliance of the noncompliance.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (d) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(l)(6) (2011).
e) The permittee must notify the Agency at such times as the permit requires before conversion or abandonment of the well or, in the case of area permits, before closure of the project.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (e) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(n) (2011).
f) A Class I or Class III injection well permit must include, and a Class V permit may include, conditions that meet the applicable requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110 to ensure that plugging and abandonment of the well will not allow the movement of fluids into or between USDWs. Where the plan meets the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110, the Agency must incorporate the plan into the permit as a permit condition. Where the Agency’s review of an application indicates that the permittee’s plan is inadequate, the Agency may require the applicant to revise the plan, prescribe conditions meeting the requirements of this subsection (f), or deny the permit. A Class VI injection well permit must include conditions that meet the requirements set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.192. Where the plan meets the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.192, the Agency must incorporate the plan into the permit as a permit condition. For purposes of this subsection (f), temporary or intermittent cessation of injection operations is not abandonment.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (f) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(o) (2011).
g) Plugging and abandonment report. Within 60 days after plugging a well or at the time of the next quarterly report (whichever is less) the owner or operator must submit a report to the Agency. If the quarterly report is due less than 15 days before completion of plugging, then the report must be submitted within 60 days. The report must be certified as accurate by the person who performed the plugging operation. Such report must consist of either of the following:
1) A statement that the well was plugged in accordance with the plan previously submitted to the Agency;
2) Where actual plugging differed from the plan previously submitted, an updated version of the plan on the form supplied by the Agency specifying the differences.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (g) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(p) (2011).
h) Duty to establish and maintain mechanical integrity.
1) The owner or operator of a Class I Class III, or Class VI injection well permitted under this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 must establish mechanical integrity prior to commencing injection or on a schedule determined by the Agency. Thereafter the owner or operator of a Class I, Class II, or Class III injection well must maintain mechanical integrity as required by 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108, and the owner or operator of a Class VI injection well must maintain mechanical integrity as required by Section 730.189. The Agency may require by permit condition that the owner or operator comply with a schedule describing when mechanical integrity demonstrations must be made.
2) When the Agency determines that a Class I or Class III injection well lacks mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108 or 730.189 (for a Class VI injection well), the Agency must give written notice of its determination to the owner or operator. Unless the Agency requires immediate cessation, the owner or operator must cease injection into the well within 48 hours of receipt of the Agency determination. The Agency may allow plugging of the well pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110 or require the permittee to perform such additional construction, operation, monitoring, reporting, and corrective action as is necessary to prevent the movement of fluid into or between USDWs caused by the lack of mechanical integrity. The owner or operator may resume injection upon written notification from the Agency that the owner or operator has demonstrated mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108.
3) The Agency may allow the owner or operator of a well that lacks mechanical integrity pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108(a)(1) to continue or resume injection, if the owner or operator has made a satisfactory showing that there is no movement of fluid into or between USDWs.
BOARD NOTE: Subsection (h) of this Section is derived from 40 CFR 144.51(q) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.182 Establishing UIC Permit Conditions
In addition to the conditions established under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.160 and Section 704.181, each UIC permit must include conditions meeting the requirements of the following Sections, when applicable. A permit for the owner or operator of a Class VI injection well must include conditions meeting the requirements of Subpart H of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a) preamble (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.183 Construction Requirements
Existing wells must achieve compliance with construction requirements as set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730 according to a compliance schedule established as a permit condition. The owner or operator of a proposed new injection well must submit plans for testing, drilling, and construction as part of the permit application. Except as authorized by an area permit, no construction may commence until a permit has been issued containing construction requirements (see Section 704.121). New wells must be in compliance with these requirements prior to commencing injection operations. Changes in construction plans during construction may be approved by the Agency as minor modifications. (See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.187.) No such changes may be physically incorporated into construction of the well prior to approval of the modification by the Agency.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(1) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.184 Corrective Action
UIC permits must require by condition corrective action as set forth in Section 704.193 and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.107 and 730.184.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(2) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.185 Operation Requirements.
The permit must establish any maximum injection volumes and pressures necessary to assure that fractures are not initiated in the confining zone, that injected fluids do not migrate into any USDW, that formation fluids are not displaced into any USDW, and to assure compliance with the 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730 operating requirements.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(3) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.186 Hazardous Waste Requirements
UIC permits must require by condition requirements for wells managing hazardous waste, as set forth in Subpart F of this Part.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(4) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.187 Monitoring and Reporting
UIC permits must require by condition monitoring and reporting requirements, as set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730. The permittee must be required to identify types of tests and methods used to generate the monitoring data. Monitoring of the nature of the injected fluids must comply with applicable analytical methods cited and described in tables IA (List of Approved Biological Methods), IB (List of Approved Inorganic Test Procedures), IC (List of Approved Test Procedures for Non-Pesticide Organic Compounds), ID (List of Approved Test Procedures for Pesticides), IE (List of Approved Radiologic Test Procedures), and IF (List of Approved Methods for Pharmaceutical Pollutants) of 40 CFR 136.3 (Identification of Test Procedures) or in appendix III of 40 CFR 261 (Chemical Analysis Test Methods), each incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), or, in certain circumstances, by other methods that have been approved in writing by the Agency.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(5) (2012).
(Source: Amended at 37 Ill. Reg. 17708, effective October 24, 2013)
Section 704.188 Plugging and Abandonment
Any permit must include a requirement that, after a cessation of operations of two years, the owner or operator must plug and abandon the well in accordance with the plan unless it does the following:
a) It provides notice to the Agency; and
b) It describes actions or procedures satisfactory to the Agency that the owner or operator will take to ensure that the well will not endanger USDWs during the period of temporary abandonment. These actions and procedures must include compliance with the technical requirements applicable to active injection wells, unless waived by the Agency.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(6) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.189 Financial Responsibility
a) The permittee, including the transferor of a permit, is required to demonstrate and maintain financial responsibility and resources to close, plug, and abandon the underground injection operation in a manner prescribed by the Agency until one of the following occurs:
1) The well has been plugged and abandoned in accordance with an approved plugging and abandonment plan pursuant to Section 704.181(f) and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.110 and 730.192, and the permittee has submitted a plugging and abandonment report pursuant to Section 704.181(g);
2) The well has been converted in compliance with Section 704.181(e); or
3) The transferor of a permit has received notice from the Agency that the owner or operator receiving transfer of the permit (the new permittee) has demonstrated financial responsibility for the well.
b) The permittee must show evidence of financial responsibility to the Agency by the submission of a surety bond or other adequate assurance, such as financial statements or other materials acceptable to the Agency. The Agency may on a periodic basis require the holder of a life-time permit to submit an estimate of the resources needed to plug and abandon the well revised to reflect inflation of such costs, and a revised demonstration of financial responsibility if necessary. For a Class VI injection well, the permittee must show evidence of financial responsibility to the Agency by the submission of an instrument that fulfills the requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.185(a), such as a financial statement or other materials necessary for an Agency evaluation of the adequacy of the submitted financial assurance.
c) The owner or operator of a Class I hazardous waste injection well must comply with the financial responsibility requirements set forth in Subpart G of this Part. The owner or operator of a Class VI injection well must comply with the financial responsibility requirements set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.185.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(7) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.190 Mechanical Integrity
A permit for any Class I or Class III injection well or injection project that lacks mechanical integrity must includea condition that prohibits injection operations until the Agency has determined pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.108 that the well has mechanical integrity. A permit for any Class V injection well must include such a condition if the Agency determines that the condition is necessary to prevent a violation of the Act or Board regulations. A permit for any Class VI injection well must include a provision that prohibits injection operations until the Agency determines pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.189 that the well has mechanical integrity.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(8) (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.191 Additional Conditions
The Agency must impose on a case-by-case basis such additional conditions as are necessary to prevent the migration of fluids into a USDW.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.52(a)(9) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.192 Waiver of Requirements by Agency
a) When injection does not occur into, through, or above a USDW, the Agency may authorize a well or project with less stringent requirements for area of review, construction, mechanical integrity, operation, monitoring, and reporting than required in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730 or Sections 704.182 through 704.191 to the extent that the reduction in requirements will not result in an increased risk of movement of fluids into a USDW.
b) When injection occurs through or above a USDW, but the radius of endangering influence when computed under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.106(a) is smaller or equal to the radius of the well, the Agency may authorize a well or project with less stringent requirements for operation, monitoring, and reporting than required in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730 or Sections 704.182 through 704.191 to the extent that the reduction in requirements will not result in an increased risk of movement of fluids into a USDW.
c) When reducing requirements under subsection (a) or (b) of this Section, the Agency must prepare a fact sheet under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705.143 explaining the reasons for the action.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.16 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.193 Corrective Action
a) Coverage. An applicant for a Class I or Class III injection well permit must identify the location of all known wells within the injection well’s area of review that penetrate the injection zone. For such wells that are improperly sealed, completed, or abandoned, the applicant must also submit a plan consisting of such steps or modifications as are necessary to prevent movement of fluid into USDWs (“corrective action”). Where the plan is adequate, the Agency must incorporate it into the permit as a condition. Where the Agency’s review of an application indicates that the permittee’s plan is inadequate (based on the factors in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.107), the Agency must require the applicant to revise the plan, prescribe a plan for corrective action as a condition of the permit under subsection (b) of this Section, or deny the application.
b) Requirements.
1) Existing injection wells. Any permit issued for an existing injection well requiring corrective action must include a compliance schedule requiring any corrective action accepted or prescribed under subsection (a) of this Section to be completed as soon as possible.
2) New injection wells. No permit for a new injection well may authorize injection until all required corrective action has been taken.
