ILLINOIS POLLUTION
CONTROL BOARD
January
24, 2002
IN THE MATTER OF:
)
)
PROPOSED AMENDMENTS TO TIERED
)
R00-19(C)
APPROACH TO CORRECTIVE ACTION
)
(Rulemaking
-
Land)
OBJECTIVES (TACO) (MTBE):
35
ILL.
)
ADM.
CODE 742
)
Adopted Rule.
Final Notice.
OPINION AND ORDER OF THE BOARD (by C.A.
Manning, N.J.
Melas, R.C.
Flemal):
By today’s order,
the Board adopts
amendments to the Tiered Approach to Corrective
Action Objectives (TACO) found at Part 742 of the Board’s land regulations
(35
Iii.
Adm.
Code 742).
The TACO rules were originally adopted by the Board on June
5,
1997.
See
Tiered Approach to Corrective Action Objectives
(TACO):
35
Ill. Adm.
Code 742,
R97-
12(A) (June
5,
1997).
Part 742
contains procedures for developing remediation objectives
based on risks to human health and the environment posed by environmental conditions
at sites
undergoing remediation in the Site Remediation Program, the Leaking Underground Storage
Tank Program,
and pursuant to the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Part B
permits and closures.1
PROCEDURAL HISTORY
Background
On May 15, 2000, the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (Agency) submitted
proposed amendments to the TACO regulations.
The Board accepted this matter for hearing
on
May 18, 2000.
On July 27, 2000,
the Board moved the Agency’s proposed rulemaking to
first notice.
In doing so, the Board divided the proposal into two subdockets, A and B.2
On
1
The TACO regulations provide for a three-tiered approach to
cleanup objectives.
Under a
Tier 1
analysis, an applicant compares levels of contaminants of concern at the remediation site
to pre-determined remediation objectives.
See
Tiered Approach to Corrective Action
Objectives (TACO):
35
Ill. Adm. Code 742, R97-12(A) (June
5,
1997).
Fora Tier 2 analysis,
an applicant uses site-specific information and equations set forth in the rules to develop
alternative remediation objectives for contaminants of èoncern.
Id.
Finally,
a Tier 3
analysis
provides greater flexibility by allowing an applicant to develop site-specific remediation
objectives using alternative parameters not found in Tier
1
or Tier 2.
Id.
2
The Subdocket A amendments were adopted on December 21,
2000 (Proposed Amendments
to Tiered Approach to Corrective Action Objectives
(TACO):
35
Ill.
Adm.
Code 742,
R00-
19(A) (Dec.
21,
2000)), and the Subdocket B amendments were adopted on July’26,
2001
2
June 7, 2001,
the Board
opened this Subdocket C for the purpose ofaddressing
the proposed
cleanup standards for methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) that were originally contained in
Subdocket B.
The Board adopted its first-notice opinion and order
in this matter on
September 6,
2001,
and it was published on September 21,
2001.
25 Ill. Reg.
11994.
The
Board’s second-notice
opinion and
order was adopted on December
6, 2001.
Following
adoption of the second-notice
opinion and order,
the Board submitted the proposal to the Joint
Committee on Administrative Rules
(JCAR) for consideration.
JCAR considered the proposal
at its January 9,
2002 meeting and voted “no objection” to the Board proceeding with the
amendments.
The Board today adopts the proposed MTBE cleanup standards which,
with only
minor exceptions, are identical to those amendments that were originally proposed by the
Board at first notice.
The Board has coordinated this rulemaking with another pending Agency proposal that
will add groundwater quality standards for MTBE.
See generally
Proposed MTBE
Groundwater Quality Standards Amendments:
35
Ill.
Adm.
Code 620, R01-14.
Today the
Board also adopts the proposed amendments in R01-14.
Subdocket C Amendments
There have been only a few minor, non-substantive changes to the rule from that
proposed by the Board in its
first-notice opinion and order.
These minor changes amount to
basically typographical changes prompted by comments from JCAR.
The Board received two
public comments during
the public comment period:
one comment from the Agency and one
from the Illinois Petroleum Council.
The public comments did not seek to change the
substance of the rule proposed at first notice.
Rather, both public comments
supported the
substance ofthe Board’s proposed addition of MTBE.
As a result,
no changes were made to
the substance of the rule in response to the public comments.
For a more detailed discussion
of the public comments,
please see
the Board’s second-notice opinion and order.
Proposed
Amendments to
Tiered Approach to Corrective Action Objectives
(TACO) (MTBE):
35
Ill.
Adm.
Code 742,
R00-19(C)) (Dec.
6,
2001).
Based on the record developed through hearing and public comments,
the Board has
determined that MTBE should be added to the TACO regulations.
Accordingly, the Board
adopts these amendments to
35
Ill.
Adm.
Code 742.
ORDER
The Board hereby adopts these amendments to the TACO regulations and directs the
Clerk to file the following adopted amendments with the Secretary ofState.
(Proposed Amendments to Tiered
Approach to Corrective Action Objectives (TACO):
35 Ill.
Adm.
Code 742,
R00-19(B) (July 26, 2001)).
3
TITLE
35:
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
SUBTITLE G:
WASTE DISPOSAL
CHAPTER I:
POLLUTION CONTROL BOARD
SUBCHAPTER f:
RISK BASED CLEANUP OBJECTIVES
PART 742
TIERED APPROACH TO CORRECTIVE ACTION OBJECTIVES
SUBPART A:
INTRODUCTION
Section
742.100
Intent and Purpose
742.105
Applicability
742.110
Overview of Tiered Approach
742.115
Key Elements
742.120
Site Characterization
SUBPART B:
GENERAL
Section
742.200
Definitions
742.205
Severability
742.2 10
Incorporations by Reference
742.215
Determination ofSoil Attenuation Capacity
742.220
Determination ofSoil Saturation Limit
742.225
Demonstration of Compliance with Remediation Objectives
742.230
Agency Review and Approval
SUBPART C:
EXPOSURE ROUTE EVALUATIONS
Section
742.300
Exclusion ofExposure
Route
742.305
Contaminant Source
and Free Product Determination
742.3 10
Inhalation Exposure Route
742.315
Soil Ingestion Exposure Route
742.320
Groundwater Ingestion Exposure Route
SUBPART D:
DETERMINING AREABACKGROUND
Section
742.400
Area Background
742.405
Determination ofArea Background for Soil
742.410
Determination ofArea Background for Groundwater
742.415
Use ofArea Background Concentrations
SUBPART
E:
TIER
1
EVALUATION
4
Section
742.500
Tier
1
Evaluation Overview
742.505
Tier
1
Soil and Groundwater Remediation Objectives
742.510
Tier
1
Remediation Objectives
Tables
SUBPART
F:
TIER 2 GENERAL EVALUATION
Section
742.600
Tier 2 Evaluation Overview
742.605
Land Use
742.6 10
Chemical and Site Properties
SUBPART
G:
TIER 2 SOIL EVALUATION
Section
742.700
Tier 2 Soil Evaluation Overview
742.705
Parameters for Soil Remediation Objective Equations
742.710
SSL Soil
Equations
742.7 15
RBCA Soil Equations
742.720
Chemicals with Cumulative Noncarcinogenic Effects
SUBPART H:
TIER 2 GROUNDWATER EVALUATION
Section
742.800
Tier 2 Groundwater Evaluation Overview
742.805
Tier 2 Groundwater Remediation Objectives
742.8 10
Calculations to Predict Impacts from Remaining Groundwater Contamination
SUBPART
I:
TIER 3 EVALUATION
Section
742.900
Tier 3 Evaluation Overview
742.905
Modifications ofParameters
742.9 10
Alternative Models
742.9 15
Formal Risk Assessments
742.920
Impractical Remediation
742.925
Exposure Routes
742.93 0
Derivation ofToxicological Data
SUBPART
J:
INSTITUTIONAL CONTROLS
Section
742.1000
Institutional Controls
742.1005
No Further Remediation Letters
742.1010
Environmental Land Use Controls
742.1012
Federally Owned Property:
Land Use Control Memorandums ofAgreement
742.1015
Ordinances
742.1020
Highway Authority Agreements
Section
742.1100
Engineered Barriers
742.1105
Engineered Barrier Requirements
TABLE A
TABLE B
TABLE C
TABLE D
TABLE E
TABLE F
TABLE G
TABLE H
APPENDIX B
Tier
1
Tables and Illustrations
ILLUSTRATION A
Tier 1
Evaluation
TABLE A
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectives for Residential Properties
TABLE B
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectives for IndustriallCommercial Properties
TABLE C
pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics
for the Soil Component ofthe Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class I
Groundwater)
TABLE D
pH Specific Soil Remediation Objectives for Inorganics and Ionizing Organics
for the Soil Component ofthe Groundwater Ingestion Route (Class II
Groundwater)
TABLE E
Tier
1
Groundwater Remediation Objectives forthe Groundwater Component of
the Groundwater Ingestion Route
TABLE F
Values Used to
Calculate the Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectives for the Soil
Component ofthe Groundwater Ingestion Route
APPENDIX
C
Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations
ILLUSTRATION A
Tier 2 Evaluation for Soil
ILLUSTRATION B
Tier 2 Evaluation for Groundwater
ILLUSTRATION C
US Department ofAgriculture Soil Texture Classification
TABLE A
SSL Equations
TABLE B
SSL Parameters
TABLE C
RBCA Equations
5
SUBPART K:
ENGINEERED BARRIERS
APPENDIX A
General
ILLUSTRATION A
Developing Soil Remediation Objectives Underthe Tiered Approach
ILLUSTRATION B
Developing Groundwater Remediation Objectives Under the Tiered
Approach
Soil Saturation Limits
(Csat)
for Chemicals Whose Melting Point is Less than
30°C
Tolerance Factor (K)
Coefficients
ANI+1
for W
Test ofNormality, forN~2(1)50
Percentage Points ofthe W Test for n=3(1)50
Similar-Acting Noncarcinogenic Chemicals
Similar-Acting Carcinogenic Chemicals
Concentrations ofInorganic Chemicals in Background Soils
Chemicals Whose Tier
1
Class I Groundwater Remediation Objective Exceeds
the
1
in 1,000,000
Cancer Risk Concentration
6
TABLE D
TABLE E
TABLE F
TABLE G
TABLE H
TABLE I
TABLE J
TABLE K
RBCA Parameters
Default Physical and Chemical Parameters
Methods for Determining Physical Soil Parameters
Error Function (erf)
Q/C
Values By Source Area
K~Values for Ionizing Organics as a Function ofpH (cm3/g or L/kg or
cm3water/gsoii)
Values to be Substituted for k1~ork~
when Evaluating Inorganics as a Function
ofpH
(cm3/g or L/kg or cm3water/gsoji)
Parameter Estimates for Calculating Water-Filled Soil Porosity
(0w)
AUTHORITY:
Implementing Sections 22.4, 22.12, Title XVI,
and Title XVII and authorizedby
Sections 27 and 58.5 ofthe Environmental Protection Act 415
ILCS
5/22.4,
22.12, 27, and
58.5
and Title XVI and Title XVII.
SOURCE:
Adopted in R97-12(A) at 21111.
Reg. 7942, effective July
1,
1997; amended in R97-
12(B) at 21111. Reg. 16391, effective December 8,
1997; amended in R97-12(C) at 22 Ill. Reg.
10847,
effective June 8,
1998; amended in R00-19(A) at 25 Ill. Reg. 651, effective January 6,
2001; amended in R00-19(B) at 25 Ill.
Reg.
10374, effective August 15,2001; amended in R00-
19(C) at 26 Ill.
Reg.
____,
effective
_____
NOTE:
Capitalization indicates statutory language.
Section 742.APPENDIX A:
General
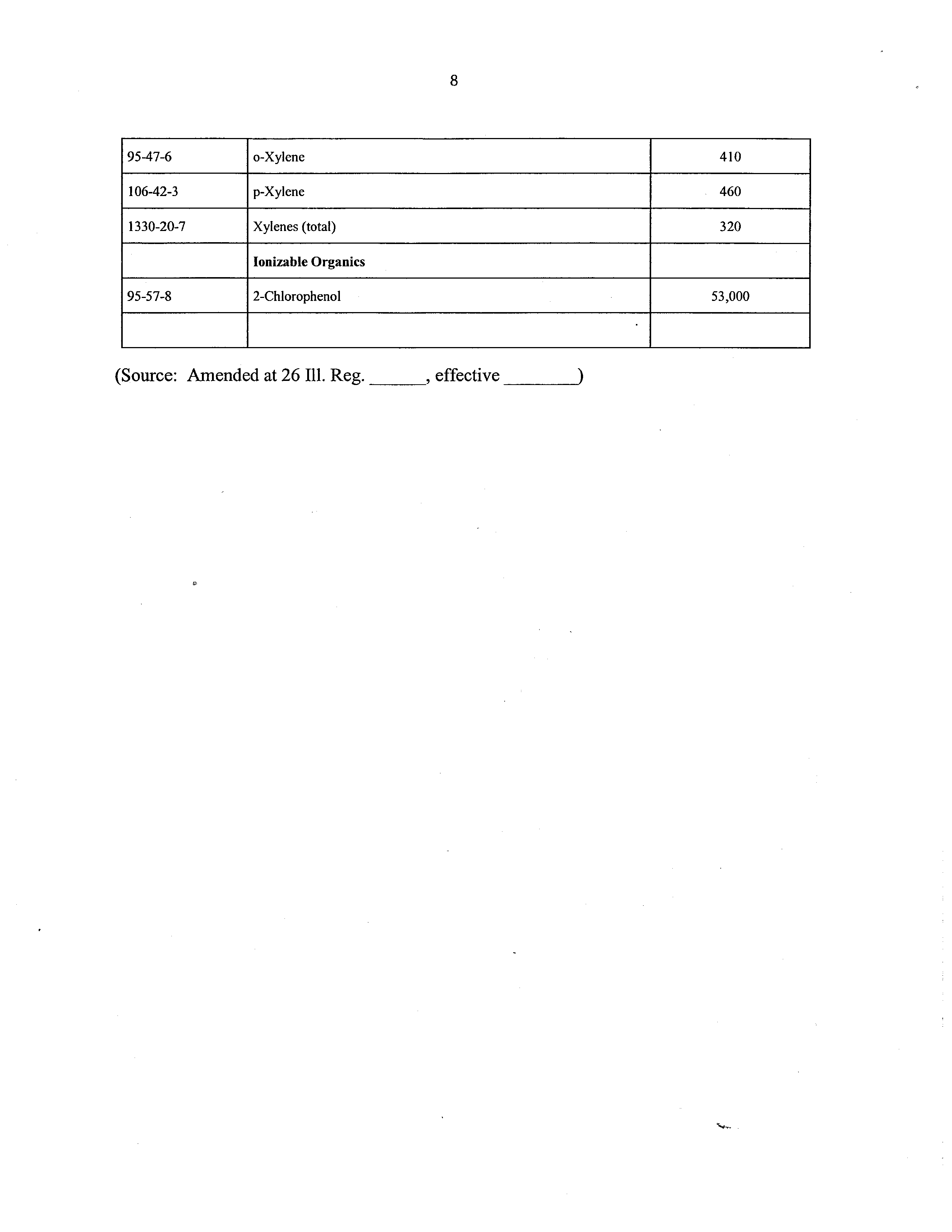
Section 742.TABLE A:
Soil Saturation Limits (Csat)for Chemicals Whose Melting Point is Less
than 30°C
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Csat (mg/kg)
67-64-1
Acetone
100,000
71-43-2
Benzene
870
111-44-4
Bis(2.chloroethyl)ether
3,300
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
31,000
75-27-4
Bromodichioromethane (Dichlorobromomethane)
3,000
75-25-2
Bromoform
1,900
71-36-3
Butanol
10,000
85-68-7
Butyl benzylphthalate
930
75-15-0
Carbon disulfide
720
56-23-5
Carbon tetrachloride
1,100
108-90-7
Chlorobenzene (Monochlorobenzene)
680
124-48-1
Chlorodibromomethane (Dibromochloromethane)
1,300
67-66-3
Chloroform
2,~0O
7
96-12-8
1 ,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
1,400
106-93-4
1 ,2-Dibromoethane (Ethylene dibromide)
2,800
84-74-2
Di-n-butyl phthalate
2,300
95-50-1
1 ,2-Dichlorobenzene (o-Dichlorobenzene)
560
75-34-3
1,1-Dichloroethane
1,700
107-06-2
1 ,2-Dichloroethane (Ethylenedichloride)
1,800
75-35-4
1,1-Dichloroethylene
1,500
156-59-2
cis-1
,2-Dichloroethylene
1,200
156-60-5
trans-I
,2-Dichloroethylene
3,100
78-87-5
1,2-Dichloropropane
1,100
542-75-6
1 ,3-Dichloropropene (1 ,3-Dichloropropylene,
cis
+
trans)
1,400
84-66-2
Diethyl phthalate
2,000
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl phthalate
10,000
100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
400
77-47-4
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
2,200
78-59-1
Isophorone
4,600
74-83-9
Methyl
bromide (Bromomethane)
3,200
1634-04-4
Methyl
tert butyl etherMethyl tertiary-butyl ether
75-09-2
Methylene chloride (Dichioromethane)
2,400
98-95-3
Nitrobenzene
1,000
100-42-5
Styrene
1,500
127-18-4
Tetrachloroethylene (Perchloroethylene)
240
108-88-3
Toluene
650
120-82-1
1 ,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
3,200
71-55-6
1,1,1 -Trichloroethane
1,200
79-00-5
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
1,800
79-01-6
Trichloroethylene
1,300
108-05-4
Vinyl
acetate
2,700
75-01-4
Vinyl chloride
1,200
8
95-47-6
o-Xylene
410
106-42-3
p-Xylene
460
1330-20-7
Xylenes (total)
320
Ionizable Organics
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
53,000
(Source:
Amended at 26 Ill. Reg.
_______,
effective
_________
9
Section 742.APPENDIX A: General
Section 742.TABLE E: Similar-Acting Noncarcinogenic Chemicals
Kidney
Central Nervous System
Acetone
Butanol (Ingestion only)
Cadmium (Ingestion only)
Cyanide (amenable)
Cblorobenzene
2,4 Dimethylphenol
Dalapon
Endrin
1,1
Dichioroethane
Manganese
Di n octyl phthalate (Ingestion only)
2
Methylphenol
Endosulfan
Mercury (Inhalation only)
Ethylbenzene
Styrene (Inhalation only)
Fluoranthene
Toluene (Inhalation only)
Nitrobenzene
Xylcnes (Ingestion only)
Pyrene
Toluene (Ingestion only)
Circulatory System
2,4,5
Tricholorphenol
Antimony
Vinyl Acetate (Ingestion only)
Barium (Ingestion only)
2,4
D
Liver
cis
1,2 Dichloroethylene (Ingestion only)
Acenaphthene
Nitrobenzene
Acetone (Ingestion only)
trans
1,2
Dichioroethylene (Ingestion only)
Butylbenzyl phthalate (Ingestion only)
2,4
Dimethylphenol
Chlorobenzene (Ingestion only)
1,1
Dichioroethylene (Ingestion only)
F
luorene
Di n octyl phthalate (Ingestion only)
Styrene (Ingestion only)
Endrin
Zinc
Ethylbenzene
Fluoranthene
Gastrointestinal System
Nitrobenzene
Beryllium (Ingestion only)
Picloram
Endothall
Styrene (Ingestion only)
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene (Ingr~’-ET?1 w?75 253 m?475 253 l?S?BT?
2,4,5
TP (Silvex)
Methyl bromide (Ingestion only)
Toluene (Ingestion only)
1,2,4
Trichlorobenzcne (Inhalation only)
—,
.,—
Reproductive System
Barium (Inhalation only)
10
.11
Carbon disulfide
2
Chiorophenol (Ingestion only~
1,2 Dibromo
3
Chioroprop
Dinoseb
Ethylbenzene (Inhalation only)
Methoxychlor
Phenol
Cholinesterase Inhibition
Aldicarb
Carbofuran
Decreased Body Weight Gains
and Circulatory System Effects
Atrazine
/
(Inhalation only)
Simazine
Adrenal Gland
Nitrobenzene
1
~
A
m~
~_1_1_~~~~_1_
,L,’+
i
rieiuorooenzerie (ingestion only)
TT__~..
Methyl bromide (Inhalation only)
Naphthalene (Inhalation
Toluene (Inhalation only)
\Tinyl acetate (Inhalation only)
I~une System
2,4
Dichloronhenol
Respiratory System
Dichloropropane (Inhalation only)
1,2
1,3
Dichloropropylene (Inhalation
nn1v’~
(Inhalation only)
p
Chloroaniline
Mercury (Ingestion only)
11
Adrenal Gland
Nitrobenzene
1 ,2,4-Trichlorobenzene (Ingestion only)
Kidney
Acetone (Ingestion only)
Cadmium (Ingestion only)
Chlorobenzene
Dalapon
1,1 -Dichloroethane
Di-n-octvl Dhthalate (lunestion only)
Endosulfan
Ethylbenzene
Fluoranthene
Methyl tort butyl ether (Inhalation only)
Methyl tertiary-butyl ether (Inhalation only)
Nitrobenzene
Pyrene
Toluene (Ingestion
only)
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
Vinyl acetate (Ingestion only)
Liver
Acenaphthene
Acetone (Ingestion only)
Butylbenzyl phthalate (Ingestion only)
Chlorobenzene (Ingestion only)
l,1-Dichloroethylene (Ingestion only)
Di-n-octyl phthalate (Ingestion only)
Endrin
Ethylbenzene
Fluoranthene
Methyl tert butyl ether (Inhalation only)
Methyl tertiary-butyl ether (Inhalation only)
Nitrobenzene
Picloram
Styrene (Ingestion only)
2,4,5-TP
(Silvex)
Toluene (Ingestion only)
1 ,2,4-Trichlorobenzene (Inhalation only)
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
Central Nervous System
Butanol (Ingestion only)
Cyanide (amenable)
2,4 Demethylphenol2,4-Dimethylphenol
Endrin
Manganese
2,Methylphenol2-Methylphenol
Mercury (Inhalation only)
Styrene (Inhalation only)
Toluene (Inhalation only)
Xylenes (Ingestion only)
Circulatory System
Antimony
Barium (Ingestion only)
2,4-D
cis- 1 ,2-Dichloroethylene (Ingestion only)
Nitrobenzene
trans-1 ,2-Dichloroethylene (Ingestion only)
2,4-Dimethylphenol
Fluoranthene
Fluorene
Styrene (Ingestion only)
Zinc
Gastrointestinal System
Beryllium (Ingestion only)
Endothall
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene (Ingestion only)
Methylbromide (Ingestion only)
Methyl tert butyl ether ~Ingestiononly~
Methyl tertiary-butyl ether (Ingestion only)
12
Immune System
2.4-Dichlorophenol
p-Chloroaniline
Mercury (Ingestion only)
Reproductive System
Barium (Inhalation only)
Boron (Ingestion only)
Carbon disulfide
2-Chlorophenol (Ingestion only)
1,2 Dibromo-3-Chloropropane (Inhalation only)
Dinoseb
Ethylbenzene (Inhalation only)
Methoxychlor
Phenol
Respiratory System
1 ,2-Dichloropropane (Inhalation only)
1 ,3-Dichloropropylene tThhalation only)
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene Unahalation Inhalation-only)
Methyl bromide (Inhalation only)
Naphthalene (Inhalation only)
Toluene (Inhalation only)
Vinyl acetate (Inhalation only)
Cholinesterase Inhibition
Aldicarb
Carbofuran
•Decreased Body Weight Gains
and Circulatory System Effects
Atrazine
Simazine
(Source:
Amended at 26 Ill. Reg.
_____,
effective
______
Section 742.APPENDIX B: Tier
1
Tables and
Illustrations
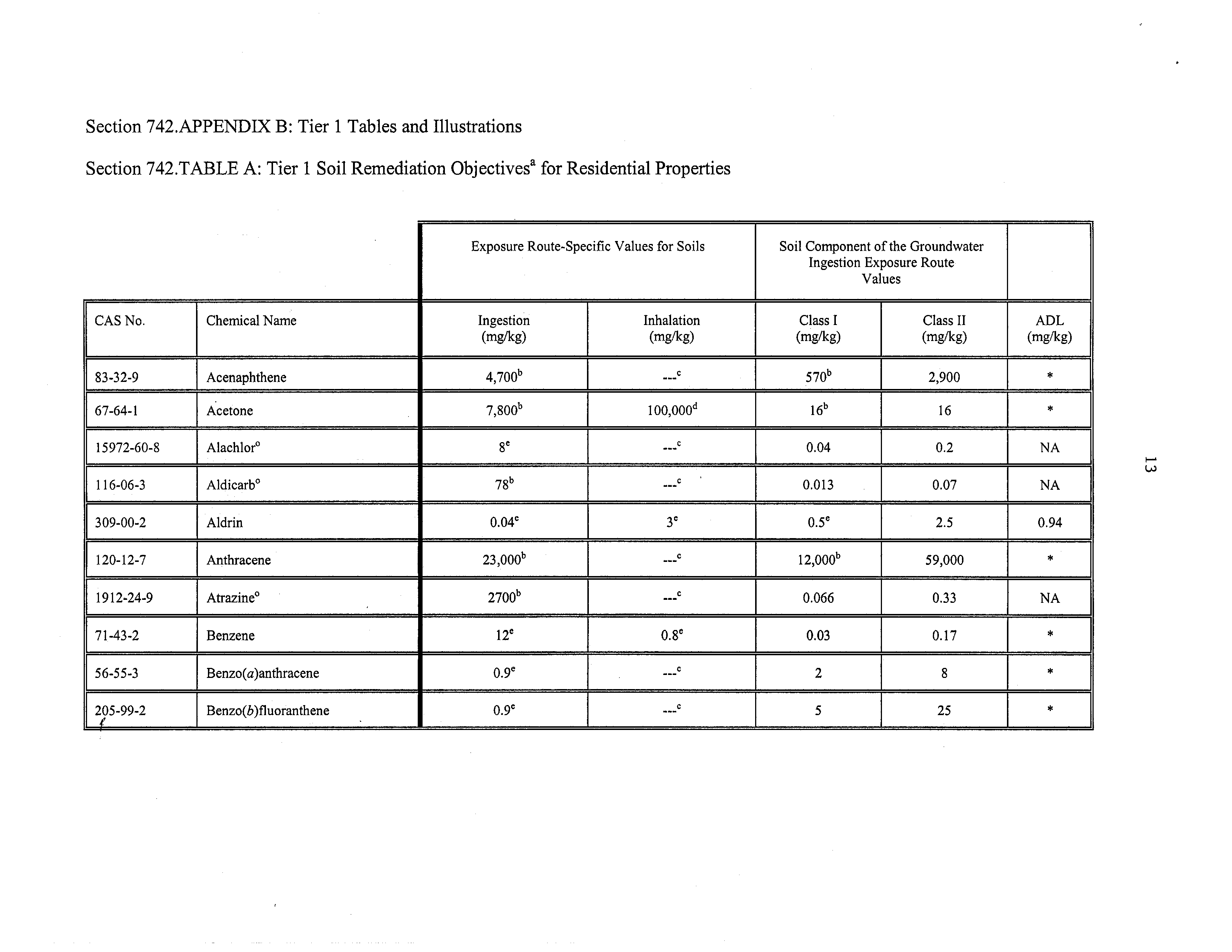
Section 742.TABLE A: Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectivesa for Residential Properties
Soil
Component ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
83-32-9
Acenaphthene
4,700b
c
570b
2,900
*
67-64-1
Acetone
7800b
100000d
16b
16
J
*
15972-60-8
Alachlor°
8e
C
0.04
0.2
NA
116-06-3
Aldicarb°
78b
C
0.013
0.07
NA
309-00-2
Aldrin
o.o4e
3C
o.5e
2.5
0.94
120-12-7
Anthracene
23,000b
c
12000b
59,000
*
1912-24-9
Atrazine°
•
2700b
C
0.066
0.33
NA
71-43-2
Benzene
12e
o.8e
0.03
0.17
*
56-55-3
Benzo(a)anthracene
Ø~9C
C
2
8
*
205-99-2
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
•
Ø~9C
C
5
25
*
L~i
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
207-08-9
Benzo(k)fluroanthene
9C
C
49
250
*
50-32-8
Benzo(a)pyrene
0~09e,f
C
8
82
*
111-44-4
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
0,6e
02e,f
0.0004
0.66