3) Injection pressure limitation. The Agency may require as a permit condition that injection pressure in the injection zone does not exceed hydrostatic pressure at the site of any improperly completed or abandoned well within the area of review. This pressure limitation must satisfy the corrective action requirement. Alternatively, such injection pressure limitation can be part of a compliance schedule and last until all other required corrective action has been taken.
4) Class III injection wells only. When setting corrective action requirements the Agency must consider the overall effect of the project on the hydraulic gradient in potentially affected USDWs and the corresponding changes in potentiometric surfaces and flow directions rather than the discrete effect of each well. If a decision is made that corrective action is not necessary based on the determinations above, the monitoring program required in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.133(b) must be designed to verify the validity of such determinations.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.55 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.194 Maintenance and Submission of Records
The Agency must include, as a condition to any UIC permit, a requirement that the owner or operator of the injection well must establish and maintain such records, make such reports, conduct such monitoring, and provide such other information as the Agency deems necessary to determine whether the owner or operator has acted or is acting in compliance with the Act and Board regulations.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.17 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
SUBPART F: REQUIREMENTS FOR WELLS INJECTING HAZARDOUS WASTE
Section 704.201 Applicability
This Subpart F applies to a generator of hazardous waste and to the owner or operator of any hazardous waste management facility that uses any class of well to inject hazardous wastes accompanied by a manifest. (See also Section 704.124.)
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.14(a) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.202 Authorization
The owner or operator of any well that is used to inject hazardous wastes accompanied by a manifest or delivery document was required to apply for authorization to inject, as specified in Section 704.161(b)(1)(B), before August 2, 1984.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.14(b) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.203 Requirements
In addition to requiring compliance with the applicable requirements of this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730, the owner or operator of any facility described in Section 704.202 must comply with the following requirements:
a) Notification. The owner or operator must comply with the notification requirements of section 3010 of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (42 USC 6901 et seq.).
b) Identification number. The owner or operator must comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.111.
c) Manifest system. The owner or operator must comply with the applicable recordkeeping and reporting requirements for manifested wastes in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.171.
d) Manifest discrepancies. The owner or operator must comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.172.
e) Operating record. The owner or operator must comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.173(a), (b)(1), and (b)(2).
f) Annual report. The owner or operator must comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.175.
g) Unmanifested waste report. The owner or operator must comply with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.176.
h) Personnel training. The owner or operator must comply with the applicable personnel training requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 724.116.
i) Certification of closure. When abandonment is completed, the owner or operator must submit to the Agency certification by the owner or operator and certification by an independent registered professional engineer that the facility has been closed in accordance with the specifications in Section 704.188.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.14(c) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
SUBPART G: FINANCIAL RESPONSIBILITY FOR CLASS I HAZARDOUS WASTE INJECTION WELLS
Section 704.210 Applicability
Sections 704.212, 704.213, and 704.240 apply to the owner or operator of an existing or new Class I Hazardous waste injection well, except as provided otherwise in this Subpart G.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.60 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.211 Definitions
a) “Plugging and abandonment plan” or “plan” means the plan for plugging and abandonment prepared in accordance with Sections 704.150 and 704.181(f).
b) “Current plugging and abandonment cost estimate” or “current cost estimate” means the most recent of the estimates prepared in accordance with Sections 704.212(a), (b), and (c).
c) “Parent corporation” means a corporation that directly owns at least 50 percent of the voting stock of the corporation that is the injection well owner or operator; the latter corporation is deemed a “subsidiary” of the parent corporation.
d) The following terms are used in the specifications for the financial test for plugging and abandonment. The definitions are intended to represent the common meanings of the terms as they are generally used by the business community.
“Assets” means all existing and all probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity.
“Current assets” means cash or other assets or resources commonly identified as those that are reasonably expected to be realized in cash or sold or consumed during the normal operating cycle of the business.
“Current liabilities” means obligations whose liquidation is reasonably expected to require the use of existing resources properly classifiable as current assets or the creation of other current liabilities.
“Independently audited” refers to an audit performed by an independent certified public accountant in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards.
“Liabilities” means probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events.
“Net working capital” means current assets minus current liabilities.
“Net worth” means total assets minus total liabilities and is equivalent to owner’s equity.
“Tangible net worth” means the tangible assets that remain after deducting liabilities; such assets would not include intangibles such as goodwill and rights to patents or royalties.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.61 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.212 Cost Estimate for Plugging and Abandonment
a) The owner or operator must prepare a written estimate, in current dollars, of the cost of plugging the injection well in accordance with the plugging and abandonment plan, as specified in Sections 704.150 and 704.181(f). The cost estimate must equal the cost of plugging and abandonment at the point in the facility’s operating life when the extent and manner of its operation would making plugging and abandonment the most expensive, as indicated by its plan.
b) The owner or operator must adjust the cost estimate for inflation within 30 days after each anniversary of the date on which the first cost estimate was prepared. The adjustment must be made as specified in subsections (b)(1) and (b)(2) of this Section, using an inflation factor derived from the annual update to “Oil and Gas Lease Equipment and Operating Costs 1987 to [Date]” published by the U.S. Department of Treasury. The inflation factor is the result of dividing the latest published annual Index by the Index for the previous years.
1) The first adjustment is made by multiplying the cost estimate by the inflation factor. The result is the adjusted cost estimate.
2) Subsequent adjustments are made by multiplying the latest adjusted cost estimate by the latest inflation factor.
BOARD NOTE: Corresponding 40 CFR 144.62(b) cites “Oil and Gas Field Equipment Cost Index” without attribution of its source. The Board has located a publication entitled “Oil and Gas Lease Equipment and Operating Costs 1987 to [Date].” It is assembled by the U.S. Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration. It is available only on the Internet at www.eia.doe.gov. The Board replaced the federally cited reference with this document. The full link for the document (in March 2006) is as follows: http://www.eia.doe.gov/pub/oil_gas/natural_gas/data_publications/cost_indices_equipment_production/current/coststudy.html .
c) The owner or operator must review the cost estimate whenever a change in the plan increases the cost of plugging and abandonment. The revised cost estimate must be adjusted for inflation as specified in subsection (b) of this Section.
d) The owner or operator must keep the following at the facility during the operating life of the facility: the latest cost estimate prepared in accordance with subsections (a) and (c) of this Section and, when this estimate has been adjusted in accordance with subsection (b) of this Section, the latest adjusted cost estimate.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.62 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.213 Financial Assurance for Plugging and Abandonment
An owner or operator of each facility must establish financial assurance for the plugging and abandonment of each existing and new Class I hazardous waste injection well. The owner or operator must choose one of the following financial assurance mechanisms:
a) A trust fund (Section 704.214);
b) A surety bond guaranteeing payment (Section 704.215);
c) A surety bond guaranteeing performance (Section 704.216);
d) A letter of credit (Section 704.217);
e) Insurance (Section 704.218); or
f) The financial test and corporate guarantee (Section 704.219);
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63 preamble (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.214 Trust Fund
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by establishing a trust fund that conforms to the requirements of this Section and submitting an original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Agency. An owner or operator of a Class I injection well injecting hazardous waste must submit the original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement to the Agency with the permit application or for approval to operate under rule. The trustee must be an entity that has the authority to act as a trustee and whose trust operations are regulated and examined by a Federal or State agency.
b) The wording of the trust agreement must be as specified in Section 704.240, and the trust agreement must be accompanied by a formal certification of acknowledgment. Schedule A of the trust agreement must be updated within 60 days after a change in the amount of the current cost estimate covered by the agreement.
c) Payments into the trust fund must be made annually by the owner or operator over the term of the initial permit or over the remaining operating life of the injection well as estimated in the plan, whichever period is shorter; this period is hereafter referred to as the “pay-in period.” The payments into the trust fund must be made as follows:
1) For a new well, the first payment must be made before the initial injection of hazardous waste. The owner or operator must submit a receipt to the Agency from the trustee for this payment before the initial injection of hazardous waste. The first payment must be at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in Section 704.240, divided by the number of years in the pay-in period. Subsequent payments must be made no later than 30 days after each anniversary date of the first payment. The amount of each subsequent payment must be determined by this formula:
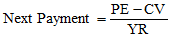
Where:
PE is the current cost estimate
CV is the current value of the trust fund
Y is the number of years remaining in the pay-in period.