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
46C
31000d
3,600
31,000”
*
75-27-4
Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane)
be
3000d
0.6
0.6
*
75-25-2
Bromoform
81e
53e
0.8
0.8
*
71-36-3
1
Butanol
7800b
J
10,000”
17b
17
NA
85-68-7
•
Butyl
benzyl phthalate
16,000”
930d
930d
930d
*
86-74-8
Carbazole
32c
C
o.6e
2.8
NA
1563-66-2
Carbofuran°
390”
C
0.22
1.1
NA
75-15-0
Carbon disulfide
7,800”
720d
32b
160
*
f
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
Ui
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
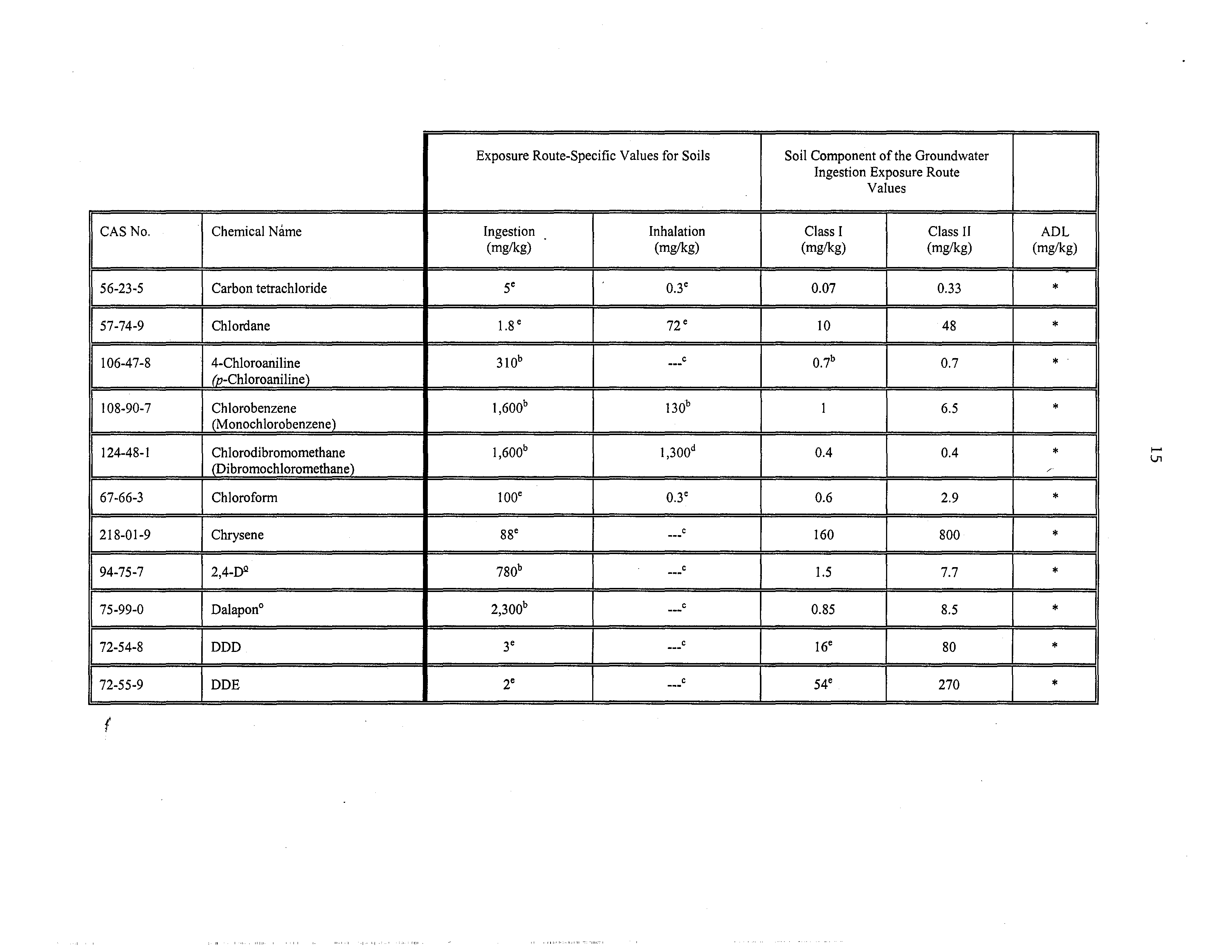
56-23-5
Carbon tetrachioride
5e
0.3e
0.07
0.33
*
57749
Chlo,~1ane
l,8e
72e
10
48
*
106-47-8
4-Chboroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline)
310”
C
07b
0.7
*
108-90-7
Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene)
1,6001~
130b
1
6.5
*
124-48-1
Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane)
1,600b
1300d
0.4
0.4
*
‘~
67-66-3
Chloroform
bOOC
Ø3C
0.6
2.9
*
218-01-9
Chrysene
88e
C
160
800
*
94-75-7
2,4-Do
780b
•
C
1,5
7•7
*
75-99-0
Dalapon°
2300b
,,C
0.85
8.5
72-54-8
DDD
3e
C
I6e
80
*
72-55-9
f
DDE
2e
C
54e
270
*
f
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil
Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
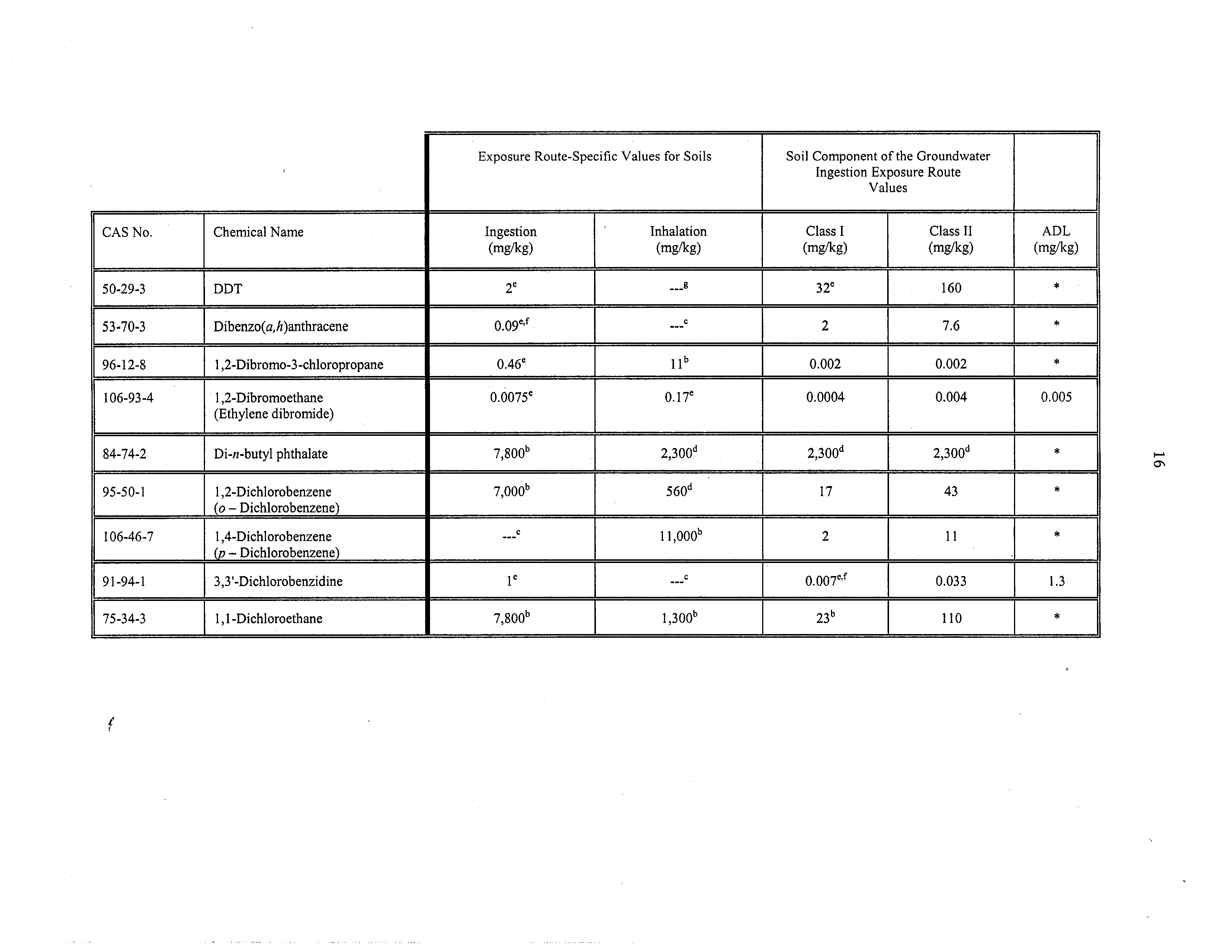
50-29-3
DDT
2e
32e
160
*
53-70-3
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
009e,f
C
2
7.6
*
96-12-8
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
0.46e
11b
0.002
0.002
1
*
106-93-4
1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide)
0.0075e
o.17e
0.0004
0.004
0,005
84-74-2
Di-n-butyl phthalate
7,800b
2,300”
2,300d
2300d
*
95-50-1
l,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o
—
Dichlorobenzene)
7000b
560d
~
17
43
*
106-46-7
1 ,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p
—
Dichlorobenzene)
,,,C
11,000”
2
11
*
91-94-1
3,3’-Dichlorobenzidine
be
,__C
0007e,f
0.033
1.3
75-34-3
1,1-Dichloroethane
7,800”
l,300”
23b
110
*
f
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class
II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
107-06-2
1,2-Dichioroethane
(Ethylene dichloride)
7C
Ø4~
0.02
0.1
*
7s~3s~4
1,1-Dichloroethylene
700b
1,500”
0.06
0.3
*
156-59-2
cis-b,2-Dichloroethylene
780”
1200d
0.4
1,1
*
156-60-5
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
1,600b
3100d
0.7
3,4
*
78-87-5
1,2-Dichloropropane
9C
15b
0.03
0.15
*
542-75-6
1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichboropropylene,
cis
+
trans)
6.4e
1.le
o.oo4e
0,02
0.005
60-57-I
DieIdrin~
0.04e
Ic
0,004e
0.02
0.603
84-66-2
Diethyl phthalate
63,000”
2,000”
470b
470
*
105-67-9
2,4-Dimethylphenol
1600b
~C
9b
9
*
121-14-2
f
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
o.9e
C
00008e,f
0.0008
0.250
—4
f
S
Soil Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
Exposure Route-Specific Valuesfor Soils
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
606-20-2
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
0.9e
,,C
00007e,f
0.0007
0.260
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl phthalate
1,600”
10000d
10,000”
10,000”
*
115-29-7
Endosulfan°
470b
c
18b
90
*
145-73-3
Endothall°
1600b
---C
0.4
0.4
NA
72-20-8
Endrin
23b
C
1
5
*
100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
7,800”
400d
13
19
*
206-44-0
Fluoranthene
3,100”
---C
4300”
21,000
*
86-73-7
Fluorene
3100b
560b
2,800
*
76-44-8
Heptachior
ole
ØJ~
23
110
0.871
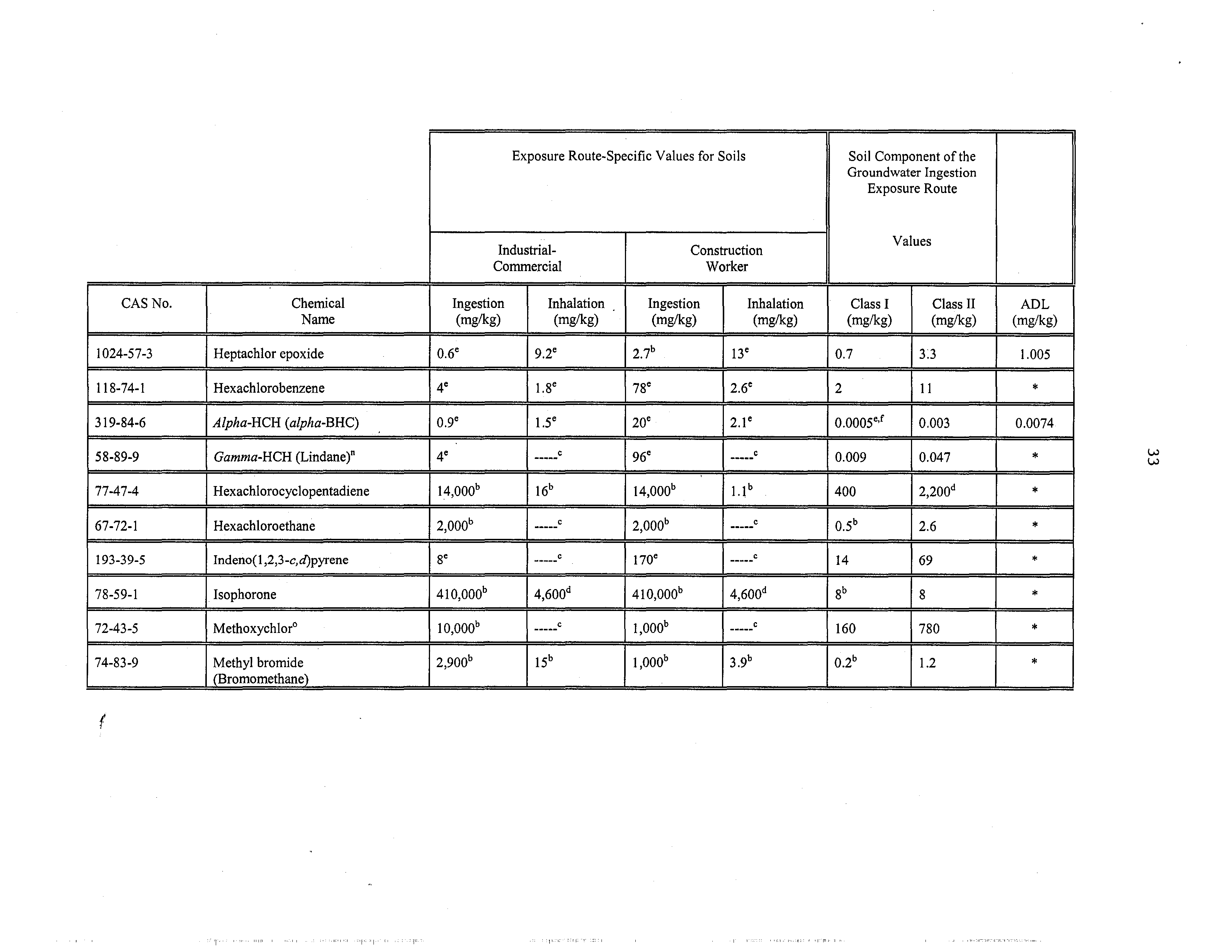
1024-57-3
Heptachlorepoxide
ØQ7C
5C
0.7
3.3
1.005
118-74-1
Hexachlorobenzene
o.4e
le
2
11
*
3 19-84-6
Alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC)
o.le
o.8e
0,0005e,f
0.003
0.0074
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil
Component ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
58~89~9
Gamma-HCH
(Lindane)°
o.se
C
0.009
0.047
*
77-47-4
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
550b
10b
400
2,200”
*
67-72-I
Hexachloroethane
78”
,.c
05b
2.6
*
193-39-5
Indeno(b,2,3-c~d)pyrene
0.9°
14
69
‘K
78-59-1
lsophorone
,
15,600”
r
4600d
8b
8
*
72-43-5
Methoxychlor°
390”
160
780
‘K
74-83-9
Methylbromide
(Bromomethane)
110”
,
10b
02”
1.2
‘K
1634-04-4
Mcthyl tort
butvl etherMethyl
tertiary-butyl ether
780”
8800d
‘K
75-09-2
Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane)
85c
l3e
0.02C
0.2
*
95-48-7
2-Methylphenol
(o
—
Cresol)
3,900b
C
15b
15
*
91-20-3
Naphthalene
1,600
b
1
70b
12
b
18
*
18-95-3
Nitrobenzene
39”
92b
01b,f
0.1
0.26
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil
Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
Ni
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
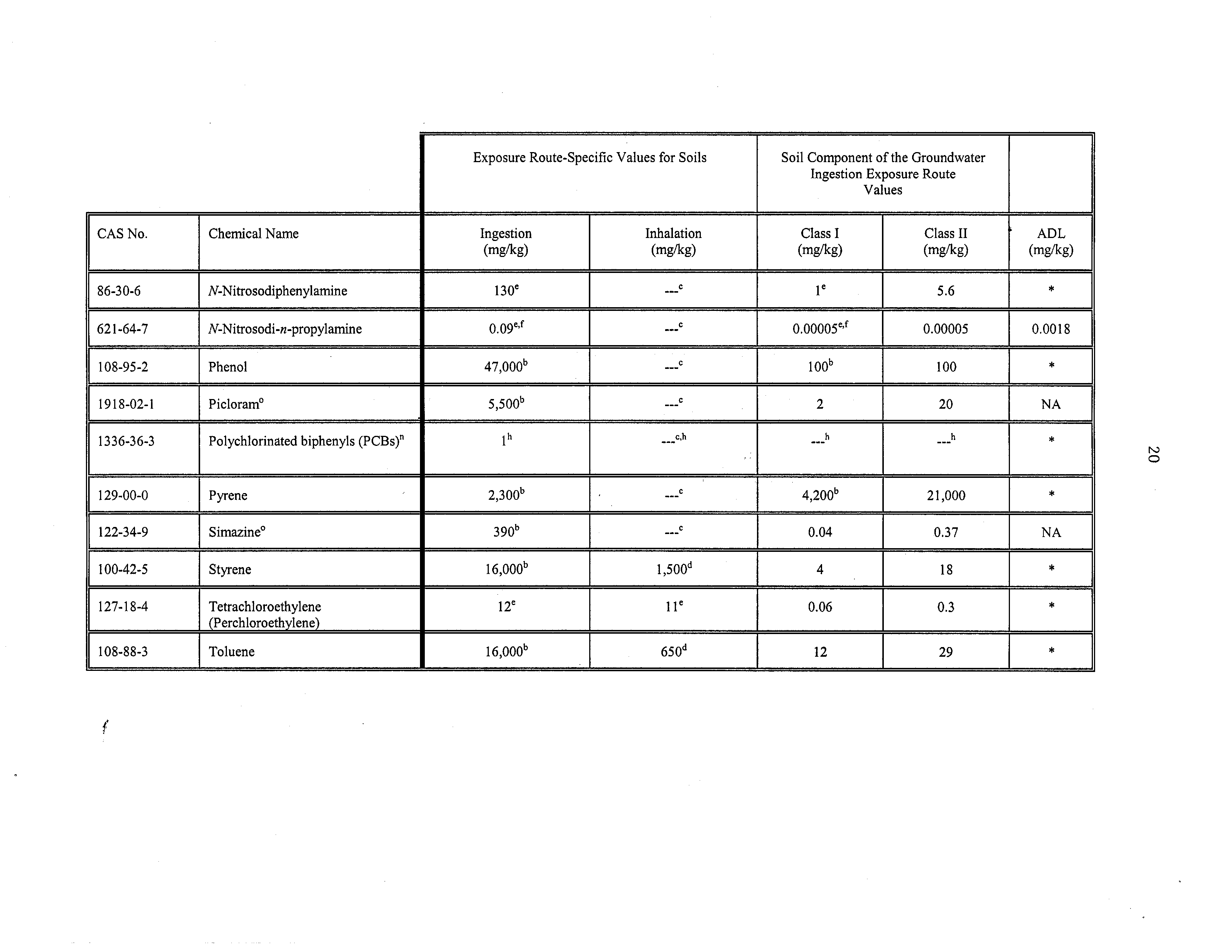
86-30-6
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
130e
C
be
5.6
*
621-64-7
N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine
009e,f
~C
000005e,f
0.00005
0.0018
108-95-2
Phenol
47000b
100b
100
J
*
1918-02-I
Picloram°
5,500”
---C
2
20
NA
1336-36-3
Polychlorinatedbiphenyls (PCBs)°
1”
..h
.h
*
129-00-0
Pyrene
2300b
,,~,C
4200b
21,000
‘K
122-34-9
Simazine°
390b
C
0.04
0.37
NA
100-42-5
Styrene
16000b
1500d
4
18
*
127-18-4
Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene)
l2e
11°
0.06
0.3
‘K
108-88-3
Toluene
16000b
650d
12
29
*
(
Exposure Route-Specific Valuesfor
Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
8001-35-2
Toxaphene’
0.6°
89°
31
150
‘K
120-82-1
l,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
780”
3,200”
5
53
‘K
71-55-6
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
1,200”
2
9.6
*
79-00-5
I,l,2-Trichloroethane
310”
1800d
0.02
0.3
‘K
79-01-6