2) If an owner or operator establishes a trust fund as specified in this Section, and the value of that trust fund is less than the current cost estimate when a permit is issued for the injection well, the amount of current cost estimate still to be paid into the trust fund must be paid in over the pay-in period as defined in subsection (c) of this Section. Payments must continue to be made no later than 30 days after each anniversary date of the first payment made pursuant to this Part. The amount of each payment must be determined by this formula:
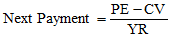
Where:
PE is the current cost estimate
CV is the current value of the trust fund
Y is the number of years remaining in the pay-in period.
d) The owner or operator may accelerate payments into the trust fund or the owner or operator may deposit the full amount of the current cost estimate at the time the fund is established. However, the owner or operator must maintain the value of the fund at no less than the value that the fund would have if annual payments were made as specified in subsection (c) of this Section.
e) If the owner or operator establishes a trust fund after having used one or more alternate financial assurance mechanisms, the owner or operator’s first payment must be in at least the amount that the fund would contain if the trust fund were established initially and annual payments made according to specifications of this Section.
f) After the pay-in period is completed, whenever the current cost estimate changes the owner or operator must compare the new estimate with the trustee’s most recent annual valuation of the trust fund. If the value of the fund is less than the amount of the new estimate, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the change in the cost estimate, must either deposit an amount into the fund so that its value after this deposit at least equals the amount of the current cost estimate, or obtain other financial assurance to cover the difference.
g) If the value of the trust fund is greater than the total amount of the current cost estimate, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate.
h) If an owner or operator substitutes other financial assurance for all or part of the trust fund, the owner or operator may submit a written request to the Agency for release of the amount in excess of the current cost estimate covered by the trust fund.
i) Within 60 days after receiving a request from the owner or operator for release of funds as specified in subsection (g) or (h) of this Section, the Agency must instruct the trustee to release to the owner or operator such funds as the Agency specifies in writing.
j) After beginning final plugging and abandonment, an owner and operator or any other person authorized to perform plugging and abandonment may request reimbursement for plugging and abandonment expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. Within 60 days after receiving bills for plugging and abandonment activities, the Agency must determine whether the plugging and abandonment expenditures are in accordance with the plan or otherwise justified, and if so, it must instruct the trustee to make reimbursement in such amounts as the Agency specifies in writing. If the Agency has reason to believe that the cost of plugging and abandonment will be significantly greater than the value of the trust fund, it may withhold reimbursement of such amounts as it deems prudent until it determines, in accordance with Section 704.222 that the owner or operator is no longer required to maintain financial assurance.
k) The Agency must agree to termination of the trust when either of the following occurs:
1) The owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance; or
2) The Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(a) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.215 Surety Bond Guaranteeing Payment
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this Section and submitting the bond to the Agency with the application for a permit or for approval to operate under rule. The bond must be effective before the initial injection of hazardous waste. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
BOARD NOTE: The U.S. Department of the Treasury updates Circular 570, “Companies Holding Certificates of Authority as Acceptable Sureties on Federal Bonds and as Acceptable Reinsuring Companies,” on an annual basis pursuant to 31 CFR 223.16. Circular 570 is available on the Internet from the following website: http://www.fms.treas.gov/c570/ .
b) The wording of the surety bond must be as specified in Section 704.240.
c) The owner or operator who uses a surety bond to satisfy the financial assurance requirement must also establish a standby trust fund. All payments made under the terms of the bond must be deposited by the surety directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in Section 704.214, except that the following limitations apply:
1) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the surety bond; and
2) Until the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to this Section, the following are not required:
A) Payments into the trust fund as specified in Section 704.214;
B) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement to show current cost estimates;
C) Annual valuations as required by the trust agreement; and
D) Notices of non-payment as required by the trust agreement.
d) The bond must guarantee that the owner or operator will fulfill the following requirements:
1) It will fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum of the bond before the beginning of plugging and abandonment of the injection well;
2) It will fund the standby trust fund in an amount equal to the penal sum within 15 days after an order to begin plugging and abandonment is issued by the Board or a U.S. district court or other court of competent jurisdiction; or
3) It will provide alternate financial assurance, and obtain the Agency’s written approval of the assurance provided, within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the bond from the surety.
e) Under the terms of the bond, the surety will become liable on the bond obligation when the owner or operator fails to perform as guaranteed by the bond.
f) The penal sum of the bond must be in amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in Section 704.220.
g) Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Agency.
h) Under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during 120 days beginning on the date of the receipt of the notice of cancellation by both owner or operator and the Agency as evidenced by the returned receipts.
i) The owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Agency has given prior written consent based on receipt of evidence of alternate financial assurance.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(b) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.216 Surety Bond Guaranteeing Performance
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by obtaining a surety bond that conforms to the requirements of this Section and submitting the bond to the Agency. An owner or operator of a new facility must submit the bond to the Agency with the permit application or for approval to operate under rule. The bond must be effective before injection of hazardous waste is started. The surety company issuing the bond must, at a minimum, be among those listed as acceptable sureties on Federal bonds in Circular 570 of the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
BOARD NOTE: The U.S. Department of the Treasury updates Circular 570, “Companies Holding Certificates of Authority as Acceptable Sureties on Federal Bonds and as Acceptable Reinsuring Companies,” on an annual basis pursuant to 31 CFR 223.16. Circular 570 is available on the Internet from the following website: http://www.fms.treas.gov/c570/ .
b) The wording of the surety bond must be as specified in Section 704.240.
c) The owner or operator who uses a surety bond to satisfy the financial assurance requirement must also establish a standby trust fund. All payments made under the terms of the bond must be deposited by the surety directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements specified in Section 704.214, except that the following limitations apply:
1) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the surety bond; and
2) Until the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to this Section, the following are not required:
A) Payments into the trust fund as specified in Section 704.214;
B) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement to show current cost estimates;
C) Annual valuations as required by the trust agreement; and
D) Notices of non-payment as required by the trust agreement.
d) The bond must guarantee that the owner or operator will fulfill the following requirements:
1) It will perform plugging and abandonment in accordance with the plan and other requirements of the permit for the injection well whenever required to do so; or
2) It will provide alternate financial assurance, and obtain the Agency’s written approval of the assurance provided, within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the bond from the surety.
e) Under the terms of the bond, the surety will become liable on the bond obligation when the owner or operator fails to perform as guaranteed by the bond. Following a determination that the owner or operator has failed to perform plugging and abandonment in accordance with the plan and other permit requirements when required to do so, under terms of the bond the surety must perform plugging and abandonment as guaranteed by the bond or must deposit the amount of the penal sum into the standby trust fund.
f) The penal sum of the bond must be in an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate.
g) Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the penal sum, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the penal sum to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the penal sum may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Agency.
h) Under the terms of the bond, the surety may cancel the bond by sending notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and to the Agency. Cancellation may not occur, however, during 120 days beginning on the date of the receipt of the notice of cancellation by both owner or operator and the Agency as evidenced by the returned receipts.
i) The owner or operator may cancel the bond if the Agency has given prior written consent. The Agency must provide such written content when either of the following occurs:
1) An owner or operator substitute alternate financial assurance; or
2) The Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
j) The surety will not be liable for deficiencies in the performance of plugging and abandonment by the owner or operator after the Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(c) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.217 Letter of Credit
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by obtaining an irrevocable standby letter of credit that conforms to this Section and submitting the letter to the Agency. An owner or operator of an injection well must submit the letter of credit to the Agency during submission of the permit application or for approval to operate under rule. The letter of credit must be effective before initial injection of hazardous waste. The issuing institution must be entity that has the authority to issue letters of credit and whose letter-of-credit operations are regulated and examined by a federal or State agency.
b) The wording of the letter of credit must be as specified in Section 704.240.
c) An owner or operator who uses a letter of credit to satisfy the financial assurance requirement must also establish a standby trust fund. Under the terms of the letter of credit, all amounts paid pursuant to a draft by the Agency must be deposited by the issuing institution directly into the standby trust fund in accordance with instructions from the Agency. This standby trust fund must meet the requirements of the trust fund specified in Section 704.214, except that the following limitations apply:
1) An original, signed duplicate of the trust agreement must be submitted to the Agency with the letter of credit; and
2) Unless the standby trust fund is funded pursuant to this Section, the following are not required:
A) Payments into the trust fund as specified in Section 704.214;
B) Updating of Schedule A of the trust agreement to show current cost estimates;
C) Annual valuations as required by the trust agreement; and
D) Notices of non-payment as required by the trust agreement.
d) The letter of credit must be accompanied by a letter from the owner or operator referring to the letter of credit by number, issuing institution and date, and providing the following information: the USEPA identification number, name and address of the facility, and the amount of funds assured for plugging and abandonment of the well by the letter of credit.
e) The letter of credit must be irrevocable and issued for a period of at least one year. The letter of credit must provide that the expiration date will be automatically extended for a period of at least one year unless, at least 120 days before the current expiration date, the issuing institution notifies both the owner or operator and the Agency by certified mail of a decision not to extend the expiration date. Under the terms of the letter of credit, the 120 days will begin on the date when both the owner or operator and the Agency have received the notice, as evidenced by the return receipts.
f) The letter of credit must be issued in an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in Section 704.220.
g) Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the amount of the credit, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the amount of the letter of credit to be increased so that it at least equals the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the amount of the letter of credit may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Agency.
h) Following a determination that the owner or operator has failed to perform final plugging and abandonment in accordance with the plan and other permit requirements when required to do so, the Agency may draw on the letter of credit.
i) If the owner or operator does not establish alternate financial assurance and obtain written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice from the issuing institution that it has decided not to extend the letter of credit beyond the current expiration date, the Agency must draw on the letter of credit. The Agency may delay the drawing if the issuing institution grants an extension of the term of the credit. During the last 30 days of any such extension the Agency must draw on the letter of credit if the owner or operator has failed to provide alternate financial assurance and obtain written approval of such assurance from the Agency.
j) The Agency must return the letter of credit to the issuing institution for termination when:
1) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance; or
2) The Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(d) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.218 Plugging and Abandonment Insurance
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by obtaining insurance that conforms to this Section and submitting a certificate of such insurance to the Agency. An owner or operator of a new injection well must submit the certificate of insurance to the Agency with the permit application or for approval operate under rule. The insurance must be effective before injection starts. At a minimum, the insurer must be licensed to transact the business of insurance, or eligible to provide insurance as an excess or surplus lines insurer, in one or more States.
b) The wording of the certificate of insurance must be as specified in Section 704.240.
c) The policy must be issued for a face amount at least equal to the current cost estimate, except as provided in Section 704.220. The term “face amount” means the total amount the insurer is obligated to pay under the policy. Actual payments by the insurer will not change the face amount, although the insurer’s future liability will be lowered by the amount of the payments.
d) The policy must guarantee that funds will be available whenever final plugging and abandonment occurs. The policy must also guarantee that once plugging and abandonment begins, the insurer will be responsible for paying out funds, up to an amount equal to the face amount of the policy, upon the direction of the Agency to such party or parties as the Agency specifies.