Trichloroethylene
58e
5e
0.06
0.3
‘K
108-05-4
Vinyl acetate
78,000”
1000b
170”
170
‘K
75-01-4
Vinyl chloride
0.46e
o,28e
‘
O.Olf
0.07
‘K
108-38-3
m-Xylene
1600001)
420d
210
210
‘K
95-47-6
o-Xylene
160,000”
410d
190
190
‘K
106-42-3
p-Xylene
-
160,000”
46O’~
200
200
‘K
Ni
(
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the Groundwater
Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
Ni
Ni
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class
II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
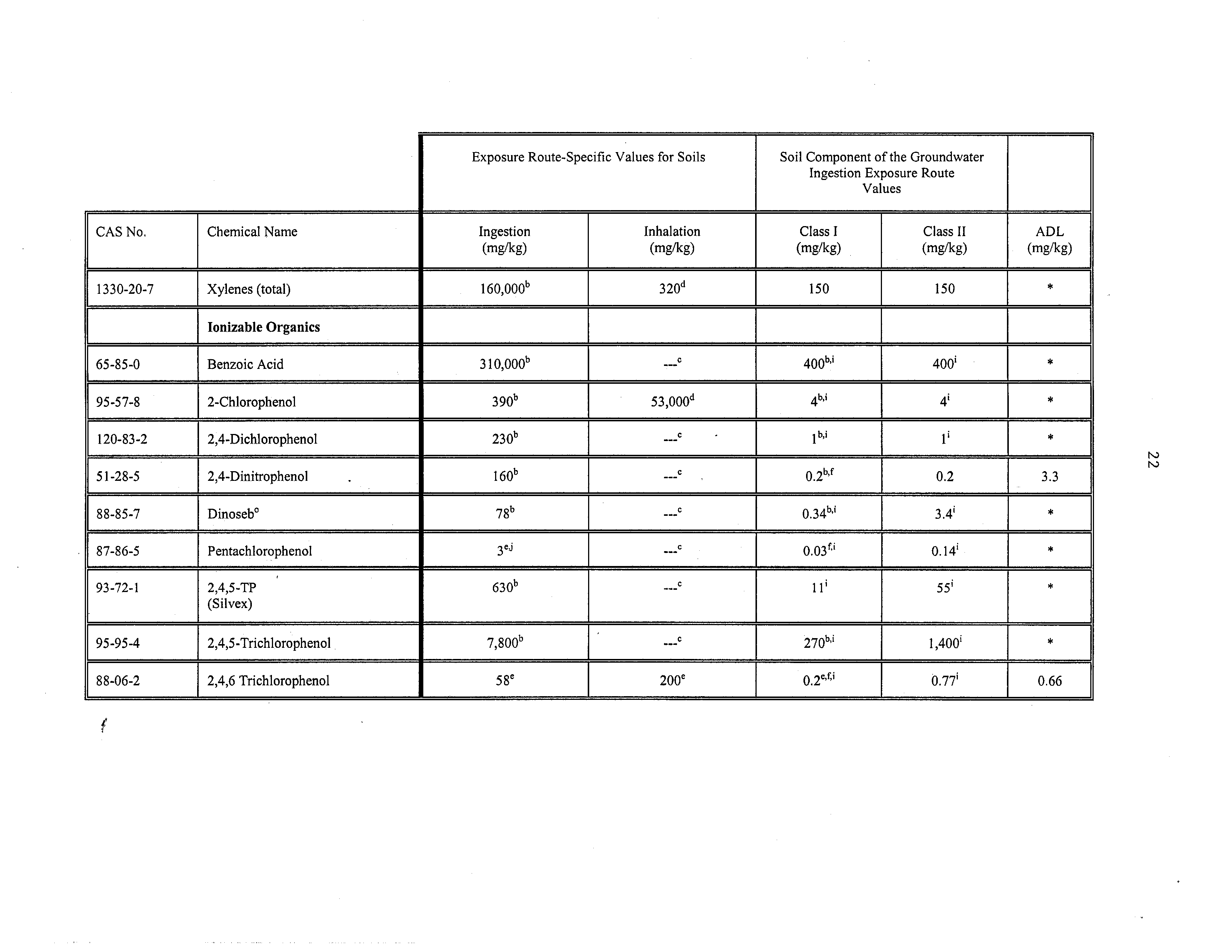
1330-20-7
Xylenes (total)
160,000”
320d
150
150
‘K
Ionizable Organics
65-85-0
Benzoic Acid
310,000”
---C
400b,i
400i
‘K
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
390b
53,000”
4b,l
4’
*
120-83-2
2,4-Dichlorophenol
230b
c
.
1b,i
1
*
51-28-5
2,4-Dinitrophenol
160b
•
02b,f
0.2
3.3
88-85-7
Dinoseb°
78”
---C
034”~’
3.4’
‘K
87-86-5
Pentachlorophenol
3°~
---C
0,03f,
o.14~
‘K
93-72-1
2,4,5-TP
(Silvex)
630b
C
11’
55’
*
95-95-4
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
7,800”
~C
270b,i
l,400i
*
88-06-2
2,4,6 Trichlorophenol
58e
200e
02e~f~i
0.77’
0.66
f
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
Soil Component
ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
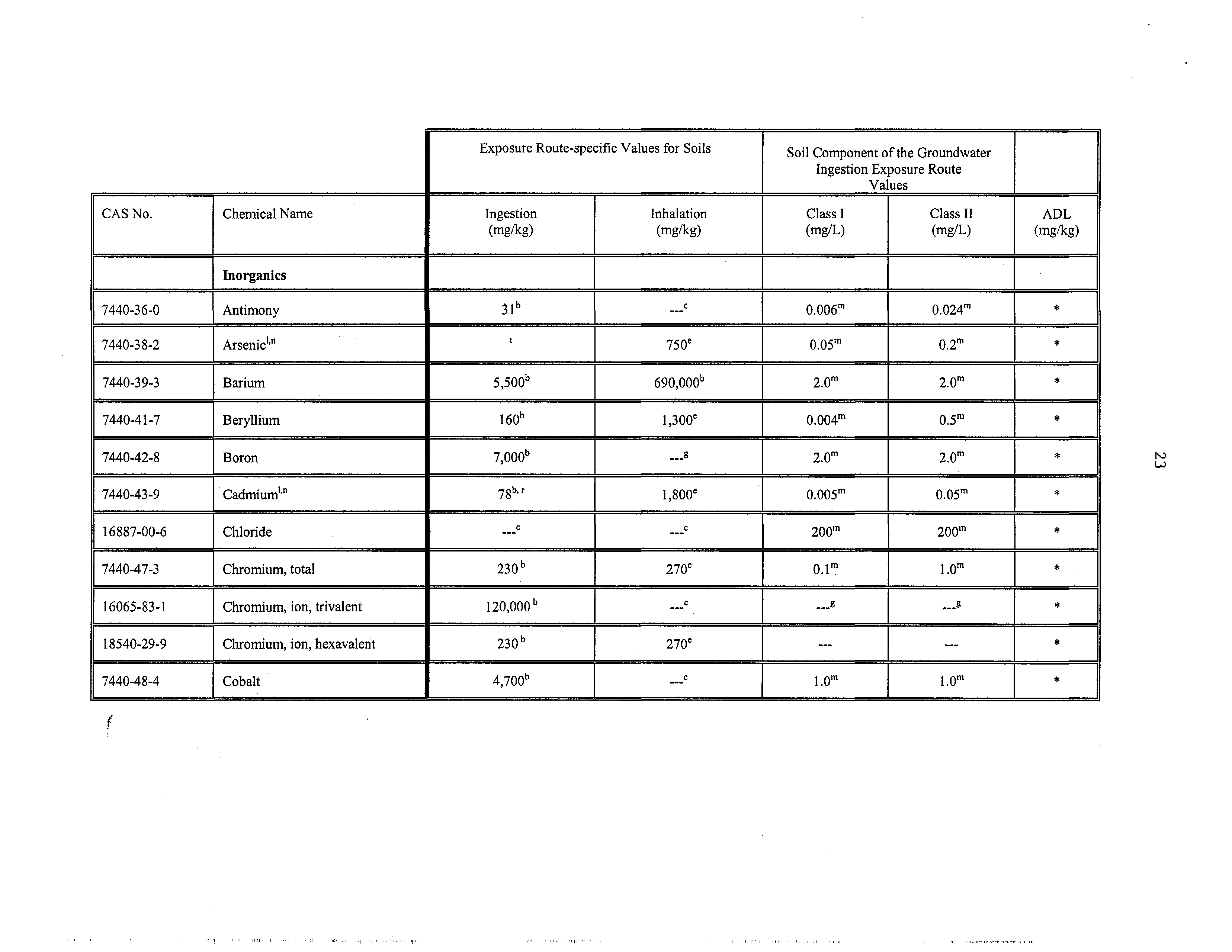
Inorganics
7440-36-0
Antimony
31b
---C
0.024m
‘K
7440-38-2
Arsenic”°
t
750e
0.05m
0.2”
*
7440-39-3
Barium
5500b
690000b
2.0”’
2.0”’
*
7440-41-7
Beryllium
160”
1,300°
0.O04~
Q,5m
‘K
7440-42-8
Boron
7000b
2.o~
2.o~
‘K
7440-43-9
Cadmium”°
78b,r
l,800e
0.005”’
o.osm
‘K
16887-00-6
Chloride
C
C
20O~
200”’
*
7440-47-3
Chromium,
total
230”
270e
01”’
l.Om
*
16065-83-I
Chromium,
ion, trivalent
120,000”
..~
-
g
*
18540-29-9
Chromium, ion, hexavalent
230”
270°
*
7440-48-4
Cobalt
4,700b
,,C
l.om
-
1.0”’
‘K
N.i
Ui
f
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
Soil Component ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/L)
Class
II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
7440-50-8
Copper°
2,900”
---~
0.65”’
0.65”’
‘K
57~l2~5
Cyanide (amenable)
1,600b
---C
02q,m
06q,m
*
7782-41-4
Fluoride
4700”
---C
4.0”’
4.0”’
‘K
15438-31-0
Iron
C
C
5Ølfl
5.0”’
‘K
7439-92-1
Lead
400k
C
o.0o75~
0.1”’
‘K
7439-96-5
Manganese
3,700b
69,000b
•
0.15m
lo.o~
‘K
7439-97-6
Mercury”’”
23”
10b
0.002~
1
o.ol~
‘K
7440-02-0
Nickel’
1600b
l3,000e
0.1”’
2,0”
‘K
14797-55-8
Nitrate as N”
130,000”
~C
10,0q
100q
*
7782-49-2
Selenium”’
390”
C
0.o5~
‘K
Ni
Exposure Route-specific Values for Soils
Soil Component ofthe Groundwater
Ingestion Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
7440-22-4
Silver
390”
C
o,osm
*
14808-79-8
Sulfate
---C
C
400”’
400”’
*
7440-28-0
Thallium
6.3~
C
0.002~
o.o2~
‘K
7440-62-2
Vanadium
550b
C
0.049m
o.l~
‘K
7440-66-6
Zinc’
23000b
•
~e
5,Øm
10”
*
“K“
indicates that the ADL is less than
or equal to the specified
remediation objective.
NA means not available; no PQL or
EQL available
in USEPA analytical methods.
Ni
Ui
(
Chemical Name and Soil Remediation Obiective Notations
a
Soil remediation objectives
based on human health criteria only.
b
Calculated values correspond to atarget hazard quotient of 1.
C
No toxicity criteria available for theroute of exposure.
d
Soil saturation concentration (C
sat)
=
the concentration at which the absorptive limits ofthe soil particles, the solubility limits of theavailable soil moisture, and saturation
of soil poreair havebeenreached.
Above the soil saturation concentration, the assumptions regarding vapor transport to air and/ordissolved phase transport to
groundwater (for chemicals which are liquid
at ambient soil temperatures) havebeen violated, and alternative modeling approaches are required.
Calculated values correspond to acancer risk level of
1 in
1,000,000.
Level is
at or belowContractLaboratory Program required quantitation limit for Regular Analytical Services (RAS),
g
Chemical-specific properties are such that this route is not of concern at any soil contaminant concentration.
40
CFR 761
contains applicability requirements and methodologies for the development of PCB
remediation objectives.
Requests for approval of a Tier 3
evaluation must
address the applicability of40
CFR 761.
Soil
remediation objective for pH of 6.8. Ifsoil pH
is other than 6.8, refer to Appendix B,
Tables C and D of this Part.
Ingestion soil remediation objective adjusted by a factor of 0.5
to account for dermal route.
k
A preliminary remediation goal of 400 mg/kg hasbeen set for lead based on
Revised Interim Soil Lead Guidancefor CERCLA Sites and RCRA Corrective Action Facilities,
OSWER Directive #9355.4-12.
Potential for soil-plant-human
exposure.
m
The person conducting the remediation hasthe option
to use:
1) TCLP
or SPLP test results to comparewith the remediation objectives listed
in this Table; or 2) the total
amount of contaminant in the soil sample results to compare with pH specificremediation objectives listed in Appendix B, Table C or D ofthis
Part.
(See Section
742.5 10.)
If the
person conducting the remediation wishes to calculate soil remediation objectives based on background concentrations, this
should be done in accordance
with Subpart D of this Part.
The
Agencyreserves the right to evaluate the potential for remaining contaminant concentrations to
pose significantthreatsto
crops, livestock, or wildlife.
°
For agrichemical facilities, remediation objectives for surficial
soils which arebased
on field application rates may be more appropriate for currently registered pesticides.
Consult the Agency for further information.
“
For
agrichemical facilities,
soil
remediation objectives based on
site-specific background concentrations ofNitrate as N may be
more appropriate.
Such determinations
shall be
conducted in accordance with the procedures set forth in Subparts D and Iof this Part.
q
The TCLP extraction must be done using waterat a pH of 7.0.
Value based on dietaryReference Dose.
Value for Ingestion based
on Reference Dose for Mercuric chloride (CAS No. 7487-94-7); value for Inhalation based on
Reference Concentration for elemental Mercury
(CAS No.
7439-97-6).
For
the
ingestion route for arsenic, see 742.Appendix A, Table G.
U
Value based on Reference Dose
for Thallium sulfate (CAS No. 7446-b 8-6).
(Source:
Amended at 26 Ill. Reg.
_____,
effective
______
f
Section 742.APPENDIX B: Tier
1
Tables and Illustrations
Section 742.Table B: Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectivesa for Industrial/Commercial Properties
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
ExposureRoute
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Classll
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
83-32-9
Acenaphthene
120,000”
C
120000b
570b
2,900
*
67-64-I
Acetone
200,000b
100000d
200000b
100000d
16b
16
‘K
15972-60-8
Alachlor°
72e
C
1,600°
•
C
0.04
0.2
NA
116-06-3
Aldicarb°
2,000b
C
200”
C
0.013
0.07
NA
309-00-2
Aldrin
0.3e
•
6.6e
61”
93e
o.se
2.5
0.94
120-12-7
Anthracene
610,000b
610000b
12000b
59,000
‘K
1912-24-9
Atrazine°
72,000”
C
7100b
C
0.066
0.33
NA
71-43-2
Benzene
loot
1.6°
2,300e
2.2e
0.03
0.17
‘K
Ni
—4
f
Exposure Route-SpecificValues for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
•
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
56-55-3
Benzo(a)anthracene
8°
C
b7Oe
C
2
8
‘K
205-99-2
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
8e
C
b7Oe
C
5
25
‘K
207-08-9
Benzo(k)fluroanthene
78e
C
l,700e
C
49
250
‘K
50-32-8
Benzo(a)pyrene
0.8°
C
l7e
C
8
82
‘K
111-44-4
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
SC
Q47C
75~
0.66°
O.OO04°~”
0.0004
0.66
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
4bOe
31000d
4,100”
31,000”
3,600
31,000”
‘K
75-27-4
Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane)
92°
3,000”
2,000°
3,000”
0.6
j
0.6
‘K
75-25-2
Bromoform
720°
lOOC
b6,000e
140°
0.8
0.8
‘K
71-36-3
Butanol
200000b
10,000”
200,000b
10000d
17b
17
NA
85-68-7
Butyl benzyl phthalate
410,000”
930”
410000b
930”
930”
930”
*
86-74-8
,
Carbazole
•
290e
C
6,200e
C
0.6°
2.8
NA
Ni
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
J
Name
~
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
J
Inhalation
~
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class
II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
1563-66-2
Carbofuran°
10,000”
C
1000b
C
0.22
1.1
NA
75-15-0
Carbon disulfide
200,000”
720”
20,000b
90b
32b
160
‘K
56-23-5
Carbon tetrachloride
44e
0.64°
410”
0.90e
0.07
0.33
‘K
57-74-9
Chlordane
l.6e
b4Oe
100b
22b
10
48
*
106-47-8
4—Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline)
8200b
C
820b
~
07b
0.7
‘K
108-90-7
Chloroben±ene
(Monochlorobenzene)
41,000”
210”
4100b
13b
1
6.5
‘K
124-48-
Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane)
41,000”
1300d
41000b
1,300”
0.4
0.4
‘K
67-66-3
Chloroform
940°
0.54e
2000b
f
0.76e
0.6
2.9
‘K
218-01-9
Chrysene
780°
C
l7,000e
°
160
800
‘K
94757
12,4D0
20000b
C
2,000”
C
,5
7,7
‘K
Ni
“C
(
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil
Component ofthe
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class
II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
75-99-0
Dalapon°
61,000”
C
6,100b
C
0.85
8.5
‘K
72-54-8
DDD
24e
C
520e
C
b6e
80
‘K
72-55-9
DDE
17C
C
370°
C
54e
270
‘K
50-29-3
DDT
17°
1,500°
100”
2,l00e
32e
160
‘K
53-70-3
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
0.8°
C
17°
C
2
7.6
‘K
96-12-8
l,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
~e
17b
89e
0~11b
0.002
0.002
*
106-93-4
1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide)
o.o7~
0.32°
1.5°
0.45e
0.0004
0.004
0.005
84-74-2
Di-n-butyl phthalate
200,000”
2,300”
200,000”
2,300d
2300d
2,300”
‘K
95-50-1
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o
—
Dichlorobenzene)
180,000”
560d
18,000b
310b
17
43
‘K
106-46-7
l,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p
—
Dichlorobenzene)
C
17,000”
C
340”
2
11
‘K
Ui
(
Exposure
Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil
Component ofthe
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure
Route
Values
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
91-94-1
3,3’-Dichlorobenzidine
13e
C
280e
C
0007e,f
-0.033
1.3
75-34-3
l,1~Dichloroethane
200,000”
1700d
200000b
f
130b
23b
110
*
107-06-2
l,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride)
63e
0.70~
l,400e
0.99°
I
0.02
0.1
*
75-35-4
b,l-Dichloroethyleñe
18,000”
1500d
1800b
300w
0.06
0,3
‘K
156-59-2
cis~l,2~Dichloroethy1ene
20000b
1,200”
20,000”
11,200”
0.4
1.1
‘K
156-60-5
Trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
41,000”
3100d
41000b
13,100”
0.7
3.4
‘K
78-87-5
1,2-Dichloropropane
84e
23”
l,800e
0.50”
0.03
J
0.15
‘K
542-75-6
1,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichloropropylene,
cis
+
trans)
57°
2.le
~•39b
0.004e
0.02
0.005
60-57-I
Dieldrin”
o.4e
2.2e
7.8°
3.be
0.004°
0.02
0.603
84-66-2
Diethyl
phthalate
~
2000d
1000000b
2,000”
470b
470
‘K
Ui
(
Exposure Route-SpecificValuesfor Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil
Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
105-67-9
2,4-Dimethylphenol
41000b
C
41,000”
9b
9
‘K
121-14-2
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
8.4°
C
180°
C
00008e,f
0.0008
0.250
606-20-2
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
8.4°
C
b80e
C
00007e.t’
0.0007
0.260
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl phthalate
41,000°
10,000’s
4100b
10000d
10000d
10000d
‘K
115-29-7
Endosulfan2
12000”
C
1200b
c
18b
90
*
145-73-3
Endothall°
4l,000C
C
4100b
C
0.4
0.4
NA
72-20-8
Endrin
6b01~
6~b
C
5
‘K
100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
200,000”
400”
20000b
58b
13
19
‘K
206-44-0
Fluoranthene
82000b
82000b
4300b
21,000
‘K
86-73-7
Fluorene
82,000”
82000b
C
560”
2,800
‘K
76-44-8
Heptachlor
be
Il~
28e
b6e
23
110
‘K
Ui
Ni
(
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil
Component ofthe
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
1024-57-3
Heptachlorepoxide
0.6°
9.2°
12.7”
J
13°
0.7
33
1.005
118-74-1
Hexachlorobenzene
4e
l.8e
J
78°
2.6°
2
11
‘K
3 19-84-6
Alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC)
0.9°
l.5e
J
20e
2.le
J
0,0005e~f
0.003
0.0074
5
8-89-9
Gamma-HCH
(Lindane)”
4e
C
96°
C
0.009
0.047
*
77-47-4
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
14,000”
16b
J
14000b
1,1b
I
400
2,200d
‘K
67-72-1
Hexachloroethane
2,000”
C
2000b
05b
2.6
‘K
193-39-5
Indeno(l,2,3-c,d)pyrene
8e
C
l7oe
C
14
69
‘K
78-59-b
Isophorone
410,000”
4,600”
410,000”
4,600”
8b
8
‘K
72-43-5
Methoxychlor°
10,000b
C
1000b
C
160
780
‘K
74-83-9
Methyl
bromide
(Bromomethane)
2,900b
15b
1000b
13.9”
,J
0•2b
1.2
‘K
Ui
Ui
(
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class
II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
1634-04-4
Methyl tcrt butyl
otherMethyl
20,000b
8800d
2.000”
140”
0.32
0.32
*
tertiary-butyb ether
75-09-2
Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane)
760°
24e
12,000”
34C
0.02e
0.2
‘K
95-48-7
2-Methylphenol
(o
—
Cresol)
100,000”
C
100000b
e
15b
15
‘K
86-30-6
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
l,200e
C
25,000°
C
le
5.6
‘K
621-64-7
N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine
0,8C
C
18e
C
000005e,f
0.00005
0.0018
91-20-3
Naphthalene
41,000”
270”
4,100”
18b
12b
18
‘K
98-95-3
Nitrobenzene
1000b
140b
1,000b
9,4b
01b,f
0.1
0.26
108-95-2
Phenol
1,000,000”
1205000b
c
100b
*
1918-02-1
Picloram°
140,000”
C
14000b
C
2
20
NA
1336-36-3
Polychlorinatedbiphenybs (PCBs)”
I”
C,h
c,h
h
h
bf29-OO-O
Pyrene
-
61,000”
C
61,000”
C
4200b
21,000
‘K
Ui
Expostire Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component
of the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
122-34-9
Simazine°
10,000b
C
1000b
C
0.04
0.37
NA
100-42-5