e) After beginning plugging and abandonment, an owner or operator or any other person authorized to perform plugging and abandonment may request reimbursement for plugging and abandonment expenditures by submitting itemized bills to the Agency. Within 60 days after receiving bills for plugging and abandonment activities, the Agency must determine whether the plugging and abandonment expenditures are in accordance with the plan or otherwise justified, and if so, it must instruct the insurer to make reimbursement in such amounts as the Agency specifies in writing. If the Agency has reason to believe that the cost of plugging and abandonment will be significantly greater than the face amount of the policy, it may withhold reimbursement of such amounts as it deems prudent until it determines, in accordance with Section 704.222, that the owner or operator is no longer required to maintain financial assurance for plugging and abandonment of the injection well.
f) The owner or operator must maintain the policy in full force and effect until the Agency consents to termination of the policy by the owner or operator, as specified in subsection (j) of this Section. Failure to pay the premium, without substitution of alternate financial assurance, will constitute a significant violation of these regulations, warranting such remedy as the Agency deems necessary. Such violation will be deemed to begin upon receipt by the Agency of a notice of future cancellation, termination or failure to renew due to non-payment of the premium, rather than upon the date of expiration.
g) Each policy must contain provisions allowing assignment to a successor owner or operator. Such assignment may be conditional upon consent of the insurer, provided such consent is not unreasonably refused.
h) The policy must provide that the insurer may not cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy except for failure to pay the premium. The automatic renewal of the policy must, at a minimum, provide the insured with the option of renewal at the face amount of the expiring policy. If there is a failure to pay the premium, the insurer may elect to cancel, terminate, or fail to renew the policy by sending notice by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Agency. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur, however, during 120 days beginning with the date of receipt of the notice by both the Agency and the owner or operator, as evidenced by the return of receipts. Cancellation, termination, or failure to renew may not occur and the policy will remain in full force and effect in the event that on or before the date of expiration any of the following occurs:
1) The Agency deems the injection well abandoned;
2) The permit is terminated or revoked or a new permit is denied;
3) Plugging and abandonment is ordered by the Board, a U.S. district court, or any other court of competent jurisdiction;
4) The owner or operator is named as debtor in a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under 11 USC (Bankruptcy); or
5) The premium due is paid.
i) Whenever the current cost estimate increases to an amount greater than the face amount of the policy, the owner or operator, within 60 days after the increase, must either cause the face amount to be increased to an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate and submit evidence of such increase to the Agency, or obtain other financial assurance to cover the increase. Whenever the current cost estimate decreases, the face amount may be reduced to the amount of the current cost estimate following written approval by the Agency.
j) The Agency must give written consent to the owner or operator that the owner or operator may terminate the insurance policy when either of the following occurs:
1) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance; or
2) The Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(e) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.219 Financial Test and Corporate Guarantee
a) An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by demonstrating that the owner or operator passes a financial test as specified in this Section. To pass this test the owner or operator must meet the criteria of either subsection (a)(1) or (a)(2) of this Section:
1) The owner or operator must have each of the following:
A) Two of the following three ratios: A ratio of total liabilities to net worth less than 2.0; a ratio of the sum of net income plus depreciation, depletion, and amortization to total liabilities greater than 0.1; and a ratio of current assets to current liabilities greater than 1.5;
B) Net working capital and tangible net worth each at least six times the sum of the current cost estimate;
C) A tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and
D) Assets in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of the owner or operator’s total assets or at least six times the sum of the current cost estimate.
2) The owner or operator must have each of the following:
A) A current rating for the owner or operator’s most recent bond issuance of AAA, AA, A, or BBB, as issued by Standard and Poor’s, or Aaa, Aa, A, or Baa, as issued by Moody’s;
B) A tangible net worth at least six times the sum of the current cost estimate;
C) A tangible net worth of at least $10 million; and
D) Assets located in the United States amounting to at least 90 percent of the owner or operator’s total assets or at least six times the sum of the current cost estimates.
b) The phrase “current cost estimate” as used in subsection (a) of this Section refers to the cost estimate required to be shown in paragraphs 1 through 4 of the letter from the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer, as specified in Section 704.240.
c) To demonstrate that the owner or operator meets this test, the owner or operator must submit the following items to the Agency:
1) A letter signed by the owner’s or operator’s chief financial officer and worded as specified in Section 704.240;
2) A copy of the independent certified public accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements for the latest completed fiscal year; and
3) A special report from the owner’s or operator’s independent certified public accountant to the owner or operator stating that the following are true:
A) The accountant has compared the data that the letter from the chief financial officer specifies as having been derived from the independently audited, year-end financial statements for the latest fiscal year with the amounts in such financial statements; and
B) In connection with that procedure, no matters came to the accountant’s attention that caused the accountant to believe that the specified data should be adjusted.
d) An owner or operator of a new injection well must submit the items specified in subsection (c) of this Section to the Agency within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in subsection (c) of this Section.
e) After the initial submission of items specified in subsection (c) of this Section, the owner or operator must send updated information to the Agency within 90 days after the close of each succeeding fiscal year. This information must consist of all three items specified in subsection (c) of this Section.
f) If the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (a) of this Section, the owner or operator must send notice to the Agency intent to establish alternate financial assurance. The notice must be sent by certified mail within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year for which the year-end financial data show that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements. The owner or operator must provide the alternate financial assurance within 120 days after the end of such fiscal year.
g) The Agency may, based on a reasonable belief that the owner or operator may no longer meet the requirements of subsection (a) of this Section, require reports of financial condition at any time from the owner or operator in addition to those specified in subsection (c) of this Section. If the Agency finds, on the basis of such reports or other information, that the owner or operator no longer meets the requirements of subsection (a), the owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance within 30 days after notification of such a finding.
h) The Agency may disallow use of this test on the basis of qualifications in the opinion expressed by the independent certified public accountant in the accountant’s report on examination of the owner’s or operator’s financial statements (see subsection (c)(2) of this Section). An adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion will be cause for disallowance. The Agency must evaluate other qualifications on an individual basis. The owner or operator must provide alternate financial assurance within 30 days after notification of the disallowance.
i) The owner or operator is no longer required to submit the items specified in subsection (c) of this Section when either of the following occurs:
1) An owner or operator substitutes alternate financial assurance; or
2) The Agency releases the owner or operator in accordance with Section 704.222.
j) An owner or operator may meet the requirements of this Section by obtaining a written guarantee, hereafter referred to as “corporate guarantee.” The guarantor must be the parent corporation of the owner or operator. The guarantor must meet the requirements for owners or operators in subsections (a) through (h) of this Section and must comply with the terms of the corporate guarantee. The wording of the corporate guarantee must be as specified in Section 704.240. The corporate guarantee must accompany the items sent to the Agency, as specified in subsection (c) of this Section. The terms of the corporate guarantee must provide that the following limitations apply:
1) If the owner or operator fails to perform plugging and abandonment of the injection well covered by the corporate guarantee in accordance with the plan and other permit requirements whenever required to do so, the guarantor must do so or establish a trust fund, as specified in Section 704.214 in the name of the owner or operator.
2) The corporate guarantee must remain in force unless the guarantor sends notice of cancellation by certified mail to the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts. Cancellation may not occur, however, during the 120 days beginning on the date of receipt of the notice of cancellation by both the owner or operator and the Agency, as evidenced by the return receipts.
3) If the owner or operator fails to provide alternate financial assurance and obtain the written approval of such alternate assurance from the Agency within 90 days after receipt by both the owner or operator and the Agency of a notice of cancellation of the corporate guarantee from the guarantor, the guarantor must provide such alternative financial assurance in the name of the owner or operator.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(f) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.220 Multiple Financial Mechanisms
An owner or operator may satisfy the financial assurance requirement by establishing more than one financial mechanism per injection well. These mechanisms are limited to trust funds, surety bonds guaranteeing payment into a trust fund, letter of credit, and insurance. The mechanisms must be as specified in Sections 704.214, 704.215, 704.217, and 704.218, respectively, except that it is the combination of mechanisms, rather than the single mechanism, that must provide financial assurance for an amount at least equal to the current cost estimate. If an owner or operator uses a trust fund in combination with a surety bond or letter of credit, the owner or operator may use that trust fund as the standby trust fund for the other mechanisms. A single standby trust may be established for two or more mechanisms. The Agency may invoke any or all of the mechanisms to provide for plugging and abandonment of the injection well.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(g) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.221 Financial Mechanism for Multiple Facilities
An owner or operator may use a financial assurance mechanism specified in Sections 704.213 or 704.220 to meet the financial assurance requirement for more than one injection well. Evidence of financial assurance submitted to the Agency must include a list showing, for each injection well, the USEPA identification number, name, address, and the amount of funds for plugging and abandonment assured by the mechanisms. The operator must provide sufficient financial assurance to the Agency to plug and abandon all of the wells the operator has in Illinois. The amount of funds available through the mechanism must be no less than the sum of funds that would be available if a separate mechanism has been established and maintained for each injection well. In directing funds available through the mechanism for plugging and abandonment of any of the injection wells covered by the mechanism, the Agency may direct only the amount of funds designated for that injection well, unless the owner or operator agrees to use additional funds available under the mechanism.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(h) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.222 Release of the Owner or Operator
Within 60 days after receiving certifications from the owner or operator and an independent registered professional engineer that plugging and abandonment has been accomplished in accordance with the plan, the Agency must notify the owner or operator in writing that the owner or operator is no longer required by this Subpart G to maintain financial assurance for plugging and abandonment of the injection well, unless the Agency has reason to believe that plugging and abandonment has not been in accordance with the plan.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.63(i) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.230 Incapacity
a) An owner or operator must notify the Agency by certified mail of the commencement of a voluntary or involuntary proceeding under 11 USC (Bankruptcy), naming the owner or operator as debtor, within 10 business days after the commencement of the proceeding. A guarantor of a corporate guarantee as specified in Section 704.219 must make such a notification if the guarantor is named as debtor, as required under the terms of guarantee in Section 704.240.