Styrene
-
410000”
1,500”
41000b
430b
4
18
‘K
127-18-4
Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene)
b1o~
20°
2,400°
28e
0.06
0.3
‘K
108-88-3
Toluene
410,000”
650”
410,000”
42”
12
29
‘K
8001-35-2
Toxaphene”
5.2e
170°
blOc
240e
31
150
‘K
120-82-1
l,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
20,000”
3,200d
2000b
920”
5
53
‘K
71-55-6
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
C
1,200d
1,200d
2
9.6
‘K
79-00-5
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
8,200”
1,800d
8200b
1,800”
0.02
0.3
*
79-01-6
Trichloroethylene
520e
8.9e
1200b
12°
0.06
0.3
‘K
108-05-4
Vinyl acetate
1,000,000”
1600b
200000b
10”
170”
170
*
Ui
Ui
(
Exposure
Route-Specific Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil Component
ofthe
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
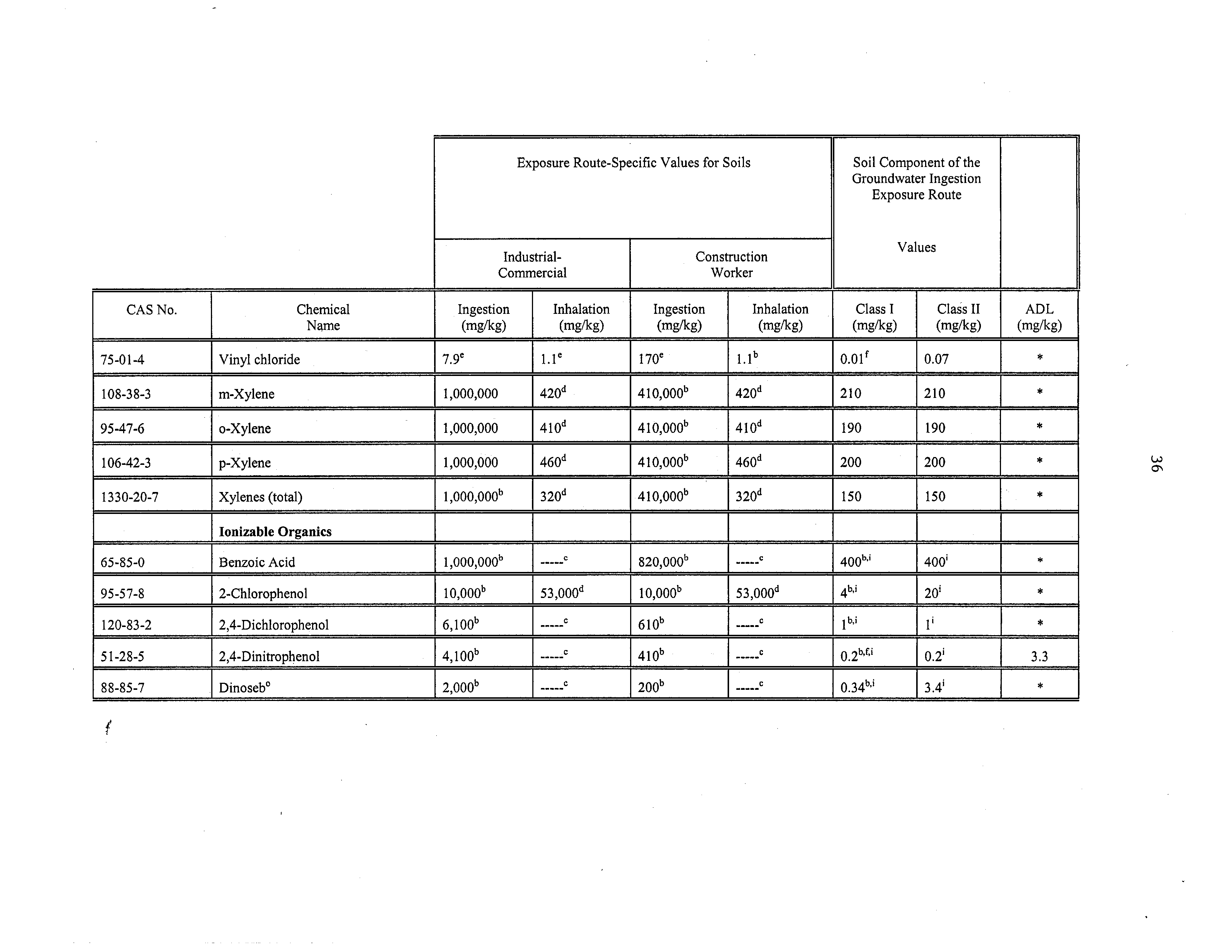
75-01-4
Vinyl chloride
7.9°
1.l~
170°
1~1b
0.01”
0.07
‘K
108-38-3
m-Xylene
1,000,000
420”
410,000b
420”
210
210
‘K
95-47-6
o-Xylene
1,000,000
410”
410000b
~10d
190
190
106-42-3
p~xylene
1,000,000
460”
410,000”
460”
200
200
*
1330-20-7
Xybenes (total)
1,000,000”
320”
410,000”
•
J
3~0d
150
150
‘K
Ionizable Organics
I
65-85-0
Benzoic Acid
1,000,000”
C
820,000”
40O”~
400’
*
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
10,000”
53,000’~
10,000”
53,000”
4b,i
20’
‘K
120-83-2
2,4-Dichiorophenol
6100b
C
610b
C
1b,i
1’
‘K
51-28-5
2,4-Dinitrophenol
4100b
C
410b
c
02b,~i
J
0.2’
33
88-85-7
Dinoseb°
2000b
C
200b
034b,~
341
‘K
f
Ui
C.,
Exposure Route-SpecificValues for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
Soil
Component of
the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
CAS
No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/kg)
Class II
(mg/kg)
ADL
(mg/kg)
87-86-5
Pentachlorophenol
24°~
C
520°~
C
1
o.o3~~
0.14’
J
‘K
93-72-1
2,4,5-TP
(Silvex)
16000b
C
1600b
C
11’
T
I
95-95-4
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
•
200000b
C
•
C
270b,i
jl400’
‘K
88-06-2
2,4,6- Trichlorophenol
520°
390e
11,000°
s4o~
O.2°’~’
I
Q,771
0.66
Ui
—4
(
Soil
Component
of
the
Groundwater Ingestion
Exposure Route
Values
Exposure Route-Specific
Values for Soils
Industrial-
Commercial
Construction
Worker
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
Inorganics
f________________
I___________
7440-36-0
Antimony
820”
C
82b
C
1
o.oo6~
0.024m
‘K
7440-38-2
Arsenic”’
‘
l,200e
61b
25,000°
o.os~
o.2~
‘K
7440-39-3
Barium
140000b
910000b
j
1~000b
870000b
2.0~
2.o~
‘K
7440-41-7
Beryllium
4,loob
I
2,lOOe
J
410”
44,000°
0.004°’
0.5~
‘K
7440-42-8
Boron
i8o,ooob
11,000,000
18,000b
1,000,000
2.Om
2.0w
‘K
7440-43-9
Cadmium~”
2,ooo”~
2,800°
I
2001),r
59,000°
0.005°’
o.osm
‘K
16887-00-6
Chloride
C
C
C
C
200°’
200”’
*
7440-47-3
Chromium, total
6,100b
420°
1
4100b
690”
0.l~
l.O~
‘K
16065-83-1
Chromium, ion,
trivalent
1000000b
C
j
310000b
c
g
g
18540-29-9
Chromium, ion, hexavalent
6,100”
420°
4,100”
690”
j
‘K
Ui
(
Exposure Route-SpecificValues for
Soils
Soil
Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
ExposureRoute
Values
Industrial-
Construction
Commercial
Worker
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
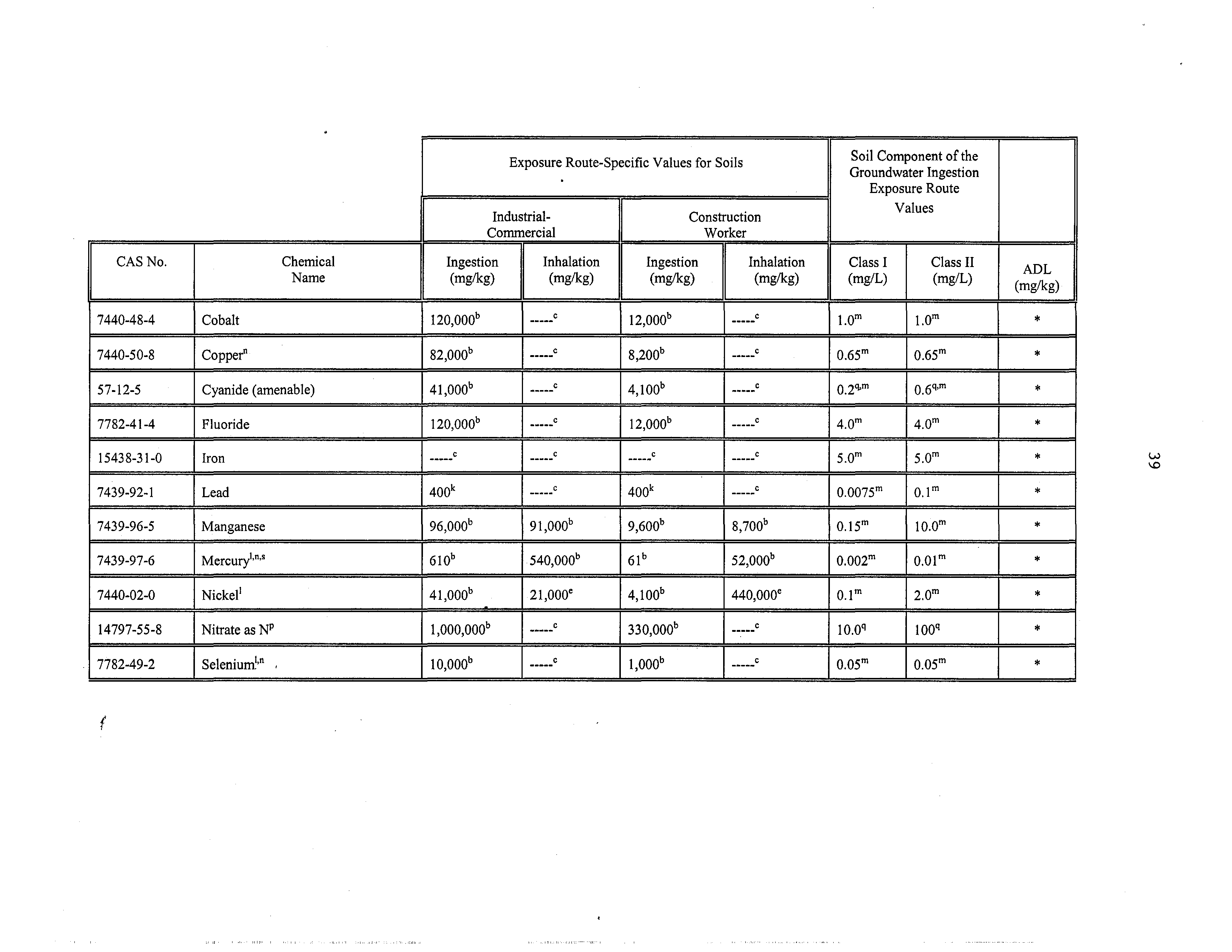
7440-48-4
Cobalt
~20000b
C
l2ooob
C
f
1.0”’
1.0°’
‘K
7440-50-8
Copper”
82,000”
c
8,200b
C
0.65”’
0.65m
‘K
57-12-5
Cyanide (amenable)
41,000”
C
4100”
C
0.2~°’
06q,m
*
7782-41-4
Fluoride
120000b
C
12000b
C
4.0°’
4.om
‘K
15438-31-0
Iron
C
C
C
C
s.om
5.0°’
‘K
7439-92-1
Lead
400k
C
400k
C
0.0075°’
0.lm
‘K
7439-96-5
Manganese
91,000b
9600b
8,700b
0.15°’
lO.Om
‘K
7439-97-6
Mercury”’”
610b
540,000”
61b
52,000b
0.002°’
0.01°’
‘K
7440-02-0
Nickel’
41,000b
-
21,ooo~
4,100”
440,000°
o.l~
2.o~
‘K
14797-55-8
NitrateasN”
1000000b
C
330000”
~C
10,0q
100q
‘K
7782-49-2
Selenium!”’
10,000”
1000b
C
0.05°’
0.05m
‘K
Ui
‘.0
(
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Ingestion
(mg/kg)
Inhalation
(mg/kg)
Class
I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
ADL
(mg/kg)
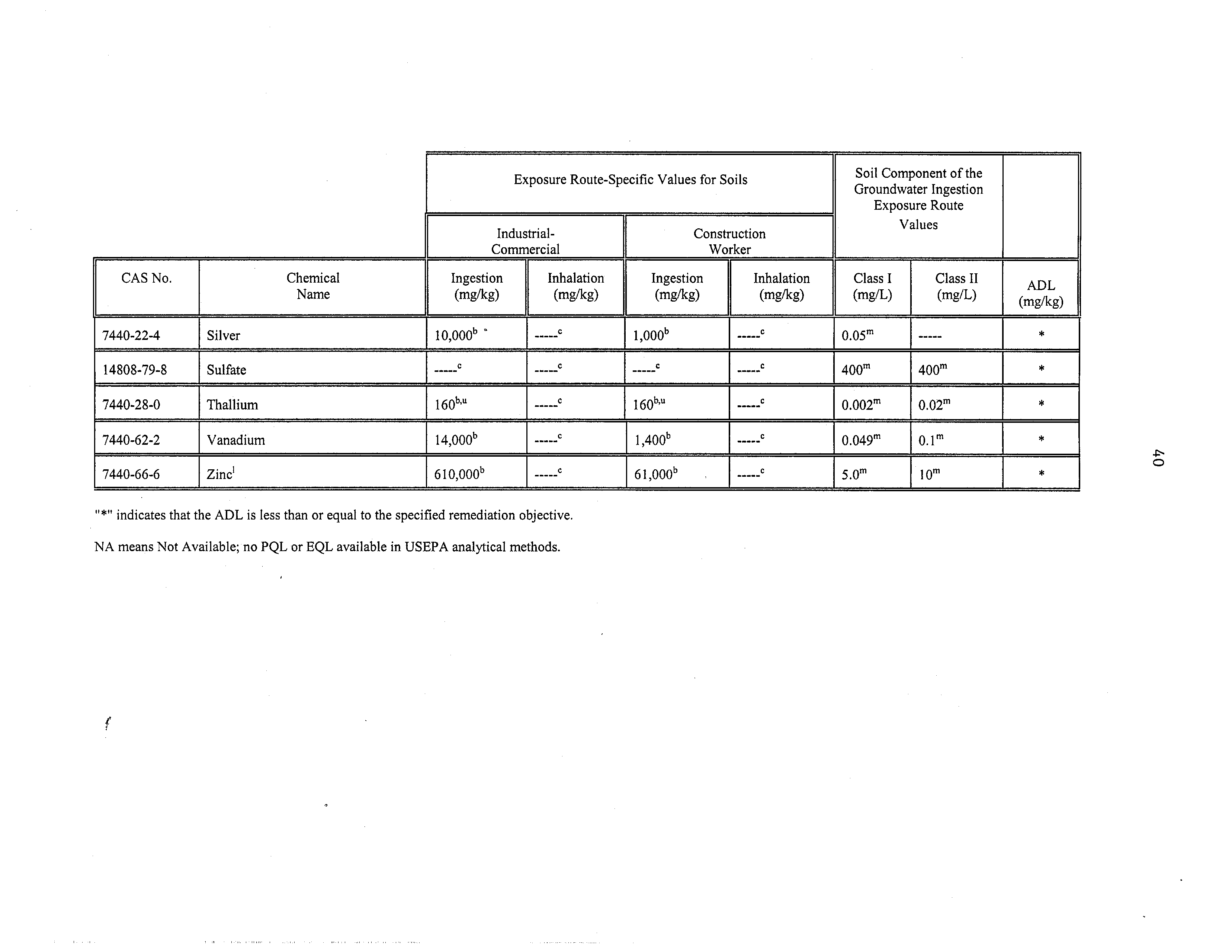
7440-22-4
Silver
1
10000b
-
C
1000b
C
‘K
14808-79-8
Sulfate
C
C
C
C
400°’
400”’
‘K
7440-28-0
Thallium
160”’
C
160””
C
0.002°’
0.02°’
‘K
7440-62-2
Vanadium
14,000b
C
1
1,400”
C
0.049°’
0.lm
‘K
7440-66-6
Zinc’
610000b
C
61,000”
•
C
5.om
10”
‘K
“K“
indicates that the
ADL is
less than or equal
to the specified
remediation objective.
NA means Not Available; no PQL or EQL available in USEPA
analytical methods.
Exposure Route-Specific Values for Soils
Soil Component of the
Groundwater Ingestion
_____________________
_______________________________
Exposure Route
Industrial-
Construction
Values
Commercial
Worker
(
41
Chemical Name
and Soil
Remediation ObjectiveNotations (2nd, 5th thru
8th Columns)
a
Soil remediation objectives based on human healthcriteria only.
b
Calculated valuescorrespond to atarget hazardquotient of 1.
C
No toxicity criteria available
for this route ofexposure.
“
Soil saturation concentration (C~,at)
=
the concentration at whichthe absorptive
limits ofthe soil particles, the solubility limits
of theavailable
soil moisture, and saturation of soil poreair have been reached.
Abovethe soil saturation concentration, the
assumptions regarding vapor transportto air and/ordissolved phase transportto groundwater (for chemicals which are liquid
at
ambient soil temperatures) have been violated, and
alternative modeling approaches are required.
Calculated values correspond to a cancerrisk level of I in 1,000,000.
Level
is at or belowContractLaboratory Program requiredquantitation limit for Regular Analytical Services
(RAS).
g
Chemical-specific propertiesare such that this route
is not of concern at anysoil contaminant concentration.
“
40 CFR
761
contains applicability requirementsand methodologies for thedevelopment of PCB remediation objectives.
Requests for approval of aTier 3
evaluation must address the applicability of 40 CFR 761.
Soil remediation objective for pHof 6.8. Ifsoil pH is other than 6.8, referto Appendix B, Tables C
and D in this Part.
Ingestion soil remediation
objective
adjusted by afactor of
0.5
to account for dermal route.
~ A preliminary remediation goal of 400
mg/kg hasbeen set for
lead based on
RevisedInterim Soil Lead Guidancefor CERCLA
Sites and RCRA Corrective Action Facilities,
OSWER Directive #9355.4-12.
Potential for soil-plant-human exposure.
m
The person conductingtheremediationhas theoption to use: (1) TCLP or SPLP test results to compare with the remediation
objectives listed in this Table; or (2) thetotal amount ofcontaminant in the soil sample results to compare with pH specific
remediation objectives listed in Appendix B, Table C or D of this Part.
(SeeSection 742.510.)
Ifthe personconductingthe
remediation wishes to calculate soil remediation objectives based on background concentrations, this shouabe done in
accordance with Subpart D of this Part.
-
“
The Agencyreserves the right to evaluate thepotential for remaining contaminant concentrations to pose significant threats to
crops, livestock, or wildlife.
For agrichemical
facilities, remediation objectives for surficial soils whichare based on field application rates may be more
appropriate for currently registered pesticides.
Consult theAgency for further information.
1’
For agrichemical
facilities, soil remediation objectives based on site-specific background concentrations of Nitrate as N may be
more appropriate.
Such determinations shall be conductedin accordance with theprocedures setforth in Subparts D and Iof
this Part.
q
TheTCLP extractionmust be done using water at apHof 7.0.
Value based on dietaryReference Dose.
Value for Ingestion based on Reference Dose
for Mercuric chloride (CAS No. 7487-94-7); value for Inhalation based on
Reference Concentration for elemental Mercury(CAS No. 7439-97-6).
°
For the ingestion route for arsenic for industrial/commercial,
see 742.Appendix A, Table G.
“Value based on Reference Dose for Thallium sulfate (CAS No. 7446-18-6).
“Calculated values correspond to soil
concentrations that should not resultin air concentrations that exceed criteria for
workplace air.
(Source:
Amended at 26
Ill. Reg.