b) An owner or operator who fulfills Section 704.213 by obtaining a letter of credit, surety bond, or insurance policy will be deemed to be without the required financial assurance in the event of bankruptcy, insolvency or a suspension or revocation of the license or charter of the issuing institution. The owner or operator must establish other financial assurance within 60 days after such an event.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.64 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.240 Wording of the Instruments
The Agency must promulgate standardized forms based on 40 CFR 144.70 (Wording of the Instruments), incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(b), with such changes in wording as are necessary under Illinois law. Any owner or operator required to establish financial assurance under this Subpart G must do so only upon the standardized forms promulgated by the Agency. The Agency may reject any financial assurance document that is not submitted on such standardized forms.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.70 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
SUBPART H: ISSUED PERMITS
Section 704.260 Transfer
a) Transfer by modification. Except as provided in subsection (b) of this Section, a permit may be transferred by the permittee to a new owner or operator only if the permit has been modified or reissued (under Sections 704.261 through 704.264) to identify the new permittee and incorporate such other requirements as may be necessary under the appropriate Act. The new owner or operator to whom the permit is transferred must comply with all the terms and conditions specified in such permit.
b) Automatic transfers. As an alternative to transfers under subsection (a) of this Section, any UIC permit for a well not injecting hazardous or injecting carbon dioxide for geologic sequestration waste may be automatically transferred to a new permittee if each of the following conditions are fulfilled:
1) The current permittee notifies the Agency at least 30 days in advance of the proposed transfer date in subsection (b)(2) of this Section;
2) The notice includes a written agreement between the existing and new permittees containing a specific date for transfer of permit responsibility, coverage and liability between them and the notice demonstrates that the financial responsibility requirements of Section 704.189 will be met by the new permittee and that the new permittee agrees to comply with all the terms and conditions specified in the permit to be transferred under subsection (b) of this Section; and
3) The Agency does not notify the existing permittee and the proposed new permittee of its intent to modify or reissue the permit. A modification under this subsection (b) may also be a minor modification under Section 704.264. If this notice is not received, the transfer is effective on the date specified in the agreement mentioned in subsection (b)(2) of this Section.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.38 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.261 Modification
When the Agency receives any information (for example, it inspects the facility; it receives information submitted by the permittee, as required in the permit (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.140 through 702.152); it receives a request for modification or reissuance; or it conducts a review of the permit file), it may determine whether or not one or more of the causes listed in Sections 704.262 and 704.263 for modification or reissuance exist. If cause exists, the Agency may modify or reissue the permit accordingly, subject to the limitations of Section 704.263 and may request an updated application if necessary. When a permit is modified, only the conditions subject to modification are reopened. If cause does not exist under Sections 704.261 through 704.264, the Agency may not modify or reissue the permit. If a permit modification satisfies the criteria in Section 704.264 for “minor modifications” the permit may be modified without a draft permit or public review. Otherwise, a draft permit must be prepared and other procedures in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705 followed.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.39 preamble (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.262 Causes for Modification
a) The following are causes for modification of a permit. For a Class I hazardous waste injection well or a Class III or Class IV injection well, any of the following may be cause for reissuance of the permit, as well as for permit modification. For all other injection wells, the following may be cause for reissuance of the permit, as well as for permit modification, when the permittee requests or agrees:
1) Alterations. There are material and substantial alterations or additions to the permitted facility or activity that occurred after permit issuance that justify the application of permit conditions that are different or absent in the existing permit.
2) Information. Permits other than for a Class III injection well may be modified during their terms for this cause only if the information was not available at the time of permit issuance (other than revised regulations, guidance, or test methods) and would have justified the application of different permit conditions at the time of issuance. For an area permit, this cause must include any information indicating that cumulative effects on the environment are unacceptable.
3) New statutory requirements or regulations. The standards or regulations on which the permit was based have been changed by statute, through promulgation of new or amended standards or regulations, or by judicial decision after the permit was issued. A permit other than for a Class I hazardous waste injection well or a Class III or Class VI injection well may be modified during their terms for this cause only as follows:
A) The Agency may modify the permit when standards or regulations on which the permit was based have been changed by statute or amended standards or regulations.
B) The permittee may request modification when all of the following occur:
i) The permit condition requested to be modified was based on a provision of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730;
ii) The Board has revised, withdrawn, or modified that provision on which the permit condition was based; and
iii) The permittee requests modification in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705.128 within 90 days after the effective date of the changed statute or amended standards or regulations on which the request is based.
C) For judicial decisions, a court of competent jurisdiction has remanded and stayed Board promulgated regulations, if the remand and stay concern that portion of the regulations on which the permit condition was based or if a request is filed by the permittee in accordance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705.128 within 90 days after judicial remand.
4) Compliance schedules. The Agency determines good cause exists for modification of a compliance schedule, such as an act of God, strike, flood, materials shortage, or other events over which the permittee has little or no control and for which there is no reasonably available remedy.
5) Basis for modification of Class VI permits. Additionally, for Class VI injection wells, whenever the Agency determines that permit changes are necessary based on any of the following:
A) A reevaluation of the area of review undertaken pursuant to Section 730.184(e)(1);
B) Any amendments to the testing and monitoring plan made pursuant to Section 730.190(j);
C) Any amendments to the injection well plugging plan made pursuant to Section 730.192(c);
D) Any amendments to the post-injection site care and site closure plan made pursuant to Section 730.193(a)(3);
E) Any amendments to the emergency and remedial response plan made pursuant to Section 730.194(d); or
F) A review of monitoring or testing results conducted in accordance with permit requirements.
b) The following are causes to modify or, alternatively, to reissue a permit:
1) The Agency has received notification (as required in the permit, see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.152(c)) of a proposed transfer of the permit. A permit also may be modified to reflect a transfer after the effective date of an automatic transfer (35 Ill. Adm. Code 702.182(b)), but it must not be reissued after the effective date of the transfer, except upon the request of the new permittee.
2) A determination that the waste being injected is a hazardous waste, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 721.103, either because the definition has been revised, or because a previous determination has been changed.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.39 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.263 Well Siting
Suitability of the well location must not be considered at the time of permit modification unless new information or standards indicate that a threat to human health or the environment exists that was unknown at the time of permit issuance or unless required under the Act [415 ILCS 5]. However, certain modifications may require site location suitability approval pursuant to Section 39.2 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/39.2].
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.39(c) (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.264 Minor Modifications
Upon the consent of the permittee, the Agency may modify a permit to make the corrections or allowances for changes in the permitted activity listed in this Section, without following the procedures of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705. Any permit modification not processed as a minor modification under this Section must be made for cause and with a 35 Ill. Adm. Code 705 draft permit and public notice, as required in Sections 704.261 through 704.263. Minor modifications may only involve the following changes:
a) Correcting typographical errors;
b) Requiring more frequent monitoring or reporting by the permittee;
c) Changing an interim compliance date in a schedule of compliance, provided the new date is not more than 120 days after the date specified in the existing permit and does not interfere with attainment of the final compliance date requirement; or
d) Allowing for a change in ownership or operational control of a facility where the Agency determines that no other change in the permit is necessary, provided that a written agreement containing a specific date for transfer of permit responsibility, coverage, and liability between the current and new permittees has been submitted to the Agency; or
e) Changing quantities or types of fluids injected that are within the capacity of the facility as permitted andwhich the Agency has determined would not interfere with the operation of the facility or its ability to meet conditions described in the permit and would not change its classification.
f) Changing construction requirements approved by the Agency pursuant to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 704.182 (establishing UIC permit conditions), provided that any such alteration must comply with this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730.
g) Amending a plugging and abandonment plan that has been updated under Section 704.181(e).
h) Amending a Class VI injection well testing and monitoring plan, plugging plan, post-injection site care and site closure plan, or emergency and remedial response plan, where the Agency determines that the modifications merely clarify or correct the plan.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.41 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
SUBPART I: REQUIREMENTS FOR CLASS V INJECTION WELLS
Section 704.279 General
This Subpart I sets forth the requirements applicable to the owner or operator of a Class V injection well. Additional requirements listed elsewhere in this Part may also apply. Where they may apply, those other requirements are referenced rather than repeated in this Subpart I. The requirements described in this Subpart I and elsewhere in this Part are intended to protect USDWs and are part of the UIC program established under Section 13(c) of the Act [415 ILCS 5/13(c)].
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.79 (2005). USEPA wrote corresponding subpart G of 40 CFR 144 in a question-and-answer format to make it easier to understand the regulatory requirements. The Board has abandoned that format in favor of a more traditional approach of using clear statements of the requirements and their applicability.
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.280 Definition of a Class V Injection Well
Section 704.106 defines the six classes of injection wells, including a Class V injection well, as regulated under this Subpart I. Typically, Class V injection wells are shallow wells used to place a variety of fluids directly below the land surface. However, if the fluids placed in the ground qualify as a hazardous waste under RCRA, the well is either a Class I or Class IV injection well, not a Class V injection well. Similarly, a carbon sequestration well is a Class VI injection well (or a Class II injection well under specified circumstances), not a Class V injection well. Examples of Class V injection wells are described in Section 704.281.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.80 (2011).
(Source: Amended at 36 Ill. Reg. 1613, January 20, 2012)
Section 704.281 Examples of Class V Injection Wells
The following are examples of Class V injection wells to which this Subpart I applies:
a) Air conditioning return flow wells used to return to the supply aquifer the water used for heating or cooling in a heat pump;
b) A large capacity cesspool, including a multiple-dwelling, community, or regional cesspool, or any other device that receives sanitary wastes containing human excreta that has an open bottom and, sometimes, perforated sides. The UIC requirements do not apply to a single family residential cesspool, nor do they apply to a non-residential cesspool that receives solely sanitary waste and which has the capacity to serve fewer than 20 persons a day;
c) A cooling water return flow well that is used to inject water previously used for cooling;
d) A drainage well that is used to drain surface fluids, primarily storm runoff, into a subsurface formation;
e) A dry well that is used for the injection of wastes into a subsurface formation;
f) A recharge well that is used to replenish the water in an aquifer;
g) A salt water intrusion barrier well that is used to inject water into a fresh aquifer to prevent the intrusion of salt water into the fresh water;
h) A sand backfill and other backfill well that is used to inject a mixture of water and sand, mill tailings, or other solids into mined out portions of a subsurface mine whether what is injected is a radioactive waste or not;
i) A septic system well that is used to inject the waste or effluent from a multiple dwelling, business establishment, community, or regional business establishment septic tank. The UIC requirements do not apply to a single family residential septic system well, nor to a non-residential septic system well that is used solely for the disposal of sanitary waste and which has the capacity to serve fewer than 20 persons a day;
j) A subsidence control well (not used for the purpose of oil or natural gas production) that is used to inject fluids into a non-oil-and-gas-producing zone to reduce or eliminate subsidence associated with the overdraft of fresh water;
k) An injection well associated with the recovery of geothermal energy for heating, aquaculture, and production of electric power;
l) A well that is used for solution mining of conventional mines, such as stopes leaching;
m) A well that is used to inject spent brine into the same formation from which it was withdrawn after extraction of halogens or their salts;
n) An injection well that is used in experimental technologies;
o) An injection well that is used for in situ recovery of lignite, coal, tar sands, and oil shale; and
p) A motor vehicle waste disposal well that receives or which has received fluids from vehicular repair or maintenance activities, such as an auto body repair shop, an automotive repair shop, a new or used car dealership, a specialty repair shop (e.g., transmission and muffler repair shop), or any facility that does any vehicular repair work. Fluids disposed in this type of well may contain organic and inorganic chemicals in concentrations that exceed the maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) established by the primary drinking water regulations (35 Ill. Adm. Code 611). These fluids also may include waste petroleum products and may contain contaminants, such as heavy metals and volatile organic compounds, that pose risks to human health.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.81 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.282 Protection of Underground Sources of Drinking Water
This Subpart I requires that an owner or operator of a Class V injection well must not allow movement of fluid into USDWs that might cause endangerment of the USDW, that the owner or operator must comply with the UIC requirements in this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730, that the owner or operator must comply with any other measures required by the State or USEPA to protect USDWs, and that the owner or operator must properly close its well when the owner or operator is through using it. The owner or operator also must submit basic information about its well, as described in Section 704.283.
a) Prohibition of fluid movement.
1) As described in Section 704.122(a), an owner’s or operator’s injection activity cannot allow the movement of fluid containing any contaminant into USDWs if the presence of that contaminant may cause a violation of the primary drinking water standards under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611, may cause a violation of other health-based standards, or may otherwise adversely affect the health of persons. This prohibition applies to the owner’s or operator’s well construction, operation, maintenance, conversion, plugging, closure, or any other injection activity.
2) If the Agency learns that an owner’s or operator’s injection activity may endanger a USDW, the Agency may require the owner or operator to close its well, require the owner or operator to get a permit, or require other actions listed in Section 704.122(c), (d), or (e).
b) Closure requirements. An owner or operator must close the well in a manner that complies with the above prohibition of fluid movement. Also, the owner or operator must dispose of or otherwise manage any soil, gravel, sludge, liquids, or other materials removed from or adjacent to its well in accordance with all applicable federal, State, and local regulations and requirements.
c) Other requirements in this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730. Beyond this Subpart I, the owner and operator are subject to other UIC program requirements in this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730. While most of the relevant requirements are repeated or referenced in this Subpart I for convenience, the owner or operator needs to read all of this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730 to fully understand the entire UIC program.
d) Other State requirements. This Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730 define minimum federally-derived UIC requirements. The Agency has the flexibility to establish additional or more stringent requirements based on the authorities in this Part, 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730, and the Act [415 ILCS 5], if such additional requirements are determined to be necessary to protect USDWs. The owner and operator must comply with any such additional requirements. The owner or operator should contact the Agency to learn more.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.82 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.283 Notification of a Class V Injection Well
The owner or operator of a Class V injection well needs to provide basic “inventory information” about its well to the Agency, if the owner or operator has not done so already. The owner or operator also needs to provide any additional information that the Agency requests in accordance with the provisions of the UIC regulations.
a) Inventory requirements. Unless the owner or operator knows it has already satisfied the inventory requirements in Section 704.128 that were in effect prior to the issuance of this Subpart I, the owner or operator must give the Agency certain information about itself and its injection operation.
BOARD NOTE: In the corresponding note to 40 CFR 144.83(a), USEPA states that this information is requested on national form “Inventory of Injection Wells,” USEPA Form 7520-16, incorporated by reference in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 720.111(a). Although USEPA Form 7520-16 is acceptable to USEPA, the Agency may develop alternative forms for use in this State.
1) The owner or operator of a new or existing Class V injection well must contact the Agency to determine what information it must submit and by when it must submit that information.
2) The following is the information that the owner or operator must submit:
A) No matter what type of Class V injection well is owned or operated, the owner or operator must submit at least the following information for each Class V injection well:i) The facility name and location;
ii) The name and address of a legal contact person for the facility;
iii) The ownership of the facility;
iv) The nature and type of the injection well or wells; and
v) The operating status of the injection well or wells.
B) Illinois is designated a “Primacy State” by USEPA. Corresponding 40 CFR 144.83(a)(2)(ii) relates exclusively to “Direct Implementation” states, so the Board has omitted it. This statement maintains structural consistency with the federal regulations.
C) The owner or operator must provide a list of all wells it owns or operates, along with the following information for each well. (A single description of wells at a single facility with substantially the same characteristics is acceptable.)
i) The location of each well or project given by Township, Range, Section, and Quarter-Section, according to the U.S. Land Survey System;
ii) The date of completion of each well;
iii) The identification and depth of the underground formations into which each well is injecting;
iv) The total depth of each well;
v) A construction narrative and schematic (both plan view and cross-sectional drawings);
vi) The nature of the injected fluids;
vii) The average and maximum injection pressure at the wellhead;
viii) The average and maximum injection rate; and
ix) The date of the last inspection.
3) The owner and operator is responsible for knowing about, understanding, and complying with these inventory requirements.
b) Illinois is designated a “Primacy State” by USEPA. Corresponding 40 CFR 144.83(b) relates exclusively to “Direct Implementation” states, so the Board has omitted it. This statement maintains structural consistency with the federal regulations.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.83 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.284 Permit Requirements
No permit is required for a Class V injection well, unless the owner or operator falls within an exception described in subsection (b) of this Section.
a) General authorization by rule. With certain exceptions listed in subsection (b) of this Section, an owner’s or operator’s Class V injection activity is “authorized by rule,” meaning that the owner and operator has to comply with all the requirements of this Subpart I and the rest of this Part and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and 730, but the owner or operator does not need to get an individual permit. Well authorization expires once the owner or operator has properly closed its well, as described in Section 704.282(b).
b) Circumstances in which permits or other actions are required. If an owner or operator fits into one of the categories listed below, its Class V injection well is no longer authorized by rule. This means that the owner or operator has to either get a permit or close its injection well. The owner or operator can find out whether its well falls into one of these categories by contacting the Agency. Subparts D and H of this Part tell an owner or operator how to apply for a permit and describe other aspects of the permitting process. Subpart C of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 702 and Subpart E of this Part outline some of the requirements that apply to the owner or operator if it gets a permit. An owner or operator must either obtain a permit or close its injection well if any of the following is true:
1) The owner or operator fails to comply with the prohibition against fluid movement in Section 704.122(a) and described in Section 704.282(a) (in which case, the owner or operator must get a permit, close its well, or comply with other conditions determined by the Agency);
2) The Class V injection well is a large-capacity cesspool (in which case, the owner or operator must close its well as specified in the additional requirements set forth in Section 704.288) or the Class V injection well is a motor vehicle waste disposal well in a groundwater protection area or a sensitive groundwater area (in which case, the owner or operator must either close its well or get a permit, as specified in the additional requirements set forth in Section 704.288). New motor vehicle waste disposal wells and new cesspools are prohibited;
BOARD NOTE: A new motor vehicle waste disposal well or a new cesspool is one for which construction had not commenced prior to April 5, 2000. See 40 CFR 144.84(a)(2).
3) The owner or operator is specifically required by the Agency to get a permit (in which case, the authorization by rule expires on the effective date of the permit issued, or the owner or operator is prohibited from injecting into its well upon the occurrence of either of the following:
A) The failure of the owner and operator to submit a permit application in a timely manner, as specified in a notice from the Agency; or
B) The effective date of a permit denial; or
4) The owner or operator has failed to submit inventory information to the Agency, as described in Section 704.283(a) (in which case, the owner and operator is prohibited from injecting into the well until it complies with the inventory requirements).