______,
effective
______
42
Section 742.APPENDIX B: Tier
1
Tables and Illustrations
Section 742.TABLE E: Tier
1
Groundwater Remediation Objectives for the Groundwater
Component ofthe Groundwater Ingestion Route
Groundwater Remediation Objective
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
83-32-9
Acenaphthene
0.42
2.1
67-64-b
Acetone
0.7
0.7
15972-60-8
Alachlor
0.002°
0.ObC
116-06-3
Aldicarb
0.003°
0.0b5C
309-00-2
Aldrin
o.oI4a
0.07
120-12-7
Anthracene
2.1
10.5
1912-24-9
Atrazine
0.003C
0.015C
71-43-2
Benzene
0.005”
0.025”
56-55-3
Benzo(a)anthracene
0.000b3a
0.00065
205-99-2
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
0.00018”
0.0009
207-08-9
Benzo(k)fluroanthene
0.00017~
0.00085
50-32-8
Benzo(a)pyrene
0.0002”~
0.002°
lb 1-44-4
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
o.ola
0.01
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (Di(2-
ethylhexyl)phthalate)
0.006°
0.06°
75-27-4
Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane)
0.0002~
-
0.0002
75-25-2
Bromoform
o.oola
0.001
71-36-3
Butanol
0.7
0.7
85-68-7
-
Butyl benzyl phthalate
1.4
7.0
86-74-8
Carbazole
---
---
1563-66-2
Carbofuran
0.04C
0.2C
75-15-0
Carbon disulfide
0.7
3.5
56-23-5
Carbon tetrachloride
0.005”
0.025C
57-74-9
Chlordane
0.002°
0.OlC
43
Groundwater Remediation Objective
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
108-90-7
Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene)
0.lC
0.SC
124-48-I
Chlorodibromomethane
(Dibromochloromethane)
0.14
0.14
67-66-3
Chloroform
0.0002a
0.001
218-01-9
Chrysene
0.OOb5a
0.0075
94-75-7
2,4-D
0.07C
0.35C
75-99-0
Dalapon
0.2°
2.OC
72-54-8
DDD
0.Ob4a
0.07
72-55-9
DDE
0.01”
0.05
~0-29-3
DDT
0.0O6~
0.03
53-70-3
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
0.0003a
0.0015
96-12-8
b,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
0.0002°
0.0002”
106-93-4
1,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylene dibromide)
0.00005”
0.0005C
84-74-2
Di.~n-butylphthalate
0.7
3,5
95-50-1
1 ,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o
—
Dichlorobenzene)
0.6C
1.5°
106-46-7
1
,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p
—
Dichlorobenzene)
0.075”
0.375°
9 1-94-1
3,3’-Dichlorobenzidine
0.02~
0.1
75-34-3
b,1-Dichloroethane
0.7
-
3.5
107-06-2
b,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylene dichloride)
0.005°
I
0.025C
Il,l-Djchloroethylene”
0.007”
0.035C
156-59-2
cis-l
,2-Dichboroethylene
-
0.07C
0.2°
156-60-5
trans-b
,2-Dichloroethylene
0. bC
Ø5C
78-87-5
1 ,2-Dichloropropane
0.005C
f
0.025C
542-75-6
1 ,3-Dichloropropene
(1 ,3-Dichloropropylene,
cis
+
trans)
0.001”
0.005
44
Groundwater Remediation Objective
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class
I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
60-57-b
Dieldrin
o.oo9a
0.045
84-66-2
Diethyl phthalate
5.6
5.6
121-14-2
2,4-Dinitrotoluene”
o.00002a
0.00002
606-20-2
J
2,6-Dinitrotoluene”
0.0003 l~
0.00031
88-85-7
Dinoseb
0.007”
0.07C
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl phthalate
0.14
0.7
115-29-7
Endosulfan
0.042
0.21
145-73-3
Endothall
0.1”
0.1”
72-20-8
Endrin
0.002C
-
0.01”
100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
Ø7C
f
l.0C
206-44-0
Fluoranthene
0.28
1.4
86-73-7
Fluorene
-
0.28
1.4
76-44-8
Heptachlor
0.0004”
0.002”
1024-57-3
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0002”
0.001”
lb 8-74-1
Hexachlorobenzene
o.00006a
0.0003
319-84-6
.
alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC)
0.0001b~
0.00055
58-89-9
Gamma-HCH (Lindane)
0.0002C
0.001”
77-47-4
Hexachborocyclopentadiene
0.05”
0.5”
67-72-1
Hexachloroethane
0.007
0.035
193-39-5
Indeno(l ,2,3-c,d)pyrene
0.00043a
0.00215
78-59-I
Isophorone
1.4
1.4
72-43-5
Methoxychior
0.04”
0.2”
74-83-9
Methyl bromide
(Bromomethane)
0.0098
0.049
1634-04-4
Methyl tert butyl etherMethyl tertiary-
0.07
0.07
butyl ether
75-09-2
Methylene chloride
(Dichloromethane)
0.005C
0.05”
9 1-20-3
Naphthalene
0.14
0.22
98-95-3
Nitrobenzeneb
0.0035
f
0.0035
45
Groundwater Remediation Objective
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
86-30-6
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
0.0032 a
0.0 16
621-64-7
N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine
0.0018
a
0.0018
87-86-5
Pentachlorophenol
0.001”
0.005”
108-95-2
Phenol
0.lC
0.1”
1918-02-I
Picloram
0.5C
5ØC
1336-36-3
Polychlorinatedbiphenyls (PCB5)
0.0005”
0.0025”
129-00-0
Pyrene
0.21
1.05
122-34-9
Simazine
0.004”
0.04C
100-42-5
Styrene
0.lC
Ø~5C
93-72-1
2,4,5-TP
(Silvex)
0.05”
I
0.25”
127-18-4
Tetrachloroethylene
(Perchloroethylene)
0.005”
0.025”
108-88-3
Toluene
1.0”
2.5”
8001-35-2
Toxaphene
-
0.003C
0.0l5C
l20~82-l
b,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.07C
o•7C
71-55-6
b,l,l-Trichloroethane”
0.2C
1.0”
79-00-5
1,l,2-Trichloroethane
0.005C
0.05”
179-01-6
Trichloroethylene
0.005”
0.025C
108-05-4
Vinyl acetate
7.0
7.0
75-01-4
Vinyl chloride
0.002C
0.01”
1330-20-7
Xylenes (total)
10.0”
10.0”
Ionizable
Organics
65-85-0
Benzoic Acid
28
28
106-47-8
4-Chloroaniline
Co-Chboroaniline)
0.028
0.028
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
0.035
-
0.175
120-83-2
2,4-Dichlorophenol
0.021
0.021
105-67-9
2,4-Dimethylphenol
0.14
0.14
51-28-5
2,4-Dinitrophenol
0.014
0.014
95-48-7
2-Methylphenol
(o
—
Cresol)
0.35
0.35
I
Groundwater Remediation Objective
46
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class
I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
95-95-4
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
,
0.7
3.5
88-06-2
2,4,6 Trichlorophenol
Inorganics
0.01
a
0.05
7440-36-0
Antimony
0.006C
0.024C
7440-38-2
Arsenic
-
0.05”
0.2”
7440-39-3
Barium
2.0C
2.0”
7440-41-7
Beryllium
0.004”
0.5C
7440-42-8
Boron
2.0”
2.0”
7440-43-9
Cadmium
0.005”
o.os”
16887-00-6
Chloride
200”
200C
7440-47-3
Chromium, total
0.1”
1.0”
18540-29-9
Chromium, ion, hexavalent
---
---
7440-48-4
Cobalt
1.0”
l.OC
7440-50-8
Copper
57-12-5
lCyanide
7782-41-4
IFluoride
15438-31-0
llron
7439-92-1
Lead
7439-96-5
1Manganese
7439-97-6
Mercury
0.65”
0.2C
4.0”
5.OC
0.0075C
0.15C
0.002c
0.65”
0.6C
4ØC
5~ØC
0.bC
10.0C
0.01”
7440-02-0
INk
1
0.1”
2.0”
14797-55-8
Nitrate as N
lO.OC
bOOC
7782-49-2
Selenium
0.05C
0.05C
7440-22-4
Silver
0.05”
---
14808-79-8
Sulfate
400C
400”
47
Groundwater Remediation Objective
CAS No.
I
Chemical Name
-
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
7440-28-0
Thallium
0.002C
0.02”
7440-62-2
Vanadium”
0.049
0.1
7440-66-6
Zinc
5.0C
1
ØC
Chemical Name and Groundwater RemediationObiective Notations
a
Thegroundwater remediation objective is equal to the ADL for carcinogens according to theprocedures specified in 35
Ill.
Adm.
Code620.
b
Oral Reference Dose and/orReference Concentration under review by USEPA.
Listed values subject to change.
C
Value listed is also the Groundwater Quality Standardfor this chemical pursuantto 35
Ill. Adm. Code620.4 10 for Class I
Groundwater or 35
III. Adm.
Code620.420 for Class II Groundwater.
(Source:
Amended at
26 Ill.
Reg.
_____,
effective
______
48
Section
742.APPENDIX
B:
Tier
1
Tables and Illustrations
Section
742TABLE
F:
Values Used to
Calculate the Tier
1
Soil
Remediation Objectives for the
Soil Component ofthe Groundwater Ingestion Route
GW0bJ Concentrationused to Calculate
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectives”
CAS No.
----
—
Chemical Name
--~-—--~-~-----
-
-
Class
I
-
--mgIL~
--
20b
Class II
---
(mgfI~
-
10
83-32-9
Acenaphthene
67-64-b
Acetone
40b
4.0
15972-60-8
Alachlor
0.002C
0.01”
116-06-3
Aldicarb
0.003C
0.015”
309-00-2
Aldrin
5.OE-6”
2.SE-5
120-12-7
Anthracene
1912-24-9
Atrazine
0.003”
0.015”
7j~3-2
56-55-3
Benzene
Benzo(a)anthracene
0.005C
0.0001”
J
0.025C
0.0005
205-99-2
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
0.0001”
0.0005
207-08-9
Benzo(k)fluroanthene
0.001”
0.005
50-32-8
Benzo(a)pyrene
0.0002a,C
0.002”
111-44-4
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
8.OE-5”
8.OE-5
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (Di(2-
ethylhexyl)phthalate)
0.O06~
T
j
0.06”
75-27-4
Bromodichloromethane
(Dichlorobromomethane)
o~
1”
0.1
75-25-2
Bromoform
01b
0.01
71-36-3
Butanol
40b
4.0
85-68-7
Butyl benzyl phthalate
7.0”
J
86-74-8
Carbazole
J
0.02
1563-66-2
Carbofuran
ØØ4C
0.2”
75-15-0
Carbon disulfide
4.0”
20
56-23-5
Carbon tetrachloride
0.005”
0.025”
57-74-9
Chlordane
0.002”
0.OlC
49
GW0bJ Concentration used to Calculate
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectivesa
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
108-90-7
Chlorobenzene
(Monochlorobenzene)
0.lC
0.5C
124-48-I
fChlorodibromomethane
J
0.06”
0.06
67_66-3
J
Chloroform
01b
0.5
218-01-9
JChrysene
01b
0.05
J
94-75-7
J
2,4-D
0.07”
0.35C
75-99-0
Dalapon
0.2”
2.0”
72-54-8
IDDD
-.
00004b
0.002
j
72-55-9
I
DDE
-
00003b
0.0015
j
50-29-3
I
DDT
00003b
0.0015
)
53-70-3
I
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
1 .OE-5”
5.OE-5
t96-12-8
b,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
0.0002”
0.0002C
106-93-4
b,2-Dibromoethane
(Ethylenedibromide)
0.00005””’
0.0005C
84-74-2
Di-n-butyl phthalate
4.0”
20
95-50-1
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(o
—
Dichlorobenzene)
0.6”
1
5C
106-46-7
b,4-Dichlorobenzene
(p
—
Dichlorobenzene)
0.075”
~
0.375”
91-94-1
3,3’-Dichlorobenzidine
0.0002”
0.001
75-34-3
1,1-Dichloroethane
4.0”
20
107-06-2
1,2-Dichloroethane
(Ethylenedichloride)
0.005”
0.025C
75-35-4
1,l-Dichloroethylene
0.007”
0.03
5C
156-59-2
cis-1,2-Dichloroethybene
0.07C
0.2”
156-60-5
trans-b,2-Dichloroethylene
0. IC
Ø5C
78-97-5
I,2-Dichloropropane
0.005C
0.025C
542-75-6
b,3-Dichloropropene
(1,3-Dichioropropylene,
cis
+
trans)
0.0005”
0.0025
50
GW0bJ Concentration used to Calculate
Tier I
Soil Remediation Obiectivesa
CAS No.
Chemical
Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
160-57-1
Dieldrin
5.OE-6”
2.5E-5
84-66-2
Diethyl
phthalate
30”
(
30
1121-14-2
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
0.0001”
0.0001
1606-20-2
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
0.0001
0.0001
88-85-7
Dinoseb
0.007”
0.07”
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl phthalate
0.7”
3.5
115-29-7
Endosulfan
02b
1.0
1145-73-3
Endothall
0.lC
0.1”
172-20-8
Endrin
0.002C
0.01”
1100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
0.7”
-
1.0”
206-44-0
Fluoranthene
1.0”
5.0
86-73-7
Fluorene
1.0”
5.0
76-44-8
Heptachlor
0.0004”
0.002”
1024-57-3
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0002C
0.OOlC
118-74-I
Hexachlorobenzene
0.001”
0.005
319-84-6
alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC)
1 .OE-5”
5.OE-5
58-89-9
Gamma-HCH
(Lindane)
0.0002”
0.OOlC
77-47-4
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
0.05”
0.5C
67-72-1
Hexachloroethane
0.007
0.03
5
193-39-5
Indeno(1 ,2,3-c,d)pyrene
O.00Olt~
0.0005
78-59-1
Isophorone
1.4
1.4
72-43-5
Methoxychlor
0.04”
0.2C
74-83-9
Methyl bromide
005b
0.25
(Bromomethane)
1634-04-4
Methyl tort butyl etherMethyl tertiary-
0.07
0.07
butyb ether
75-09-2
Methylene chloride
0.005”
0.05”
(Dichloromethane)
91-20-3
Naphthalene
0.14
0.22
98-95-3
Nitrobenzene
0.02”
0.02
51
GW0~~
Concentration used to Calculate
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Obiectivesa
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
1918-02-1
IPicloram
Ø5C
5ØC
1336-36-3
IPolychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
---
---
129-00-0
fpyrene
-
10b
5.0
122-34-9
Simazine
0.004C
0.04”
100-42-5
Styrene
0.1”
0.5C
93-72-1
1
2,4,5-TP
I(Silvex)
0.05C
0.25C
127-18-4
ITetrachloroethylene
J
(Perchloroethylene)
0.005”
0.025”
108-88-3
Toluene
l.OC
2.5”
8001-35-2
Toxaphene
0.003”
0.015”
120-82-1
1 ,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.07”
0.7C
71-55-6
l,1,l-Trichloroethane2
0.2C
1.0”
79-00-5
1,1 ,2-Trichloroethane
0.005C
0.05C
79-01-6
Trichloroethylene
0.005”
0.025”
108-05-4
Vinyl acetate
40b
40
75-01-4
Vinyl chloride
0.002”
0.01”
1330-20-7
Xylenes (total)
Ionizable Organics
bO.OC
bO.0C
65-85-0
Benzoic Acid
bOO”
100
106-47-8
4-Chloroaniline
(p-Chloroaniline)
o~
1”
0.1
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
02”
(
1.0
120-83-2
2,4-Dichlorophenol
o~
1”
0.1
105-67-9
2,4-Dimethylphenol
0.7”
0.7
51-28-5
2,4-Dinitrophenol
0.04”
0.04
95-48-7
2-Methybphenol
(o
—
Cresol)
20b
f
J~
2.0
86-30-6
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
0.02”
0.1
52
GW0~~
Concentration used to Calculate
Tier
1
Soil Remediation Objectivesa
CAS
No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
621-64-7
N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine
I .OE-5”
1 .OE-5
87-86-5
Pentachlorophenol
0.001””’
0.005”
108-95-2
Phenol
0.1”
0.1”
195-95-4
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
4.0”
20
88-06-2
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
0.008”
0.04
I_________________
Inorganics
17440-36-0
Antimony
0.006’
0.024C
17440-38-2
E
Arsenic
0.05C
0.2”
7440-39-3
Barium
2.OC
2.0’
7440-41-7
Beryllium
0.004C
0.5C
7440-42-8
Boron
2.0C
2.0”
7440-43-9
Cadmium
0.005”
0.05C
16887-00-6
Chloride
200”
200C
7440-47-3
Chromium, total
0. lC
1.0”
18540-29-9
Chromium, ion, hexavalent
---
---
7440-48-4
Cobalt
l.OC
1.0C
7440-50-8
Copper
•
0.65”
O.65C
57-12-5
Cyanide
0.2’
0.6”
7782-41-4
Fluoride
4.0”
4.0C
1
15438-31-0
Iron
5.0”
5.0C
7439-92-b
Lead
0.0075”
0.1”
7439-96-5
Manganese
0.15”
1 0.O~
7439-97-6
Mercury
0.002C
0.OlC
7440-02-0
Nickel
0.1”
2.OC
14797-55-8
Nitrateas N
10.0”
lOOC
7782-49-2
Selenium
0.05”
0.OSC
7440-22-4
Silver
0.05”
---
114808-79-8
Sulfate
400”
400”
53
GW0~~
Concentration used to Calculate
Tier
1
Soil RemediationObiectivesa
CAS No.