5) Illinois is designated a “Primacy State” by USEPA. Corresponding 40 CFR 144.84(b)(5) relates exclusively to “Direct Implementation” states, so the Board has omitted it. This statement maintains structural consistency with the federal regulations.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.84 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.285 Applicability of the Additional Requirements
a) Large-capacity cesspools. The additional requirements set forth in Section 704.288 apply to a new and existing large-capacity cesspool. If the owner or operator is using a septic system for these type of wastes, the owner or operator is not subject to the additional requirements in Section 704.288.
b) Motor vehicle waste disposal wells existing on April 5, 2000. If the owner or operator has a Class V motor vehicle waste disposal well, the additional requirements in Section 704.288 apply to that owner or operator if the well is located in a ground water protection area or other sensitive ground water area that is identified by the Agency, the Board, or USEPA Region 5.
BOARD NOTE: An existing motor vehicle waste disposal well is one for which construction had commenced prior to April 5, 2000. See 40 CFR 144.83(a)(1)(i) and (a)(1)(ii), as added at 64 Fed. Reg. 68568 (December 7, 1999). Corresponding 40 CFR 144.85(b) provides that the additional requirements apply Statewide if the State or the USEPA Region fails to identify sensitive groundwater areas. The Board has not included this Statewide applicability provision by virtue of 14.1 through 14.6 and Sections 17.1 through 17.4 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/14.1-14.6 and 17.1-17.4], Section 8 of the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55/8], and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 through 620.
c) New Motor Vehicle Waste Disposal Wells. The additional requirements in Section 704.288 apply to a new motor vehicle waste disposal well.
BOARD NOTE: A new motor vehicle waste disposal well is one for which construction had not commenced prior to April 5, 2000. See 40 CFR 144.85(c) (2005).
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.85 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.286 Definitions
“State drinking water source assessment and protection program” is a new approach to protecting drinking water sources, specified in section 1453 of the 1996 Amendments to the Safe Drinking Water Act (42 USC 300j-13).
BOARD NOTE: Under the federal requirements, states must prepare and submit for USEPA approval a program that sets out how each state must conduct local assessments, including the following: delineating the boundaries of areas providing source waters for public water systems; identifying significant potential sources of contaminants in such areas; and determining the susceptibility of public water systems in the delineated areas to the inventoried sources of contamination. The Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55] and the regulations at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620 adopted pursuant to that law and Sections 14.1 through 14.6 and 17.1 through 17.4 of the Environmental Protection Act [415 ILCS 14.1-14.6 and 17.1-17.4] and the regulations at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 through 617 adopted under those provisions are major segments of the required Illinois program.
“Complete local source water assessment for groundwater protection areas.” When USEPA has approved a state’s drinking water source assessment and protection program, the state must begin to conduct local assessments for each public water system in that state. For the purposes of this Subpart I, local assessments for community water systems and non-transient non-community systems are complete when the four following requirements are met:
The State must delineate the boundaries of the assessment area for community and non-transient non-community water systems, as such are defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.101;
The State must identify significant potential sources of contamination in these delineated areas;
The State must determine the susceptibility of community and non-transient non-community water systems in the delineated area to such contaminants; and
The Agency must make the completed assessments available to the public.
BOARD NOTE: The Agency administers the “Illinois Source Water Assessment and Protection Program,” which is intended to comply with the federal source water assessment requirements of SDWA Section 1453 (42 USC 300j-13).
“Groundwater protection area” is a geographic area near or surrounding a community or non-transient non-community water system, as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.101, that uses groundwater as a source of drinking water. For the purposes of this Subpart I, the Board considers a “setback zone,” as defined in Section 3.61 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/3.61] and regulated pursuant to Sections 14.1 through 14.6 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/14.1-14.6], to be a “groundwater protection area,” as intended by corresponding 40 CFR 144.86(c). (See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 and 616.) These areas receive priority for the protection of drinking water supplies and federal law requires the State to delineate and assess these areas under section 1453 of the federal Safe Drinking Water Act, 42 USC 300j-13. The additional requirements in Section 704.288 apply to an owner or operator if its Class V motor vehicle waste disposal well is in a groundwater protection area for either a community water system or a non-transient non-community water system.
BOARD NOTE: USEPA stated in corresponding 40 CFR 144.86(c) that in many states these areas will be the same as wellhead protection areas delineated as described in section 1428 of the federal SDWA (42 USC 300h-7).
“Community water system,” as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.101, is a public water system that serves at least 15 service connections used by year-round residents or which regularly serves at least 25 year-round residents.
“Non-transient, non-community water system,” as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.101, is a water system that is not a community water system and which regularly serves at least 25 of the same people over six months a year. These may include systems that provide water to schools, day care centers, government or military installations, manufacturers, hospitals or nursing homes, office buildings, and other facilities.
“Delineation.” Once the State’s drinking water source assessment and protection program is approved by USEPA, the State must begin delineating its local assessment areas. “Delineation” is the first step in the assessment process in which the boundaries of groundwater protection areas are identified.
“Other sensitive groundwater areas.” The State may also identify other areas in the State in addition to groundwater protection areas that are critical to protecting USDWs from contamination. For the purposes of this Subpart I, the Board considers a “regulated recharge area,” as defined in Section 3.67 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/3.67] and regulated pursuant to Sections 17.1 through 17.4 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/17.1-17.4], to be an “other sensitive groundwater area,” as intended by corresponding 40 CFR 144.86(g). (See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 through 617.) These other sensitive groundwater areas may include areas such as areas overlying sole-source aquifers; highly productive aquifers supplying private wells; continuous and highly productive aquifers at points distant from public water supply wells; areas where water supply aquifers are recharged; karst aquifers that discharge to surface reservoirs serving as public water supplies; vulnerable or sensitive hydrogeologic settings, such as glacial outwash deposits, eolian sands, and fractured volcanic rock; and areas of special concern selected based on a combination of factors, such as hydrogeologic sensitivity, depth to groundwater, significance as a drinking water source, and prevailing land-use practices.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.86 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.287 Location in a Groundwater Protection Area or Another Sensitive Area
a) A person is subject to Section 704.288 if the person owns or operates an existing motor vehicle well and that person is located in a groundwater protection area or another sensitive groundwater area. If the State fails to identify these areas within the federally specified time frames, the additional requirements of Section 704.288 must apply to all existing motor vehicle waste disposal wells within this State.
BOARD NOTE: Corresponding 40 CFR 144.87(a) provides that the “new requirements” apply statewide if the State or the USEPA Region fails to identify sensitive groundwater areas. The Board has interpreted “new requirements” as synonymous with “additional requirements” elsewhere in this Subpart I. Sections 14.1 through 14.6 and 17.1 through 17.4 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/14.1-14.6 and 17.1-17.4] and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 through 617 designate protected groundwater resources and allow the designation of other sensitive areas for protection. Further, the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55], and the regulations adopted as 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620 under that statute, protect the quality of all groundwater resources in Illinois.
b) Groundwater protection areas. Many segments of corresponding 40 CFR 144.87(b) set forth requirements applicable to the State only. Other requirements apply to the regulated community contingent on the regulatory status of the Illinois groundwater protection program. The Board has codified the requirements applicable to the State in this subsection (b) for the purpose of informing the regulated public and clarifying the requirements on the regulated community.
1) For the purpose of this Subpart I, USEPA requires States to complete all local source water assessments for groundwater protection areas by January 1, 2004. Once a local assessment for a groundwater protection area is complete every existing motor vehicle waste disposal well owner in that groundwater protection area has one year to close the well or receive a permit. If the State fails to complete all local assessments for groundwater protection areas by January 1, 2004, the following may occur:
A) The new requirements in this Subpart I apply to all existing motor vehicle waste disposal wells in the State, and the owner or operator of a motor vehicle waste disposal well located outside of the areas of the completed area assessments for groundwater protection areas must have closed its well or obtained a permit by January 1, 2005.
B) USEPA may have granted a state an extension for up to one year from the January 1, 2004 deadline if the state was making reasonable progress toward completing the source water assessments for groundwater protection areas. States must have applied for the extension by June 1, 2003. If a state failed to complete the assessments for the remaining groundwater protection areas by the extended date, the rule requirements apply to all motor vehicle waste disposal wells in the state, and the owner or operator of a motor vehicle waste disposal well located outside of groundwater protection areas with completed assessments must have closed its well or received a permit by January 1, 2006.
2) The Agency must extend the compliance deadline for specific motor vehicle waste disposal wells for up to one year if it determines that the most efficient compliance option for the well is connection to a sanitary sewer or installation of new treatment technology and the extension is necessary to implement the compliance option.
BOARD NOTE: Any Agency determination of the most efficient compliance option is subject to Board review pursuant to Section 40 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/40].
c) Other sensitive groundwater areas. The owner or operator of an existing motor vehicle waste disposal well within another sensitive groundwater area has until January 1, 2007 to receive a permit or close the well. If the State failed to identify these additional sensitive groundwater areas by January 1, 2004, the additional requirements of Section 704.288 apply to all motor vehicle waste disposal wells in the State effective January 1, 2007, unless they are subject to a different compliance date pursuant to subsection (b) of this Section. If USEPA has granted the State an extension of the time to delineate sensitive groundwater areas, the owner or operator of an existing motor vehicle waste disposal well within a sensitive groundwater area has until January 1, 2008 to close the well or receive a permit, unless the owner or operator is subject to a different compliance date pursuant to subsection (b) of this Section. If the State has been granted an extension and fails to delineate sensitive areas by the extended date, an owner or operator has until January 1, 2008 to close the well or receive a permit, unless it is subject to a different compliance date pursuant to subsection (b) of this Section.
BOARD NOTE: Corresponding 40 CFR 144.87(c) provides that the State had until January 1, 2004 to identify sensitive groundwater areas. It also provides that USEPA may extend that deadline for up to an additional year if the State is making reasonable progress towards identifying such areas and the State had applied for the extension by June 1, 2003. The Board has not included these provisions relating to deadlines for State action because they impose requirements on the State, rather than on regulated entities. Further, the corresponding federal rule provides that the “new requirements” apply statewide if the State or the USEPA Region fails to identify sensitive groundwater areas and that “the rule requirements” apply in the event of an extension granted by USEPA and the State fails to delineate sensitive areas. The Board has interpreted “new requirements” and “rule requirements” as synonymous with “additional requirements” as used elsewhere in this Subpart I. Sections 17.1 through 17.4 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/17.1-17.4], Section 8 of the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55/8], and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615 through 620 protect groundwater resources and allow the designation of sensitive areas.
d) Finding out if a well is in a groundwater protection area or sensitive groundwater area. The Agency must make that listing available for public inspection and copying upon request. Any interested person may contact the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency, Bureau of Water, Division of Public Water Supplies at 1021 North Grand Ave. East, P.O. Box 19276, Springfield, Illinois 62794-9276 (217-785-8653) to obtain information on the listing or to determine if any Class V injection well is situated in a groundwater protection area or another sensitive groundwater area.
e) Changes in the status of the State drinking water source assessment and protection program. If the State assesses a groundwater protection area for groundwater supplying a new community water system or a new non-transient non-community water system after January 1, 2004, or if the State re-delineates the boundaries of a previously delineated groundwater protection area to include an additional area, the additional regulations of Section 704.288 would apply to any motor vehicle waste disposal well in such an area. The additional regulations apply to the affected Class V injection well one year after the State completes the local assessment for the groundwater protection area for the new drinking water system or the new re-delineated area. The Agency must extend this deadline for up to one year if it determines that the most efficient compliance option for the well is connection to a sanitary sewer or installation of new treatment technology and the extension is necessary to implement the compliance option.
BOARD NOTE: Any Agency determination of the most efficient compliance option is subject to Board review pursuant to Section 40 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/40].
f) If the State elects not to delineate the additional sensitive groundwater areas, the additional regulations of Section 704.288 apply to all Class V injection wells in the State, regardless of the location, on January 1, 2007, or January 1, 2008 if an extension has been granted as provided in subsection (c) of this Section, except for wells in groundwater protection areas that are subject to different compliance deadlines explained in subsection (b) of this Section.
g) Application of requirements outside of groundwater protection areas and sensitive groundwater areas. The Agency must apply the additional requirements in Section 704.288 to an owner or operator, even if the owner’s or operator’s well is not located in the areas listed in subsection (a) of this Section, if the Agency determines that the application of those additional requirements is necessary to protect human health and the environment.
BOARD NOTE: Any Agency determination to apply the additional requirements of Section 704.288 is subject to Board review pursuant to Section 40 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/40]. The Board has omitted certain segments of corresponding 40 CFR 144.87 that encouraged State actions, since those segments did not impose requirements on the regulated community.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.87 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.288 Additional Requirements
Additional requirements are as follows:
a) Additional Requirements for Large-Capacity Cesspools Statewide. See Section 704.285 to determine the applicability of these additional requirements.
1) If the cesspool is existing (operational or under construction by April 5, 2000), the following requirements apply:
A) The owner or operator must have closed the well by April 5, 2005.
B) The owner or operator must have notified the Agency of its intent to close the well at least 30 days prior to closure.
BOARD NOTE: In the corresponding note to 40 CFR 144.83(a), USEPA states that this information is requested on the federal form entitled “Preclosure Notification for Closure of Injection Wells.” Although the form “Preclosure Notification for Closure of Injection Wells” is acceptable to USEPA, the Agency may develop alternative forms for use in this State.
2) If the cesspool is new or converted (construction not started before April 5, 2000) it is prohibited.
BOARD NOTE: Corresponding 40 CFR 144.88(b)(2) sets forth a federal effective date of April 5, 2000 for the prohibition.
b) Additional Requirements for Motor Vehicle Waste Disposal Wells. See Section 704.285 to determine the applicability of these additional requirements.
1) If the motor vehicle waste disposal well is existing (operational or under construction by April 5, 2000) the following applies:
A) If the well is in a groundwater protection area, the owner or operator must close the well or obtain a permit within one year after the completion of the local source water assessment; the Agency must extend the closure deadline, but not the permit application deadline, for up to one year if it determines that the most efficient compliance option is connection to a sanitary sewer or installation of new treatment technology and the extension is necessary to implement the compliance option;
B) If the well is in an other sensitive groundwater area, the owner or operator must close the well or obtain a permit by January 1, 2007; the Agency may extend the closure deadline, but not the permit application deadline, for up to one year if it determines that the most efficient compliance option is connection to a sanitary sewer or installation of new treatment technology and the extension is necessary to implement the compliance option;
C) If the owner or operator plans to seek a waiver from the ban and apply for a permit by the date the owner or operator submits its permit application, the owner or operator must meet the maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for drinking water, set forth in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611, at the point of injection while the permit application is under review, if the owner or operator chooses to keep operating the well;
D) If the owner or operator receives a permit, the owner or operator must comply with all permit conditions by the dates specified in its permit, if the owner or operator chooses to keep operating the well, including requirements to meet MCLs and other health-based standards at the point of injection, follow best management practices, and monitor the injectate and sludge quality;
E) If the State has not completed all of its local assessments by January 1, 2004 (or by the extended date if the State has obtained an extension, as described in Section 704.287), and the well is outside an area with a completed assessment, the owner or operator must have closed the well or obtained a permit by January 1, 2005, unless the State obtained an extension, as described in Section 704.287(b), in which case the deadline was January 1, 2006; the Agency must have extended the closure deadline, but not the permit application deadline, for up to one year if it determined that the most efficient compliance option was connection to a sanitary sewer or installation of new treatment technology and the extension was necessary to implement the compliance option;
F) If the State had not delineated other sensitive groundwater areas by January 1, 2004, and the well is outside of an area with a completed assessment, the owner or operator must close the well or obtain a permit regardless of its location by January 1, 2007, unless the State obtains an extension as described in Section 704.287(c), in which case the deadline is January 2008; or
G) If the owner or operator plans to close its well, the owner or operator must notify the Agency of its intent to close the well (this includes closing the well prior to conversion) by at least 30 days prior to closure.
BOARD NOTE: In the corresponding note to 40 CFR 144.83(a), USEPA states that this information is requested on the federal form entitled “Preclosure Notification for Closure of Injection Wells.” Although the form “Preclosure Notification for Closure of Injection Wells” is acceptable to USEPA, the Agency may develop alternative forms for use in this State.
BOARD NOTE: Any Agency determination of the most efficient compliance option under subsection (b)(1)(A), (b)(1)(B), or (b)(1)(E) of this Section is subject to Board review pursuant to Section 40 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/40].
2) If the motor vehicle waste disposal well is new or converted (construction not started before April 5, 2000) it is prohibited.
BOARD NOTE: Corresponding 40 CFR 144.88(b)(2) sets forth a federal effective date of April 5, 2000 for the prohibition.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.88 (2000).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)
Section 704.289 Closure of a Class V Injection Well
The following describes the requirements for closing or converting a Class V injection well:
a) Closure.
1) Prior to closing a Class V large-capacity cesspool or motor vehicle waste disposal well, the owner or operator must plug or otherwise close the well in a manner that complies with the prohibition of fluid movement set forth in Section 704.122 and summarized in Section 704.282(a). The owner or operator must also dispose of or otherwise manage any soil, gravel, sludge, liquids, or other materials removed from or adjacent to the well in accordance with all applicable federal, State, and local regulations and requirements, as described in Section 704.282(b).
2) Closure does not mean that the owner or operator needs to cease operations at its facility, only that the owner or operator needs to close its well. A number of alternatives are available for disposing of waste fluids. Examples of alternatives that may be available to motor vehicle stations include the following: recycling and reusing wastewater as much as possible; collecting and recycling petroleum-based fluids, coolants, and battery acids drained from vehicles; washing parts in a self-contained, recirculating solvent sink, with spent solvents being recovered and replaced by the supplier; using absorbents to clean up minor leaks and spills, and placing the used materials in approved waste containers and disposing of them properly; using a wet vacuum or mop to pick up accumulated rain or snow melt, and if allowed, connecting floor drains to a municipal sewer system or holding tank, and if allowed, disposing of the holding tank contents through a publicly owned treatment works (POTW). The owner or operator should check with the POTW that it might use to see if the POTW would accept the owner’s or operator’s wastes. Alternatives that may be available to owners and operators of a large-capacity cesspool include the following: conversion to a septic system; connection to a sewer; or installation of an on-site treatment unit.
b) Conversions. In limited cases, the Agency may authorize the conversion (reclassification) of a motor vehicle waste disposal well to another type of Class V well. Motor vehicle wells may only be converted if the two conditions of subsections (b)(1) and (b)(2) of this Section are fulfilled, subject to the conditions of subsection (b)(3) of this Section:1) All motor vehicle fluids are segregated by physical barriers and are not allowed to enter the well; and
2) Injection of motor vehicle waste is unlikely based on a facility’s compliance history and records showing proper waste disposal.
3) The use of a semi-permanent plug as the means to segregate waste is not sufficient to convert a motor vehicle waste disposal well to another type of Class V injection well.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR 144.89 (2005).
(Source: Amended at 31 Ill. Reg. 605, effective December 20, 2006)