Chemical Name
Class I
(mg/L)
Class II
(mg/L)
7440-28-0
Thallium
0.002”
0.02C
7440-62-2
Vanadium
0.049
0.1
7440-66-6
Zinc
5.0’’
10”
Chemical Name and Groundwater RemediationObiective Notations
a
The Equation S17
is used to calculate the Soil Remediation Objectivefor the Soil Component of the Groundwater Ingestion
Route; this
equationrequires calculation oftheTarget Soil Leachate Concentration (Cv) from Equation S 18:
C,,,
=
DF
x
GWQbJ.
“
Value listed is the WaterHealthBased Limit (HBL)for this chemical from Soil Screening Guidance:
User’s Guide,
incorporated by reference at Section 742.21 0.
TheHBL is equal to the non-zero MCLG (ifavailable); theMCL (if available)
or, for carcinogens~
acancer risk of 1.OE-6, andfor noncarcinogens is equal to a Hazard Quotient of 1.0.
NOTE:
These GW0~~
concentrations are not equal
to the Tier 1 Groundwater RemediationObjectives for the Direct Ingestion ofGroundwater
Component of the Groundwater Ingestion Route, listed in Section 742.Appendix B, Table E.
Value listed is also the Groundwater Quality Standard for this chemicalpursuantto 35
Ill. Adm. Code 620.4 10 for Class I
Groundwater or 35
Ill. Adm.
Code 620.420 for Class II Groundwater.
(Source:
Amended at 26 Ill. Reg.
_____,
effective
______
Section 742.APPENDIX C: Tier 2 Tables and Illustrations
Section 742.Table E: Default Physical
and
Chemical Parameters
Lii
CAS
No.
~
.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (5)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air(Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water (D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K0~)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2~)
(d~’)
Neutral Organics
83-32-9
Acenaphthene
4.24
0.0421
7.69E-6
0.00636
7,080
0.0034
67-64-1
Acetone
1,000,000
0.124
l.b4E-5
0.00159
0.575
0.0495
15972-60-8
Alachbor
242
0.0198
5.69B-6
0.000001 32
394
No Data
116-06-3
Abdicarb
6,000
0.0305
7.19E-6
0.0000000574
12
0.00109
309-00-2
Abdrin
0.18
0.0132
4.86E-6
0.00697
2,450,000
0.00059
120-12-7
Anthracene
0.0434
0.0324
7.74E-6
0.00267
29,500
0.00075
1912-24-9
Atrazine
70
0.0258
6.69E-6
0.00000005
451
No Data
71-43-2
Benzene
1,750
0.088
9.80E-6
0.228
58.9
0.0009
f
Lii
Lii
CAS
No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
~
Diffusivity in
Water (D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(KOC)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2k)
(d1)
56-55-3
Benzo(a)anthracene
0.0094
0.0510
9,00E-6
0.000137
398,000
0,00051
205-99-2
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
0.0015
0.0226
5.56E-6
0.00455
1,230,000
0.00057
207-08-9
Benzo(k)fluoranthene
0.0008
0.0226
5.56E-6
0.000034
1,230,000
0.00016
65-85-0
Benzoic Acid
3,500
0.0536
7.97E-6
0.0000631
0.600
No Data
50-32-8
Benzo(a)pyrene
0.00162
0.043
9.OOE-6
0.0000463
1,020,000
0.00065
111-44-4
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
17,200
0.0692
7.53E-6
0.000738
15.5
0.00 19
117-81-7
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
0.34
0.0351
3.66E-6
0.00000418
15,100,000
0.0018
75-27-4
Bromodichloromethane
6,740
0.0298
1
.06E-5
0.0656
55.0
No Data
75-25-2
Bromoform
3,100
0.0149
l.03E-5
0.0219
87.1
0.0019
71-36-3
Butanol
74,000
0.0800
9.30E-6
0.000361
6.92
0.01283
85-68-7
Butyl Benzyl Phthalate
2.69
0.0174
4.83E-6
0.00005 17
57,500
0.00385
86-74-8
Carbazole
7.48
0.0390
7.03E-6
0.000000626
3,390
No Data
f
Lii
C.’
CAS No.
Chemicai
Solubility in
Water(5)
(mg/L)
.
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water (D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K0~)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2~)
(d’)
1563-66-2
Carbofuran
320
0.0249
6.63E-6
.00377
37
No Data
75-15-0
Carbon Disulfide
1,190
0.104
b.OOE-5
1.24
45.7
No Data
56-23-5
Carbon Tetrachloride
793
0.0780
8.80E-6
1.25
174
0.0019
57-74-9
Chiordane
0.056
0.0118
4.37E-6
0.00199
120,000
0.00025
106-47-8
p-Chloroaniline
5,300
0.0483
lObE-S
0.0000136
66.1
No Data
108-09-7
Chlorobenzene
472
0.0730
8.70E-6
0.152
219
0.0023
124-48-I
Chlorodibromomethane
2,600
0.0196
b.05E-5
0.0321
63.1
0.00385
67-66-3
Chloroform
7,920
0.104
l.OOE-5
0.15
39.8
0.00039
95-57-8
2-Chlorophenol
22,000
0.0501
9.46E-6
0.016
388
No Data
218-01-9
Chrysene
0.0016
0.0248
6.21E-6
0.00388
398,000
0.00035
94-75-7
2,4-D
680
0.0231
7.31E-6
0.00000041
451
0.00385
72-54-8
4,4’-DDD
0.09
0.0169
4.76E-6
0.000164
1,000,000
0.000062
(
Li’
—.1
CAS No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water(S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water(D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant (H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K0,)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(X)
(d~’)
72-55-9
4,4-DDE
0.12
0.0144
5.87E-6
0.000861
4,470,000
0.000062
50-29-3
4,4’-DDT
0.025
0.0137
4.95E-6
0.000332
2,630,000
0.000062
75-99-0
Dabapon
900,000
0.0414
9.46E-6
0.00000264
5.8
0.005775
53-70-3
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
0.00249
0.0202
5.18E-6
0.000000603
3,800,000
0.00037
96-12-8
I,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
1,200
0.0212
7.02E-6
0.00615
182
0.001925
106-93-4
l,2-Dibromoethane
4,200
0.0287
8.06E-6
0.0303
93
0.005775
84-74-2
Di-n-butyl Phthalate
11.2
0,0438
7.86E-6
0.0000000385
33,900
0.03013
95-50-1
l,2-Dichlorobenzene
156
0.0690
7.90E-6
0.0779
617
0.0019
106-46-7
b,4-Dichlorobenzene
73.8
0.0690
7.90E-6
0.0996
617
0.0019
91-94-1
3,3-Dichlorobenzidine
3.11
0.0194
6.74E-6
0.000000164
724
0.0019
(
Li’
CAS No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water(D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant (H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(KOC)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(~)
(d1)
75-34-3
l,l-Dichloroethane
5,060
0.0742
b.OSE-5
0.23
31.6
0.0019
107-06-2
I,2-Dichloroethane
8,520
0.104
9.90E-6
0.0401
17.4
0.0019
75-35-4
l,b-Dichloroethylene
2,250
0.0900
b.04E-5
1.07
58.9
0.0053
156-59-2
Cis-l,2-Dichloroethylene
3,500
0.0736
l.13E-5
0.167
35.5
0.00024
156-60-5
Trans-l,2-Dichloroethylene
6,300
0.0707
l.19E-5
0.385
52.5
0.00024
120-83-2
2,4-Dichlorophenol
4,500
0.0346
8.77E-6
0.00013
147
0.00027
78-87-S
l,2-Dichloropropane
2,800
0.0782
8.73~E-6
0.115
43.7
0.00027
542-75-6
1,3-Dichloropropylene
(cis + trans)
2,800
0.0626
b.OOE-5
0.726
45.7
0.061
60-57-1
Dieldrin
0.195
0.0125
4.74E-6
0.000619
21,400
0.00032
84-66-2
Diethyl Phthalate
1,080
0.0256
6.35E-6
0.0000185
288
0.00619
105-67-9
2,4-Dimethybphenol
7,870
0.0584
8.69E-6
0.000082
209
-
0.0495
51-28-5
2,4-Dinitrophenol
2,790
0.0273
9.06E-6
0.0000182
0.01
0.00132
f
Li’
‘.0
CAS
No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (5)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water(D~)
(cm2fs)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant (H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K0~)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2.)
(d-’)
121-14-2
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
270
0.203
7.06E-6
0.0000038
95.5
0.00192
606-20-2
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
182
0.0327
7.26E-6
0.0000306
69.2
0.00192
88-85-7
Dinoseb
52
0.0215
6.62E-6
0.0000189
1,120
0.002817
117-84-0
Di-n-octyl Phthalate
0.02
0.0151
3.58E-6
0.00274
83,200,000
0.0019
115-29-7
Endosulfan
0.51
0.01 15
4.55E-6
0.000459
2,140
0.07629
145-73-3
Endothall
21,000
0.0291
8.07E-6
0.0000000107
0.29
No Data
72-20-8
Endrin
0.25
0.0125
4.74E-6
0.000308
12,300
0.00032
100-41-4
Ethylbenzene
169
0.0750
7.80E-6
0.323
363
0.003
206-44-0
Fluoranthene
0.206
0.0302
6.35E-6
0.00066
107,000
0.00019
86-73-7
Fluorene
1.98
0.0363
7.88E-6
0.00261
13,800
0.000691
76-44-8
Heptachlor
0.18
0.01 12
5.69E-6
60.7
1,410,000
0.13
1024-57-3
Heptachlor epoxide
0.2
0.0 132
4.23B-6
0.00039
83,200
0.00063
(
0.’
CAS No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air(Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity in
Water(D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(KOC)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2.)
(d’)
118-74-I
Hexachlorobenzene
6.2
0.0542
5.91E-6
0.0541
55,000
0.00017
3 19-84-6
Alpha-HCH (alpha-BHC)
2.0
0.0142
7.34E-6
0.000435
1,230
0.0025
58-89-9
Gamma-HCH (Lindane)
6.8
0.0142
7.34E-6
0.000574
1,070
0,0029
77-47-4
Hexachiorocyclo-
Pentadiene
1.8
0.0161
7.2bE-6
1.11
200,000
0.012
67-72-b
Hexachloroethane
50
0.0025
6.80E-6
0.159
1,780
0.00192
193-39-5
Indeno(l,2,3-c,d)pyrene
0.000022
0.0190
5.66E-6
0.0000656
3,470,000
0.00047
78-59-1
Isophorone
12,000
0.0623
6.76E-6
0.000272
46.8
0.01238
7439-97-6
Mercury
---
0.0307
6.30E-6
0.467
---
No Data
72-43-5
Methoxychlor
0.045
-
0.0156
4.46E-6
0.000648
97,700
0.0019
74-83-9
Methyl Bromide
15,200
0.0728
l.2bE-5
0.256
10.5
0.01824
1634-04-4
Methyl tort but’,’l etherMethyl
51.000
~LU~2
1.1OE-5
0.0241
jj,.~
No Data
tertiary-butyb ether
75-09-2
Methylene Chloride
13,000
0.101
l.l7E-5
0.0898
11.7
0.012
~5-48-7
2-Methylphenol
-
26,000
0.0740
8.30E-6
0.0000492
91.2
0.0495
C.’
CAS
No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water(S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air(Di)
(cm2/s)
Diffusivity
in
Water (D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K00)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2.)
(d~)
91-20-3
Naphthalene
31.0
0.0590
7.50E-6
0.0198
2,000
0.0027
98-95-3
Nitrobenzene
2,090
0.0760
8.60E-6
0.000984
64.6
0.00176
86-30-6
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
35.1
0.03 12
6.35E-6
0.000205
1,290
0.01
621-64-7
N-Nitrosodi-n-propybamine
9,890
0.0545
8.l7E-6
0.0000923
24.0
0.0019
87-86-S
Pentachlorophenol
1,950
0.0560
6.1OE-6
0.000001
592
0.00045
108-95-2
Phenol
82,800
0.0820
9.bOE-6
0.0000163
28.8
0.099
1918-02-I
Picloram
430
0.0255
5.28E-6
0.00000000166
1.98
No Data
1336-36-3
Polychlorinatedbiphenyls
(PCB5)
0.7
a
a
a
309,000
No Data
129-00-0
Pyrene
0.135
0.0272
7.24E-6
0.000451
105,000
0.00018
122-34-9
Simazine
-
5
0.027
7.36E-6
0.0000000133
133
No Data
100-42-5
Styrene
310
0.0710
8.OOE-6
0.113
776
0.0033
93-72-1
2,4,5-TP (Silvex)
31
0.0194
5.83E-6
0.0000000032
-
5,440
No Data
f
C.’
CAS
No.
-
Chemical
Solubility in
Water (5)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2fs)
Diffusivity in
Water (D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant (H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K0~)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2.)
(d~)
127-18-4
Tetrachloroethylene
200
0.0720
8.20E-6
0.754
155
0.00096
108-88-3
Toluene
526
0.0870
8.60E-6
0.272
182
0.011
8001-35-2
Toxaphene
0.74
0.0116
4.34E-6
0.000246
257,000
NoData
120-82-1
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
300
0.0300
8.23E-6
0.0582
1,780
0.0019
71-55-6
l,l,1-Trichloroethane
1,330
0.0780
8.80E-6
0.705
110
0.0013
79-00-5
b,b,2-Trichloroethane
4,420
0.0780
8.80E-6
0.0374
50.1
0.00095
79-01-6
Trichloroethylene
1,100
0.0790
9.bOE-6
0.422
166
0.00042
95-95-4
2,4,5-Trichlorophenob
1,200
0.0291
7.03E-6
0.000178
1,600
0.00038
88-06-2
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
800
0.0318
6.25E-6
0.000319
381
0.00038
108-05-4
Vinyl Acetate
20,000
0.0850
9.20E-6
0.021
5.25
No Data
57-01-4
Vinyl Chloride
2,760
0.106
b.23E-6
1.11
18.6
0.00024
108-38-3
m-Xylene
161
0.070
7.80E-6
0.301
407
0.0019
f
CAS No.
Chemical
Solubility in
Water(S)
(mg/L)
Diffusivity in
Air (Di)
(cm2/s)
~
Diffusivity in
Water(D~)
(cm2/s)
Dimensionless
Henry’s Law
Constant
(H’)
(25°C)
Organic
Carbon
Partition
Coefficient
(K00)
(L/kg)
First
Order
Degradation
Constant
(2.)
(d~’)
95-47-6
o-Xybene
178
0.087
lOGE-S
0.213
363
0.0019
106-42-3
p-Xybene
185
0.0769
8.44E-6
0.3
14
389
0.0019
1330-20-7
Xybenes (total)
186
0.0720
9.34E-6
0.25
260
0.0019
Chemical
Abstracts Service (CAS) registry number. This number in the format xxx-xx-x, is unique
for each chemical
and allows
efficient searching on computerized data bases.
“Soil
Remediation objectives are determined pursuant to 40 CFR 761, as incorporated by reference at Section 732.104
(the USEPA “PCB Spill
Cleanup Policy”), for most sites;
persons remediating sites
should consult with BOL if calculation of Tier 2 soil remediation objectives is desired.
(Source:
Amended at 26 Iii. Reg.
______,
effective
______
(
64
IT
IS
SO
ORDERED.
I, Dorothy M.
Gunn, Clerk of the Illinois Pollution Control Board,
certify that the
Board adopted the above opinion and order on January
24,
2002,
by
a vote of 7-0.
Dorothy M.
Gunn,
Clerk
Illinois Pollution Control Board